Deck 21: Movement and Muscle at Work: Plasticity in Response to Use and Disuse
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Movement and Muscle at Work: Plasticity in Response to Use and Disuse
1
The dynamic nature of muscle tissue is known as
A) exercise training.
B) exercise physiology.
C) sliding filament theory.
D) muscle plasticity.
A) exercise training.
B) exercise physiology.
C) sliding filament theory.
D) muscle plasticity.
D
2
Adding structural proteins to individual muscle cells is known as
A) atrophy.
B) hypertrophy.
C) hyperplasia.
D) muscle plasticity.
A) atrophy.
B) hypertrophy.
C) hyperplasia.
D) muscle plasticity.
B
3
In response to exercise training, the muscles in adult mammals change as
A) muscle cells of one fiber type die and are replaced by muscle cells of different fiber types.
B) new muscle cells are produced and work along with existing muscle cells.
C) proteins in muscle cells are broken down and replaced by proteins with different properties.
D) existing muscle proteins change from one isoform to another.
A) muscle cells of one fiber type die and are replaced by muscle cells of different fiber types.
B) new muscle cells are produced and work along with existing muscle cells.
C) proteins in muscle cells are broken down and replaced by proteins with different properties.
D) existing muscle proteins change from one isoform to another.
C
4
Endurance exercise involves
A) few repetitions of movements involving low force and aerobic metabolism.
B) few repetitions of movements involving high force and aerobic metabolism.
C) repetitive movements involving high force and anaerobic metabolism.
D) repetitive movements involving low force and aerobic metabolism.
A) few repetitions of movements involving low force and aerobic metabolism.
B) few repetitions of movements involving high force and aerobic metabolism.
C) repetitive movements involving high force and anaerobic metabolism.
D) repetitive movements involving low force and aerobic metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Isoforms of myosin are
A) different conformations of the same protein triggered by different cellular conditions.
B) versions of myosin that have the same function but different kinetics.
C) versions of myosin that perform different cellular functions.
D) versions of myosin that occur in different locations in the cell.
A) different conformations of the same protein triggered by different cellular conditions.
B) versions of myosin that have the same function but different kinetics.
C) versions of myosin that perform different cellular functions.
D) versions of myosin that occur in different locations in the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In which order are motor units recruited as the load on a muscle increases?
A) Fast glycolytic, fast oxidative, slow oxidative
B) Fast oxidative, slow oxidative, fast glycolytic
C) Slow oxidative, fast oxidative, fast glycolytic
D) Slow oxidative, fast glycolytic, fast oxidative
A) Fast glycolytic, fast oxidative, slow oxidative
B) Fast oxidative, slow oxidative, fast glycolytic
C) Slow oxidative, fast oxidative, fast glycolytic
D) Slow oxidative, fast glycolytic, fast oxidative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The recruitment order of different fiber types matches and reinforces their cellular properties because
A) Type I fibers are recruited most frequently, and this helps to maintain their oxidative properties.
B) Type IIa fibers are recruited most frequently and are the most efficient in their use of ATP.
C) Type I fibers are recruited most frequently because they have the largest diameters.
D) Type IIb fibers are recruited most frequently and thus require the largest stores of glycogen.
A) Type I fibers are recruited most frequently, and this helps to maintain their oxidative properties.
B) Type IIa fibers are recruited most frequently and are the most efficient in their use of ATP.
C) Type I fibers are recruited most frequently because they have the largest diameters.
D) Type IIb fibers are recruited most frequently and thus require the largest stores of glycogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In humans, endurance training typically causes _______ muscle fibers to be converted to _______.
A) Type I; Type IIx
B) Type I; Type IIa
C) Type IIa; Type IIx
D) Type IIx; Type IIa
A) Type I; Type IIx
B) Type I; Type IIa
C) Type IIa; Type IIx
D) Type IIx; Type IIa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose you take a muscle biopsy from an elite athlete and perform a histological analysis on the sample. You find that the muscle cells are relatively small in diameter, contain high numbers of mitochondria, and have an unusually large proportion of Type IIa myosin. The athlete is most likely a
A) marathoner.
B) bodybuilder.
C) 100 m sprinter.
D) mile runner.
A) marathoner.
B) bodybuilder.
C) 100 m sprinter.
D) mile runner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
To identify the cellular signals responsible for exercise effects in human muscle, scientists can examine
A) mRNA expression in blood samples.
B) protein activation in blood samples.
C) information obtained from muscle biopsy samples.
D) information obtained from muscle samples obtained from cadavers.
A) mRNA expression in blood samples.
B) protein activation in blood samples.
C) information obtained from muscle biopsy samples.
D) information obtained from muscle samples obtained from cadavers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Resistance exercise involves _______ repetitions per unit time of movements involving _______ force and _______ metabolism.
A) few; high; anaerobic
B) few; low; aerobic
C) many; high; anaerobic
D) many; low; aerobic
A) few; high; anaerobic
B) few; low; aerobic
C) many; high; anaerobic
D) many; low; aerobic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Resistance training increases muscle mass primarily by increasing the
A) number of muscle cells.
B) length of muscle cells.
C) diameter of muscle cells.
D) thickness of the extracellular space in the muscle.
A) number of muscle cells.
B) length of muscle cells.
C) diameter of muscle cells.
D) thickness of the extracellular space in the muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In skeletal muscle cells, resistance training typically results in an increase in
A) the number of mitochondria.
B) the amount of Type IIx myosin.
C) muscle fiber diameter.
D) muscle fiber length.
A) the number of mitochondria.
B) the amount of Type IIx myosin.
C) muscle fiber diameter.
D) muscle fiber length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Glycolytic muscle fibers contain _______ and myosin isoforms that go through the cross-bridge cycle _______.
A) low levels of SR Ca2+-ATPase; slowly
B) high levels of SR Ca2+-ATPase; slowly
C) low levels of SR Ca2+-ATPase; rapidly
D) high levels of SR Ca2+-ATPase; rapidly
A) low levels of SR Ca2+-ATPase; slowly
B) high levels of SR Ca2+-ATPase; slowly
C) low levels of SR Ca2+-ATPase; rapidly
D) high levels of SR Ca2+-ATPase; rapidly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A single motor unit typically consists of
A) equal numbers of slow oxidative, fast oxidative, and fast glycolytic fibers.
B) mostly fast glycolytic fibers along with a few fast oxidative and slow oxidative fibers.
C) only a single fiber type.
D) a single muscle fiber and the motor neuron that innervates it.
A) equal numbers of slow oxidative, fast oxidative, and fast glycolytic fibers.
B) mostly fast glycolytic fibers along with a few fast oxidative and slow oxidative fibers.
C) only a single fiber type.
D) a single muscle fiber and the motor neuron that innervates it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Refer to the figure shown.
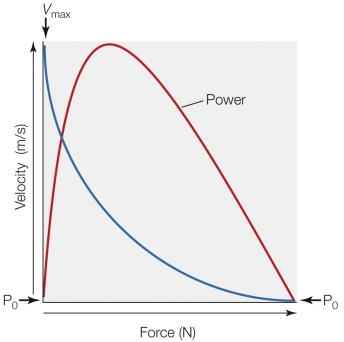 If the muscle represented in the figure can produce a maximal force of 20 N and has a Vmax of 1 m/s, what is its maximal power output?
If the muscle represented in the figure can produce a maximal force of 20 N and has a Vmax of 1 m/s, what is its maximal power output?
A) 2 watts
B) 10 watts
C) 20 watts
D) 200 watts
 If the muscle represented in the figure can produce a maximal force of 20 N and has a Vmax of 1 m/s, what is its maximal power output?
If the muscle represented in the figure can produce a maximal force of 20 N and has a Vmax of 1 m/s, what is its maximal power output?A) 2 watts
B) 10 watts
C) 20 watts
D) 200 watts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the figure shown.
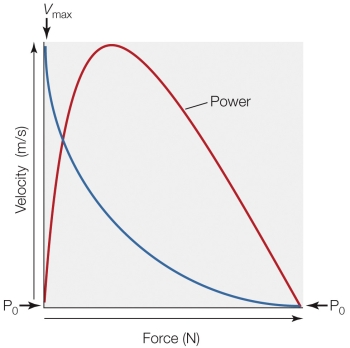 If the muscle represented in the figure can produce a maximal power of 6 watts and has a Vmax of 1.5 m/s, what is its maximum isometric force?
If the muscle represented in the figure can produce a maximal power of 6 watts and has a Vmax of 1.5 m/s, what is its maximum isometric force?
A) 0 newtons
B) 4 newtons
C) 9 newtons
D) 40 newtons
 If the muscle represented in the figure can produce a maximal power of 6 watts and has a Vmax of 1.5 m/s, what is its maximum isometric force?
If the muscle represented in the figure can produce a maximal power of 6 watts and has a Vmax of 1.5 m/s, what is its maximum isometric force?A) 0 newtons
B) 4 newtons
C) 9 newtons
D) 40 newtons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose you are comparing several muscles from the same animal. Which muscle would have the highest power output?
A) Muscle length = 20 cm, cross-sectional area = 10 cm2, composed primarily of fast oxidative fibers
B) Muscle length = 20 cm, cross-sectional area = 10 cm2, composed primarily of fast glycolytic fibers
C) Muscle length = 20 cm, cross-sectional area = 20 cm2, composed primarily of slow oxidative fibers
D) Muscle length = 20 cm, cross-sectional area = 20 cm2, composed primarily of fast glycolytic fibers
A) Muscle length = 20 cm, cross-sectional area = 10 cm2, composed primarily of fast oxidative fibers
B) Muscle length = 20 cm, cross-sectional area = 10 cm2, composed primarily of fast glycolytic fibers
C) Muscle length = 20 cm, cross-sectional area = 20 cm2, composed primarily of slow oxidative fibers
D) Muscle length = 20 cm, cross-sectional area = 20 cm2, composed primarily of fast glycolytic fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Fast glycolytic fibers can generate more power than slow oxidative fibers of similar diameter because they
A) produce more force per cross-sectional area.
B) shorten more rapidly.
C) use ATP more efficiently.
D) have much more myosin per cross-sectional area.
A) produce more force per cross-sectional area.
B) shorten more rapidly.
C) use ATP more efficiently.
D) have much more myosin per cross-sectional area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A training program that increased the proportion of slow oxidative fibers in a muscle would _______ the muscle's maximum _______.
A) increase; isometric force
B) increase; power output
C) decrease; isometric force
D) decrease; power output
A) increase; isometric force
B) increase; power output
C) decrease; isometric force
D) decrease; power output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Many athletes engage in resistance training to increase the speed at which they can perform motions required for their sports. Which statement best explains the effect of resistance training on speed?
A) It increases the proportion of the fastest myosin isoforms.
B) It increases myosin expression of Type IIa and decreases Type IIx expression.
C) It increases the power output of the muscles, improving their ability to move loads.
D) It increases the number of mitochondria in the muscles, increasing the ATP supply.
A) It increases the proportion of the fastest myosin isoforms.
B) It increases myosin expression of Type IIa and decreases Type IIx expression.
C) It increases the power output of the muscles, improving their ability to move loads.
D) It increases the number of mitochondria in the muscles, increasing the ATP supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Resistance training of skeletal muscle would normally result in an increase in the
A) muscle's maximum oxygen consumption.
B) muscle's maximum isometric force.
C) muscle's maximum unloaded shortening velocity.
D) number of capillaries in the muscle.
A) muscle's maximum oxygen consumption.
B) muscle's maximum isometric force.
C) muscle's maximum unloaded shortening velocity.
D) number of capillaries in the muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Experiments that combine endurance and resistance training indicate that
A) resistance training prevents endurance training from having any effect on skeletal muscle.
B) resistance and endurance training can produce some of their characteristic effects on skeletal muscle simultaneously.
C) resistance and endurance training have identical effects on skeletal muscle.
D) resistance and endurance training produce different effects but activate the same cellular pathways.
A) resistance training prevents endurance training from having any effect on skeletal muscle.
B) resistance and endurance training can produce some of their characteristic effects on skeletal muscle simultaneously.
C) resistance and endurance training have identical effects on skeletal muscle.
D) resistance and endurance training produce different effects but activate the same cellular pathways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In skeletal muscle, endurance exercise
A) increases VEGF levels, causing increased angiogenesis and leading to greater numbers of capillaries.
B) increases the number of capillaries, allowing greater VEGF expression.
C) decreases the number of capillaries, causing decreased VEGF expression.
D) decreases VEGF levels, causing decreased angiogenesis and leading to fewer capillaries.
A) increases VEGF levels, causing increased angiogenesis and leading to greater numbers of capillaries.
B) increases the number of capillaries, allowing greater VEGF expression.
C) decreases the number of capillaries, causing decreased VEGF expression.
D) decreases VEGF levels, causing decreased angiogenesis and leading to fewer capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Endurance exercise generates signals in muscle cells, such as
A) high ATP.
B) VEGF.
C) high partial pressures of oxygen.
D) low calcium.
A) high ATP.
B) VEGF.
C) high partial pressures of oxygen.
D) low calcium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Endurance training produces the greatest percentage increase in expression of genes encoding
A) sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase.
B) Type IIx myosin.
C) the mitochondrial enzyme succinate dehydrogenase.
D) hexokinase.
A) sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase.
B) Type IIx myosin.
C) the mitochondrial enzyme succinate dehydrogenase.
D) hexokinase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the figure shown.
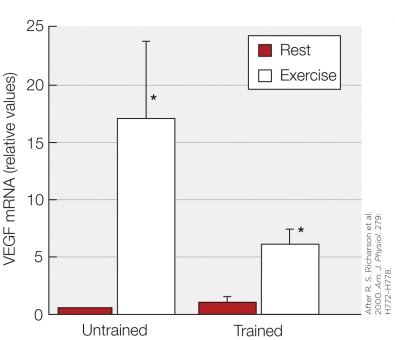 According to the data in the figure, a single bout of endurance exercise
According to the data in the figure, a single bout of endurance exercise
A) increases VEGF mRNA levels, and the increase is greater in muscle that is not used in exercising.
B) increases VEGF mRNA levels, and the increase is greater in muscle that has been trained.
C) decreases VEGF mRNA levels, and the decrease is greater in muscle that has been trained.
D) decreases VEGF mRNA levels, and the decrease is greater in muscle that is not used in exercising.
 According to the data in the figure, a single bout of endurance exercise
According to the data in the figure, a single bout of endurance exerciseA) increases VEGF mRNA levels, and the increase is greater in muscle that is not used in exercising.
B) increases VEGF mRNA levels, and the increase is greater in muscle that has been trained.
C) decreases VEGF mRNA levels, and the decrease is greater in muscle that has been trained.
D) decreases VEGF mRNA levels, and the decrease is greater in muscle that is not used in exercising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A single bout of exercise increases VEGF mRNA less in a trained muscle than in an untrained muscle. The most plausible explanation for this difference is that trained muscle has more
A) capillaries, so intracellular oxygen delivery remains higher during exercise.
B) mitochondria, so it can generate much more force than untrained muscle.
C) capillaries, so intracellular oxygen delivery remains lower during exercise.
D) mitochondria, so it does not need more capillaries.
A) capillaries, so intracellular oxygen delivery remains higher during exercise.
B) mitochondria, so it can generate much more force than untrained muscle.
C) capillaries, so intracellular oxygen delivery remains lower during exercise.
D) mitochondria, so it does not need more capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In skeletal muscle cells, endurance exercise training typically produces
A) increases in creatine phosphate levels.
B) increases in the mitochondrial enzyme citrate synthase activity.
C) increased phosphorylation of IGF-1.
D) increased myosin IIb expression.
A) increases in creatine phosphate levels.
B) increases in the mitochondrial enzyme citrate synthase activity.
C) increased phosphorylation of IGF-1.
D) increased myosin IIb expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Increases in mitochondrial number and capillary number
A) increase the power of fast glycolytic muscle.
B) permit the muscle cells to use more oxygen per unit time.
C) increase the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
D) increase the oxygen-storage capacity of the muscle.
A) increase the power of fast glycolytic muscle.
B) permit the muscle cells to use more oxygen per unit time.
C) increase the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
D) increase the oxygen-storage capacity of the muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Endurance training increases the amounts of both glycogen and lipid stored in muscle cells. This most directly increases the
A) shortening velocity of the muscle cells when unloaded.
B) force output of the muscle cells in an isometric contraction.
C) amount of work that can be performed before the cells are depleted of fuel.
D) maximum frequency at which the cells can produce distinct twitch contractions.
A) shortening velocity of the muscle cells when unloaded.
B) force output of the muscle cells in an isometric contraction.
C) amount of work that can be performed before the cells are depleted of fuel.
D) maximum frequency at which the cells can produce distinct twitch contractions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Refer to the figure shown.
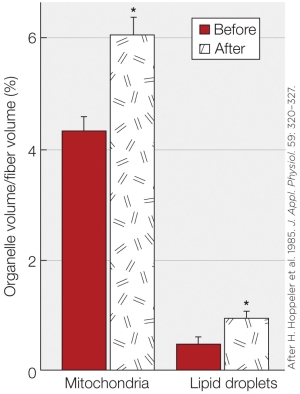 The figure illustrates a part of the typical response of skeletal muscle to
The figure illustrates a part of the typical response of skeletal muscle to
A) endurance training.
B) resistance training.
C) immobilization.
D) detraining following resistance training.
 The figure illustrates a part of the typical response of skeletal muscle to
The figure illustrates a part of the typical response of skeletal muscle toA) endurance training.
B) resistance training.
C) immobilization.
D) detraining following resistance training.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Bob has been sedentary for several years. As a New Year's resolution, he starts an intense exercise program, but after three months he stops exercising completely. What was the likely effect of the program on his heart mass while he was exercising, and what is the most likely outcome a year later?
A) His heart mass most likely increased during the exercise program and has remained at the same larger size.
B) His heart mass most likely increased during the exercise program and then decreased to its previous size.
C) His heart mass most likely decreased during the exercise program and has remained at the same smaller size.
D) His heart mass most likely decreased during the exercise program and has increased to its previous size.
A) His heart mass most likely increased during the exercise program and has remained at the same larger size.
B) His heart mass most likely increased during the exercise program and then decreased to its previous size.
C) His heart mass most likely decreased during the exercise program and has remained at the same smaller size.
D) His heart mass most likely decreased during the exercise program and has increased to its previous size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Burmese pythons are a uniquely useful model for studies of cardiac hypertrophy because their heart(s)
A) anatomy is very similar to that of humans.
B) increase in size very rapidly in response to exercise training.
C) increase in size very rapidly in response to feeding.
D) are highly resistant to atrophy and hypertrophy.
A) anatomy is very similar to that of humans.
B) increase in size very rapidly in response to exercise training.
C) increase in size very rapidly in response to feeding.
D) are highly resistant to atrophy and hypertrophy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the figure showing the changes in heart mass of Burmese pythons 3 days after feeding (DPF), infusion with plasma from fed or fasted snakes, or infusion with a solution of bovine serum albumin (BSA) with or without three specific fatty acids (FA) found in blood of fed snakes.
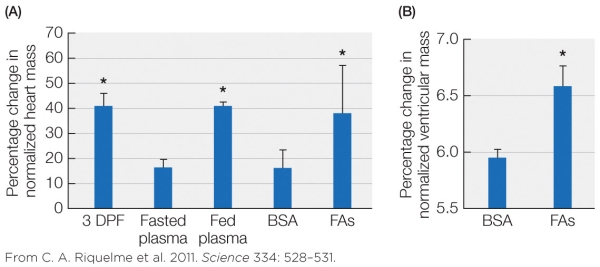 According to the figure, feeding increases heart mass primarily through
According to the figure, feeding increases heart mass primarily through
A) the influence of an unknown hormone in the blood.
B) the influence of the three fatty acids tested.
C) nervous signals generated when the stomach stretches.
D) the action of bovine serum albumin.
 According to the figure, feeding increases heart mass primarily through
According to the figure, feeding increases heart mass primarily throughA) the influence of an unknown hormone in the blood.
B) the influence of the three fatty acids tested.
C) nervous signals generated when the stomach stretches.
D) the action of bovine serum albumin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the figure shown.
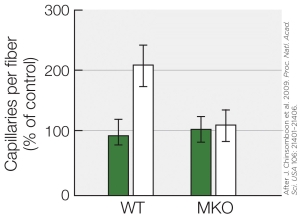 What is the likely treatment in this figure?
What is the likely treatment in this figure?
A) Microgravity
B) Resistance training
C) Endurance training
D) Resistance training followed by detraining
 What is the likely treatment in this figure?
What is the likely treatment in this figure?A) Microgravity
B) Resistance training
C) Endurance training
D) Resistance training followed by detraining

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the figure shown.
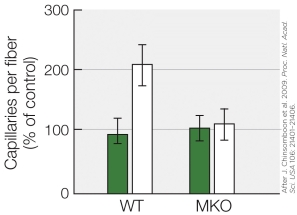 What best explains the results for the experimental group of mice on the right of the figure?
What best explains the results for the experimental group of mice on the right of the figure?
A) The group of mice on the right lacked PGC-1α
B) The group of mice on the right was the control group
C) The group of mice on the right had an extra copy of PGC-1α
D) The group of mice on the right lacked myostatin
 What best explains the results for the experimental group of mice on the right of the figure?
What best explains the results for the experimental group of mice on the right of the figure?A) The group of mice on the right lacked PGC-1α
B) The group of mice on the right was the control group
C) The group of mice on the right had an extra copy of PGC-1α
D) The group of mice on the right lacked myostatin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which statement about muscle atrophy is true?
A) Muscle atrophy occurs only in pathological conditions.
B) Muscle proteins are degraded only when atrophy is taking place.
C) Atrophy of muscle makes amino acids available for other systems in the body.
D) Muscle protein synthesis stops completely in muscles that are undergoing atrophy.
A) Muscle atrophy occurs only in pathological conditions.
B) Muscle proteins are degraded only when atrophy is taking place.
C) Atrophy of muscle makes amino acids available for other systems in the body.
D) Muscle protein synthesis stops completely in muscles that are undergoing atrophy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Experiments involving microgravity can be used to study the cellular processes involved in
A) resistance training.
B) endurance training.
C) muscle atrophy.
D) muscle development.
A) resistance training.
B) endurance training.
C) muscle atrophy.
D) muscle development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Atrophy of muscles due to disuse is accompanied by a shift in fiber type from _______ fibers to _______ fibers.
A) faster and more glycolytic; slower and more oxidative
B) slower and more oxidative; faster and more glycolytic
C) faster and more oxidative; slower and more glycolytic
D) Type IIx; Type I
A) faster and more glycolytic; slower and more oxidative
B) slower and more oxidative; faster and more glycolytic
C) faster and more oxidative; slower and more glycolytic
D) Type IIx; Type I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Based on the phenotype of patients who have been paralyzed for a substantial period of time, scientists have inferred that the default fiber type of skeletal muscle is
A) fast oxidative.
B) fast glycolytic.
C) slow oxidative.
D) slow glycolytic.
A) fast oxidative.
B) fast glycolytic.
C) slow oxidative.
D) slow glycolytic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Sarcopenia, or age-related loss of muscle mass, is
A) due entirely to disuse atrophy as older people become less active.
B) due entirely to reduction in size of individual muscle fibers in aging individuals.
C) due entirely to reduction in the number of muscle fibers in aging individuals.
D) inevitable, but the rate of muscle loss can be minimized by resistance training.
A) due entirely to disuse atrophy as older people become less active.
B) due entirely to reduction in size of individual muscle fibers in aging individuals.
C) due entirely to reduction in the number of muscle fibers in aging individuals.
D) inevitable, but the rate of muscle loss can be minimized by resistance training.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the muscles of elderly people,
A) the ability to repair cellular damage is lost, leading to sarcopenia.
B) muscle deteriorates due to the same processes that lead to atrophy when muscle is unloaded.
C) muscle becomes unresponsive to training, leading to sarcopenia.
D) normal repair and hypertrophy processes are still active but less effective than in younger people.
A) the ability to repair cellular damage is lost, leading to sarcopenia.
B) muscle deteriorates due to the same processes that lead to atrophy when muscle is unloaded.
C) muscle becomes unresponsive to training, leading to sarcopenia.
D) normal repair and hypertrophy processes are still active but less effective than in younger people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Studies of bears indicate that their adaptations for a lifestyle that involves hibernation include
A) pronounced muscle hypertrophy during hibernation.
B) reduced rates of muscle atrophy during hibernation.
C) increased muscle protein synthesis during hibernation.
D) no muscle atrophy during hibernation.
A) pronounced muscle hypertrophy during hibernation.
B) reduced rates of muscle atrophy during hibernation.
C) increased muscle protein synthesis during hibernation.
D) no muscle atrophy during hibernation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the figure shown.
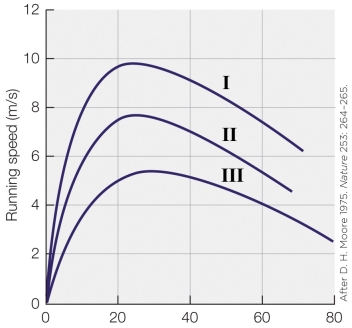 What is the most logical label for the x axis?
What is the most logical label for the x axis?
A) Age (years)
B) Development (days)
C) Force (N)
D) Velocity (m/s)
 What is the most logical label for the x axis?
What is the most logical label for the x axis?A) Age (years)
B) Development (days)
C) Force (N)
D) Velocity (m/s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the figure shown.
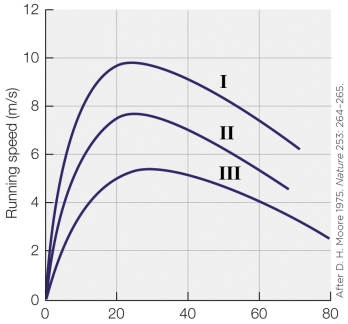 An elite distance runner would display a curve that is closest to
An elite distance runner would display a curve that is closest to
A) curve I.
B) curve II.
C) curve III.
D) a curve that is much higher than curve I.
 An elite distance runner would display a curve that is closest to
An elite distance runner would display a curve that is closest toA) curve I.
B) curve II.
C) curve III.
D) a curve that is much higher than curve I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
"Double-muscled" animals such as Belgian Blue cattle and whippets have naturally occurring mutations in the gene encoding the protein
A) myostatin.
B) myosin.
C) IGF-1.
D) Akt.
A) myostatin.
B) myosin.
C) IGF-1.
D) Akt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Myostatin mutations that increase muscle mass may not be favored by evolution because
A) larger muscles in animals that have impaired myostatin production actually produce less force than normal muscles.
B) larger muscles fatigue more rapidly in myostatin-null animals.
C) impaired atrophy may deprive myostatin-null animals of the amino acids needed for physiological processes in non-muscle tissues.
D) the high degree of conservation of the myostatin sequence in different tetrapods indicates that the gene is not important in most animals.
A) larger muscles in animals that have impaired myostatin production actually produce less force than normal muscles.
B) larger muscles fatigue more rapidly in myostatin-null animals.
C) impaired atrophy may deprive myostatin-null animals of the amino acids needed for physiological processes in non-muscle tissues.
D) the high degree of conservation of the myostatin sequence in different tetrapods indicates that the gene is not important in most animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Binding of IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1) to its receptor on a skeletal muscle cell membrane leads to _______ protein synthesis and _______ protein degradation.
A) increased; decreased
B) increased; increased
C) decreased; increased
D) decreased; decreased
A) increased; decreased
B) increased; increased
C) decreased; increased
D) decreased; decreased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Cachexia, or muscle wasting (loss of muscle mass), is a common complication of cancer. A muscle biopsy sample from a cancer patient would likely show
A) increased activation of PI3-kinase.
B) decreased levels of myostatin.
C) decreased phosphorylation of Akt.
D) decreased mRNA levels of atrophy promoting genes.
A) increased activation of PI3-kinase.
B) decreased levels of myostatin.
C) decreased phosphorylation of Akt.
D) decreased mRNA levels of atrophy promoting genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which drug would likely be the most effective for restoring muscle mass in a cancer patient undergoing chemotherapy?
A) A drug that blocks insulin receptors
B) A drug that activates the myostatin receptor
C) A drug that activates transcription of atrophy genes
D) A drug that enhances phosphorylation of Akt
A) A drug that blocks insulin receptors
B) A drug that activates the myostatin receptor
C) A drug that activates transcription of atrophy genes
D) A drug that enhances phosphorylation of Akt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which drug would likely be the most effective for restoring muscle mass in a cancer patient undergoing chemotherapy?
A) A drug that blocks insulin receptors
B) A drug that blocks the IGF-1 receptor
C) A drug that blocks the myostatin receptor
D) A drug that inhibits phosphorylation of Akt
A) A drug that blocks insulin receptors
B) A drug that blocks the IGF-1 receptor
C) A drug that blocks the myostatin receptor
D) A drug that inhibits phosphorylation of Akt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
There currently is great scientific interest in identifying genetic polymorphisms that underlie different individual responses to exercise training. The muscle size and bulk of a champion bodybuilder, for example, might be due in part to a missense mutation in the
A) IGF-1 gene.
B) androgen receptor.
C) myostatin gene.
D) Akt gene.
A) IGF-1 gene.
B) androgen receptor.
C) myostatin gene.
D) Akt gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which experimental treatment would most likely increase levels of IGF-1 protein in a rat's plantaris muscle?
A) Putting the hindlimb in a cast for two weeks
B) Cutting the motor neurons that normally innervate the plantaris
C) Putting a running wheel in the rat's cage so that it can perform voluntary endurance exercise
D) Surgically removing the rat's other calf muscles to overload the plantaris
A) Putting the hindlimb in a cast for two weeks
B) Cutting the motor neurons that normally innervate the plantaris
C) Putting a running wheel in the rat's cage so that it can perform voluntary endurance exercise
D) Surgically removing the rat's other calf muscles to overload the plantaris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Satellite cells
A) are stem cells that fuse into existing muscle cells to add nuclei to the muscle cells.
B) are stem cells that fuse into existing muscle cells to add cytoplasm to the muscle cells.
C) provide metabolic support to other muscle cells by processing lactate and other wastes.
D) are muscle cells that are not connected to tendons or other connective tissue.
A) are stem cells that fuse into existing muscle cells to add nuclei to the muscle cells.
B) are stem cells that fuse into existing muscle cells to add cytoplasm to the muscle cells.
C) provide metabolic support to other muscle cells by processing lactate and other wastes.
D) are muscle cells that are not connected to tendons or other connective tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The number of myonuclei in a muscle cell is important to the process of muscle repair and hypertrophy because each nucleus must
A) transcribe mRNA to serve as a template for protein synthesis.
B) translate protein to overcome protein degradation.
C) recycle proteins that are being degraded.
D) duplicate its DNA to make additional muscle cells.
A) transcribe mRNA to serve as a template for protein synthesis.
B) translate protein to overcome protein degradation.
C) recycle proteins that are being degraded.
D) duplicate its DNA to make additional muscle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which factor would most likely lead to muscle hypertrophy?
A) Increased levels of stress hormones, such as glucocorticoids
B) Increased intake of dietary protein
C) Increased caloric intake
D) Decreased levels of dietary protein
A) Increased levels of stress hormones, such as glucocorticoids
B) Increased intake of dietary protein
C) Increased caloric intake
D) Decreased levels of dietary protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In humans, the vastus lateralis is a mixed fiber type muscle from which biopsies are often taken in exercise studies. Why might it be particularly worthwhile to use a mixed fiber type muscle in studies of exercise training?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Describe how force, speed, and power output differ among muscle fibers of different fiber types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Explain how the cellular effects of endurance training improve the balance between ATP supply and demand during extended exercise. Refer to specific changes that occur and indicate whether they increase or decrease ATP supply or ATP demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain how endurance training increases the ability of muscle cells to use oxygen. Include three specific cellular effects of endurance training and explain how each one increases oxygen uptake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Describe the effects of exercise training on cardiac muscle and identify how they are similar to the effects of either endurance or resistance training on skeletal muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Describe what happens to the muscle cells at the molecular level in a person's biceps when the person has to wear a cast for a broken arm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Describe the effects of wearing a cast for a broken foot on whole-muscle performance in a person's calf muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
List two experimental techniques used to study muscle atrophy in animal or human models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using humans versus rodents for experimental studies of muscle plasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Compare and contrast the effects of resistance and endurance exercise on skeletal muscle tissue. What changes in protein expression occur in each mode of training? How do the overall effects on the muscle cells and the whole muscle differ between the two modes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



