Deck 23: External Respiration: the Physiology of Breathing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: External Respiration: the Physiology of Breathing
1
One of the exceptional adaptations of tuna is
A) their exceptionally large gill mass to body mass ratio.
B) their exceptionally large gill surface area.
C) their exceptionally high pressure opercular suction pump.
D) their exceptionally fast opercular pumping rate.
A) their exceptionally large gill mass to body mass ratio.
B) their exceptionally large gill surface area.
C) their exceptionally high pressure opercular suction pump.
D) their exceptionally fast opercular pumping rate.
B
2
During high-speed swimming, many fish rely on a method of ventilation called
A) ram ventilation.
B) opercular pumping ventilation.
C) the opercular suction pump.
D) buccal pressure pumping ventilation.
A) ram ventilation.
B) opercular pumping ventilation.
C) the opercular suction pump.
D) buccal pressure pumping ventilation.
A
3
Which statement is the most accurate definition of external respiration?
A) Bulk flow (convection) of air or water to and from the gas-exchange membrane.
B) The process by which O2 is transported to the gas-exchange membrane from the environmental medium and by which CO2 is transported away from the membrane into the environmental medium.
C) The process by which CO2 is transported to the gas-exchange membrane from the environmental medium and O2 is transported away from the membrane into the environmental medium.
D) Diffusion of O2 and CO2 across the gas exchange membrane.
A) Bulk flow (convection) of air or water to and from the gas-exchange membrane.
B) The process by which O2 is transported to the gas-exchange membrane from the environmental medium and by which CO2 is transported away from the membrane into the environmental medium.
C) The process by which CO2 is transported to the gas-exchange membrane from the environmental medium and O2 is transported away from the membrane into the environmental medium.
D) Diffusion of O2 and CO2 across the gas exchange membrane.
B
4
Which animal is an example of a bimodal breather?
A) Dog
B) Frog
C) Lizard
D) Crocodile
A) Dog
B) Frog
C) Lizard
D) Crocodile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The rate of O2 uptake by the breathing organ depends on the
A) volume flow of air or water per unit of time.
B) amount of O2 removed from each unit of volume.
C) amount of CO2 needing to be removed.
D) volume flow of respiratory medium per unit time and the amount of O2 removed from each unit volume.
A) volume flow of air or water per unit of time.
B) amount of O2 removed from each unit of volume.
C) amount of CO2 needing to be removed.
D) volume flow of respiratory medium per unit time and the amount of O2 removed from each unit volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which morphology sets up the least efficient gas exchange?
A) Cocurrent gas exchange
B) Convex current gas exchange
C) Cross-current gas exchange
D) Countercurrent gas exchange
A) Cocurrent gas exchange
B) Convex current gas exchange
C) Cross-current gas exchange
D) Countercurrent gas exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Refer to the figure shown.
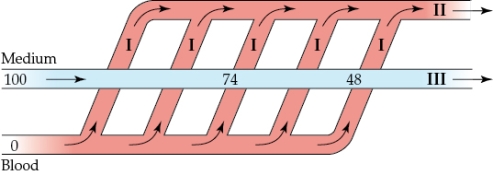 The diagram is referring to what physiological process?
The diagram is referring to what physiological process?
A) Cocurrent gas exchange
B) Countercurrent gas exchange
C) Nondirectional ventilation and gas exchange
D) Cross-current gas exchange
 The diagram is referring to what physiological process?
The diagram is referring to what physiological process?A) Cocurrent gas exchange
B) Countercurrent gas exchange
C) Nondirectional ventilation and gas exchange
D) Cross-current gas exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Refer to the figure shown.
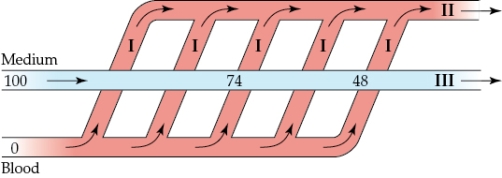 At I in the diagram, O2 partial pressures are _______ the corresponding medium values and _______ from left to right.
At I in the diagram, O2 partial pressures are _______ the corresponding medium values and _______ from left to right.
A) lower than; increase
B) lower than; decrease
C) higher than; increase
D) higher than; decrease
 At I in the diagram, O2 partial pressures are _______ the corresponding medium values and _______ from left to right.
At I in the diagram, O2 partial pressures are _______ the corresponding medium values and _______ from left to right.A) lower than; increase
B) lower than; decrease
C) higher than; increase
D) higher than; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Refer to the figure shown.
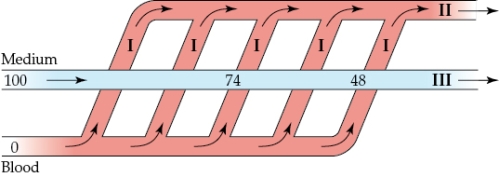 O2 partial pressures at II in the diagram are always _______ those at III.
O2 partial pressures at II in the diagram are always _______ those at III.
A) equal to
B) lower than
C) higher than
D) half of
 O2 partial pressures at II in the diagram are always _______ those at III.
O2 partial pressures at II in the diagram are always _______ those at III.A) equal to
B) lower than
C) higher than
D) half of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
CO2 is more easily transferred into water across respiratory membranes compared to O2 because CO2
A) is more soluble in water.
B) moves faster.
C) is a smaller molecule.
D) has a higher cohesive force.
A) is more soluble in water.
B) moves faster.
C) is a smaller molecule.
D) has a higher cohesive force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Refer to the figure shown.
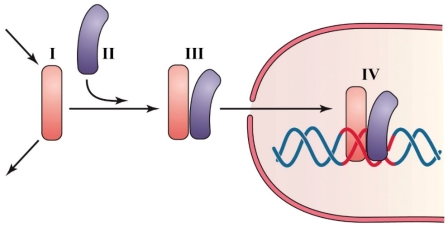 Which area indicates free HIF-1?
Which area indicates free HIF-1?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which area indicates free HIF-1?
Which area indicates free HIF-1?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Refer to the figure shown.
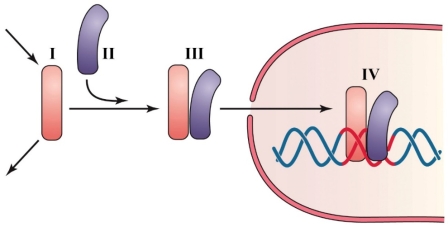 When O2 in a cell drops
When O2 in a cell drops
A) more of compound I is created via enzymatic reactions.
B) more of compound II is created via enzymatic reactions.
C) more of compound I is produced by inhibiting its breakdown.
D) product III formation is catalyzed directly by low O2.
 When O2 in a cell drops
When O2 in a cell dropsA) more of compound I is created via enzymatic reactions.
B) more of compound II is created via enzymatic reactions.
C) more of compound I is produced by inhibiting its breakdown.
D) product III formation is catalyzed directly by low O2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
HIF-1 and HIF-2 can help increase the O2-carrying ability of the blood by
A) increasing the secretion of erythropoietin.
B) increasing ventilation rate.
C) decreasing the diffusion distance at the lungs.
D) increasing circulation rate.
A) increasing the secretion of erythropoietin.
B) increasing ventilation rate.
C) decreasing the diffusion distance at the lungs.
D) increasing circulation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Walking around at an altitude of 5000 m, you could expect which of the following responses at the whole-body level?
A) increase in the secretion of erythropoietin in certain cells
B) increase in heart rate
C) decreasing the diffusion distance at the lungs
D) increase in formation of HIF-1
A) increase in the secretion of erythropoietin in certain cells
B) increase in heart rate
C) decreasing the diffusion distance at the lungs
D) increase in formation of HIF-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which animal is likely to have the highest O2 and CO2 exchange percentage via the skin?
A) Goldfish
B) Bullfrog larva
C) Lungless salamander
D) Adult bullfrog
A) Goldfish
B) Bullfrog larva
C) Lungless salamander
D) Adult bullfrog

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In all vertebrates, the central pattern generators for breathing are located in the
A) cerebellum.
B) lungs.
C) cortex.
D) medulla.
A) cerebellum.
B) lungs.
C) cortex.
D) medulla.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the figure shown.
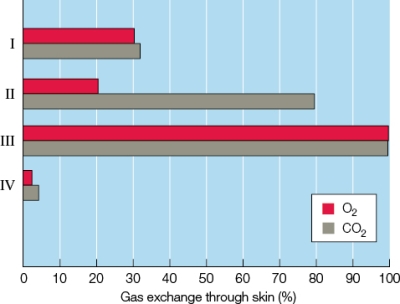 Of the animals in the figure, which one represents a primarily aquatic animal using lungs as the primary source for O2 uptake?
Of the animals in the figure, which one represents a primarily aquatic animal using lungs as the primary source for O2 uptake?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Of the animals in the figure, which one represents a primarily aquatic animal using lungs as the primary source for O2 uptake?
Of the animals in the figure, which one represents a primarily aquatic animal using lungs as the primary source for O2 uptake?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How does a typical teleost fish, such as a goldfish, maintain ventilation of its gills when stationary in the water column?
A) With a buccal pressure pump
B) With an opercular suction pump
C) Via ram ventilation
D) With both a buccal pressure pump and an opercular suction pump
A) With a buccal pressure pump
B) With an opercular suction pump
C) Via ram ventilation
D) With both a buccal pressure pump and an opercular suction pump

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Choose the best statement regarding buccal-opercular pumping.
A) The opercular pump develops positive pressure while the buccal pump is being refilled, and the buccal pump sucks while the opercular pump is being emptied.
B) The opercular pump sucks while the buccal pump is being refilled, and the buccal pump sucks while the opercular pump is being emptied.
C) The opercular pump sucks while the buccal pump is being refilled, and the buccal pump develops positive pressure while the opercular pump is being emptied.
D) The opercular pump develops positive pressure while the buccal pump is being refilled, and the buccal pump develops positive pressure while the opercular pump is being emptied.
A) The opercular pump develops positive pressure while the buccal pump is being refilled, and the buccal pump sucks while the opercular pump is being emptied.
B) The opercular pump sucks while the buccal pump is being refilled, and the buccal pump sucks while the opercular pump is being emptied.
C) The opercular pump sucks while the buccal pump is being refilled, and the buccal pump develops positive pressure while the opercular pump is being emptied.
D) The opercular pump develops positive pressure while the buccal pump is being refilled, and the buccal pump develops positive pressure while the opercular pump is being emptied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Fish make use of _______ exchange in their gills.
A) cross-current
B) concurrent
C) cocurrent
D) countercurrent
A) cross-current
B) concurrent
C) cocurrent
D) countercurrent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement about air-breathing fish is false?
A) In most air-breathing fish, some part or branch of the alimentary canal has become specialized as an air-breathing organ.
B) Most air-breathing fish have lost gill function.
C) Air-breathing fish typically void most of their CO2 into the water.
D) Many air-breathing fish are able to shunt blood.
A) In most air-breathing fish, some part or branch of the alimentary canal has become specialized as an air-breathing organ.
B) Most air-breathing fish have lost gill function.
C) Air-breathing fish typically void most of their CO2 into the water.
D) Many air-breathing fish are able to shunt blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An adult bullfrog excretes CO2 primarily through its
A) skin.
B) gills.
C) lungs.
D) cloaca.
A) skin.
B) gills.
C) lungs.
D) cloaca.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
During metamorphosis, a frog utilizes which gas-exchange organs?
A) Gills only
B) Lungs only
C) Gills and lungs
D) Gills, skin, and lungs
A) Gills only
B) Lungs only
C) Gills and lungs
D) Gills, skin, and lungs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
During the _______ developmental stage, the bullfrog splits oxygen uptake (roughly 50:50) between the gills and the skin.
A) aquatic tadpole
B) air-breathing tadpole
C) postmetamorphic froglet
D) adult
A) aquatic tadpole
B) air-breathing tadpole
C) postmetamorphic froglet
D) adult

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the figure shown.
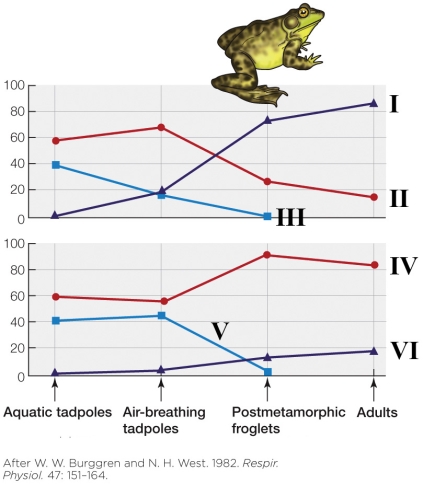 Which pair of lines best represents the lungs of the bullfrog?
Which pair of lines best represents the lungs of the bullfrog?
A) I and IV
B) II and IV
C) I and VI
D) III and V
 Which pair of lines best represents the lungs of the bullfrog?
Which pair of lines best represents the lungs of the bullfrog?A) I and IV
B) II and IV
C) I and VI
D) III and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure shown.
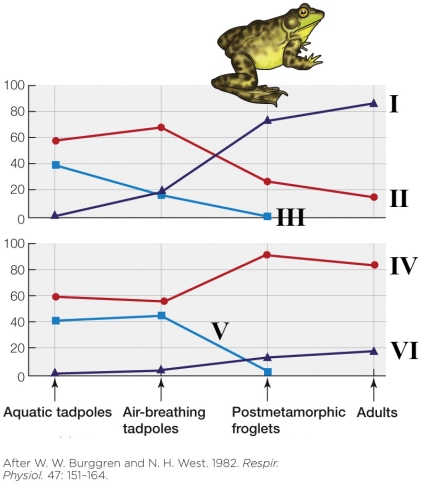 Which line best represents the excretion of CO2 via the skin?
Which line best represents the excretion of CO2 via the skin?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which line best represents the excretion of CO2 via the skin?
Which line best represents the excretion of CO2 via the skin?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which is primarily responsible for moving air into the lungs of a lizard?
A) The buccal pump
B) The buccopharyngeal pump
C) The intercostal muscles
D) The diaphragm
A) The buccal pump
B) The buccopharyngeal pump
C) The intercostal muscles
D) The diaphragm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which statement is a recently discovered similarity between alligator respiration and bird respiration?
A) Cross-current gas exchange takes place.
B) Air sacs are present.
C) Ventilation is tidal.
D) Ventilation is unidirectional.
A) Cross-current gas exchange takes place.
B) Air sacs are present.
C) Ventilation is tidal.
D) Ventilation is unidirectional.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Crocodilians and turtles have _______ lungs, which have a significantly _______ surface area compared to _______ lungs.
A) unicameral; smaller; multicameral
B) multicameral; smaller; unicameral
C) multicameral; greater; unicameral
D) unicameral; greater; multicameral
A) unicameral; smaller; multicameral
B) multicameral; smaller; unicameral
C) multicameral; greater; unicameral
D) unicameral; greater; multicameral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which animal group(s) ventilate(s) with the use of negative pressure?
A) Reptiles
B) Mammals
C) Amphibians
D) Both reptiles and mammals
A) Reptiles
B) Mammals
C) Amphibians
D) Both reptiles and mammals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In which structure does diffusion of oxygen to capillaries not play a major role?
A) Terminal bronchioles
B) Respiratory bronchioles
C) Alveolar ducts
D) Alveolar sacs
A) Terminal bronchioles
B) Respiratory bronchioles
C) Alveolar ducts
D) Alveolar sacs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Pulmonary surfactant
A) keeps the alveoli from collapsing by reducing the surface tension.
B) inflates the alveoli by increasing the surface tension.
C) keeps the alveoli from collapsing by increasing the surface tension.
D) increases the rate of gas exchange across the alveoli by the secretion of phospholipids.
A) keeps the alveoli from collapsing by reducing the surface tension.
B) inflates the alveoli by increasing the surface tension.
C) keeps the alveoli from collapsing by increasing the surface tension.
D) increases the rate of gas exchange across the alveoli by the secretion of phospholipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
During heavy exercise, we observe a significant increase in the use of the _______ for exhalation compared to resting conditions.
A) diaphragm
B) internal intercostals
C) external intercostals
D) sternocleidomastoid
A) diaphragm
B) internal intercostals
C) external intercostals
D) sternocleidomastoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The volume of air in the lungs following a complete exhalation of the expiratory reserve volume is
A) one-half the inspiratory reserve volume.
B) called the tidal volume.
C) very close to 0 mL.
D) called the residual volume.
A) one-half the inspiratory reserve volume.
B) called the tidal volume.
C) very close to 0 mL.
D) called the residual volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the inspiratory reserve volume is 3000 mL, the tidal volume is 500 mL, the expiratory reserve volume is 1000 mL, and the residual volume is 1000 mL, what is the vital capacity?
A) 3500 mL
B) 4500 mL
C) 5000 mL
D) 5500 mL
A) 3500 mL
B) 4500 mL
C) 5000 mL
D) 5500 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the mammalian alveoli, the partial pressure of O2 is _______ that of atmospheric air and the CO2 partial pressure is _______ that of atmospheric air.
A) higher than; lower than
B) lower than; higher than
C) lower than; lower than
D) the same as; higher than
A) higher than; lower than
B) lower than; higher than
C) lower than; lower than
D) the same as; higher than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which animal group(s) has(have) a true diaphragm?
A) Reptiles and mammals
B) Birds and mammals
C) Mammals
D) Birds
A) Reptiles and mammals
B) Birds and mammals
C) Mammals
D) Birds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In mammals, ventilation is modulated by the chemosensation of
A) CO2.
B) CO2 and H+.
C) CO2 and O2.
D) CO2, H+, and O2.
A) CO2.
B) CO2 and H+.
C) CO2 and O2.
D) CO2, H+, and O2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Hypoxia factors can respond to hypoxia (along with other possible cofactors or coactivators) with all of the following responses except
A) increased erythropoiesis.
B) increased synthesis of glucose transporters.
C) increased synthesis of enzymes of aerobic metabolism.
D) the promotion of angiogenesis.
A) increased erythropoiesis.
B) increased synthesis of glucose transporters.
C) increased synthesis of enzymes of aerobic metabolism.
D) the promotion of angiogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A rise in arterial blood CO2 partial pressure by 5 mm Hg would increase ventilation frequency in humans. This mechanism would likely trigger increased ventilation in
A) all vertebrates.
B) just terrestrial vertebrates.
C) just aquatic vertebrates.
D) all animals.
A) all vertebrates.
B) just terrestrial vertebrates.
C) just aquatic vertebrates.
D) all animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which circumstance would increase ventilation frequency in humans?
A) A reduction in arterial blood CO2 partial pressure by 15 mm Hg
B) A rise in venous blood CO2 partial pressure by 15 mm Hg
C) A reduction in arterial blood O2 partial pressure by 15 mm Hg
D) A rise in venous blood O2 partial pressure by 15 mm Hg
A) A reduction in arterial blood CO2 partial pressure by 15 mm Hg
B) A rise in venous blood CO2 partial pressure by 15 mm Hg
C) A reduction in arterial blood O2 partial pressure by 15 mm Hg
D) A rise in venous blood O2 partial pressure by 15 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose you are comparing blood samples and samples of alveolar gas from two native Peruvians resting in their dwellings-one at sea level and one at 4500 m altitude. The O2 partial pressure would likely be the most similar in
A) their alveolar gas.
B) their arterial blood.
C) their venous blood.
D) the air in their tracheas.
A) their alveolar gas.
B) their arterial blood.
C) their venous blood.
D) the air in their tracheas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When lowlanders first ascend to high altitude, which of the following occurs?
A) Hypoventilation
B) Bradycardia
C) Lowering of V̇o2max
D) Hyperventilation
A) Hypoventilation
B) Bradycardia
C) Lowering of V̇o2max
D) Hyperventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The rate at which new air is brought into the alveoli and other respiratory pathways is called the
A) alveolar minute volume.
B) respiratory minute volume.
C) tidal volume.
D) ventilation rate.
A) alveolar minute volume.
B) respiratory minute volume.
C) tidal volume.
D) ventilation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
As mammals get smaller, lung volume _______ and breathing frequency _______.
A) increases exponentially; increases exponentially
B) decreases exponentially; increases exponentially
C) decreases proportionally; increases exponentially
D) increases proportionally; decreases proportionally
A) increases exponentially; increases exponentially
B) decreases exponentially; increases exponentially
C) decreases proportionally; increases exponentially
D) increases proportionally; decreases proportionally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Bird respiration is characterized by _______ air flow and _______ gas exchange.
A) nondirectional; countercurrent
B) unidirectional; cross-current
C) nondirectional; cross-current
D) unidirectional; countercurrent
A) nondirectional; countercurrent
B) unidirectional; cross-current
C) nondirectional; cross-current
D) unidirectional; countercurrent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Refer to the figure shown.
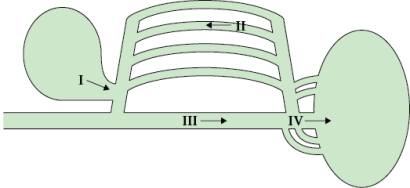 Which of the arrows in the figure is showing air movement during inhalation incorrectly?
Which of the arrows in the figure is showing air movement during inhalation incorrectly?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which of the arrows in the figure is showing air movement during inhalation incorrectly?
Which of the arrows in the figure is showing air movement during inhalation incorrectly?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Refer to the figure shown.
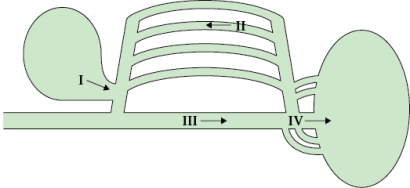 The figure represents the respiratory system of which group of animals?
The figure represents the respiratory system of which group of animals?
A) Amphibians
B) Reptiles
C) Birds
D) Fish
 The figure represents the respiratory system of which group of animals?
The figure represents the respiratory system of which group of animals?A) Amphibians
B) Reptiles
C) Birds
D) Fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which structure(s) is(are) primarily responsible for gas exchange in the bird respiratory system?
A) Mesobronchus
B) Secondary bronchi
C) Parabronchi
D) Air sacs
A) Mesobronchus
B) Secondary bronchi
C) Parabronchi
D) Air sacs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Branchial papulae are essentially gill processes in which major animal group?
A) Annelids
B) Horseshoe crabs
C) Aquatic snails
D) Sea stars
A) Annelids
B) Horseshoe crabs
C) Aquatic snails
D) Sea stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The evolution of sheetlike gills occurred in which major animal group?
A) Annelids
B) Horseshoe crabs
C) Echinoderms
D) Molluscs
A) Annelids
B) Horseshoe crabs
C) Echinoderms
D) Molluscs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The evolution of the mantle cavity into a lung occurred in which major animal group?
A) Annelids
B) Horseshoe crabs
C) Sea stars
D) Snails
A) Annelids
B) Horseshoe crabs
C) Sea stars
D) Snails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An aquatic decapod crustacean moves water through the branchial chamber and ventilates the gills with its
A) opercular pump.
B) buccal pump.
C) mouth.
D) scaphognathite.
A) opercular pump.
B) buccal pump.
C) mouth.
D) scaphognathite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which statement about land crab respiration is true?
A) Most land crabs have evolved lungs.
B) They allow their gills to go dry and ventilate them with air.
C) Their gills are ventilated with water.
D) O2 is taken up chiefly by their branchial-chamber epithelium.
A) Most land crabs have evolved lungs.
B) They allow their gills to go dry and ventilate them with air.
C) Their gills are ventilated with water.
D) O2 is taken up chiefly by their branchial-chamber epithelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The entrance to the gas exchange system of insects is via
A) spiracles.
B) the mouth.
C) the scaphognathite.
D) the branchial chamber.
A) spiracles.
B) the mouth.
C) the scaphognathite.
D) the branchial chamber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Although tracheoles run between cells, they also very commonly penetrate _______ cells.
A) flight muscle
B) nervous system
C) circulatory system
D) heart muscle
A) flight muscle
B) nervous system
C) circulatory system
D) heart muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A key mechanism of gas transport through the tracheal system is
A) muscular contraction.
B) the scaphognathite.
C) diffusion.
D) spiracle size.
A) muscular contraction.
B) the scaphognathite.
C) diffusion.
D) spiracle size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Comparing insect and vertebrate breathing,
A) vertebrates rely on conspicuous ventilation and insects rely on diffusion.
B) both use conspicuous ventilation and diffusion.
C) insects rely on conspicuous ventilation and insects rely on diffusion.
D) both rely on diffusion and only vertebrates rely on conspicuous ventilation.
A) vertebrates rely on conspicuous ventilation and insects rely on diffusion.
B) both use conspicuous ventilation and diffusion.
C) insects rely on conspicuous ventilation and insects rely on diffusion.
D) both rely on diffusion and only vertebrates rely on conspicuous ventilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the main vulnerability of the insect respiratory system?
A) The release of accumulated CO2 is slow.
B) It is susceptible to evaporative water loss.
C) It must be continually ventilated.
D) O2 uptake is very slow.
A) The release of accumulated CO2 is slow.
B) It is susceptible to evaporative water loss.
C) It must be continually ventilated.
D) O2 uptake is very slow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Aquatic insects sometimes have evaginations of the body surface called _______ that are densely supplied with trachea and covered with a thin cuticle.
A) gills
B) book lungs
C) tracheal gills
D) spiracles
A) gills
B) book lungs
C) tracheal gills
D) spiracles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe a bimodal breather and the advantages that bimodal breathing can offer an animal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The O2 partial pressure in the blood leaving a breathing organ is considered the best single measure of the breathing organ's effectiveness. Why is the partial pressure of blood going toward the breathing organ not an effective measure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Compare and contrast cocurrent gas exchange with countercurrent gas exchange and indicate which is more efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Several morphological features of the bird respiratory system allow for more efficient gas exchange. Describe these features.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What are the major stimuli for increasing ventilation in fish?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast the uptake of O2 and the excretion of CO2 in bullfrog tadpoles and adults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Describe the quality of the gas within the alveoli of the mammalian lung and explain how it differs from atmospheric air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How do both CO2 and H+ stimulate ventilation in mammals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Describe the physiological advantages of the bird respiratory system that make it more efficient than the mammalian system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How do insects combat the evaporative water loss that is inherent in a tracheal system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



