Deck 28: Water and Salt Physiology of Animals in Their Environments
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/87
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Water and Salt Physiology of Animals in Their Environments
1
Why have scientists never found European eel eggs or hatchlings in their European freshwater habitats?
A) Larvae do not emerge from buried mud until almost fully grown.
B) Eggs are buried and develop on moist land.
C) Spawning takes place in the west North Atlantic Ocean.
D) Young are developed internally and only released from the mother when close to fully grown.
A) Larvae do not emerge from buried mud until almost fully grown.
B) Eggs are buried and develop on moist land.
C) Spawning takes place in the west North Atlantic Ocean.
D) Young are developed internally and only released from the mother when close to fully grown.
C
2
In terms of its lifecycle, the European eel is classified as
A) anadromous.
B) catadromous.
C) hyperosmotic.
D) hyposmotic.
A) anadromous.
B) catadromous.
C) hyperosmotic.
D) hyposmotic.
B
3
Why is the European eel classified as catadromous?
A) It is hyperosmotic to freshwater.
B) It is hyposmostic to seawater.
C) It migrates to the ocean to spawn.
D) It migrates to freshwater to spawn.
A) It is hyperosmotic to freshwater.
B) It is hyposmostic to seawater.
C) It migrates to the ocean to spawn.
D) It migrates to freshwater to spawn.
C
4
If the osmolarity of freshwater is 100 mOsm, the freshwater animals would regulate their blood to an osmolarity of about _______ mOsm.
A) 80
B) 90
C) 100
D) 120
A) 80
B) 90
C) 100
D) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the blood osmolarity of a freshwater animal is 100 mOsm, the freshwater osmolarity is about _______ mOsm.
A) 90
B) 100
C) 110
D) 120
A) 90
B) 100
C) 110
D) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All freshwater animals regulate their blood osmotic pressures at levels _______ to fresh water.
A) isosmotic
B) hyperosmotic
C) hyposmotic
D) isotonic
A) isosmotic
B) hyperosmotic
C) hyposmotic
D) isotonic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Freshwater animals are
A) hyperosmotic regulators.
B) hyposmotic regulators.
C) isosmotic conformers.
D) hyperosmotic conformers.
A) hyperosmotic regulators.
B) hyposmotic regulators.
C) isosmotic conformers.
D) hyperosmotic conformers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which organism has the highest concentration of sodium ions in its plasma?
A) Freshwater mussels
B) Crayfish
C) Brown trout
D) Frogs
A) Freshwater mussels
B) Crayfish
C) Brown trout
D) Frogs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Freshwater animals tend to
A) lose water and gain ions.
B) gain water and ions.
C) gain water and lose ions.
D) lose water and ions.
A) lose water and gain ions.
B) gain water and ions.
C) gain water and lose ions.
D) lose water and ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a crayfish's antennal gland is damaged, which function is lost?
A) Sensation
B) Chemical detection
C) Defenses
D) Chemical consistency
A) Sensation
B) Chemical detection
C) Defenses
D) Chemical consistency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The antennal gland opens at the base of the
A) first antenna.
B) second antenna.
C) first limb.
D) second limb.
A) first antenna.
B) second antenna.
C) first limb.
D) second limb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The integument of freshwater crayfish is no more than _______ as permeable to water and sodium as the integument of marine decapods of the same size.
A) 10%
B) 12%
C) 15%
D) 21%
A) 10%
B) 12%
C) 15%
D) 21%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Fresh water animals' integuments have low permeability so that
A) ATP production is great enough to maintain normal blood composition.
B) the rate of ion exchange is maximized without the expenditure of energy.
C) the rate of water exchange is minimized without the expenditure of energy.
D) ATP production is great enough to maintain normal intracellular fluid concentration.
A) ATP production is great enough to maintain normal blood composition.
B) the rate of ion exchange is maximized without the expenditure of energy.
C) the rate of water exchange is minimized without the expenditure of energy.
D) ATP production is great enough to maintain normal intracellular fluid concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which animal has the lowest osmotic U/P ratio?
A) Clawed toad
B) Goldfish
C) Mosquito larva
D) Crayfish
A) Clawed toad
B) Goldfish
C) Mosquito larva
D) Crayfish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which organelle is the most important in moving sodium and chloride in freshwater animals?
A) Nucleus
B) Mitochondria
C) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
D) Lysosomes
A) Nucleus
B) Mitochondria
C) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
D) Lysosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In frogs, if the sodium concentration in the ambient environment increased, sodium intake from the environment would
A) continue to occur by diffusion.
B) continue to occur by facilitated diffusion.
C) continue to occur by primary active transport.
D) cease to occur by diffusion.
A) continue to occur by diffusion.
B) continue to occur by facilitated diffusion.
C) continue to occur by primary active transport.
D) cease to occur by diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In frogs, if the chloride concentration in the ambient environment increased, chloride intake from the environment would
A) continue to occur by diffusion.
B) continue to occur by facilitated diffusion.
C) continue to occur by active transport.
D) cease to occur by diffusion.
A) continue to occur by diffusion.
B) continue to occur by facilitated diffusion.
C) continue to occur by active transport.
D) cease to occur by diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Due to chloride active transport in the gills of freshwater fish, the epithelial cells of the gills
A) become increasingly negative because chloride ions are negative.
B) become increasingly positive because chloride ions are positive.
C) are neutral because each chloride ion is exchanged with a sodium ion.
D) are neutral because each chloride ion is exchanged with a bicarbonate ion.
A) become increasingly negative because chloride ions are negative.
B) become increasingly positive because chloride ions are positive.
C) are neutral because each chloride ion is exchanged with a sodium ion.
D) are neutral because each chloride ion is exchanged with a bicarbonate ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Due to sodium active transport in gills of freshwater fish, the epithelial cells of the gills
A) become increasingly negative because sodium ions are negative.
B) become increasingly positive because sodium ions are positive.
C) are neutral because each sodium ion is exchanged with a proton.
D) are neutral because each sodium ion is exchanged with a chloride ion.
A) become increasingly negative because sodium ions are negative.
B) become increasingly positive because sodium ions are positive.
C) are neutral because each sodium ion is exchanged with a proton.
D) are neutral because each sodium ion is exchanged with a chloride ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which statement about sodium movement in frogs is true?
A) Sodium moves across the skin by energy-requiring mechanisms.
B) Sodium movement regulates acid-base levels.
C) Sodium movement is directly associated with bicarbonate movement.
D) Sodium moves across the skin by energy-requiring mechanisms, and its movement regulates acid-base levels.
A) Sodium moves across the skin by energy-requiring mechanisms.
B) Sodium movement regulates acid-base levels.
C) Sodium movement is directly associated with bicarbonate movement.
D) Sodium moves across the skin by energy-requiring mechanisms, and its movement regulates acid-base levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement about chloride movement in frogs is false?
A) Chloride moves across the skin by energy-requiring mechanisms.
B) Chloride movement regulates to acid-base levels.
C) Chloride movement is directly associated with bicarbonate movement.
D) Chloride movement is directly associated with proton movement.
A) Chloride moves across the skin by energy-requiring mechanisms.
B) Chloride movement regulates to acid-base levels.
C) Chloride movement is directly associated with bicarbonate movement.
D) Chloride movement is directly associated with proton movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In adult freshwater fish, the major site of sodium exchange is the
A) kidney.
B) gill.
C) heart.
D) skin.
A) kidney.
B) gill.
C) heart.
D) skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In early freshwater fish larvae, the major site of chloride exchange is the
A) kidney.
B) gill.
C) skin.
D) heart.
A) kidney.
B) gill.
C) skin.
D) heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In adult freshwater teleosts, ion exchange occurs in the
A) gill lamellae.
B) gill arches.
C) gill filaments.
D) skin.
A) gill lamellae.
B) gill arches.
C) gill filaments.
D) skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Based on the immunohistochemistry method used, the most common proteins found in the cells of gills in freshwater teleosts are
A) Na+-K+-ATPases.
B) Na+/Cl- cotransporters.
C) Na+/Cl-/K+ cotransporters.
D) Na+-K+-ATPases and Na+/Cl-/K+ cotransporters.
A) Na+-K+-ATPases.
B) Na+/Cl- cotransporters.
C) Na+/Cl-/K+ cotransporters.
D) Na+-K+-ATPases and Na+/Cl-/K+ cotransporters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If you were to apply an inhibitor that shuts down the mitochondria, what would occur in the gills of freshwater fish?
A) Chloride cells would cease to function.
B) Pavement cells would increase in function.
C) Sodium uptake would be unaffected.
D) Urination would cease.
A) Chloride cells would cease to function.
B) Pavement cells would increase in function.
C) Sodium uptake would be unaffected.
D) Urination would cease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a researcher applies BAPTA, a calcium chelator (binds calcium), to the environment of freshwater fish, the
A) number of chloride cells in the fish will increase.
B) number of chloride cells in the fish will decrease.
C) number of chloride cells in the fish will remain the same.
D) oxygen uptake ability in the fish will increase.
A) number of chloride cells in the fish will increase.
B) number of chloride cells in the fish will decrease.
C) number of chloride cells in the fish will remain the same.
D) oxygen uptake ability in the fish will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
MRCs are abundant with Na+-K+-ATPases. In each cell, there are about _______ Na+-K+-ATPase molecules.
A) 100,000
B) 1,000,000
C) 10,000,000
D) 100,000,000
A) 100,000
B) 1,000,000
C) 10,000,000
D) 100,000,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You conduct an experiment in which you make the environment of freshwater fish highly basic. You then isolate the ionocytes and conduct an immunocytochemistry technique. Under these conditions, you would be most likely to observe _______ in Cl-/HCO3- protein expression.
A) a drastic increase
B) a drastic decrease
C) a slight decrease
D) no change in
A) a drastic increase
B) a drastic decrease
C) a slight decrease
D) no change in

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
You perform an immunocytochemistry technique on fish MRCs and you observe that the Cl-/HCO3- countertransport protein is expressed in greater quantities than normal. The fish must have been living in a(n) _______ environment.
A) acidic
B) basic
C) pure water
D) neutral
A) acidic
B) basic
C) pure water
D) neutral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The bicarbonate that is pumped out of the gills, from freshwater fish into the water, comes from
A) carbon dioxide.
B) consumption of food rich in sodium bicarbonate.
C) protein metabolism.
D) glycolysis.
A) carbon dioxide.
B) consumption of food rich in sodium bicarbonate.
C) protein metabolism.
D) glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which statement about chloride cells is false?
A) They produce a lot of carbon dioxide.
B) They take up a lot of nutrients, such as glucose and fatty acids.
C) They are surrounded by pavement cells.
D) They are found in the gills of freshwater fish in greater quantities than pavement cells.
A) They produce a lot of carbon dioxide.
B) They take up a lot of nutrients, such as glucose and fatty acids.
C) They are surrounded by pavement cells.
D) They are found in the gills of freshwater fish in greater quantities than pavement cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Gills in freshwater crayfish provide a(n)
A) advantage for oxygen intake but a disadvantage for water intake.
B) advantage for oxygen intake and an advantage for water intake.
C) disadvantage for oxygen intake and a disadvantage for water intake.
D) disadvantage for oxygen intake but an advantage for water intake.
A) advantage for oxygen intake but a disadvantage for water intake.
B) advantage for oxygen intake and an advantage for water intake.
C) disadvantage for oxygen intake and a disadvantage for water intake.
D) disadvantage for oxygen intake but an advantage for water intake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement best describes the movement of sodium in freshwater fish?
A) Sodium is lost by excretion in urine (2-3 µmole per day) and diffusion across the body (240 µmole per day).
B) Sodium is lost by excretion in urine (240 µmole per day) and diffusion across the body (2-3 µmole per day).
C) Sodium is lost by excretion in urine (2-3 µmole per day) and diffusion across the body (2-3 µmole per day).
D) Sodium is lost by excretion in urine (100 µmole per day) and diffusion across the body (200 µmole per day).
A) Sodium is lost by excretion in urine (2-3 µmole per day) and diffusion across the body (240 µmole per day).
B) Sodium is lost by excretion in urine (240 µmole per day) and diffusion across the body (2-3 µmole per day).
C) Sodium is lost by excretion in urine (2-3 µmole per day) and diffusion across the body (2-3 µmole per day).
D) Sodium is lost by excretion in urine (100 µmole per day) and diffusion across the body (200 µmole per day).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Freshwater fish lose about _______ µmoles of sodium per day.
A) 100
B) 200
C) 240
D) 260
A) 100
B) 200
C) 240
D) 260

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Squids' inner body fluid is
A) hyposmotic to seawater.
B) hyperosmotic to seawater.
C) isosmotic to seawater.
D) sometimes hyperosmotic and sometimes hyposmotic to seawater.
A) hyposmotic to seawater.
B) hyperosmotic to seawater.
C) isosmotic to seawater.
D) sometimes hyperosmotic and sometimes hyposmotic to seawater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If an octopus has an osmolarity of 300 mOsm, the environment it lives in must have an osmolarity of _______ mOsm.
A) 150
B) 200
C) 250
D) 300
A) 150
B) 200
C) 250
D) 300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the sodium concentration in a squid's body fluid is 456 mmol/kg of H2O, the intracellular sodium concentration is _______ mmol/kg of H2O.
A) 5
B) 300
C) 456
D) 1056
A) 5
B) 300
C) 456
D) 1056

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the potassium concentration in a squid's body fluid is 22 mmol/kg of H2O, the intracellular potassium concentration is _______ mmol/kg of H2O.
A) 5
B) 12
C) 22
D) 400
A) 5
B) 12
C) 22
D) 400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The blood osmotic pressure of marine teleosts is about _______ mOsm _______ than the environmental osmotic pressure.
A) 300; lower
B) 300; higher
C) 600; higher
D) 600; lower
A) 300; lower
B) 300; higher
C) 600; higher
D) 600; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a marine teleost drinks seawater,
A) it immediately rehydrates the animal.
B) it immediately desiccates the animal.
C) it must process the excess sodium chloride consumed at the gills.
D) it must process the excess sodium chloride consumed at the kidney.
A) it immediately rehydrates the animal.
B) it immediately desiccates the animal.
C) it must process the excess sodium chloride consumed at the gills.
D) it must process the excess sodium chloride consumed at the kidney.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When a marine teleost drinks seawater, what occurs initially in the gut?
A) Water from the body tissues moves into the gut.
B) Salts from the body tissues moves into the gut.
C) Peristaltic action increases.
D) Water is actively transported from the gut into the tissues.
A) Water from the body tissues moves into the gut.
B) Salts from the body tissues moves into the gut.
C) Peristaltic action increases.
D) Water is actively transported from the gut into the tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The kidneys of marine teleosts produce urine at a rate that is _______ compared to freshwater teleosts.
A) higher
B) lower
C) similar
D) more variable
A) higher
B) lower
C) similar
D) more variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Choose the likely explanation for the evolution of salt glands in ocean birds.
A) Ocean birds eliminate too much water via their kidneys such that they cannot process the excess salt.
B) All ocean birds need to be able to drink seawater.
C) Ocean bird kidneys cannot significantly concentrate urine enough to eliminate the excess salts consumed in their diet.
D) Ocean bird kidneys cannot significantly eliminate uric acid enough to eliminate the excess salts consumed in their diet.
A) Ocean birds eliminate too much water via their kidneys such that they cannot process the excess salt.
B) All ocean birds need to be able to drink seawater.
C) Ocean bird kidneys cannot significantly concentrate urine enough to eliminate the excess salts consumed in their diet.
D) Ocean bird kidneys cannot significantly eliminate uric acid enough to eliminate the excess salts consumed in their diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why is volume regulation at odds with ionic regulation in marine teleost fish?
A) Volume regulation is not at odds with ionic regulation in marine teleost fish, only in freshwater teleost fish.
B) Salts in the marine teleost absorb water from the ocean, which must be eliminated.
C) In order to maintain osmotic balance, salts must be taken in from the ocean water.
D) The only way to obtain water is to drink it, which loads more salt into the animal which must be eliminated.
A) Volume regulation is not at odds with ionic regulation in marine teleost fish, only in freshwater teleost fish.
B) Salts in the marine teleost absorb water from the ocean, which must be eliminated.
C) In order to maintain osmotic balance, salts must be taken in from the ocean water.
D) The only way to obtain water is to drink it, which loads more salt into the animal which must be eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Choose the best description of a typical marine shark.
A) Hyperosmotic and hyperionic to ocean water
B) Hyperosmotic but hypoionic to ocean water
C) Hypoosmotic but hyperionic to ocean water
D) Hypoosmotic and hypoionic to ocean water
A) Hyperosmotic and hyperionic to ocean water
B) Hyperosmotic but hypoionic to ocean water
C) Hypoosmotic but hyperionic to ocean water
D) Hypoosmotic and hypoionic to ocean water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which statement regarding ionic movement across the gills of marine animals is true?
A) Sodium moves faster than chloride because of the overall positive charge inside the gill epithelium.
B) Sodium moves faster than chloride because of the overall negative charge inside the gill epithelium.
C) Sodium moves slower than chloride because of the overall positive charge inside the gill epithelium.
D) Sodium moves slower than chloride because of the overall negative charge inside the gill epithelium.
A) Sodium moves faster than chloride because of the overall positive charge inside the gill epithelium.
B) Sodium moves faster than chloride because of the overall negative charge inside the gill epithelium.
C) Sodium moves slower than chloride because of the overall positive charge inside the gill epithelium.
D) Sodium moves slower than chloride because of the overall negative charge inside the gill epithelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The chloride channels in the mitochondria-rich cells of marine teleosts are located on the _______ membrane(s).
A) apical
B) basolateral
C) blood cell
D) apical and basolateral
A) apical
B) basolateral
C) blood cell
D) apical and basolateral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In mitochondria-rich cells of marine teleosts, Cl- enters the cell through the
A) apical membrane by simple diffusion and exits via the basolateral membrane by secondary active transport.
B) basolateral membrane by simple diffusion and exits via the apical membrane by secondary active transport.
C) basolateral membrane by secondary active transport and exits via the apical membrane by simple diffusion.
D) apical membrane by secondary active transport and exits via the basolateral membrane by simple diffusion.
A) apical membrane by simple diffusion and exits via the basolateral membrane by secondary active transport.
B) basolateral membrane by simple diffusion and exits via the apical membrane by secondary active transport.
C) basolateral membrane by secondary active transport and exits via the apical membrane by simple diffusion.
D) apical membrane by secondary active transport and exits via the basolateral membrane by simple diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which animal is not a hyposmotic regulator?
A) Arthropod that lives in saline water
B) Marine reptile
C) Marine mammal
D) Marine echinoderm
A) Arthropod that lives in saline water
B) Marine reptile
C) Marine mammal
D) Marine echinoderm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Species that are able to survive only within a narrow range of ambient salinities are called
A) conformers.
B) stenohaline.
C) euryhaline.
D) xeric.
A) conformers.
B) stenohaline.
C) euryhaline.
D) xeric.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Animals that leave a saltwater environment to breed in a freshwater environment are known as
A) anadromous.
B) catadromous.
C) anadromous and euryhaline.
D) catadromous and stenohaline.
A) anadromous.
B) catadromous.
C) anadromous and euryhaline.
D) catadromous and stenohaline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Animals that leave a freshwater environment to breed in a saltwater environment are known as
A) anadromous.
B) catadromous.
C) anadromous and stenohaline.
D) catadromous and stenohaline.
A) anadromous.
B) catadromous.
C) anadromous and stenohaline.
D) catadromous and stenohaline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the figure shown.
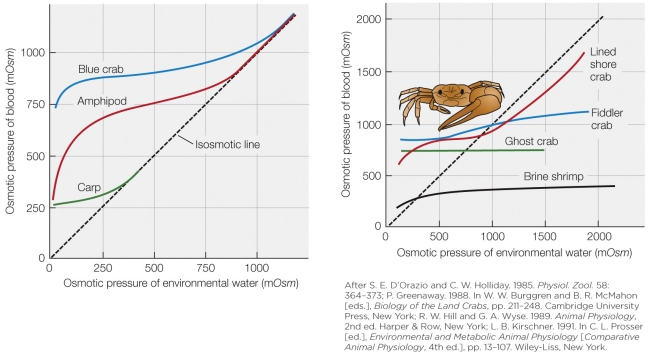 How would you categorize the blue crab?
How would you categorize the blue crab?
A) Hyperosmotic regulator
B) Hyper-isosmotic regulator
C) Hypo-isosmotic regulator
D) Hyperosmotic conformer
 How would you categorize the blue crab?
How would you categorize the blue crab?A) Hyperosmotic regulator
B) Hyper-isosmotic regulator
C) Hypo-isosmotic regulator
D) Hyperosmotic conformer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Refer to the figure shown.
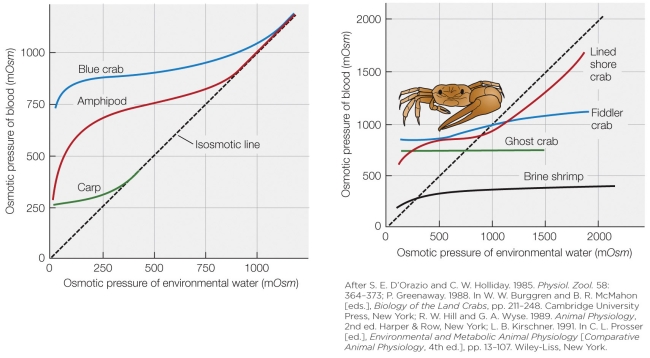 Overall, which animal represented in the graph is the best osmotic regulator?
Overall, which animal represented in the graph is the best osmotic regulator?
A) Blue crab
B) Lined shore crab
C) Brine shrimp
D) Carp
 Overall, which animal represented in the graph is the best osmotic regulator?
Overall, which animal represented in the graph is the best osmotic regulator?A) Blue crab
B) Lined shore crab
C) Brine shrimp
D) Carp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Refer to the figure shown.
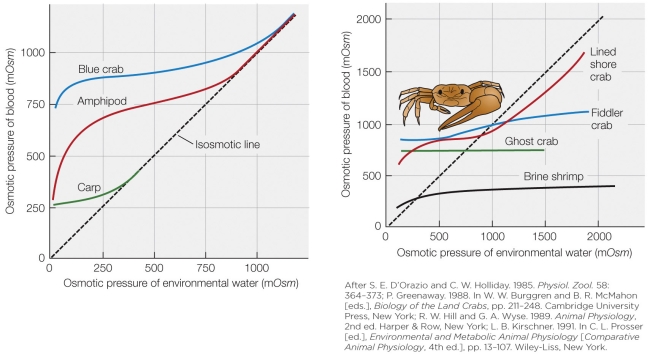 Taking into account both numerical scales and shape on both graphs, which line most closely represents that of a Pacific salmon?
Taking into account both numerical scales and shape on both graphs, which line most closely represents that of a Pacific salmon?
A) Blue crab
B) Carp
C) Fiddler crab
D) Brine shrimp
 Taking into account both numerical scales and shape on both graphs, which line most closely represents that of a Pacific salmon?
Taking into account both numerical scales and shape on both graphs, which line most closely represents that of a Pacific salmon?A) Blue crab
B) Carp
C) Fiddler crab
D) Brine shrimp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If you take a freshwater animal and transfer it to seawater for 60 days, what do you expect to see when you perform immunocytochemistry?
A) Increased aquaporin expression in the intestinal epithelia, and decreased NKCC expression in the gill lamellae
B) Increased aquaporin expression in the intestinal epithelia, and increased NKCC expression in the gill lamellae
C) Decreased aquaporin expression in the intestinal epithelia, and increased NKCC expression in the gill lamellae
D) Decreased aquaporin expression in the intestinal epithelia, and decreased NKCC expression in the gill lamellae
A) Increased aquaporin expression in the intestinal epithelia, and decreased NKCC expression in the gill lamellae
B) Increased aquaporin expression in the intestinal epithelia, and increased NKCC expression in the gill lamellae
C) Decreased aquaporin expression in the intestinal epithelia, and increased NKCC expression in the gill lamellae
D) Decreased aquaporin expression in the intestinal epithelia, and decreased NKCC expression in the gill lamellae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Why are stickleback populations especially useful for understanding physiological evolution?
A) Sticklebacks are catadromous.
B) Sticklebacks are found all over the world.
C) There are many isolated populations of sticklebacks in landlocked freshwater lakes.
D) Sticklebacks have been around as a species for millions of years.
A) Sticklebacks are catadromous.
B) Sticklebacks are found all over the world.
C) There are many isolated populations of sticklebacks in landlocked freshwater lakes.
D) Sticklebacks have been around as a species for millions of years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Newly landlocked populations of sticklebacks are in danger of
A) excessive predation.
B) the low osmotic pressure of freshwater.
C) the lack of ability to reproduce.
D) a lack of omega-3 fatty acids.
A) excessive predation.
B) the low osmotic pressure of freshwater.
C) the lack of ability to reproduce.
D) a lack of omega-3 fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Animals that can live in dry, water poor environments are called
A) anadromous.
B) xeric.
C) catadromous.
D) stenohaline.
A) anadromous.
B) xeric.
C) catadromous.
D) stenohaline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
To survive the disappearance of their pond, the lungfish
A) crawls in search of the nearest body of water.
B) reproduces and the young enter a state of suspended animation.
C) creates a cocoon and enters a state of metabolic depression.
D) creates a cocoon and continues normal metabolism.
A) crawls in search of the nearest body of water.
B) reproduces and the young enter a state of suspended animation.
C) creates a cocoon and enters a state of metabolic depression.
D) creates a cocoon and continues normal metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which substance produces nitrogen waste when catabolized?
A) Lipids
B) Carbohydrates
C) Proteins
D) Triglycerides
A) Lipids
B) Carbohydrates
C) Proteins
D) Triglycerides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Virtually all the resistance to water across the integument of xeric animals resides
A) in the thickness of the epidermis.
B) in microscopically thin lipid layers.
C) in the physical toughness of the integument.
D) in the tightness of the interlocking scales.
A) in the thickness of the epidermis.
B) in microscopically thin lipid layers.
C) in the physical toughness of the integument.
D) in the tightness of the interlocking scales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which description for mammals breathing in hot environments, is the most accurate?
A) The walls of the nasal passage are warmed by the process of inhalation. Cold exhaled air gets warmed as it passes by these warmed surfaces.
B) The walls of the nasal passage are warmed by the process of inhalation. Warm exhaled air gets warmed as it passes by these warmed surfaces.
C) The walls of the nasal passage are cooled by the process of inhalation. Cold exhaled air gets cooled as it passes by these cooled surfaces.
D) The walls of the nasal passage are cooled by the process of inhalation. Warm exhaled air gets cooled as it passes by these cooled surfaces.
A) The walls of the nasal passage are warmed by the process of inhalation. Cold exhaled air gets warmed as it passes by these warmed surfaces.
B) The walls of the nasal passage are warmed by the process of inhalation. Warm exhaled air gets warmed as it passes by these warmed surfaces.
C) The walls of the nasal passage are cooled by the process of inhalation. Cold exhaled air gets cooled as it passes by these cooled surfaces.
D) The walls of the nasal passage are cooled by the process of inhalation. Warm exhaled air gets cooled as it passes by these cooled surfaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which animal has the highest weight-specific total rate of evaporative water loss?
A) Screech owl
B) Zebra finch
C) Budgerigar
D) House wren
A) Screech owl
B) Zebra finch
C) Budgerigar
D) House wren

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Refer to the figure shown.
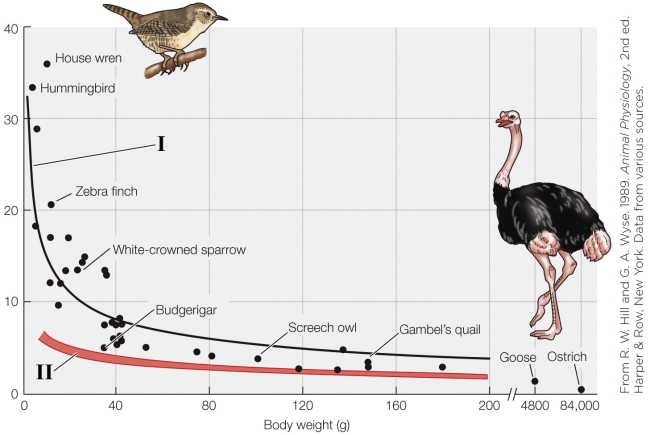 The line indicated by the number I represents
The line indicated by the number I represents
A) total evaporative water loss.
B) cutaneous water loss.
C) respiratory water loss.
D) metabolic water production.
 The line indicated by the number I represents
The line indicated by the number I representsA) total evaporative water loss.
B) cutaneous water loss.
C) respiratory water loss.
D) metabolic water production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Refer to the figure shown.
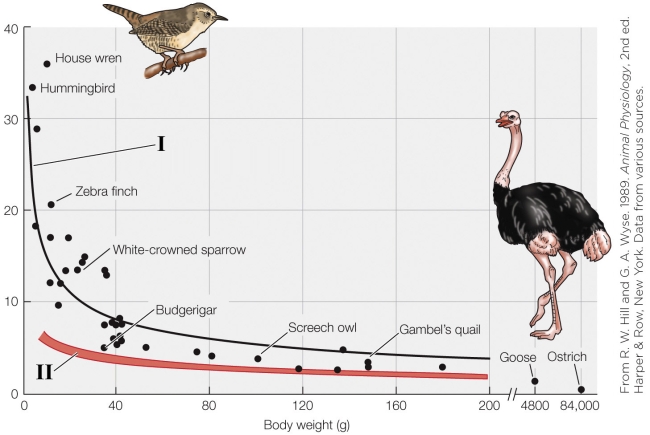 The line indicated by the number II represents
The line indicated by the number II represents
A) total evaporative water loss.
B) cutaneous water loss.
C) respiratory water loss.
D) metabolic water production.
 The line indicated by the number II represents
The line indicated by the number II representsA) total evaporative water loss.
B) cutaneous water loss.
C) respiratory water loss.
D) metabolic water production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In terrestrial amphibians, the hormone ADH (antidiuretic hormone) is released from the
A) anterior pituitary.
B) hypothalamus.
C) neurohypophysis.
D) thyroid.
A) anterior pituitary.
B) hypothalamus.
C) neurohypophysis.
D) thyroid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How do amphibians in the desert prevent water loss?
A) They have significantly reduced water requirements.
B) They use burrows to avoid the heat.
C) They have very thick skin.
D) They have the ability to produce highly concentrated urine.
A) They have significantly reduced water requirements.
B) They use burrows to avoid the heat.
C) They have very thick skin.
D) They have the ability to produce highly concentrated urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In amphibians, which of the following is not an effect of ADH release?
A) Kidneys reduce the rate of urine production
B) Increases aquaporin insertion into the bladder
C) Increases ability for ventral skin surface to absorb water
D) Increases NaCl transport into the bladder
A) Kidneys reduce the rate of urine production
B) Increases aquaporin insertion into the bladder
C) Increases ability for ventral skin surface to absorb water
D) Increases NaCl transport into the bladder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Refer to the figure shown.
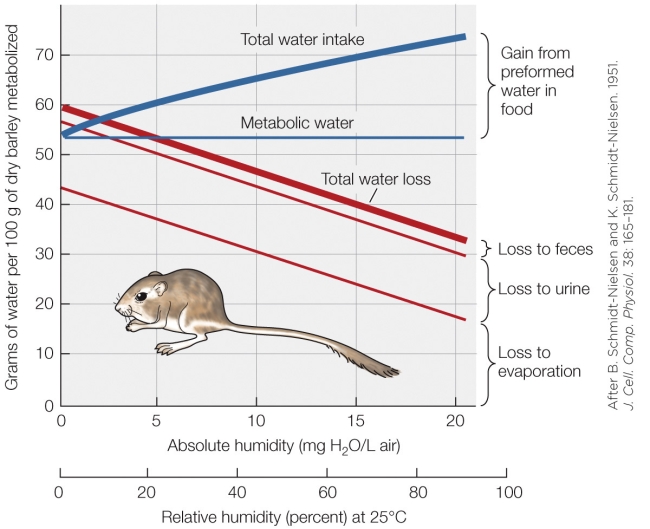 What is the greatest contributor to total water loss in this animal?
What is the greatest contributor to total water loss in this animal?
A) Humidity
B) Feces
C) Urine
D) Evaporation
 What is the greatest contributor to total water loss in this animal?
What is the greatest contributor to total water loss in this animal?A) Humidity
B) Feces
C) Urine
D) Evaporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the figure shown.
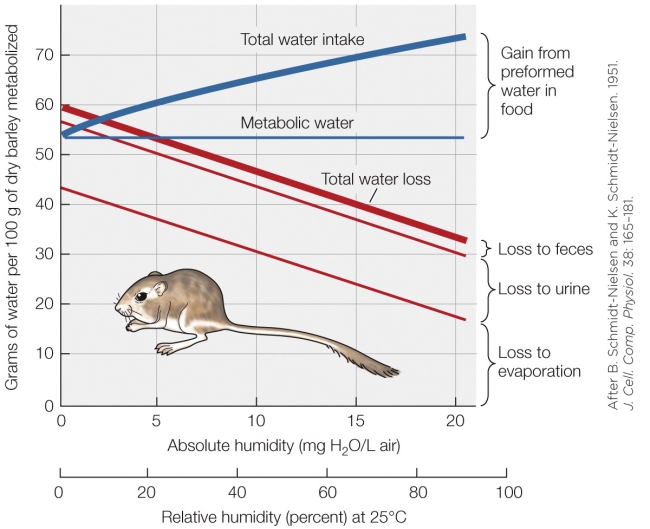 Why is preformed water in food not a consistent value?
Why is preformed water in food not a consistent value?
A) Humidity affects the amount of water in the food.
B) Increased metabolic rate affects the water absorbed from the food.
C) Metabolic water is decreased in deceased humidity.
D) Evaporative water loss increases in decreasing humidity.
 Why is preformed water in food not a consistent value?
Why is preformed water in food not a consistent value?A) Humidity affects the amount of water in the food.
B) Increased metabolic rate affects the water absorbed from the food.
C) Metabolic water is decreased in deceased humidity.
D) Evaporative water loss increases in decreasing humidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Refer to the figure shown.
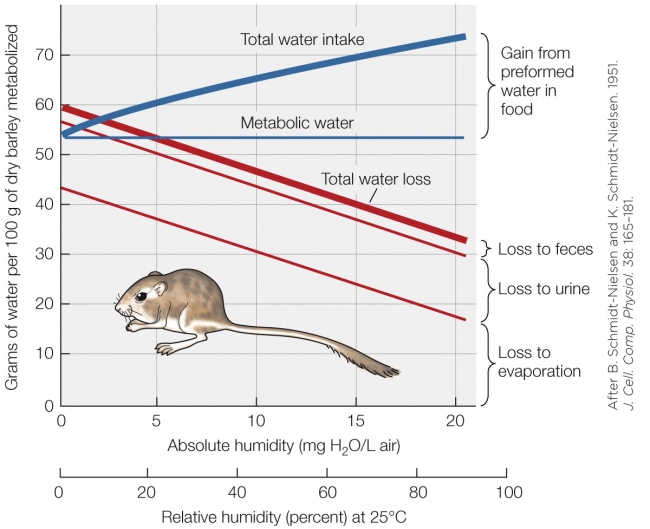 Based on the figure, is there a point where this animal is out of water balance?
Based on the figure, is there a point where this animal is out of water balance?
A) No, this animal is constantly in water balance.
B) Yes, but only at high humidity.
C) Yes, this animal is constantly out of water balance.
D) Yes, but only at very low humidity.
 Based on the figure, is there a point where this animal is out of water balance?
Based on the figure, is there a point where this animal is out of water balance?A) No, this animal is constantly in water balance.
B) Yes, but only at high humidity.
C) Yes, this animal is constantly out of water balance.
D) Yes, but only at very low humidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What characteristic do desert birds have that desert small mammals don't have?
A) They produce excessively hyperosmotic urine.
B) Their evaporative water loss is low.
C) They do not need to drink.
D) They produce feces with no moisture.
A) They produce excessively hyperosmotic urine.
B) Their evaporative water loss is low.
C) They do not need to drink.
D) They produce feces with no moisture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which hormone promotes diuresis?
A) Aldosterone
B) Antidiuretic hormone
C) Atrial natriuretic peptide
D) Diuretic hormone
A) Aldosterone
B) Antidiuretic hormone
C) Atrial natriuretic peptide
D) Diuretic hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which hormone is controlled to a major extent by the renin-angiotensin system?
A) Aldosterone
B) Antidiuretic hormone
C) Atrial natriuretic peptide
D) Diuretic hormone
A) Aldosterone
B) Antidiuretic hormone
C) Atrial natriuretic peptide
D) Diuretic hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Aldosterone causes the kidney tubules to _______ Na+ and thus promotes the _______.
A) excrete less; excretion of water
B) excrete less; retention of water
C) excrete more; retention of water
D) excrete more; excretion of water
A) excrete less; excretion of water
B) excrete less; retention of water
C) excrete more; retention of water
D) excrete more; excretion of water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
List and briefly explain three factors that determine the rate of passive exchange of water and ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Why is the permeability of a freshwater animal's integument to water and ions relatively low?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Describe the structure of the gills and explain another role they serve, in addition to being respiratory organs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



