Deck 13: How Populations Evolve
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: How Populations Evolve
1
Natural selection ________.
A) results in evolutionary adaptation
B) is a very rare phenomenon
C) does not affect allelic frequencies
D) prepares organisms for future changes in the environment
A) results in evolutionary adaptation
B) is a very rare phenomenon
C) does not affect allelic frequencies
D) prepares organisms for future changes in the environment
A
2
Natural selection can be defined as ________.
A) the evolution of a population of organisms
B) a process in which changes in gene frequencies result from evolution
C) the production of more offspring than can survive in a given environment
D) a process in which organisms with certain inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce than individuals with other traits
A) the evolution of a population of organisms
B) a process in which changes in gene frequencies result from evolution
C) the production of more offspring than can survive in a given environment
D) a process in which organisms with certain inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce than individuals with other traits
D
3
The first basic idea of evolutionary adaptation can be traced back to ________.
A) ancient Greeks about 2,500 years ago
B) Aristotle
C) Lamarck
D) Darwin
A) ancient Greeks about 2,500 years ago
B) Aristotle
C) Lamarck
D) Darwin
C
4
Which is NOT a benefit of the understanding of evolution to understanding the field of biology?
A) Understanding evolution helps us to understand molecules.
B) Understanding evolution helps us to analyze ecosystems.
C) Understanding evolution helps advance biotechnology and medicine.
D) Understanding evolution helps us to understand why stars and galaxies change over time.
A) Understanding evolution helps us to understand molecules.
B) Understanding evolution helps us to analyze ecosystems.
C) Understanding evolution helps advance biotechnology and medicine.
D) Understanding evolution helps us to understand why stars and galaxies change over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
During his trip on the Beagle,Darwin found that ________.
A) plants and animals living in temperate regions were most similar to each other, regardless of the continent on which they were found
B) plants and animals living on a continent seemed more closely related to each other than to plants and animals living in similar regions on other continents
C) fossils found on a particular continent were clearly not related to the plants and animals living on that continent today
D) plants and animals were similar on every continent and in every type of region
A) plants and animals living in temperate regions were most similar to each other, regardless of the continent on which they were found
B) plants and animals living on a continent seemed more closely related to each other than to plants and animals living in similar regions on other continents
C) fossils found on a particular continent were clearly not related to the plants and animals living on that continent today
D) plants and animals were similar on every continent and in every type of region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The common house mouse species,Mus musculus,has the following taxonomic classification: Mus,Muridae,Rodentia,Mammalia,Chordata,Animalia,Eukarya.Which part of the name is the Family?
A) Rodentia
B) Chordata
C) Muridae
D) Animalia
A) Rodentia
B) Chordata
C) Muridae
D) Animalia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which one of the following can create new alleles?
A) natural selection
B) sexual reproduction
C) mutation
D) genetic drift
A) natural selection
B) sexual reproduction
C) mutation
D) genetic drift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Natural selection generally results in ________.
A) increased genetic variation
B) a population that is better adapted to a future environment
C) a population that is adapted to its current environment
D) an increase in the size of a population
A) increased genetic variation
B) a population that is better adapted to a future environment
C) a population that is adapted to its current environment
D) an increase in the size of a population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Natural selection works on variation already present in a population.
B) Natural selection works on nonheritable traits.
C) Individuals evolve through natural selection.
D) Individual organisms evolve structures that they need.
A) Natural selection works on variation already present in a population.
B) Natural selection works on nonheritable traits.
C) Individuals evolve through natural selection.
D) Individual organisms evolve structures that they need.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In The Origin of Species,Darwin argued that the mechanism of descent with modification was ________.
A) artificial selection
B) natural selection
C) inheritance of acquired characteristics
D) uniformitarianism
A) artificial selection
B) natural selection
C) inheritance of acquired characteristics
D) uniformitarianism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The similarity of the embryos of fish,frogs,birds,and humans is evidence of ________.
A) analogy
B) common ancestry
C) genetic drift
D) decreased genetic variation
A) analogy
B) common ancestry
C) genetic drift
D) decreased genetic variation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The fossil record suggests that whales ________.
A) are descended from one branch of marine reptiles
B) are closely related to land mammals such as pigs, hippos, and cows
C) are not closely related to dolphins and porpoises, despite a superficial similarity
D) once had well-developed hind flippers
A) are descended from one branch of marine reptiles
B) are closely related to land mammals such as pigs, hippos, and cows
C) are not closely related to dolphins and porpoises, despite a superficial similarity
D) once had well-developed hind flippers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is NOT a requirement of natural selection?
A) differential reproductive success
B) overproduction of offspring
C) genetic variation
D) gene flow
A) differential reproductive success
B) overproduction of offspring
C) genetic variation
D) gene flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements about the voyage of the Beagle is TRUE?
A) Its purpose was to identify the fastest route from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean.
B) It lasted almost 2 years.
C) It turned into a tremendous opportunity for Darwin to collect fossils, plants, and animals.
D) It ended with the sinking of the ship off of the coast of Australia, almost 4 years into its journey.
A) Its purpose was to identify the fastest route from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean.
B) It lasted almost 2 years.
C) It turned into a tremendous opportunity for Darwin to collect fossils, plants, and animals.
D) It ended with the sinking of the ship off of the coast of Australia, almost 4 years into its journey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a component of the fossil record?
A) the distribution of murid rodents in Australia and Asia
B) the similarity of the forelimbs of cats and bats
C) molecular sequences
D) bones of extinct whales
A) the distribution of murid rodents in Australia and Asia
B) the similarity of the forelimbs of cats and bats
C) molecular sequences
D) bones of extinct whales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following are homologous?
A) the forelimb of a dog and the hindlimb of a cat
B) the forelimb of a dog and the forelimb of a cat
C) wings of a butterfly and wings of a sparrow
D) the mouth of a mosquito and the beak of a hummingbird
A) the forelimb of a dog and the hindlimb of a cat
B) the forelimb of a dog and the forelimb of a cat
C) wings of a butterfly and wings of a sparrow
D) the mouth of a mosquito and the beak of a hummingbird

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
________ believed that use (or lack of use)of body parts enables individual to develop certain traits that it passes on to its offspring while ________ believed that species are fixed forms that do not change over time.
A) Aristotle… Lamarck
B) Lamarck… Aristotle
C) Darwin… Aristotle
D) Lamarck… Darwin
A) Aristotle… Lamarck
B) Lamarck… Aristotle
C) Darwin… Aristotle
D) Lamarck… Darwin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
While on the Beagle,Darwin was influenced by a book by Charles Lyell that suggested that Earth was ________ and sculpted by geologic processes that ________ today.
A) old... continue
B) old... no longer occur
C) young... continue
D) young... no longer occur
A) old... continue
B) old... no longer occur
C) young... continue
D) young... no longer occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Homology is evidence of ________.
A) binomial classification
B) artificial selection
C) natural selection
D) common ancestry
A) binomial classification
B) artificial selection
C) natural selection
D) common ancestry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a population?
A) the termites infesting your house along with the microorganisms living in their guts
B) all of the termites that have ever lived
C) all organisms living in your house
D) the termites infesting your house
A) the termites infesting your house along with the microorganisms living in their guts
B) all of the termites that have ever lived
C) all organisms living in your house
D) the termites infesting your house

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What leads paleontologists to hypothesize that whales evolved from wolf-like carnivores?
A) molecular analysis of whale DNA
B) observations of fossil teeth
C) the presence of vestigial structures in both species
D) mathematical analysis using the Hardy-Weinberg formula
A) molecular analysis of whale DNA
B) observations of fossil teeth
C) the presence of vestigial structures in both species
D) mathematical analysis using the Hardy-Weinberg formula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
After surviving a bottleneck,a population recovers to the point where it consists of as many individuals as it did prior to the bottleneck.Which of the following statements is most likely to apply to this population?
A) The postbottleneck population exhibits less genetic variation than the prebottleneck population.
B) The bottleneck subjected the population to stabilizing selection.
C) The postbottleneck population has less of a chance of going extinct than did the prebottleneck population.
D) The postbottleneck population exhibits more genetic variation than the prebottleneck population.
A) The postbottleneck population exhibits less genetic variation than the prebottleneck population.
B) The bottleneck subjected the population to stabilizing selection.
C) The postbottleneck population has less of a chance of going extinct than did the prebottleneck population.
D) The postbottleneck population exhibits more genetic variation than the prebottleneck population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a characteristic of a population at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) The population is subject to natural selection.
B) The population is not evolving.
C) Genetic drift is occurring.
D) Gene flow in and out of the population occurs.
A) The population is subject to natural selection.
B) The population is not evolving.
C) Genetic drift is occurring.
D) Gene flow in and out of the population occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following examples results from stabilizing selection?
A) The birth weight at which newborn humans are most likely to survive and the average weight of newborn humans are about the same.
B) There is an increase in antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
C) There is an increase in the number of different breeds of dog.
D) Garter snakes with different coloration patterns behave differently when threatened.
A) The birth weight at which newborn humans are most likely to survive and the average weight of newborn humans are about the same.
B) There is an increase in antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
C) There is an increase in the number of different breeds of dog.
D) Garter snakes with different coloration patterns behave differently when threatened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The presence of freckles is due to a dominant allele.Four percent of the individuals in a particular population lack freckles.Use the Hardy-Weinberg formula to calculate the percentage of individuals in this population who are homozygous dominant for freckles.
A) 32%
B) 4%
C) 64%
D) 80%
A) 32%
B) 4%
C) 64%
D) 80%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is most likely to decrease genetic variation?
A) directional selection
B) mutation
C) stabilizing selection
D) diversifying selection
A) directional selection
B) mutation
C) stabilizing selection
D) diversifying selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which one of the following will prevent significant genetic drift?
A) Gene flow is absent.
B) There is genetic variation.
C) There is mutation.
D) The population size is large.
A) Gene flow is absent.
B) There is genetic variation.
C) There is mutation.
D) The population size is large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What does evolutionary fitness measure?
A) physical health
B) longevity
C) relative reproductive success
D) population size
A) physical health
B) longevity
C) relative reproductive success
D) population size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Genetic drift is the result of ________.
A) natural selection
B) chance
C) a large gene pool
D) environmental variation
A) natural selection
B) chance
C) a large gene pool
D) environmental variation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is the most likely explanation for a particular human population with a higher incidence of polydactyly (extra fingers/toes)than the human population as a whole?
A) directional selection
B) disruptive selection
C) founder effect
D) bottleneck effect
A) directional selection
B) disruptive selection
C) founder effect
D) bottleneck effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is an example of sexual selection?
A) Bacteria evolve resistance to antibiotics.
B) Cheetahs experienced a population bottleneck.
C) Peahens choose to mate with peacocks that have the most beautiful tails.
D) Female butterflies have a higher survival rate than male butterflies.
A) Bacteria evolve resistance to antibiotics.
B) Cheetahs experienced a population bottleneck.
C) Peahens choose to mate with peacocks that have the most beautiful tails.
D) Female butterflies have a higher survival rate than male butterflies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The original source of genetic variation that serves as the raw material for natural selection is ________.
A) mutation
B) gene flow
C) geographic isolation
D) random fertilization
A) mutation
B) gene flow
C) geographic isolation
D) random fertilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the Hardy-Weinberg formula,what does p² represent?
A) frequency of the dominant allele
B) frequency of heterozygotes
C) frequency of the recessive allele
D) frequency of the homozygotes for one allele
A) frequency of the dominant allele
B) frequency of heterozygotes
C) frequency of the recessive allele
D) frequency of the homozygotes for one allele

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Gene flow is accomplished by ________.
A) migration
B) sexual recombination
C) mutation
D) natural selection
A) migration
B) sexual recombination
C) mutation
D) natural selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following examples results from disruptive selection?
A) The birth weight at which newborn humans are most likely to survive and the average weight of newborn humans are about the same.
B) There is an increase in antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
C) There is an increase in the number of different breeds of dog.
D) Garter snakes with different coloration patterns behave differently when threatened.
A) The birth weight at which newborn humans are most likely to survive and the average weight of newborn humans are about the same.
B) There is an increase in antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
C) There is an increase in the number of different breeds of dog.
D) Garter snakes with different coloration patterns behave differently when threatened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is an example that results from directional selection?
A) The birth weight at which newborn humans are most likely to survive and the average weight of newborn humans are about the same.
B) There is an increase in antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
C) There is an increase in the number of different breeds of dog.
D) Garter snakes with different coloration patterns behave differently when threatened.
A) The birth weight at which newborn humans are most likely to survive and the average weight of newborn humans are about the same.
B) There is an increase in antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
C) There is an increase in the number of different breeds of dog.
D) Garter snakes with different coloration patterns behave differently when threatened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the Hardy-Weinberg formula,what does 2pq represent?
A) frequency of the dominant allele
B) frequency of heterozygotes
C) frequency of the recessive allele
D) frequency of the homozygous dominants
A) frequency of the dominant allele
B) frequency of heterozygotes
C) frequency of the recessive allele
D) frequency of the homozygous dominants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The total collection of alleles in a population at any one time makes up that population's ________.
A) gene pool
B) genotype
C) heterozygote frequency
D) allele frequency
A) gene pool
B) genotype
C) heterozygote frequency
D) allele frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the frequency of one allele in a population is 0.7 in a population with two alleles at a particular locus,what is the frequency of the alternate allele?
A) 0.09
B) 0.21
C) 0.30
D) 0.42
A) 0.09
B) 0.21
C) 0.30
D) 0.42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The founder effect differs from a population bottleneck in that the founder effect ________.
A) requires a small population
B) is a type of natural selection
C) can occur only on an oceanic island colony
D) involves the isolation of a small colony of individuals from a larger population
A) requires a small population
B) is a type of natural selection
C) can occur only on an oceanic island colony
D) involves the isolation of a small colony of individuals from a larger population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Examine the relationships between the elephants in the figure below.Which one of the following pairs is most closely related? 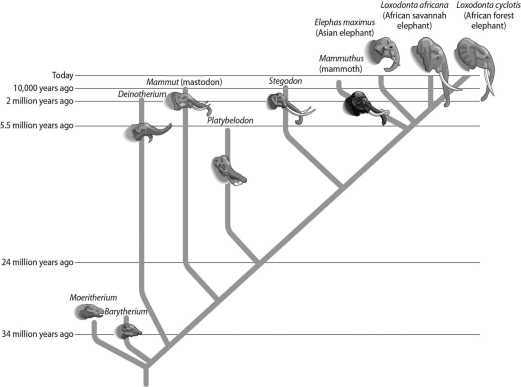
A) Deinotherium and Platybelodon
B) Barytherium and Stegodon
C) Loxodonta africana and Loxodonta cyclotis
D) Mammut and Stegodon

A) Deinotherium and Platybelodon
B) Barytherium and Stegodon
C) Loxodonta africana and Loxodonta cyclotis
D) Mammut and Stegodon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Read the following scenario to answer the questions that follow.
In order to test the susceptibility of bacteria to an antibiotic, a common laboratory test called the Bauer-Kirby Disk Diffusion test is used. First, a petri dish (a shallow, circular, transparent dish with a flat lid) is partially filled with nutrient-enriched agar (a gelatinous material). The nutrients encourage growth of specific bacterial species. The agar is poured as liquid but then typically solidifies to a soft consistency. Once the agar is set, a "lawn" of bacteria is spread such that a thin layer covers the top of the agar. Antibiotics are then applied to the lawn in a small dose, often through small saturated paper disks. The dish is typically incubated for 24-48 hours and then observed for susceptibility. If the antibiotic is effective, it will kill the bacteria and leave a clear area called the "zone of inhibition" due to inhibited bacterial growth. The area starts at the source of the antibiotic and radiates outward. Scientists measure the diameter of the zone and then compare it to an established "cutoff value" for a zone specific to antibiotic/organism combinations. A large zone of inhibition in comparison to the standard indicates susceptibility while a small or no zone indicates resistance. Consider the following image, and answer the questions that follow:
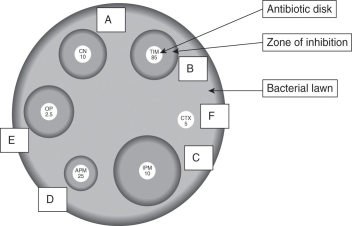
After rigorous testing,the Federal Drug Administration (FDA)must decide which of the four antibiotics to approve to fight a bacterial infection that results in high fevers and localized rashes.Which antibiotic do you predict that the FDA scientists will likely approve?
A) A
B) C
C) E
D) F
In order to test the susceptibility of bacteria to an antibiotic, a common laboratory test called the Bauer-Kirby Disk Diffusion test is used. First, a petri dish (a shallow, circular, transparent dish with a flat lid) is partially filled with nutrient-enriched agar (a gelatinous material). The nutrients encourage growth of specific bacterial species. The agar is poured as liquid but then typically solidifies to a soft consistency. Once the agar is set, a "lawn" of bacteria is spread such that a thin layer covers the top of the agar. Antibiotics are then applied to the lawn in a small dose, often through small saturated paper disks. The dish is typically incubated for 24-48 hours and then observed for susceptibility. If the antibiotic is effective, it will kill the bacteria and leave a clear area called the "zone of inhibition" due to inhibited bacterial growth. The area starts at the source of the antibiotic and radiates outward. Scientists measure the diameter of the zone and then compare it to an established "cutoff value" for a zone specific to antibiotic/organism combinations. A large zone of inhibition in comparison to the standard indicates susceptibility while a small or no zone indicates resistance. Consider the following image, and answer the questions that follow:

After rigorous testing,the Federal Drug Administration (FDA)must decide which of the four antibiotics to approve to fight a bacterial infection that results in high fevers and localized rashes.Which antibiotic do you predict that the FDA scientists will likely approve?
A) A
B) C
C) E
D) F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Examine the evolutionary tree below.This tree tells us that the amnion is found in ________. 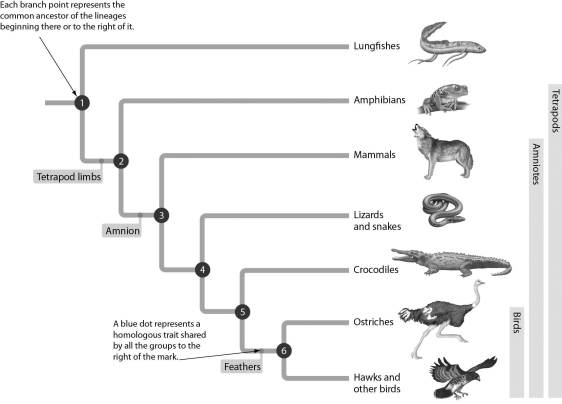
A) lungfishes and amphibians
B) amphibians only
C) mammals, lizards, and snakes only
D) mammals, lizards, snakes, crocodiles, and birds

A) lungfishes and amphibians
B) amphibians only
C) mammals, lizards, and snakes only
D) mammals, lizards, snakes, crocodiles, and birds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Scenario Questions
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
Over the past 60 years, many amphibian species have experienced significant population declines, and some species have become extinct. Scientists suspected that local human activities such as the destruction of wetlands, regional pollution, and deforestation were the main reasons for these losses. However, research over the past 20 years reveals significant amphibian population declines in protected areas of the world, such as nature preserves and parks. These global declines suggest widespread problems including increased ultraviolet radiation, acid rain, and disease. In Switzerland, for example, 14 of the 20 native amphibian species are threatened with extinction.
Some biologists urge the collection of the few remaining individuals of some of the most threatened amphibian species in order to preserve them if they become extinct in the wild.If such captive-breeding programs could produce thousands of individuals from just a few of the remaining survivors,the species will still be threatened because of ________.
A) a bottleneck effect
B) directional selection
C) mutations
D) artificial selection
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
Over the past 60 years, many amphibian species have experienced significant population declines, and some species have become extinct. Scientists suspected that local human activities such as the destruction of wetlands, regional pollution, and deforestation were the main reasons for these losses. However, research over the past 20 years reveals significant amphibian population declines in protected areas of the world, such as nature preserves and parks. These global declines suggest widespread problems including increased ultraviolet radiation, acid rain, and disease. In Switzerland, for example, 14 of the 20 native amphibian species are threatened with extinction.
Some biologists urge the collection of the few remaining individuals of some of the most threatened amphibian species in order to preserve them if they become extinct in the wild.If such captive-breeding programs could produce thousands of individuals from just a few of the remaining survivors,the species will still be threatened because of ________.
A) a bottleneck effect
B) directional selection
C) mutations
D) artificial selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The figure below shows the percent of selected DNA sequences that match between a chimpanzee and other primates.These data support the hypothesis that ________. 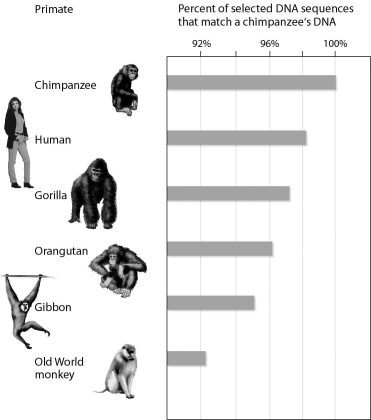
A) the chimpanzee's closest surviving relative is humans
B) chimpanzees and gibbons are the most closely related
C) orangutans are the primates least closely related to chimpanzees
D) Old World monkeys and gibbons are the most closely related

A) the chimpanzee's closest surviving relative is humans
B) chimpanzees and gibbons are the most closely related
C) orangutans are the primates least closely related to chimpanzees
D) Old World monkeys and gibbons are the most closely related

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The figure below shows what happens in insect populations when crops are sprayed with insecticides.This is an example of ________. 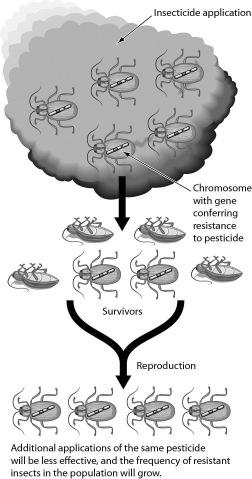
A) natural selection
B) genetic drift
C) founder effect
D) gene flow

A) natural selection
B) genetic drift
C) founder effect
D) gene flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Read the following scenario to answer the questions that follow.
In order to test the susceptibility of bacteria to an antibiotic, a common laboratory test called the Bauer-Kirby Disk Diffusion test is used. First, a petri dish (a shallow, circular, transparent dish with a flat lid) is partially filled with nutrient-enriched agar (a gelatinous material). The nutrients encourage growth of specific bacterial species. The agar is poured as liquid but then typically solidifies to a soft consistency. Once the agar is set, a "lawn" of bacteria is spread such that a thin layer covers the top of the agar. Antibiotics are then applied to the lawn in a small dose, often through small saturated paper disks. The dish is typically incubated for 24-48 hours and then observed for susceptibility. If the antibiotic is effective, it will kill the bacteria and leave a clear area called the "zone of inhibition" due to inhibited bacterial growth. The area starts at the source of the antibiotic and radiates outward. Scientists measure the diameter of the zone and then compare it to an established "cutoff value" for a zone specific to antibiotic/organism combinations. A large zone of inhibition in comparison to the standard indicates susceptibility while a small or no zone indicates resistance. Consider the following image, and answer the questions that follow:

What can you conclude about the susceptibility of the bacteria to the antibiotics?
A) The bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotic A than antibiotic C.
B) The bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotic D than antibiotic B.
C) The bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotic C than antibiotic E.
D) The bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotic D than antibiotic A.
In order to test the susceptibility of bacteria to an antibiotic, a common laboratory test called the Bauer-Kirby Disk Diffusion test is used. First, a petri dish (a shallow, circular, transparent dish with a flat lid) is partially filled with nutrient-enriched agar (a gelatinous material). The nutrients encourage growth of specific bacterial species. The agar is poured as liquid but then typically solidifies to a soft consistency. Once the agar is set, a "lawn" of bacteria is spread such that a thin layer covers the top of the agar. Antibiotics are then applied to the lawn in a small dose, often through small saturated paper disks. The dish is typically incubated for 24-48 hours and then observed for susceptibility. If the antibiotic is effective, it will kill the bacteria and leave a clear area called the "zone of inhibition" due to inhibited bacterial growth. The area starts at the source of the antibiotic and radiates outward. Scientists measure the diameter of the zone and then compare it to an established "cutoff value" for a zone specific to antibiotic/organism combinations. A large zone of inhibition in comparison to the standard indicates susceptibility while a small or no zone indicates resistance. Consider the following image, and answer the questions that follow:

What can you conclude about the susceptibility of the bacteria to the antibiotics?
A) The bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotic A than antibiotic C.
B) The bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotic D than antibiotic B.
C) The bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotic C than antibiotic E.
D) The bacteria are more susceptible to antibiotic D than antibiotic A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Read the following scenario to answer the questions that follow.
In order to test the susceptibility of bacteria to an antibiotic, a common laboratory test called the Bauer-Kirby Disk Diffusion test is used. First, a petri dish (a shallow, circular, transparent dish with a flat lid) is partially filled with nutrient-enriched agar (a gelatinous material). The nutrients encourage growth of specific bacterial species. The agar is poured as liquid but then typically solidifies to a soft consistency. Once the agar is set, a "lawn" of bacteria is spread such that a thin layer covers the top of the agar. Antibiotics are then applied to the lawn in a small dose, often through small saturated paper disks. The dish is typically incubated for 24-48 hours and then observed for susceptibility. If the antibiotic is effective, it will kill the bacteria and leave a clear area called the "zone of inhibition" due to inhibited bacterial growth. The area starts at the source of the antibiotic and radiates outward. Scientists measure the diameter of the zone and then compare it to an established "cutoff value" for a zone specific to antibiotic/organism combinations. A large zone of inhibition in comparison to the standard indicates susceptibility while a small or no zone indicates resistance. Consider the following image, and answer the questions that follow:

After 1 year of widely prescribed use,reports surface that bacterial infections disappear for up to 2 weeks after taking the prescribed antibiotic but then reappear,sometimes worse than the first time.Which of the following explanations might the FDA use to defend their choice of antibiotic to treat the infection?
A) Patients are not taking the antibiotic for the length of time prescribed and so selection for resistant bacteria that can survive a limited course of antibiotic is occurring.
B) Stabilizing selection over the year has allowed for the bacteria to remain at a high level in patients' bodies.
C) Patients' bodies are evolving over the year to create environments that are friendly to the growth of the bacteria.
D) Sexual dimorphism allowed for larger bacteria cells to outcompete smaller ones, therefore enabling larger bacteria cells to continue to multiply.
In order to test the susceptibility of bacteria to an antibiotic, a common laboratory test called the Bauer-Kirby Disk Diffusion test is used. First, a petri dish (a shallow, circular, transparent dish with a flat lid) is partially filled with nutrient-enriched agar (a gelatinous material). The nutrients encourage growth of specific bacterial species. The agar is poured as liquid but then typically solidifies to a soft consistency. Once the agar is set, a "lawn" of bacteria is spread such that a thin layer covers the top of the agar. Antibiotics are then applied to the lawn in a small dose, often through small saturated paper disks. The dish is typically incubated for 24-48 hours and then observed for susceptibility. If the antibiotic is effective, it will kill the bacteria and leave a clear area called the "zone of inhibition" due to inhibited bacterial growth. The area starts at the source of the antibiotic and radiates outward. Scientists measure the diameter of the zone and then compare it to an established "cutoff value" for a zone specific to antibiotic/organism combinations. A large zone of inhibition in comparison to the standard indicates susceptibility while a small or no zone indicates resistance. Consider the following image, and answer the questions that follow:

After 1 year of widely prescribed use,reports surface that bacterial infections disappear for up to 2 weeks after taking the prescribed antibiotic but then reappear,sometimes worse than the first time.Which of the following explanations might the FDA use to defend their choice of antibiotic to treat the infection?
A) Patients are not taking the antibiotic for the length of time prescribed and so selection for resistant bacteria that can survive a limited course of antibiotic is occurring.
B) Stabilizing selection over the year has allowed for the bacteria to remain at a high level in patients' bodies.
C) Patients' bodies are evolving over the year to create environments that are friendly to the growth of the bacteria.
D) Sexual dimorphism allowed for larger bacteria cells to outcompete smaller ones, therefore enabling larger bacteria cells to continue to multiply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Scenario Questions
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
Over the past 60 years, many amphibian species have experienced significant population declines, and some species have become extinct. Scientists suspected that local human activities such as the destruction of wetlands, regional pollution, and deforestation were the main reasons for these losses. However, research over the past 20 years reveals significant amphibian population declines in protected areas of the world, such as nature preserves and parks. These global declines suggest widespread problems including increased ultraviolet radiation, acid rain, and disease. In Switzerland, for example, 14 of the 20 native amphibian species are threatened with extinction.
When most populations of a wide-ranging amphibian species are lost and the few remaining populations are widely separated,we expect to see that ________.
A) artificial selection becomes a greater factor in microevolution
B) the founder effect becomes increasingly important
C) gene flow between populations is reduced
D) microevolution no longer occurs
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
Over the past 60 years, many amphibian species have experienced significant population declines, and some species have become extinct. Scientists suspected that local human activities such as the destruction of wetlands, regional pollution, and deforestation were the main reasons for these losses. However, research over the past 20 years reveals significant amphibian population declines in protected areas of the world, such as nature preserves and parks. These global declines suggest widespread problems including increased ultraviolet radiation, acid rain, and disease. In Switzerland, for example, 14 of the 20 native amphibian species are threatened with extinction.
When most populations of a wide-ranging amphibian species are lost and the few remaining populations are widely separated,we expect to see that ________.
A) artificial selection becomes a greater factor in microevolution
B) the founder effect becomes increasingly important
C) gene flow between populations is reduced
D) microevolution no longer occurs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Scenario Questions
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
Over the past 60 years, many amphibian species have experienced significant population declines, and some species have become extinct. Scientists suspected that local human activities such as the destruction of wetlands, regional pollution, and deforestation were the main reasons for these losses. However, research over the past 20 years reveals significant amphibian population declines in protected areas of the world, such as nature preserves and parks. These global declines suggest widespread problems including increased ultraviolet radiation, acid rain, and disease. In Switzerland, for example, 14 of the 20 native amphibian species are threatened with extinction.
Chytridiomycosis is a fungal disease first identified in 1998 as a cause of massive amphibian deaths.In some severely impacted populations,a few individuals have survived,perhaps because of some natural resistance.If these resistant individuals continue to survive and prosper,new resistant populations might emerge.This would be an example of ________.
A) genetic drift
B) natural selection
C) the founder effect
D) sexual selection
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
Over the past 60 years, many amphibian species have experienced significant population declines, and some species have become extinct. Scientists suspected that local human activities such as the destruction of wetlands, regional pollution, and deforestation were the main reasons for these losses. However, research over the past 20 years reveals significant amphibian population declines in protected areas of the world, such as nature preserves and parks. These global declines suggest widespread problems including increased ultraviolet radiation, acid rain, and disease. In Switzerland, for example, 14 of the 20 native amphibian species are threatened with extinction.
Chytridiomycosis is a fungal disease first identified in 1998 as a cause of massive amphibian deaths.In some severely impacted populations,a few individuals have survived,perhaps because of some natural resistance.If these resistant individuals continue to survive and prosper,new resistant populations might emerge.This would be an example of ________.
A) genetic drift
B) natural selection
C) the founder effect
D) sexual selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



