Deck 16: Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Physiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Physiology
1
In the spring, when a bear emerges from its den, adipose cells
A) become resistant to insulin.
B) release insulin.
C) become responsive to insulin.
D) metabolize insulin.
A) become resistant to insulin.
B) release insulin.
C) become responsive to insulin.
D) metabolize insulin.
C
2
Which diagram represents the mechanism of oxytocin release from the initial signal in the hypothalamus?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
C
3
Which diagram(s) represent(s) the process of chemical signaling from the initial signal in the hypothalamus to the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone?
A) I
B) II and III
C) II and IV
D) I and II
A) I
B) II and III
C) II and IV
D) I and II
B
4
How can the same hormone can have a completely different function in 2 different species?
A) The origin of the hormone is different.
B) The affected tissues are different.
C) The second messenger systems inside the cell bring about a different action.
D) The receptors are different.
A) The origin of the hormone is different.
B) The affected tissues are different.
C) The second messenger systems inside the cell bring about a different action.
D) The receptors are different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In order to bring about intracellular effects, steroid hormones
A) attach to receptors and cause a series of second messenger effects.
B) pass through the cell membrane and cause a series of second messenger effects.
C) attach to receptors and attach to an intracellular receptor.
D) pass through the cell membrane and attach to an intracellular receptor.
A) attach to receptors and cause a series of second messenger effects.
B) pass through the cell membrane and cause a series of second messenger effects.
C) attach to receptors and attach to an intracellular receptor.
D) pass through the cell membrane and attach to an intracellular receptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Refer to the figure shown.
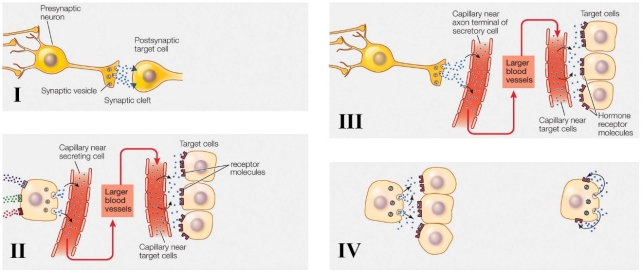 Which diagram represents a neurosecretory system?
Which diagram represents a neurosecretory system?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which diagram represents a neurosecretory system?
Which diagram represents a neurosecretory system?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which compound functions as both a hormone and a neurotransmitter?
A) Thyroid hormone
B) Cholecystokinin
C) Carbon dioxide
D) Gastrin
A) Thyroid hormone
B) Cholecystokinin
C) Carbon dioxide
D) Gastrin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which hormone is categorized incorrectly?
A) Testosterone-steroid
B) Insulin-peptide
C) Growth hormone-steroid
D) Melatonin-amine
A) Testosterone-steroid
B) Insulin-peptide
C) Growth hormone-steroid
D) Melatonin-amine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which compound bypasses second messenger systems and alters gene expression?
A) Peptides
B) Steroids
C) Thyroid hormones
D) Melatonin
A) Peptides
B) Steroids
C) Thyroid hormones
D) Melatonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which hormone has the longest half-life?
A) Melatonin
B) Insulin
C) Testosterone
D) Thyroid hormone
A) Melatonin
B) Insulin
C) Testosterone
D) Thyroid hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Neurosecretory cells
A) are not connected to the nervous system.
B) release neurotransmitters into the blood.
C) transduce neural signals into endocrine signals.
D) do not typically produce action potentials.
A) are not connected to the nervous system.
B) release neurotransmitters into the blood.
C) transduce neural signals into endocrine signals.
D) do not typically produce action potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An anatomically distinct site for the release of neurohormones is called a(n)
A) neurohemal organ.
B) anastomosis.
C) adenohypophysis.
D) paraventricular nucleus.
A) neurohemal organ.
B) anastomosis.
C) adenohypophysis.
D) paraventricular nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Why do steroid-secreting cells take longer to initiate secretion than do peptide-secreting hormones?
A) They take much longer to create.
B) The step of posttranslational processing is much longer.
C) They are not stored in vesicles, they are made on demand.
D) Only a few cells in the body actually make steroid hormones.
A) They take much longer to create.
B) The step of posttranslational processing is much longer.
C) They are not stored in vesicles, they are made on demand.
D) Only a few cells in the body actually make steroid hormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Refer to the figure shown.
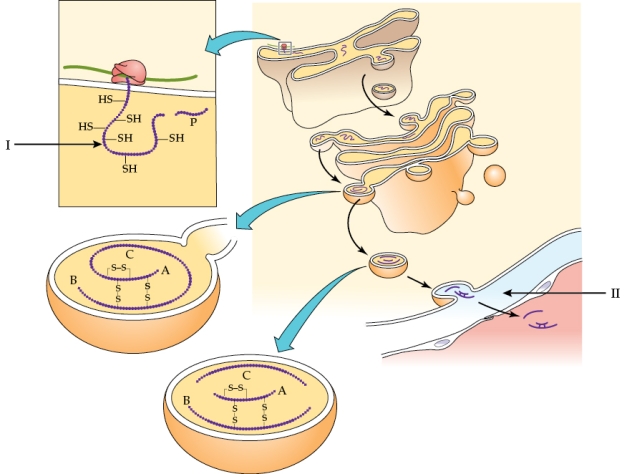 Arrow I in the diagram points to
Arrow I in the diagram points to
A) preproinsulin.
B) proinsulin.
C) the P segment.
D) insulin.
 Arrow I in the diagram points to
Arrow I in the diagram points toA) preproinsulin.
B) proinsulin.
C) the P segment.
D) insulin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Refer to the figure shown.
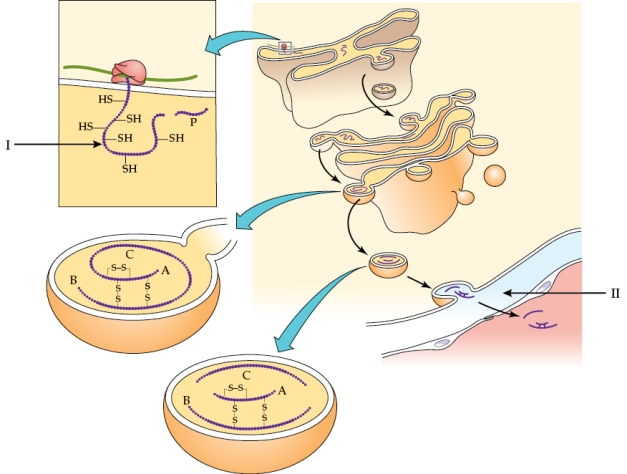 The _______ in the diagram reaches its final form through _______.
The _______ in the diagram reaches its final form through _______.
A) insulin; ribosomal cleavage
B) glucagon; ribosomal cleavage
C) insulin; posttranslational processing
D) glucagon; posttranslational processing
 The _______ in the diagram reaches its final form through _______.
The _______ in the diagram reaches its final form through _______.A) insulin; ribosomal cleavage
B) glucagon; ribosomal cleavage
C) insulin; posttranslational processing
D) glucagon; posttranslational processing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Refer to the figure shown.
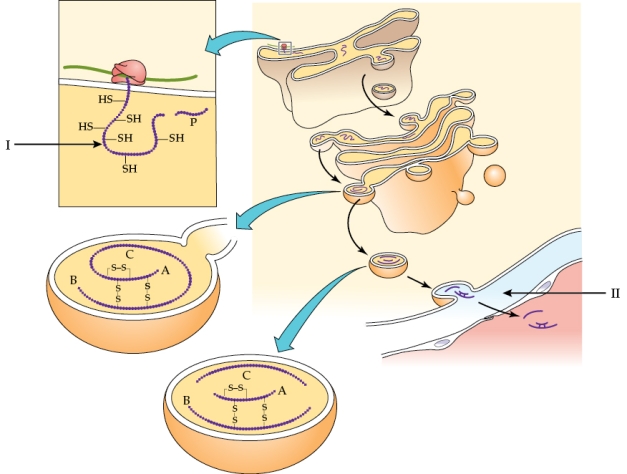 What process is represented at arrow II?
What process is represented at arrow II?
A) Storage of insulin in vesicles
B) Release of insulin into the blood
C) Transporting of proinsulin to a different part of the cell, where it will mature into insulin
D) Release of insulin and C-peptide into the blood
 What process is represented at arrow II?
What process is represented at arrow II?A) Storage of insulin in vesicles
B) Release of insulin into the blood
C) Transporting of proinsulin to a different part of the cell, where it will mature into insulin
D) Release of insulin and C-peptide into the blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which statement about insulin is true?
A) Insulin is synthesized at ribosomes, stored in vesicles, and secreted on demand.
B) Insulin is synthesized in the nucleus and released into the blood by diffusion.
C) Insulin is synthesized on demand, stored in vesicles, and secreted on demand.
D) Insulin is synthesized on demand and released into the blood by diffusion.
A) Insulin is synthesized at ribosomes, stored in vesicles, and secreted on demand.
B) Insulin is synthesized in the nucleus and released into the blood by diffusion.
C) Insulin is synthesized on demand, stored in vesicles, and secreted on demand.
D) Insulin is synthesized on demand and released into the blood by diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Testosterone is synthesized
A) at ribosomes, stored in vesicles, and secreted on demand.
B) in the nucleus and released into the blood by diffusion.
C) on demand, stored in vesicles, and secreted on demand.
D) on demand and released into the blood by diffusion.
A) at ribosomes, stored in vesicles, and secreted on demand.
B) in the nucleus and released into the blood by diffusion.
C) on demand, stored in vesicles, and secreted on demand.
D) on demand and released into the blood by diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What statement best describes the function of vasopressin cells.
A) Vasopressin cells act like neurons.
B) Vasopressin cells receive input about osmotic pressure, and, if high, release vasopressin into the circulation.
C) Vasopressin cells receive input about osmotic pressure, and, if high, generate action potentials which then activate endocrine cells in the pituitary to release vasopressin into the circulation.
D) Cells in the hypothalamus respond to high osmotic pressure and activate vasopressin cells in the pituitary, which then secrete vasopressin into the circulation.
A) Vasopressin cells act like neurons.
B) Vasopressin cells receive input about osmotic pressure, and, if high, release vasopressin into the circulation.
C) Vasopressin cells receive input about osmotic pressure, and, if high, generate action potentials which then activate endocrine cells in the pituitary to release vasopressin into the circulation.
D) Cells in the hypothalamus respond to high osmotic pressure and activate vasopressin cells in the pituitary, which then secrete vasopressin into the circulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which hormones are released by the posterior pituitary gland?
A) Vasopressin and oxytocin
B) Antidiuretic hormone and prolactin
C) Vasopressin and antidiuretic hormone
D) Prolactin and vasopressin
A) Vasopressin and oxytocin
B) Antidiuretic hormone and prolactin
C) Vasopressin and antidiuretic hormone
D) Prolactin and vasopressin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which hormone is directly responsible for milk let-down (ejection)?
A) Oxytocin
B) Prolactin
C) Follicle-stimulating hormone
D) Luteinizing hormone
A) Oxytocin
B) Prolactin
C) Follicle-stimulating hormone
D) Luteinizing hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Refer to the figure shown.
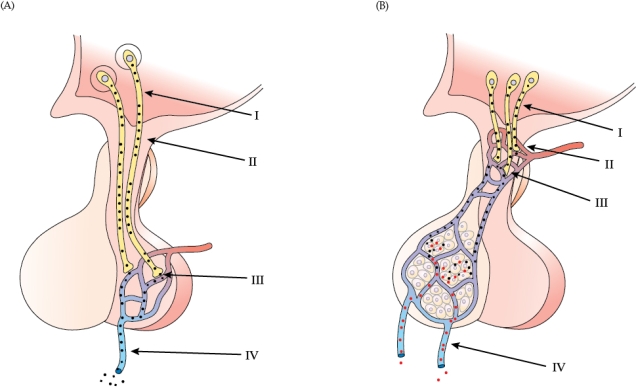 Which statement about the figures is the most accurate?
Which statement about the figures is the most accurate?
A) Only figure B contains a neurohemal organ.
B) Figures A and B contain a neurohemal organ.
C) Figures A and B contain a neurohemal organ, and figure B also contains a portal system.
D) Figures A and B contain a neurohemal organ, and figure A also contains a portal system.
 Which statement about the figures is the most accurate?
Which statement about the figures is the most accurate?A) Only figure B contains a neurohemal organ.
B) Figures A and B contain a neurohemal organ.
C) Figures A and B contain a neurohemal organ, and figure B also contains a portal system.
D) Figures A and B contain a neurohemal organ, and figure A also contains a portal system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Refer to the figure shown.
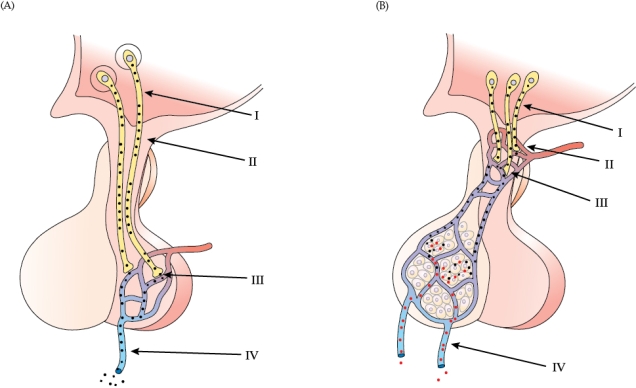 Which statement regarding the arrows is true in both figures?
Which statement regarding the arrows is true in both figures?
A) I represents secretion of a neurotransmitter.
B) II represents the neurohemal organ.
C) III represents release of a neurohormone into the general circulation.
D) IV represents venous outflow that includes the hormone.
 Which statement regarding the arrows is true in both figures?
Which statement regarding the arrows is true in both figures?A) I represents secretion of a neurotransmitter.
B) II represents the neurohemal organ.
C) III represents release of a neurohormone into the general circulation.
D) IV represents venous outflow that includes the hormone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which hormone is direct acting?
A) Thyroid-stimulating hormone
B) Prolactin
C) Adrenocorticotropic hormone
D) Follicle-stimulating hormone
A) Thyroid-stimulating hormone
B) Prolactin
C) Adrenocorticotropic hormone
D) Follicle-stimulating hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which hormone functions in skin darkening in amphibians and non-avian reptiles?
A) Melanocyte stimulating hormones
B) Thyroid hormones
C) Glucocorticoids
D) Adrenocorticotropin
A) Melanocyte stimulating hormones
B) Thyroid hormones
C) Glucocorticoids
D) Adrenocorticotropin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The most common posterior pituitary nonapeptide found in most bony fish is
A) arginine vasotocin.
B) oxytocin.
C) mesotocin.
D) isotocin.
A) arginine vasotocin.
B) oxytocin.
C) mesotocin.
D) isotocin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which statement regarding the feedback mechanisms of the HPA axis is true?
A) Glucocorticoids enhance the secretion of CRH.
B) Glucocorticoids inhibit the secretion of ACTH.
C) ACTH enhances the secretion of CRH.
D) ACTH decreases the secretion of glucocorticoids.
A) Glucocorticoids enhance the secretion of CRH.
B) Glucocorticoids inhibit the secretion of ACTH.
C) ACTH enhances the secretion of CRH.
D) ACTH decreases the secretion of glucocorticoids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Injections of _______ would likely result in the highest blood glucose levels in a mammal when measured 1 hour post injection.
A) insulin and glucagon
B) insulin and epinephrine
C) glucagon and epinephrine
D) insulin, glycogen, and epinephrine
A) insulin and glucagon
B) insulin and epinephrine
C) glucagon and epinephrine
D) insulin, glycogen, and epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure shown.
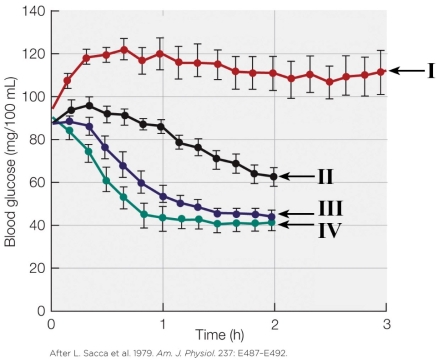 Which plot line on the graph likely represents an insulin-only treatment?
Which plot line on the graph likely represents an insulin-only treatment?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which plot line on the graph likely represents an insulin-only treatment?
Which plot line on the graph likely represents an insulin-only treatment?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the figure shown.
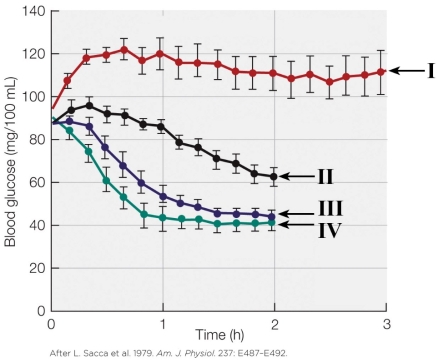 Which plot line represents antagonism toward insulin?
Which plot line represents antagonism toward insulin?
A) I
B) II
C) I, II, and III
D) IV
 Which plot line represents antagonism toward insulin?
Which plot line represents antagonism toward insulin?A) I
B) II
C) I, II, and III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is not directly part of the HPA axis?
A) ACTH
B) glucocorticoids
C) norepinephrine
D) CRH
A) ACTH
B) glucocorticoids
C) norepinephrine
D) CRH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which physiological reaction would occur in response to direct sympathetic activation?
A) Muscle protein anabolism
B) Release of glucose from muscle and liver
C) Increase in digestive activity
D) Decrease in ventilation
A) Muscle protein anabolism
B) Release of glucose from muscle and liver
C) Increase in digestive activity
D) Decrease in ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not part of the mammalian stress response?
A) Increased release of thyroid-stimulating hormone
B) Vasoconstriction of specific regions such as the skin
C) Increase in fat catabolism
D) Release of glucocorticoids
A) Increased release of thyroid-stimulating hormone
B) Vasoconstriction of specific regions such as the skin
C) Increase in fat catabolism
D) Release of glucocorticoids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement about synergistic components of the mammalian stress response is true?
A) Catecholamines amplify glucagon's effect in opposing the actions of insulin.
B) Epinephrine decreases an animal's perception of pain.
C) Epinephrine inhibits the secretion of ACTH.
D) β-endorphin enhances the secretion of ACTH.
A) Catecholamines amplify glucagon's effect in opposing the actions of insulin.
B) Epinephrine decreases an animal's perception of pain.
C) Epinephrine inhibits the secretion of ACTH.
D) β-endorphin enhances the secretion of ACTH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following occurs after a significant blood loss?
A) Increase in aldosterone secretion to decrease Na+ reabsorption
B) Increase in vasopressin secretion to increase water reabsorption
C) Increase in atrial natriuretic peptide secretion to increase blood pressure
D) Stimulation of the vessels by catecholamines to dilate the vessels and maintain blood pressure
A) Increase in aldosterone secretion to decrease Na+ reabsorption
B) Increase in vasopressin secretion to increase water reabsorption
C) Increase in atrial natriuretic peptide secretion to increase blood pressure
D) Stimulation of the vessels by catecholamines to dilate the vessels and maintain blood pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which statement about the mammalian stress response is true?
A) Glucocorticoids enhance the release of CRH.
B) Cytokines stimulate the release of CRH.
C) ACTH inhibits the production of glucocorticoids.
D) Glucocorticoids stimulate immune-system reactions, causing inflammation.
A) Glucocorticoids enhance the release of CRH.
B) Cytokines stimulate the release of CRH.
C) ACTH inhibits the production of glucocorticoids.
D) Glucocorticoids stimulate immune-system reactions, causing inflammation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During a long period between meals, there is a rise in the blood concentration of
A) insulin.
B) glucagon.
C) glycogen.
D) epinephrine.
A) insulin.
B) glucagon.
C) glycogen.
D) epinephrine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the figure shown.
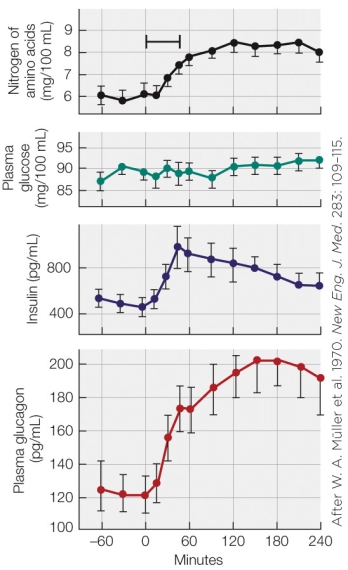 If all of the panels in the figure represent data from one treatment, this treatment was most likely
If all of the panels in the figure represent data from one treatment, this treatment was most likely
A) fasting.
B) fasting and ingestion of a high-carbohydrate meal.
C) fasting and ingestion of a high-protein meal.
D) fasting and ingestion of a high-fat meal.
 If all of the panels in the figure represent data from one treatment, this treatment was most likely
If all of the panels in the figure represent data from one treatment, this treatment was most likelyA) fasting.
B) fasting and ingestion of a high-carbohydrate meal.
C) fasting and ingestion of a high-protein meal.
D) fasting and ingestion of a high-fat meal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the figure shown.
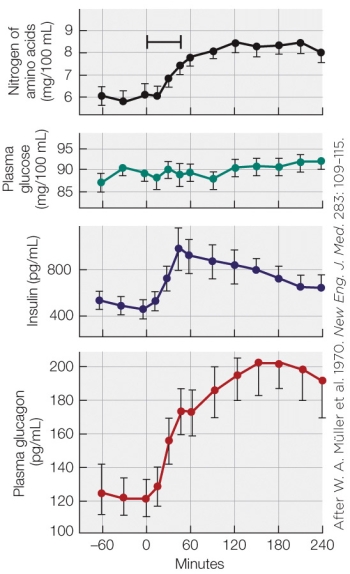 Which statement best explains the increase in insulin levels seen in the figure?
Which statement best explains the increase in insulin levels seen in the figure?
A) Insulin increases after a high-carbohydrate meal in order to enhance the removal of blood glucose.
B) Insulin increases after a high-carbohydrate meal in order to stabilize blood glucose levels and store the excess as glycogen.
C) Insulin increases after any meal in order to enhance the uptake of the broken-down biomolecules into the blood from the intestines.
D) Insulin increases after a high-protein meal in order to promote the incorporation of absorbed amino acids into body proteins.
 Which statement best explains the increase in insulin levels seen in the figure?
Which statement best explains the increase in insulin levels seen in the figure?A) Insulin increases after a high-carbohydrate meal in order to enhance the removal of blood glucose.
B) Insulin increases after a high-carbohydrate meal in order to stabilize blood glucose levels and store the excess as glycogen.
C) Insulin increases after any meal in order to enhance the uptake of the broken-down biomolecules into the blood from the intestines.
D) Insulin increases after a high-protein meal in order to promote the incorporation of absorbed amino acids into body proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Uncontrollably high blood glucose, such as in people with diabetes mellitus,
A) is uncomfortable but not a serious issue.
B) is typically fatal after a few episodes; therefore, medication is mandatory.
C) can result in eye, kidney, blood vessel, and nerve damage if not treated.
D) results in continual dehydration.
A) is uncomfortable but not a serious issue.
B) is typically fatal after a few episodes; therefore, medication is mandatory.
C) can result in eye, kidney, blood vessel, and nerve damage if not treated.
D) results in continual dehydration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which hormone related to mammalian nutrient metabolism is secreted continuously?
A) Insulin
B) Osteocalcin
C) Thyroid hormone
D) Glucocorticoids
A) Insulin
B) Osteocalcin
C) Thyroid hormone
D) Glucocorticoids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Why is iodine an essential nutrient?
A) Thyroid hormone includes iodine in its chemical structure.
B) Iodine is necessary for proper neural activity.
C) Iodine is an important antioxidant.
D) Iodine helps to create ATP.
A) Thyroid hormone includes iodine in its chemical structure.
B) Iodine is necessary for proper neural activity.
C) Iodine is an important antioxidant.
D) Iodine helps to create ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How did many countries significantly reduce iodine deficiency?
A) They supplemented iodine into crops.
B) They used iodized salt.
C) They fed cows, pigs, and chickens nutrients fortified with iodine.
D) The supplemented breakfast cereal with iodine.
A) They supplemented iodine into crops.
B) They used iodized salt.
C) They fed cows, pigs, and chickens nutrients fortified with iodine.
D) The supplemented breakfast cereal with iodine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which best explains the formation of a goiter from iodine deficiency?
A) Lack of suppression from TRH causes more thyroid hormone to be released. This continual release stimulates the thyroid and eventually causes it to grow bigger.
B) Lack of iodine causes an immune response in the thyroid causing it to swell.
C) Lack of negative feedback from thyroid hormone causes more TRH to be released. This continual release stimulates the thyroid and eventually causes it to grow bigger.
D) Positive feedback from excess thyroid hormone causes more TRH to be released. This continual release stimulates the thyroid and eventually causes it to grow bigger.
A) Lack of suppression from TRH causes more thyroid hormone to be released. This continual release stimulates the thyroid and eventually causes it to grow bigger.
B) Lack of iodine causes an immune response in the thyroid causing it to swell.
C) Lack of negative feedback from thyroid hormone causes more TRH to be released. This continual release stimulates the thyroid and eventually causes it to grow bigger.
D) Positive feedback from excess thyroid hormone causes more TRH to be released. This continual release stimulates the thyroid and eventually causes it to grow bigger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) (vasopressin) upregulates the _______ of aquaporins into the _______ membrane of the collecting duct so that more water can be _______.
A) insertion; apical; reabsorbed
B) insertion; apical; excreted
C) insertion; basal; reabsorbed
D) removal; apical; excreted
A) insertion; apical; reabsorbed
B) insertion; apical; excreted
C) insertion; basal; reabsorbed
D) removal; apical; excreted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the figure shown.
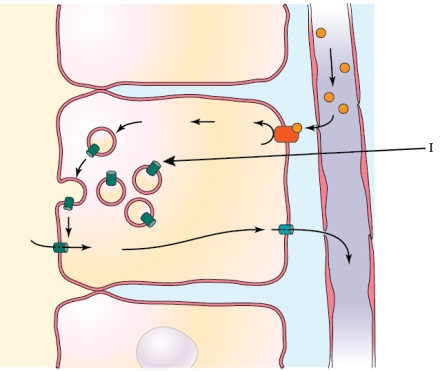 What is the structure labeled by arrow I in the diagram?
What is the structure labeled by arrow I in the diagram?
A) Na+ channel
B) Aquaporin
C) K+ channel
D) Ca2+ channel
 What is the structure labeled by arrow I in the diagram?
What is the structure labeled by arrow I in the diagram?A) Na+ channel
B) Aquaporin
C) K+ channel
D) Ca2+ channel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Refer to the figure shown.
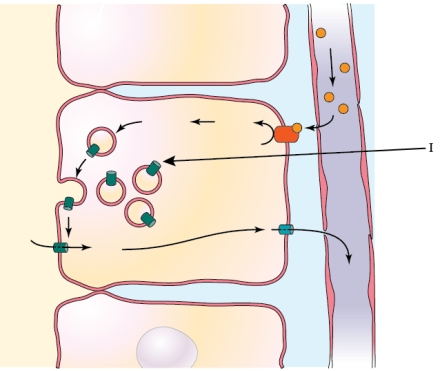 Which hormone is causing the mechanism represented in the diagram to occur?
Which hormone is causing the mechanism represented in the diagram to occur?
A) Aldosterone
B) Atrial natriuretic peptide
C) Angiotensin
D) Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin)
 Which hormone is causing the mechanism represented in the diagram to occur?
Which hormone is causing the mechanism represented in the diagram to occur?A) Aldosterone
B) Atrial natriuretic peptide
C) Angiotensin
D) Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Refer to the figure shown.
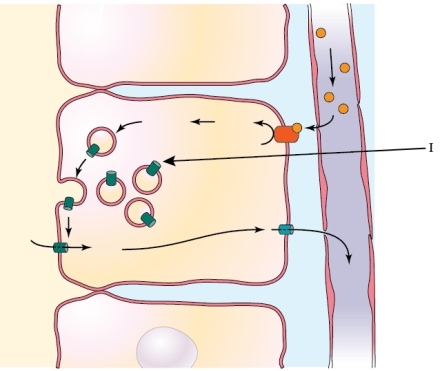 Which statement regarding the mechanism represented in the diagram is false?
Which statement regarding the mechanism represented in the diagram is false?
A) The hormone binds to a receptor
B) A second messenger system acts to shuttle storage vesicles to the membrane.
C) Storage vesicles fuse with the apical membrane.
D) Water moves from the extracellular fluid into the collecting duct.
 Which statement regarding the mechanism represented in the diagram is false?
Which statement regarding the mechanism represented in the diagram is false?A) The hormone binds to a receptor
B) A second messenger system acts to shuttle storage vesicles to the membrane.
C) Storage vesicles fuse with the apical membrane.
D) Water moves from the extracellular fluid into the collecting duct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The juxtaglomerular cells sense
A) low blood pressure in the carotid body and activate renin-angiotensin-aldosterone.
B) high blood pressure in the heart and increase urination.
C) low blood pressure and secrete renin.
D) low blood pressure and secrete angiotensin.
A) low blood pressure in the carotid body and activate renin-angiotensin-aldosterone.
B) high blood pressure in the heart and increase urination.
C) low blood pressure and secrete renin.
D) low blood pressure and secrete angiotensin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which molecule must be present for the direct production of angiotensin II?
A) Renin
B) Angiotensin I
C) Angiotensin-converting enzyme
D) Angiotensinogen
A) Renin
B) Angiotensin I
C) Angiotensin-converting enzyme
D) Angiotensinogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is responsible for secreting paracrines that inhibit renin during high blood pressure?
A) Carotid bodies
B) Macula dense cells
C) Juxtaglomerular cells
D) The atria of the heart
A) Carotid bodies
B) Macula dense cells
C) Juxtaglomerular cells
D) The atria of the heart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following would be categorized as an antagonist to aldosterone?
A) angiotensin
B) renin
C) atrial natriuretic peptide
D) antidiuretic hormone
A) angiotensin
B) renin
C) atrial natriuretic peptide
D) antidiuretic hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which statement regarding vitamin D is false?
A) Inactive vitamin D is also called cholecalciferol.
B) Vitamin D can be obtained only through diet and from vitamin supplements.
C) Cholecalciferol is converted to 25-hydroxycholecalciferol in the liver.
D) In the kidney, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol is converted to 1,25(OH)2D3, the active form of vitamin D.
A) Inactive vitamin D is also called cholecalciferol.
B) Vitamin D can be obtained only through diet and from vitamin supplements.
C) Cholecalciferol is converted to 25-hydroxycholecalciferol in the liver.
D) In the kidney, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol is converted to 1,25(OH)2D3, the active form of vitamin D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which statement about calcium metabolism is true?
A) Chief cells secrete PTH when extracellular Ca2+ is high.
B) C cells secrete calcitonin when extracellular Ca2+ is low.
C) High extracellular Ca2+ stimulates C cells and inhibits chief cells.
D) Vitamin D is converted to its active form when plasma Ca2+ is high.
A) Chief cells secrete PTH when extracellular Ca2+ is high.
B) C cells secrete calcitonin when extracellular Ca2+ is low.
C) High extracellular Ca2+ stimulates C cells and inhibits chief cells.
D) Vitamin D is converted to its active form when plasma Ca2+ is high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which term is not directly related to insect metamorphosis?
A) Ecdysis
B) Bombykol
C) Instars
D) Pupa
A) Ecdysis
B) Bombykol
C) Instars
D) Pupa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which hormone is produced by neurosecretory cells?
A) Ecdysis-triggering hormone
B) Juvenile hormone
C) Ecdysone
D) Prothoracicotropic hormone
A) Ecdysis-triggering hormone
B) Juvenile hormone
C) Ecdysone
D) Prothoracicotropic hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The insect hormone that prevents metamorphosis is
A) ecdysone.
B) prothoracicotropic hormone.
C) terpene.
D) juvenile hormone.
A) ecdysone.
B) prothoracicotropic hormone.
C) terpene.
D) juvenile hormone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How do silk growers take advantage of the knowledge of insect hormones?
A) They remove the corpora allata from silkworms to eliminate the production of juvenile hormone which causes them to pupate. This causes them to reproduce faster, creating more animals that can spin more silk.
B) They spray analog juvenile hormone on silkworms that causes them to pupate and reproduce faster, creating more animals that can spin more silk.
C) They spray analog juvenile hormone on silkworms to prevent them from pupating therefore creating larger larvae that create more silk.
D) They remove the corpora allata from silkworms to eliminate the production of juvenile hormone and prevent them from pupating. This creates larger larvae that create more silk.
A) They remove the corpora allata from silkworms to eliminate the production of juvenile hormone which causes them to pupate. This causes them to reproduce faster, creating more animals that can spin more silk.
B) They spray analog juvenile hormone on silkworms that causes them to pupate and reproduce faster, creating more animals that can spin more silk.
C) They spray analog juvenile hormone on silkworms to prevent them from pupating therefore creating larger larvae that create more silk.
D) They remove the corpora allata from silkworms to eliminate the production of juvenile hormone and prevent them from pupating. This creates larger larvae that create more silk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which one of the following is not a principle of hormonal control?
A) Hormones may interact with each other synergistically, permissively, or antagonistically.
B) Many endocrine controls operate in tightly coordinated ways with neural controls.
C) Many molecules that function as hormones in one context function as different types of chemical signals in different contexts.
D) A hormone in one species typically affects only one physiological system, although it may affect a different physiological system in a different species.
A) Hormones may interact with each other synergistically, permissively, or antagonistically.
B) Many endocrine controls operate in tightly coordinated ways with neural controls.
C) Many molecules that function as hormones in one context function as different types of chemical signals in different contexts.
D) A hormone in one species typically affects only one physiological system, although it may affect a different physiological system in a different species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Describe the two major classes of endocrine cells and how they work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Compare and contrast the synthesis, storage, and release of a peptide hormone such as insulin to those processes in a steroid hormone such as testosterone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the physiological importance of the hypothalamo-hypophysial portal system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Compare and contrast the anterior and posterior pituitary glands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Describe the terms "antagonism" and "synergy" as they relate to hormones, and give examples of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Describe the two output branches as well as the two phases of the mammalian stress response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the mechanism by which chronic stress can negatively affect the immune system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Describe how the kidney acts to conserve water when it senses low blood pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How is vitamin D involved in calcium metabolism in mammals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Name, compare, and contrast the two major types of insect metamorphosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



