Deck 24: Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in Body Fluids With an Introduction to Acid- Base Physiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in Body Fluids With an Introduction to Acid- Base Physiology
1
When oxygen binds with hemoglobin, why is this not oxidation?
A) When oxygen binds with hemoglobin, it is a full reduction reaction.
B) When oxygen binds with hemoglobin, there is no oxidation, only oxygenation.
C) Although electrons are partially transferred from iron atoms to oxygen, the transfer is not complete.
D) Although electrons are partially transferred from oxygen atoms to iron, the transfer is not complete.
A) When oxygen binds with hemoglobin, it is a full reduction reaction.
B) When oxygen binds with hemoglobin, there is no oxidation, only oxygenation.
C) Although electrons are partially transferred from iron atoms to oxygen, the transfer is not complete.
D) Although electrons are partially transferred from oxygen atoms to iron, the transfer is not complete.
C
2
Mammalian fetal hemoglobin has a _______ oxygen affinity than the mother's hemoglobin in order to _______ the maternal blood.
A) higher; load oxygen from
B) higher; transfer oxygen to
C) lower; load oxygen from
D) lower; transfer oxygen to
A) higher; load oxygen from
B) higher; transfer oxygen to
C) lower; load oxygen from
D) lower; transfer oxygen to
A
3
Which of the following is not a chemical category of respiratory pigment?
A) Hemocyanins
B) Hemerythrins
C) Chlorocruorins
D) Myoglobins
A) Hemocyanins
B) Hemerythrins
C) Chlorocruorins
D) Myoglobins
D
4
Which statement about hemoglobin is false?
A) It plays a role in CO2 transport.
B) It plays a role as a pH buffer.
C) It plays a role in N2 transport.
D) It is affected by temperature.
A) It plays a role in CO2 transport.
B) It plays a role as a pH buffer.
C) It plays a role in N2 transport.
D) It is affected by temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement comparing human adult and fetal hemoglobin is true?
A) Fetal hemoglobin contains one particular subunit that lowers its P50.
B) Fetal hemoglobin contains one particular subunit that raises its P50.
C) All subunits of fetal hemoglobin are different and result in a lower P50.
D) All subunits of fetal hemoglobin are different and result in a higher P50.
A) Fetal hemoglobin contains one particular subunit that lowers its P50.
B) Fetal hemoglobin contains one particular subunit that raises its P50.
C) All subunits of fetal hemoglobin are different and result in a lower P50.
D) All subunits of fetal hemoglobin are different and result in a higher P50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement about myoglobin is true?
A) It is a respiratory pigment found in the red blood cell.
B) It is exactly like hemoglobin but is found in a different location in the body.
C) It is a type of fetal hemoglobin.
D) It is a respiratory pigment found in muscle cytoplasm.
A) It is a respiratory pigment found in the red blood cell.
B) It is exactly like hemoglobin but is found in a different location in the body.
C) It is a type of fetal hemoglobin.
D) It is a respiratory pigment found in muscle cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Hemocyanins occur in which animal groups?
A) Molluscs
B) Arthropods
C) Echinoderms and molluscs
D) Molluscs and arthropods
A) Molluscs
B) Arthropods
C) Echinoderms and molluscs
D) Molluscs and arthropods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When the body detects _______, _______ is secreted to increase the production of red blood cells.
A) high CO2 levels; erythropoietin
B) high CO2 levels; myoglobin
C) low O2 levels; erythropoietin
D) low O2 levels; myoglobin
A) high CO2 levels; erythropoietin
B) high CO2 levels; myoglobin
C) low O2 levels; erythropoietin
D) low O2 levels; myoglobin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Respiratory pigments like hemoglobin have been labelled "honorary enzymes" because of their similarities. Choose the answer that is not one of those similarities.
A) Defined binding sites
B) Modification of the primary ligand
C) Binding site is highly specific
D) Binds to site by noncovalent, weak bonding
A) Defined binding sites
B) Modification of the primary ligand
C) Binding site is highly specific
D) Binds to site by noncovalent, weak bonding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
_______ binds to hemoglobin at the allosteric site and _______.
A) O2; increases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2
B) CO2; increases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2
C) CO2; decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2
D) O2; decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2
A) O2; increases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2
B) CO2; increases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2
C) CO2; decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2
D) O2; decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The image on a graph showing the functional relationship between the percentage of oxygenated binding sites and the O2 partial pressure is best known as
A) the saturation curve.
B) the affinity curve.
C) the P50 curve.
D) the oxygen dissociation curve.
A) the saturation curve.
B) the affinity curve.
C) the P50 curve.
D) the oxygen dissociation curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A respiratory pigment that requires a relatively low O2 partial pressure for loading has _______ affinity for O2.
A) a low
B) a high
C) no
D) a variable
A) a low
B) a high
C) no
D) a variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a healthy human at rest, what is the approximate O2 saturation of venous blood as it is leaving the tissues?
A) 75%
B) 50%
C) 25%
D) 0%
A) 75%
B) 50%
C) 25%
D) 0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Refer to the figure shown.
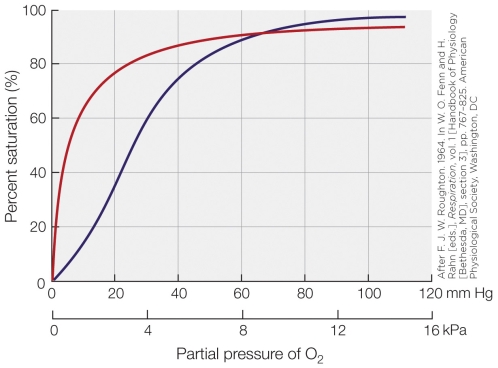 Which statement regarding the figure is false?
Which statement regarding the figure is false?
A) The right line depicts a pigment showing cooperativity.
B) The left line depicts a pigment displaying no cooperativity.
C) The left line could represent human hemoglobin.
D) The left line displays a generally higher O2 affinity compared to the right line.
 Which statement regarding the figure is false?
Which statement regarding the figure is false?A) The right line depicts a pigment showing cooperativity.
B) The left line depicts a pigment displaying no cooperativity.
C) The left line could represent human hemoglobin.
D) The left line displays a generally higher O2 affinity compared to the right line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Refer to the figure shown.
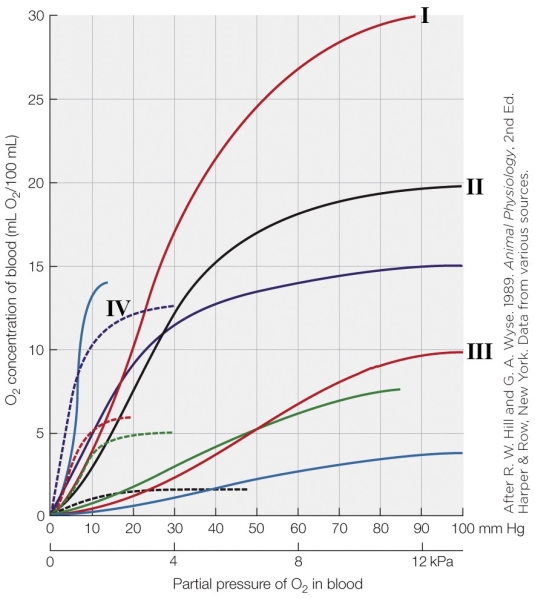 Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure would represent a diving mammal such as a Weddell seal?
Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure would represent a diving mammal such as a Weddell seal?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure would represent a diving mammal such as a Weddell seal?
Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure would represent a diving mammal such as a Weddell seal?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Refer to the figure shown.
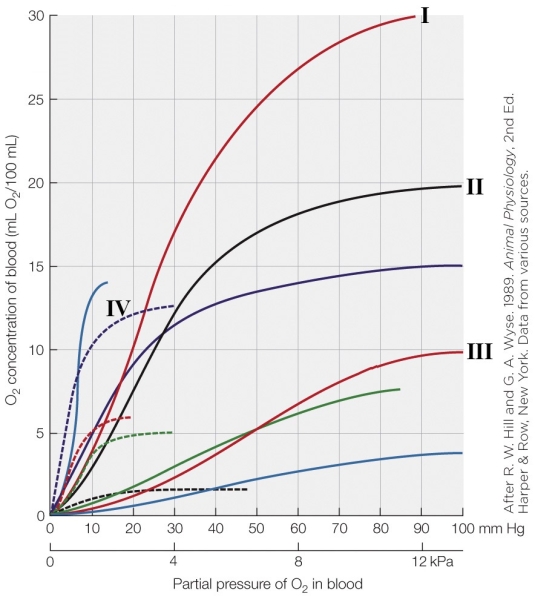 Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure would represent a hypoxia-adapted species such as a carp?
Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure would represent a hypoxia-adapted species such as a carp?
A) I
B) II
C) IV
D) V
 Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure would represent a hypoxia-adapted species such as a carp?
Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure would represent a hypoxia-adapted species such as a carp?A) I
B) II
C) IV
D) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the figure shown.
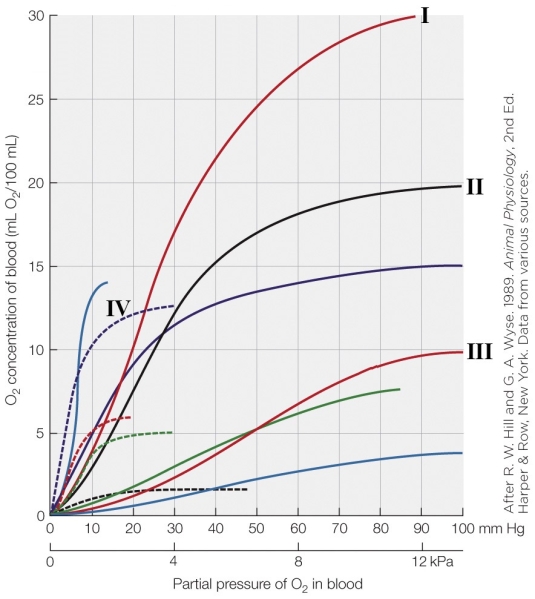 Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure carries the least amount of oxygen per unit volume of blood?
Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure carries the least amount of oxygen per unit volume of blood?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure carries the least amount of oxygen per unit volume of blood?
Which oxygen dissociation curve in the figure carries the least amount of oxygen per unit volume of blood?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Refer to the figure shown.
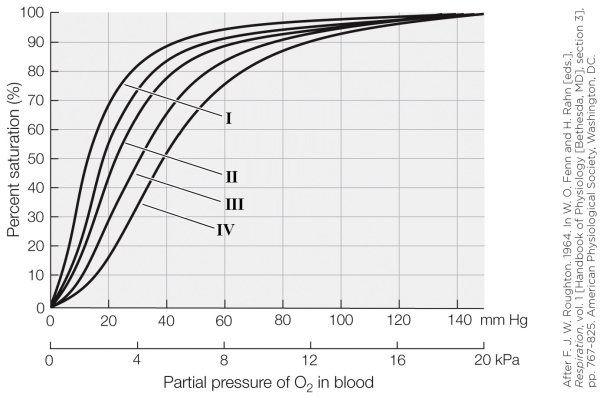 On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents a very high blood pH (e.g., 7.6)?
On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents a very high blood pH (e.g., 7.6)?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents a very high blood pH (e.g., 7.6)?
On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents a very high blood pH (e.g., 7.6)?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Refer to the figure shown.
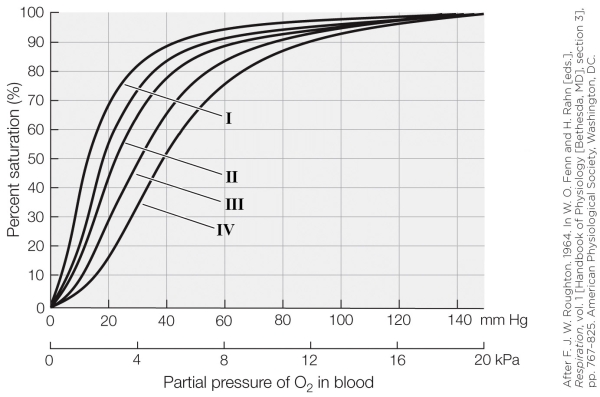 On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents blood with a high CO2 partial pressure (e.g., 80 mm Hg)?
On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents blood with a high CO2 partial pressure (e.g., 80 mm Hg)?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents blood with a high CO2 partial pressure (e.g., 80 mm Hg)?
On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents blood with a high CO2 partial pressure (e.g., 80 mm Hg)?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the figure shown.
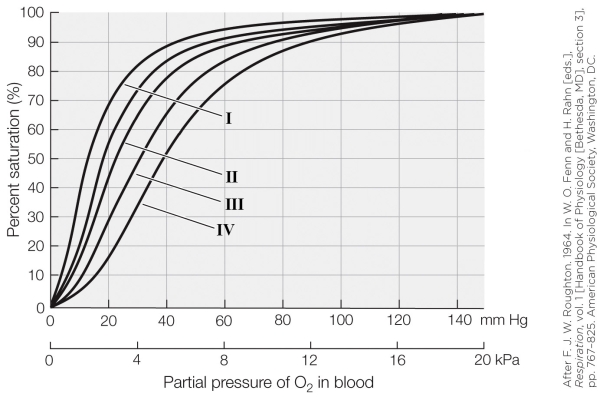 On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents a P50 of about 4 kPa?
On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents a P50 of about 4 kPa?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents a P50 of about 4 kPa?
On the graph, which oxygen dissociation curve represents a P50 of about 4 kPa?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A respiratory pigment that requires a relatively low O2 partial pressure for loading and has a high affinity for O2 would also have
A) a relatively low P50.
B) a relatively high P50.
C) no P50 at all.
D) a variable P50.
A) a relatively low P50.
B) a relatively high P50.
C) no P50 at all.
D) a variable P50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The effect of acid in reducing the affinity of hemoglobin for O2 is called the _______ effect.
A) Haldane
B) dissociation
C) Root
D) Bohr
A) Haldane
B) dissociation
C) Root
D) Bohr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which statement is not directly related to the Bohr effect?
A) The Hb‒O2 affinity increases as pH increases.
B) The Hb‒O2 affinity decreases as temperature increases.
C) The Hb‒O2 affinity decreases as CO2 partial pressure increases.
D) The Hb‒O2 affinity decreases as H+ concentration increases.
A) The Hb‒O2 affinity increases as pH increases.
B) The Hb‒O2 affinity decreases as temperature increases.
C) The Hb‒O2 affinity decreases as CO2 partial pressure increases.
D) The Hb‒O2 affinity decreases as H+ concentration increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The affinity of hemoglobin for O2 increases with
A) decreasing temperature.
B) decreasing blood pH.
C) an increase in CO2 partial pressure.
D) increasing [H+].
A) decreasing temperature.
B) decreasing blood pH.
C) an increase in CO2 partial pressure.
D) increasing [H+].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The venous blood displays a reduced O2 affinity compared to arterial blood because its
A) CO2 partial pressure is higher.
B) H+ concentration is higher.
C) hemoglobin concentration is lower.
D) CO2 partial pressure is higher and its H+ concentration is higher.
A) CO2 partial pressure is higher.
B) H+ concentration is higher.
C) hemoglobin concentration is lower.
D) CO2 partial pressure is higher and its H+ concentration is higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure shown.
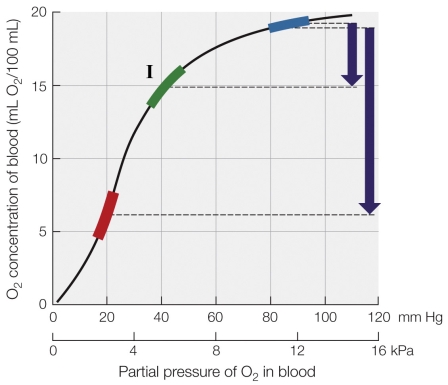 The curve on the graph
The curve on the graph
A) represents oxygen delivery by human blood at rest and during vigorous exercise.
B) is a vertebrate oxygen dissociation curve.
C) is a mammalian oxygen dissociation curve.
D) represents the increase in oxygen concentration as blood travels to the lungs.
 The curve on the graph
The curve on the graphA) represents oxygen delivery by human blood at rest and during vigorous exercise.
B) is a vertebrate oxygen dissociation curve.
C) is a mammalian oxygen dissociation curve.
D) represents the increase in oxygen concentration as blood travels to the lungs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the figure shown.
 Region I in the figure represents the
Region I in the figure represents the
A) amount of oxygen used by the tissues at rest.
B) oxygen concentration of blood in the tissues during exercise.
C) oxygen concentration of blood in the tissues at rest.
D) amount of oxygen used by the tissues during exercise.
 Region I in the figure represents the
Region I in the figure represents theA) amount of oxygen used by the tissues at rest.
B) oxygen concentration of blood in the tissues during exercise.
C) oxygen concentration of blood in the tissues at rest.
D) amount of oxygen used by the tissues during exercise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure shown.
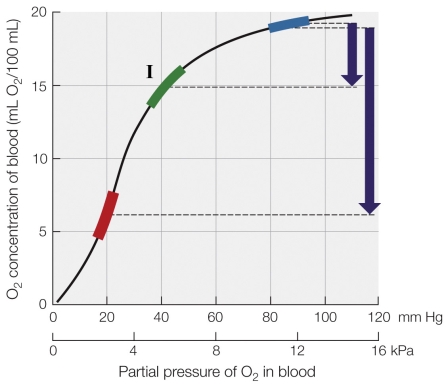 According to the figure, approximately how much more oxygen is used by the tissues during exercise compared to at rest?
According to the figure, approximately how much more oxygen is used by the tissues during exercise compared to at rest?
A) 15 mL O2/100 ml of blood
B) 10 mL O2/100 ml of blood
C) 15 mL O2/g
D) 10 mL O2/g
 According to the figure, approximately how much more oxygen is used by the tissues during exercise compared to at rest?
According to the figure, approximately how much more oxygen is used by the tissues during exercise compared to at rest?A) 15 mL O2/100 ml of blood
B) 10 mL O2/100 ml of blood
C) 15 mL O2/g
D) 10 mL O2/g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The venous O2 partial pressure below which aerobic catabolism becomes impaired is known as the
A) minimal venous O2 partial pressure.
B) critical venous reserve.
C) venous threshold.
D) critical venous O2 partial pressure.
A) minimal venous O2 partial pressure.
B) critical venous reserve.
C) venous threshold.
D) critical venous O2 partial pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the figure shown.
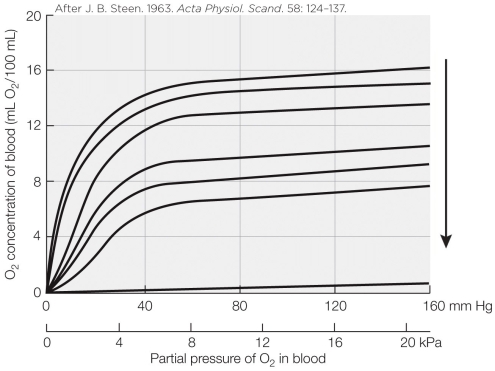
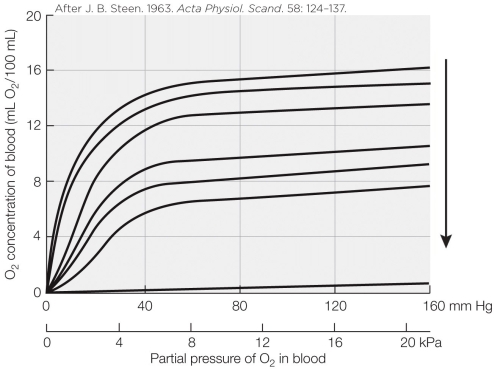 The pattern of the curves in the figure demonstrates the _______ effect.
The pattern of the curves in the figure demonstrates the _______ effect.
A) Haldane
B) Root
C) fixed-acid Bohr
D) CO2 Bohr
 The pattern of the curves in the figure demonstrates the _______ effect.
The pattern of the curves in the figure demonstrates the _______ effect.A) Haldane
B) Root
C) fixed-acid Bohr
D) CO2 Bohr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the figure shown.
 As shown in the figure, the P50 _______ declining pH.
As shown in the figure, the P50 _______ declining pH.
A) increases with
B) decreases with
C) remains constant with
D) is unrelated to
 As shown in the figure, the P50 _______ declining pH.
As shown in the figure, the P50 _______ declining pH.A) increases with
B) decreases with
C) remains constant with
D) is unrelated to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Root effect applies to which physiological mechanism?
A) The unloading of O2 in muscle tissue
B) The inflating of the swim bladder of many fish
C) The loading of O2 at the gills
D) The unloading of O2 in low pH regions of the stomach
A) The unloading of O2 in muscle tissue
B) The inflating of the swim bladder of many fish
C) The loading of O2 at the gills
D) The unloading of O2 in low pH regions of the stomach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
During chronic exposure to high altitude, increasing 2,3-DPG
A) increases Hb‒O2 affinity.
B) increases the unloading of O2 at tissues.
C) increases the loading of O2 at the lungs.
D) decreases the P50 of hemoglobin.
A) increases Hb‒O2 affinity.
B) increases the unloading of O2 at tissues.
C) increases the loading of O2 at the lungs.
D) decreases the P50 of hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Refer to the figure.
 The figure shown shows that a reduction in O2 affinity
The figure shown shows that a reduction in O2 affinity
A) impairs O2 unloading less than it enhances loading.
B) impairs O2 unloading more than it enhances loading.
C) enhances O2 unloading more than it impairs loading.
D) enhances O2 unloading less than it impairs loading.
 The figure shown shows that a reduction in O2 affinity
The figure shown shows that a reduction in O2 affinityA) impairs O2 unloading less than it enhances loading.
B) impairs O2 unloading more than it enhances loading.
C) enhances O2 unloading more than it impairs loading.
D) enhances O2 unloading less than it impairs loading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement about respiratory pigments is false?
A) They serve as major buffers of blood pH.
B) They play critical roles in CO2 transport.
C) They play critical roles in the transport of nutrients.
D) They can function as O2 stores in invertebrates.
A) They serve as major buffers of blood pH.
B) They play critical roles in CO2 transport.
C) They play critical roles in the transport of nutrients.
D) They can function as O2 stores in invertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Select the correct two functions of myoglobin.
A) Increase the rate of O2 diffusion through the mitochondria; CO2 buffering
B) Increase the rate of O2 diffusion through cytoplasm; CO2 buffering
C) Increase the rate of O2 diffusion through the mitochondria; O2 storage
D) Increase the rate of O2 diffusion through cytoplasm; O2 storage
A) Increase the rate of O2 diffusion through the mitochondria; CO2 buffering
B) Increase the rate of O2 diffusion through cytoplasm; CO2 buffering
C) Increase the rate of O2 diffusion through the mitochondria; O2 storage
D) Increase the rate of O2 diffusion through cytoplasm; O2 storage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Different respiratory pigments can pass O2 from one to another because of differences in
A) enzymatic activity.
B) affinity.
C) cooperativity.
D) diffusion rates.
A) enzymatic activity.
B) affinity.
C) cooperativity.
D) diffusion rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the figure.
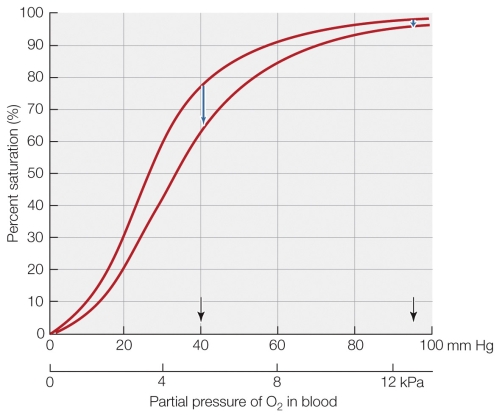
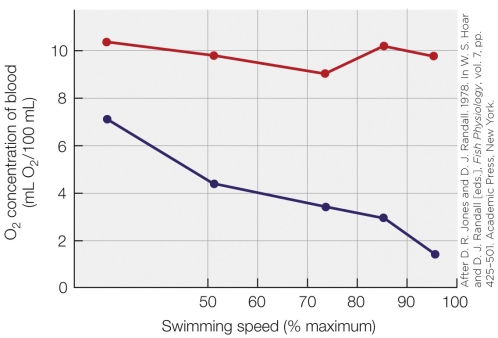 According to the figure shown, which statement is the most accurate?
According to the figure shown, which statement is the most accurate?
A) O2 concentrations of arterial blood are inversely proportional to swimming speed.
B) As O2 concentrations of blood drop in venous blood, swimming speed increases.
C) Cold-acclimated fish have a much lower saturation level during exercise than other fish do.
D) As swimming speed increases, the arterial blood remains nearly saturated while the venous blood decreases in saturation.
 According to the figure shown, which statement is the most accurate?
According to the figure shown, which statement is the most accurate?A) O2 concentrations of arterial blood are inversely proportional to swimming speed.
B) As O2 concentrations of blood drop in venous blood, swimming speed increases.
C) Cold-acclimated fish have a much lower saturation level during exercise than other fish do.
D) As swimming speed increases, the arterial blood remains nearly saturated while the venous blood decreases in saturation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In octopuses, venous saturation is about _______% at rest and about _______% during exercise.
A) 75; 25
B) 30; 30
C) 30; 10
D) 10; 10
A) 75; 25
B) 30; 30
C) 30; 10
D) 10; 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An octopus meets the increased demand for O2 at the tissues during intense exercise by
A) increasing its circulation rate.
B) pulling more O2 from the blood (from its venous reserve).
C) switching to another form of hemoglobin.
D) increasing its circulation rate and pulling more O2 from the blood (from its venous reserve).
A) increasing its circulation rate.
B) pulling more O2 from the blood (from its venous reserve).
C) switching to another form of hemoglobin.
D) increasing its circulation rate and pulling more O2 from the blood (from its venous reserve).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The P50 in a fish species adapted to a low oxygen aquatic environment would likely be _______ the P50 of a fish species adapted to a well-oxygenated aquatic environment.
A) higher than
B) equal to
C) lower than
D) extremely variable compared to
A) higher than
B) equal to
C) lower than
D) extremely variable compared to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the figure.
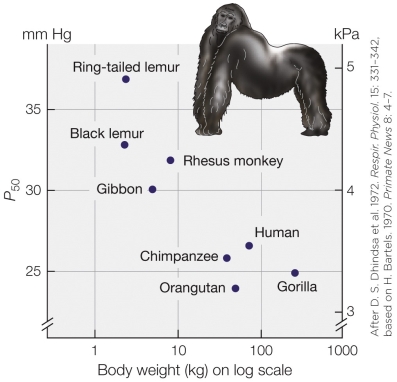 The figure shows that
The figure shows that
A) larger primates have fewer red blood cells than smaller primates do.
B) the whole blood of smaller primates has lower O2 affinity than that of larger primates.
C) the whole blood of smaller primates has greater O2 affinity than that of larger primates.
D) larger primates have more red blood cells than smaller primates do.
 The figure shows that
The figure shows thatA) larger primates have fewer red blood cells than smaller primates do.
B) the whole blood of smaller primates has lower O2 affinity than that of larger primates.
C) the whole blood of smaller primates has greater O2 affinity than that of larger primates.
D) larger primates have more red blood cells than smaller primates do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The exposure of Daphnia to O2-poor water for days would result in
A) an increase in hemoglobin concentration.
B) a change in the globin subunits produced.
C) an increase in hemoglobin concentration and a decrease in the P50 of the blood.
D) an increase in hemoglobin concentration, a decrease in the P50 of the blood, and a change in the globin subunits produced.
A) an increase in hemoglobin concentration.
B) a change in the globin subunits produced.
C) an increase in hemoglobin concentration and a decrease in the P50 of the blood.
D) an increase in hemoglobin concentration, a decrease in the P50 of the blood, and a change in the globin subunits produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Antarctic icefish compensate for the lack of circulating red blood cells with
A) an increase in the amount of hemoglobin in their plasma.
B) the use of another type of respiratory pigment.
C) an increased circulation rate.
D) a lowering of their metabolic rate, along with general inactivity.
A) an increase in the amount of hemoglobin in their plasma.
B) the use of another type of respiratory pigment.
C) an increased circulation rate.
D) a lowering of their metabolic rate, along with general inactivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In many cases, lowland people who travel to an area of high altitude for an extended period of time will develop a condition known as
A) polycythemia.
B) anemia.
C) bradycardia.
D) hypotension.
A) polycythemia.
B) anemia.
C) bradycardia.
D) hypotension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What determines the shape of the CO2 equilibrium curve?
A) The kinetics of HCO3- formation
B) The amount of dissolved CO2
C) The number of carbamate groups and the amount of dissolved CO2
D) The kinetics of HCO3- formation, the number of carbamate groups, and the amount of dissolved CO2
A) The kinetics of HCO3- formation
B) The amount of dissolved CO2
C) The number of carbamate groups and the amount of dissolved CO2
D) The kinetics of HCO3- formation, the number of carbamate groups, and the amount of dissolved CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The deoxygenation of hemoglobin promotes CO2 uptake, and the oxygenation of hemoglobin promotes the unloading of CO2. This phenomenon is called the _______ effect.
A) Root
B) fixed-acid Bohr
C) Haldane
D) CO2 Bohr
A) Root
B) fixed-acid Bohr
C) Haldane
D) CO2 Bohr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The extent of bicarbonate formation in the blood depends primarily on the
A) solubility of bicarbonate in the plasma.
B) temperature.
C) blood buffers.
D) solubility of carbonic acid.
A) solubility of bicarbonate in the plasma.
B) temperature.
C) blood buffers.
D) solubility of carbonic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The buffering effectiveness of any given buffer reaction is greatest when the prevailing pH _______ the pKʹ of the reaction.
A) is much greater than
B) matches
C) is much lower than
D) is as far away as possible from
A) is much greater than
B) matches
C) is much lower than
D) is as far away as possible from

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which species would have the highest total blood CO2 concentration?
A) Human
B) Turtle
C) Lungfish
D) Trout
A) Human
B) Turtle
C) Lungfish
D) Trout

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The key enzyme involved in the formation of bicarbonate from CO2 is
A) lactate dehydrogenase.
B) alcohol dehydrogenase.
C) carbonic anhydrase.
D) bicarbonate dehydrogenase.
A) lactate dehydrogenase.
B) alcohol dehydrogenase.
C) carbonic anhydrase.
D) bicarbonate dehydrogenase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The chloride shift refers to
A) rapid anion exchange proteins.
B) carbonic anhydrase.
C) carbamate formation.
D) the dissolving of CO2 in plasma.
A) rapid anion exchange proteins.
B) carbonic anhydrase.
C) carbamate formation.
D) the dissolving of CO2 in plasma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In mammals, the bulk of the CO2 is transported from the tissue to the lungs as
A) bicarbonate dissolved in the plasma.
B) CO2 dissolved in the plasma.
C) CO2 bound to hemoglobin.
D) bicarbonate bound to hemoglobin.
A) bicarbonate dissolved in the plasma.
B) CO2 dissolved in the plasma.
C) CO2 bound to hemoglobin.
D) bicarbonate bound to hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The alphastat hypothesis attempts to explain why _______ as temperature falls.
A) blood pH of ectotherms decreases
B) blood pH of ectotherms increases
C) muscle pH of ectotherms decreases
D) blood pH of endotherms decreases
A) blood pH of ectotherms decreases
B) blood pH of ectotherms increases
C) muscle pH of ectotherms decreases
D) blood pH of endotherms decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is(are) the main organ(s) responsible for adjusting blood pH in terrestrial animals?
A) Lungs
B) Kidneys
C) Lungs and kidneys
D) Lungs, kidneys, and liver
A) Lungs
B) Kidneys
C) Lungs and kidneys
D) Lungs, kidneys, and liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If HCO3- is retained in the body, it binds with _______ and causes the body fluids to become more _______.
A) H+ ; acidic
B) H+ ; alkaline
C) CO2 ; acidic
D) CO2 ; alkaline
A) H+ ; acidic
B) H+ ; alkaline
C) CO2 ; acidic
D) CO2 ; alkaline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If exhalation of CO2 is abnormally increased relative to production, the likely result will be
A) respiratory acidosis.
B) metabolic acidosis.
C) metabolic alkalosis.
D) respiratory alkalosis.
A) respiratory acidosis.
B) metabolic acidosis.
C) metabolic alkalosis.
D) respiratory alkalosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Sprinting until your legs give out is a great example of
A) respiratory acidosis.
B) metabolic acidosis.
C) metabolic alkalosis.
D) respiratory alkalosis.
A) respiratory acidosis.
B) metabolic acidosis.
C) metabolic alkalosis.
D) respiratory alkalosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What do the main respiratory pigments have in common?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In what way can hemoglobin be considered an "honorary enzyme"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain the significance of measurements of mixed venous O2 partial pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why is human hemoglobin a good example of evolutionary molecular design?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Compare and contrast oxygen affinity with P50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is unique about the respiratory pigments and circulatory O2 transport of the octopus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Compare and contrast the CO2 Bohr effect and the Haldane effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What determines the shape of the CO2 dissociation curve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Why are carbonic anhydrase and anion transporters important in vertebrate CO2 transport?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Why does temperature alter blood pH in ectotherms?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



