Deck 14: How Biological Diversity Evolves
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: How Biological Diversity Evolves
1
When two frog species,Rana pipiens and Rana sylvatica,mate,the offspring die early in embryonic development.This is an example of ________.
A) hybrid sterility
B) mechanical isolation
C) reduced hybrid viability
D) reduced hybrid fertility
A) hybrid sterility
B) mechanical isolation
C) reduced hybrid viability
D) reduced hybrid fertility
C
2
Which of the following describes allopatric speciation?
A) A population of squirrels is separated by the Grand Canyon. The two subpopulations evolve into two distinct species.
B) A tetraploid plant species evolves from a diploid ancestor. Both the tetraploid and diploid species are found in the same habitat.
C) One population breeds in the fall; another population breeds in the spring.
D) A male horse and a female donkey mate, producing a sterile hinny.
A) A population of squirrels is separated by the Grand Canyon. The two subpopulations evolve into two distinct species.
B) A tetraploid plant species evolves from a diploid ancestor. Both the tetraploid and diploid species are found in the same habitat.
C) One population breeds in the fall; another population breeds in the spring.
D) A male horse and a female donkey mate, producing a sterile hinny.
A
3
Which of the following would be an example of paedomorphosis?
A) starfish regenerating severed limbs
B) rapid evolution in a small, isolated population
C) two species evolving a similar appearance
D) insects that can reproduce in larval stages without reaching mature development stages
A) starfish regenerating severed limbs
B) rapid evolution in a small, isolated population
C) two species evolving a similar appearance
D) insects that can reproduce in larval stages without reaching mature development stages
D
4
The biological species concept cannot be applied to fossils.Which alternate approach to identifying species would be most useful for classifying fossil organisms?
A) an approach based on use of reproductive barriers
B) an approach based on genetic history
C) an approach based on measurable physical traits
D) an approach based on molecular biology
A) an approach based on use of reproductive barriers
B) an approach based on genetic history
C) an approach based on measurable physical traits
D) an approach based on molecular biology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Under the biological species concept,what criterion is used to assign populations of organisms to the same biological species?
A) a very similar appearance
B) being able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring
C) responding to the environment in the same way
D) having 99% of their genes in common
A) a very similar appearance
B) being able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring
C) responding to the environment in the same way
D) having 99% of their genes in common

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The type of reproductive barrier that occurs when two species mate but produce sterile hybrids is referred to as ________.
A) mechanical isolation
B) temporal isolation
C) a postzygotic barrier
D) a prezygotic barrier
A) mechanical isolation
B) temporal isolation
C) a postzygotic barrier
D) a prezygotic barrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A reproductive barrier that prevents individuals from closely related species from interbreeding is an example of ________.
A) a prezygotic barrier
B) allopatric speciation
C) sympatric speciation
D) geographic isolation of populations
A) a prezygotic barrier
B) allopatric speciation
C) sympatric speciation
D) geographic isolation of populations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Speciation requires ________.
A) periods of rapid evolutionary change
B) geographic isolation
C) long periods of time
D) genetic isolation
A) periods of rapid evolutionary change
B) geographic isolation
C) long periods of time
D) genetic isolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What type of reproductive isolating mechanism is described by a situation in which female fireflies mate only with males who emit light in a particular pattern?
A) habitat isolation
B) temporal isolation
C) mechanical isolation
D) behavioral isolation
A) habitat isolation
B) temporal isolation
C) mechanical isolation
D) behavioral isolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Uranium-235,with a half-life of 713,000,000 years,decays to lead-207.If a rock sample is determined to have one-quarter of the uranium-235 content it had when it formed,the age of the rock sample can be estimated to be approximately ________ years old.
A) 178 million
B) 713 million
C) 28.5 billion
D) 1.4 billion
A) 178 million
B) 713 million
C) 28.5 billion
D) 1.4 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Permian mass extinction is associated with ________.
A) an asteroid impact
B) global warming
C) the formation of Pangaea
D) the diversification of mammals
A) an asteroid impact
B) global warming
C) the formation of Pangaea
D) the diversification of mammals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Sympatric speciation specifically EXCLUDES ________.
A) behavioral isolation
B) postzygotic barriers
C) geographic isolation
D) temporal isolation
A) behavioral isolation
B) postzygotic barriers
C) geographic isolation
D) temporal isolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Some fish have bony fins.If the body of water they are in dries out,these fins can be used to help the fish "walk" to another body of water.In this context,bony fins are an example of ________.
A) an exaptation
B) an adaptation
C) a macroevolutionary event
D) paedomorphosis
A) an exaptation
B) an adaptation
C) a macroevolutionary event
D) paedomorphosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is the strongest piece of evidence for why some scientists believe that we are at the start of a sixth mass extinction?
A) decrease in biodiversity
B) decrease in fossil discoveries
C) decrease in allopatric species
D) decrease in hybrid fertility
A) decrease in biodiversity
B) decrease in fossil discoveries
C) decrease in allopatric species
D) decrease in hybrid fertility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The biological species concept cannot be applied to ________.
A) fungi that live on land
B) bacteria that reproduce only asexually
C) complex plants that have flowers
D) animals that use asexual and sexual reproduction
A) fungi that live on land
B) bacteria that reproduce only asexually
C) complex plants that have flowers
D) animals that use asexual and sexual reproduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Plate tectonics has been responsible for instances of all of the following EXCEPT ________.
A) volcanic explosions
B) sympatric speciation
C) allopatric speciation
D) mass extinction
A) volcanic explosions
B) sympatric speciation
C) allopatric speciation
D) mass extinction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The current geological era is the ________.
A) Paleozoic
B) Cenozoic
C) Mesozoic
D) Cambrian
A) Paleozoic
B) Cenozoic
C) Mesozoic
D) Cambrian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When brought together in a zoo,two species are capable of mating and producing fertile offspring.Why may they still be considered two distinct species?
A) Wild populations of the two species have different geographic distributions.
B) In the wild, members of one species prey upon members of the other species.
C) Zoos are not natural environments.
D) The two species look very different.
A) Wild populations of the two species have different geographic distributions.
B) In the wild, members of one species prey upon members of the other species.
C) Zoos are not natural environments.
D) The two species look very different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Feathers in birds appear to have first evolved for insulation but later conveyed a new advantage in helping create light aerodynamic surfaces.This switch in function is an example of a(n)________.
A) paedomorphosis
B) an analogy
C) an adaptation
D) exaptation
A) paedomorphosis
B) an analogy
C) an adaptation
D) exaptation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Biological species consist of groups of ________.
A) populations
B) domains
C) families
D) genera
A) populations
B) domains
C) families
D) genera

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When you go outside,it is common to hear a variety of bird songs.These songs vary among bird species as well as bird flocks.Interestingly,some bird species that are highly unrelated have very similar song qualities.What can you conclude from this phenomenon?
A) The bird songs are homologous traits.
B) The bird songs have achieved speciation after coming from allopatric species.
C) The bird songs are analogous traits.
D) The bird songs have different molecular DNA.
A) The bird songs are homologous traits.
B) The bird songs have achieved speciation after coming from allopatric species.
C) The bird songs are analogous traits.
D) The bird songs have different molecular DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The wing of a bald eagle is ________ the wing of a penguin.
A) convergent with
B) homologous to
C) unrelated to
D) analogous to
A) convergent with
B) homologous to
C) unrelated to
D) analogous to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Analogous structures are evidence of ________.
A) common ancestry
B) divergent evolution
C) stabilizing selection
D) convergent evolution
A) common ancestry
B) divergent evolution
C) stabilizing selection
D) convergent evolution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What hypothesis did Luis and Walter Alvarez test in relation to the mass extinction of dinosaurs 65 million years ago (MYA)?
A) The mass extinction 65 MYA was caused by a surge of catastrophic cyclones.
B) The mass extinction 65 MYA was caused by a slow but steady increase in climate temperatures.
C) The mass extinction 65 MYA was caused by an impact of an extraterrestrial object.
D) The mass extinction 65 MYA was caused by the loss of preferred plants for food.
A) The mass extinction 65 MYA was caused by a surge of catastrophic cyclones.
B) The mass extinction 65 MYA was caused by a slow but steady increase in climate temperatures.
C) The mass extinction 65 MYA was caused by an impact of an extraterrestrial object.
D) The mass extinction 65 MYA was caused by the loss of preferred plants for food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Homology is evidence of ________.
A) convergent evolution
B) polyploidy
C) common ancestry
D) paedomorphosis
A) convergent evolution
B) polyploidy
C) common ancestry
D) paedomorphosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which one of the following is the only domain that contains eukaryotes?
A) Animalia
B) Plantae
C) Archaea
D) Eukarya
A) Animalia
B) Plantae
C) Archaea
D) Eukarya

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following taxonomic levels is most inclusive?
A) order
B) genus
C) family
D) class
A) order
B) genus
C) family
D) class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Examine the evolutionary relationships represented in the following figure.Based upon this diagram,the two most closely related species are ________. 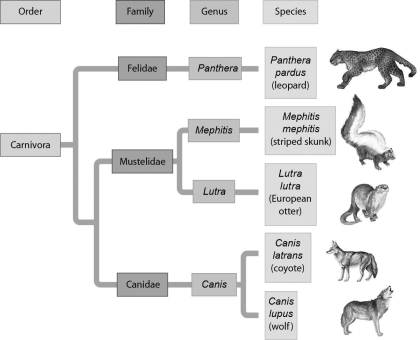
A) leopards and striped skunks
B) leopards and European otters
C) European otters and coyotes
D) coyotes and wolves

A) leopards and striped skunks
B) leopards and European otters
C) European otters and coyotes
D) coyotes and wolves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Examine the two squirrel populations in the following figure.The populations are separated by a geographic barrier.If after a long period of time the two species are no longer separated,what evidence is needed to determine if speciation has occurred? 
A) Hybrid offspring of the two populations begin to appear.
B) The two populations are not interbreeding freely.
C) One species will increase into a population size twice as large as the other species.
D) Polyploidy is creating new species.

A) Hybrid offspring of the two populations begin to appear.
B) The two populations are not interbreeding freely.
C) One species will increase into a population size twice as large as the other species.
D) Polyploidy is creating new species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why is it INCORRECT to assume that mass extinctions carry only negative impact on the evolution of life on Earth?
A) Mass extinctions are sometimes followed by periods of evolutionary change when other organism groups can flourish and expand in diversity and size.
B) Mass extinctions enable scientists to better study embryonic development in two species of organisms and therefore identify possible homology.
C) Mass extinctions enable scientists to better study paedomorphosis.
D) Mass extinctions disprove Darwin's theory of evolution.
A) Mass extinctions are sometimes followed by periods of evolutionary change when other organism groups can flourish and expand in diversity and size.
B) Mass extinctions enable scientists to better study embryonic development in two species of organisms and therefore identify possible homology.
C) Mass extinctions enable scientists to better study paedomorphosis.
D) Mass extinctions disprove Darwin's theory of evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The wing of a penguin is ________ the wing of a butterfly.
A) structurally identical to
B) superior to
C) homologous to
D) analogous to
A) structurally identical to
B) superior to
C) homologous to
D) analogous to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Molecular systematics might examine all of the following types of data EXCEPT ________.
A) proteins
B) DNA sequences
C) amino acid sequences
D) anatomical features
A) proteins
B) DNA sequences
C) amino acid sequences
D) anatomical features

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
________ is the discipline of biology that focuses on classifying organisms and determining their evolutionary relationships.
A) Taxonomy
B) Evo-devo
C) Systematics
D) Biogeography
A) Taxonomy
B) Evo-devo
C) Systematics
D) Biogeography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Examine the figure below.According to the figure,cladistic analysis indicates that crocodiles are more closely related to ________ than to ________. 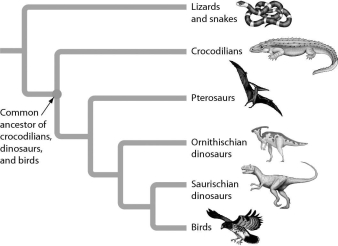
A) birds... pterosaurs
B) snakes... birds
C) Ornithischian dinosaurs… pterosaurs
D) birds... lizards

A) birds... pterosaurs
B) snakes... birds
C) Ornithischian dinosaurs… pterosaurs
D) birds... lizards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Dinosaurs (aside from the lineage that produced birds)were extinct by the end of the ________.
A) Cretaceous
B) Silurian
C) Eocene
D) Permian
A) Cretaceous
B) Silurian
C) Eocene
D) Permian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A period of mass extinction is often followed by ________.
A) explosive diversification
B) paedomorphosis
C) global warming
D) continental drift
A) explosive diversification
B) paedomorphosis
C) global warming
D) continental drift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Of the following taxonomic levels,species found within the same ________ are the most closely related.
A) family
B) phylum
C) order
D) domain
A) family
B) phylum
C) order
D) domain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An ancestral species and all its evolutionary descendants define a(n)________.
A) outgroup
B) clade
C) genus
D) ingroup
A) outgroup
B) clade
C) genus
D) ingroup

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Characid fishes are found naturally only in South America and Africa.Fossils of these fish are not found on any other continents.What is the most likely explanation of this distribution pattern?
A) These fishes arose in either Africa or South America and migrated across the South Atlantic Ocean to the other continent.
B) Characid fishes arose prior to the separation of the African and South American continents.
C) Characid fishes arose in the South Atlantic Ocean and migrated to Africa and South America.
D) Convergent evolution is responsible for the distribution of characid fishes.
A) These fishes arose in either Africa or South America and migrated across the South Atlantic Ocean to the other continent.
B) Characid fishes arose prior to the separation of the African and South American continents.
C) Characid fishes arose in the South Atlantic Ocean and migrated to Africa and South America.
D) Convergent evolution is responsible for the distribution of characid fishes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The science of naming,identifying,and classifying organisms is called ________.
A) biogeography
B) systematics
C) phylogeny
D) taxonomy
A) biogeography
B) systematics
C) phylogeny
D) taxonomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
As part of a semester-long biology field research course, you are studying reproductive barriers among four different frog species. Your goal is to determine what type of reproductive barrier likely causes the gene pools of the four different frog species to be isolated. These four species share common geographic habitats and are both anatomically and gametically compatible. Your research professor gives you the following figure to consider. After studying the figure, answer the questions that follow.
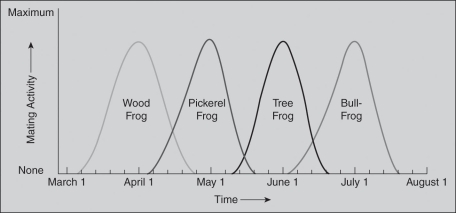
If the researchers of this study wanted to collect reliable data about natural behavior,which methodology should they choose?
A) The researchers collected multiple male and female frogs from each species and studied them in a lab environment to determine their normal breeding seasons.
B) The researchers studied multiple male and female frogs from each species in their natural environments to determine their normal breeding seasons.
C) The researchers collected multiple male and female frogs from each species, mixed males and females from each species, and studied the mixed pairs in a lab environment to determine their normal breeding seasons.
D) The researchers studied one male and female frog from each species in their natural environments to determine their normal breeding seasons.
As part of a semester-long biology field research course, you are studying reproductive barriers among four different frog species. Your goal is to determine what type of reproductive barrier likely causes the gene pools of the four different frog species to be isolated. These four species share common geographic habitats and are both anatomically and gametically compatible. Your research professor gives you the following figure to consider. After studying the figure, answer the questions that follow.

If the researchers of this study wanted to collect reliable data about natural behavior,which methodology should they choose?
A) The researchers collected multiple male and female frogs from each species and studied them in a lab environment to determine their normal breeding seasons.
B) The researchers studied multiple male and female frogs from each species in their natural environments to determine their normal breeding seasons.
C) The researchers collected multiple male and female frogs from each species, mixed males and females from each species, and studied the mixed pairs in a lab environment to determine their normal breeding seasons.
D) The researchers studied one male and female frog from each species in their natural environments to determine their normal breeding seasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
In some zoos, rare crosses between a male lion and a female tiger have produced hybrid offspring called "ligers." Male ligers are sterile but some female ligers are fertile. In the wild, lion and tiger ranges do not naturally overlap, making such a cross unlikely. Furthermore, the solitary behavior of tigers and the social organizations of lions create behavioral differences.
Applying the biological species concept,the sterility of ligers reveals that ________.
A) a new species called "ligers" is forming
B) tigers and lions are actually the same species
C) tigers and lions are separate species
D) lions are probably a subspecies of tigers
In some zoos, rare crosses between a male lion and a female tiger have produced hybrid offspring called "ligers." Male ligers are sterile but some female ligers are fertile. In the wild, lion and tiger ranges do not naturally overlap, making such a cross unlikely. Furthermore, the solitary behavior of tigers and the social organizations of lions create behavioral differences.
Applying the biological species concept,the sterility of ligers reveals that ________.
A) a new species called "ligers" is forming
B) tigers and lions are actually the same species
C) tigers and lions are separate species
D) lions are probably a subspecies of tigers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
As part of a semester-long biology field research course, you are studying reproductive barriers among four different frog species. Your goal is to determine what type of reproductive barrier likely causes the gene pools of the four different frog species to be isolated. These four species share common geographic habitats and are both anatomically and gametically compatible. Your research professor gives you the following figure to consider. After studying the figure, answer the questions that follow.

What can you conclude about the breeding characteristics of these four frog species?
A) The maximum mating activity of the four frog species at different times reduces and/or removes interbreeding.
B) The minimum mating activity of the four frog species at different times reduces and/or removes interbreeding.
C) The average mating activity of the four frog species at different times reduces and/or removes interbreeding.
D) The individual mating activity of each of the four frog species at the beginning of their mating periods reduces and/or removes interbreeding.
As part of a semester-long biology field research course, you are studying reproductive barriers among four different frog species. Your goal is to determine what type of reproductive barrier likely causes the gene pools of the four different frog species to be isolated. These four species share common geographic habitats and are both anatomically and gametically compatible. Your research professor gives you the following figure to consider. After studying the figure, answer the questions that follow.

What can you conclude about the breeding characteristics of these four frog species?
A) The maximum mating activity of the four frog species at different times reduces and/or removes interbreeding.
B) The minimum mating activity of the four frog species at different times reduces and/or removes interbreeding.
C) The average mating activity of the four frog species at different times reduces and/or removes interbreeding.
D) The individual mating activity of each of the four frog species at the beginning of their mating periods reduces and/or removes interbreeding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
In some zoos, rare crosses between a male lion and a female tiger have produced hybrid offspring called "ligers." Male ligers are sterile but some female ligers are fertile. In the wild, lion and tiger ranges do not naturally overlap, making such a cross unlikely. Furthermore, the solitary behavior of tigers and the social organizations of lions create behavioral differences.
The natural differences in the ranges of wild tigers and lions is an example of ________.
A) a prezygotic barrier
B) a postzygotic barrier
C) the impact of mutations
D) sympatric speciation
In some zoos, rare crosses between a male lion and a female tiger have produced hybrid offspring called "ligers." Male ligers are sterile but some female ligers are fertile. In the wild, lion and tiger ranges do not naturally overlap, making such a cross unlikely. Furthermore, the solitary behavior of tigers and the social organizations of lions create behavioral differences.
The natural differences in the ranges of wild tigers and lions is an example of ________.
A) a prezygotic barrier
B) a postzygotic barrier
C) the impact of mutations
D) sympatric speciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
In some zoos, rare crosses between a male lion and a female tiger have produced hybrid offspring called "ligers." Male ligers are sterile but some female ligers are fertile. In the wild, lion and tiger ranges do not naturally overlap, making such a cross unlikely. Furthermore, the solitary behavior of tigers and the social organizations of lions create behavioral differences.
The production of sterile male ligers is an example of ________.
A) sympatric speciation
B) the founder effect
C) a postzygotic barrier
D) a prezygotic barrier
In some zoos, rare crosses between a male lion and a female tiger have produced hybrid offspring called "ligers." Male ligers are sterile but some female ligers are fertile. In the wild, lion and tiger ranges do not naturally overlap, making such a cross unlikely. Furthermore, the solitary behavior of tigers and the social organizations of lions create behavioral differences.
The production of sterile male ligers is an example of ________.
A) sympatric speciation
B) the founder effect
C) a postzygotic barrier
D) a prezygotic barrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Read the following scenario to answer the following questions.
As part of a semester-long biology field research course, you are studying reproductive barriers among four different frog species. Your goal is to determine what type of reproductive barrier likely causes the gene pools of the four different frog species to be isolated. These four species share common geographic habitats and are both anatomically and gametically compatible. Your research professor gives you the following figure to consider. After studying the figure, answer the questions that follow.

Based on the independent and dependent variables represented in the figure and the information you have about common geographic habitats as well as anatomical and gametic compatibility of the four frog species,you initially conclude that reproductive barriers may be due to ________.
A) habitat isolation
B) mechanical isolation
C) temporal isolation
D) gametic isolation
As part of a semester-long biology field research course, you are studying reproductive barriers among four different frog species. Your goal is to determine what type of reproductive barrier likely causes the gene pools of the four different frog species to be isolated. These four species share common geographic habitats and are both anatomically and gametically compatible. Your research professor gives you the following figure to consider. After studying the figure, answer the questions that follow.

Based on the independent and dependent variables represented in the figure and the information you have about common geographic habitats as well as anatomical and gametic compatibility of the four frog species,you initially conclude that reproductive barriers may be due to ________.
A) habitat isolation
B) mechanical isolation
C) temporal isolation
D) gametic isolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



