Deck 14: Sensory Processes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Sensory Processes
1
Choose the best statement regarding moth audition.
A) Moths hear frequencies similar to what bats hear.
B) Moths are very sensitive to the frequencies of bat cries.
C) Moths hear only frequencies of bat cries.
D) Moths hear a broad range of frequencies including bat cries.
A) Moths hear frequencies similar to what bats hear.
B) Moths are very sensitive to the frequencies of bat cries.
C) Moths hear only frequencies of bat cries.
D) Moths hear a broad range of frequencies including bat cries.
B
2
The conversion of stimulus energy into an electrical signal is known as
A) transference.
B) transduction.
C) an action potential.
D) a graded potential.
A) transference.
B) transduction.
C) an action potential.
D) a graded potential.
B
3
Which receptor uses a metabotropic mechanism of signal transduction?
A) Photoreceptors
B) Vestibular receptors
C) Mechanoreceptors
D) Thermoreceptors
E) Auditory receptors
A) Photoreceptors
B) Vestibular receptors
C) Mechanoreceptors
D) Thermoreceptors
E) Auditory receptors
A
4
"The sensory modality or quality of sensation associated with a stimulus depends solely on which receptor cells are stimulated, rather than on how they are stimulated." This generalization is known as the
A) brain partitioning principle.
B) principle of pathway analysis.
C) principle of labeled lines.
D) principle of sensory organization.
A) brain partitioning principle.
B) principle of pathway analysis.
C) principle of labeled lines.
D) principle of sensory organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which sense is based on indirect, G protein-coupled receptor activation?
A) Vertebrate touch
B) Insect hearing
C) Insect vision
D) Vertebrate hearing
A) Vertebrate touch
B) Insect hearing
C) Insect vision
D) Vertebrate hearing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
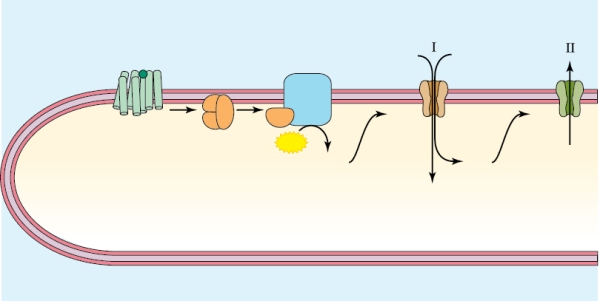
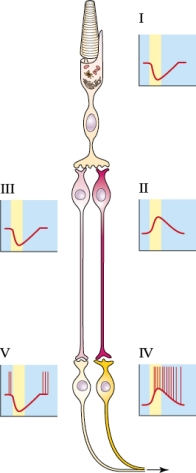
Refer to the figure shown.
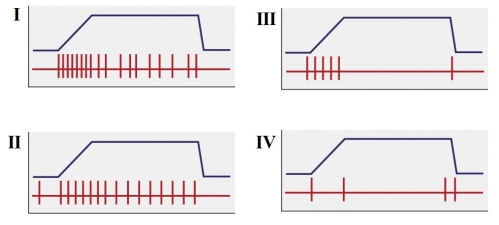 Which panel(s) would be categorized as a phasic receptor?
Which panel(s) would be categorized as a phasic receptor?
A) I
B) IV
C) I and II
D) III and IV
 Which panel(s) would be categorized as a phasic receptor?
Which panel(s) would be categorized as a phasic receptor?A) I
B) IV
C) I and II
D) III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Refer to the figure shown.
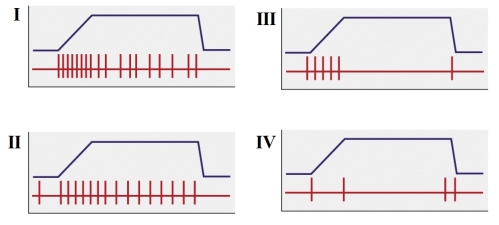 Which panel best represents the action of a Pacinian corpuscle?
Which panel best represents the action of a Pacinian corpuscle?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which panel best represents the action of a Pacinian corpuscle?
Which panel best represents the action of a Pacinian corpuscle?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When contrasting insect and mammalian sensory transduction mechanisms, which sensory modality has a fundamentally different transduction mechanism between the two animal groups?
A) touch
B) hearing
C) smell
D) tasting salt
A) touch
B) hearing
C) smell
D) tasting salt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Choose the correct statement regarding Piezo channels.
A) Piezo2 mutations in humans cause complete lack of touch reception.
B) Experimental removal of the Piezo2 gene in humans reduce touch sensitivity.
C) Experimental removal of the Piezo2 gene in humans abolishes touch sensitivity.
D) Piezo2 mutations in humans reduce touch sensitivity.
A) Piezo2 mutations in humans cause complete lack of touch reception.
B) Experimental removal of the Piezo2 gene in humans reduce touch sensitivity.
C) Experimental removal of the Piezo2 gene in humans abolishes touch sensitivity.
D) Piezo2 mutations in humans reduce touch sensitivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In insects, the most common form of auditory organ is the
A) tympanal organ.
B) statocyst.
C) cochlea.
D) bristle sensillum.
A) tympanal organ.
B) statocyst.
C) cochlea.
D) bristle sensillum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement about bat navigation is true?
A) Bats emit high-frequency sound pulses and detect the echoes reflected by the objects around them.
B) Bats emit ultra-low-frequency sound pulses and detect the echoes reflected by the objects around them.
C) In addition to detecting echoes from sound emissions, bats have keen night vision.
D) Bats navigate by detecting sounds from animals and those reflected by the objects around them.
A) Bats emit high-frequency sound pulses and detect the echoes reflected by the objects around them.
B) Bats emit ultra-low-frequency sound pulses and detect the echoes reflected by the objects around them.
C) In addition to detecting echoes from sound emissions, bats have keen night vision.
D) Bats navigate by detecting sounds from animals and those reflected by the objects around them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A bat is just a few centimeters away from a moth that it is locating and attempting to eat. What is the most likely response from the moth?
A) The nearby bat emits an ultrasonic sound, which stimulate the A1 cells in the moth's tympanic organ. This causes the moth to dive to the ground.
B) The nearby bat emits an ultrasonic sound, which stimulate the A2 cells in the moth's tympanic organ. This causes the moth to dive to the ground.
C) The nearby bat emits an ultrasonic sound, which stimulate the A2 cells in the moth's tympanic organ. This causes the moth to fly away from the source of the sound.
D) The nearby bat emits an ultrasonic sound, which stimulate the A1 cells in the moth's tympanic organ. This causes the moth to fly away from the source of the sound.
A) The nearby bat emits an ultrasonic sound, which stimulate the A1 cells in the moth's tympanic organ. This causes the moth to dive to the ground.
B) The nearby bat emits an ultrasonic sound, which stimulate the A2 cells in the moth's tympanic organ. This causes the moth to dive to the ground.
C) The nearby bat emits an ultrasonic sound, which stimulate the A2 cells in the moth's tympanic organ. This causes the moth to fly away from the source of the sound.
D) The nearby bat emits an ultrasonic sound, which stimulate the A1 cells in the moth's tympanic organ. This causes the moth to fly away from the source of the sound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which statement regarding the vertebrate hair cell is false?
A) The vertebrate hair cell is an epithelial cell.
B) Displacement toward the kinocilium produces a depolarization.
C) Displacement away from the kinocilium produces a hyperpolarization.
D) When displaced enough toward the kinocilium, the hair cell will produce a train of action potentials.
A) The vertebrate hair cell is an epithelial cell.
B) Displacement toward the kinocilium produces a depolarization.
C) Displacement away from the kinocilium produces a hyperpolarization.
D) When displaced enough toward the kinocilium, the hair cell will produce a train of action potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which statement best describes the vertebrate vestibular system?
A) Three semicircular canals detect movement via fluid that stimulates hair cells in the crista ampullaris.
B) A circular canal detects movement via fluid that stimulates the oval window.
C) Four canals, including the cochlea, detect indirect movement of hair cells.
D) The incus, malleus, and stapes detect movement by amplifying sound to the oval window.
A) Three semicircular canals detect movement via fluid that stimulates hair cells in the crista ampullaris.
B) A circular canal detects movement via fluid that stimulates the oval window.
C) Four canals, including the cochlea, detect indirect movement of hair cells.
D) The incus, malleus, and stapes detect movement by amplifying sound to the oval window.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following defines the main transduction process of sound?
A) The hair cell bending
B) The vibration of the ear drum
C) The vibration of the stapes on the oval window
D) Action potentials sent to the brain along the auditory nerve
A) The hair cell bending
B) The vibration of the ear drum
C) The vibration of the stapes on the oval window
D) Action potentials sent to the brain along the auditory nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which statement regarding the basilar membrane is false?
A) It separates the cochlea into an upper chamber and a lower chamber.
B) It is widest at its basal end and narrowest at its apical end.
C) It is stiffer at its basal end and more compliant near its apical end.
D) It responds maximally to high frequency sounds toward its basal end.
A) It separates the cochlea into an upper chamber and a lower chamber.
B) It is widest at its basal end and narrowest at its apical end.
C) It is stiffer at its basal end and more compliant near its apical end.
D) It responds maximally to high frequency sounds toward its basal end.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the ear, low-frequency sounds tend to displace
A) the whole length of the basilar membrane equally.
B) mainly the basal portion (oval window end) of the basilar membrane.
C) mainly the apex portion of the basilar membrane.
D) only the portion of the basilar membrane between the basal portion and the apex.
A) the whole length of the basilar membrane equally.
B) mainly the basal portion (oval window end) of the basilar membrane.
C) mainly the apex portion of the basilar membrane.
D) only the portion of the basilar membrane between the basal portion and the apex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The major source of auditory input to the brain comes from _______ hair cell signals.
A) lateral line
B) semicircular canal
C) inner
D) outer
A) lateral line
B) semicircular canal
C) inner
D) outer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which statement regarding fish taste is true?
A) Fish taste buds are structurally very different compared to mammalian taste buds.
B) Fish do not have taste buds.
C) Fish have taste buds on their mouth and skin.
D) Fish do not have a sense of taste, only smell.
A) Fish taste buds are structurally very different compared to mammalian taste buds.
B) Fish do not have taste buds.
C) Fish have taste buds on their mouth and skin.
D) Fish do not have a sense of taste, only smell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which sense perception depends on a metabotropic mechanism for initial signal transduction?
A) Auditory reception
B) Touch
C) Bitter taste
D) Acceleration
A) Auditory reception
B) Touch
C) Bitter taste
D) Acceleration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the figure shown.
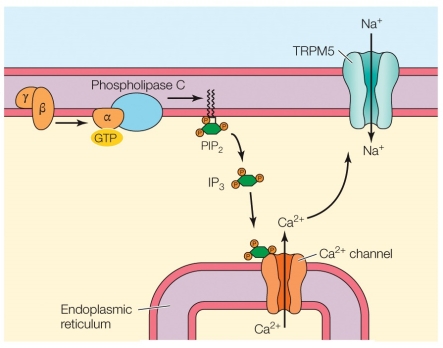 How many different (taste) qualities depend on the mechanism shown in the figure?
How many different (taste) qualities depend on the mechanism shown in the figure?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
 How many different (taste) qualities depend on the mechanism shown in the figure?
How many different (taste) qualities depend on the mechanism shown in the figure?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Refer to the figure shown.
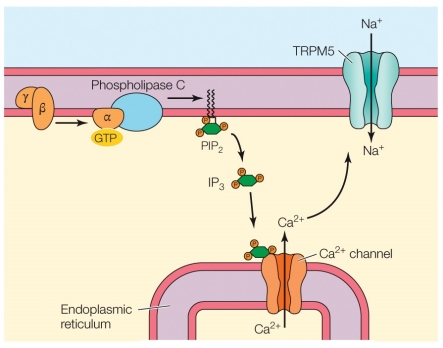 Which taste qualities are represented by the mechanism shown in the figure?
Which taste qualities are represented by the mechanism shown in the figure?
A) Sweet, sour, umami, and bitter
B) Sweet, umami, and bitter
C) Salty, umami, and bitter
D) Umami and bitter
 Which taste qualities are represented by the mechanism shown in the figure?
Which taste qualities are represented by the mechanism shown in the figure?A) Sweet, sour, umami, and bitter
B) Sweet, umami, and bitter
C) Salty, umami, and bitter
D) Umami and bitter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The family of GPCRs that sense bitter compounds is much larger and more disparate in amino acid sequence than those that sense sweet or umami. Why might this be adaptive?
A) Bitter receptors do not have to be as sensitive as those for sweet or umami.
B) The ability to distinguish between many bitter compounds allows the animal to eat the one most agreeable to its digestive system.
C) Bitter compounds are usually toxic, and so the ability to sense a wide variety of them is protective.
D) Bitter compounds usually contain dense calories, which help a species survive and thrive.
A) Bitter receptors do not have to be as sensitive as those for sweet or umami.
B) The ability to distinguish between many bitter compounds allows the animal to eat the one most agreeable to its digestive system.
C) Bitter compounds are usually toxic, and so the ability to sense a wide variety of them is protective.
D) Bitter compounds usually contain dense calories, which help a species survive and thrive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following confers odorant specificity in the Drosophila?
A) olfactory receptor expressing multiple olfactory receptor proteins
B) olfactory receptor expressing single olfactory receptor protein
C) Orco coreceptor expressing multiple olfactory receptor proteins
D) Orco coreceptor expressing single olfactory receptor protein
A) olfactory receptor expressing multiple olfactory receptor proteins
B) olfactory receptor expressing single olfactory receptor protein
C) Orco coreceptor expressing multiple olfactory receptor proteins
D) Orco coreceptor expressing single olfactory receptor protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the figure shown.
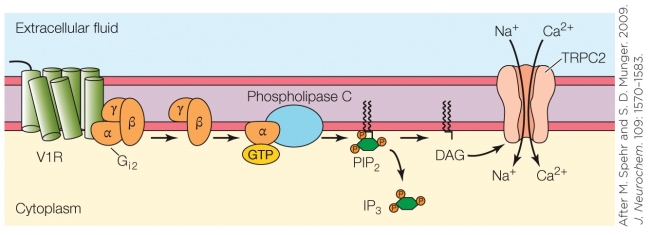 What electrical outcome on the membrane is the end result of the mechanism shown in the figure?
What electrical outcome on the membrane is the end result of the mechanism shown in the figure?
A) An action potential
B) A metabotropic response
C) Depolarization
D) Hyperpolarization
 What electrical outcome on the membrane is the end result of the mechanism shown in the figure?
What electrical outcome on the membrane is the end result of the mechanism shown in the figure?A) An action potential
B) A metabotropic response
C) Depolarization
D) Hyperpolarization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which statement regarding vertebrate olfactory receptor cells is true?
A) Their axons reside in the mucous layer.
B) They have fine, myelinated axons.
C) They undergo continuous turnover (die and are replaced).
D) Their axons are among the largest axons in the nervous system.
A) Their axons reside in the mucous layer.
B) They have fine, myelinated axons.
C) They undergo continuous turnover (die and are replaced).
D) Their axons are among the largest axons in the nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which statement about the mammalian vomeronasal organ is true?
A) It mostly detects pheromones and other chemical signals.
B) It integrates the olfactory information before sending it to the brain.
C) It interacts with the olfactory system to amplify the signal.
D) It detects chemicals from greater distances than olfaction does.
A) It mostly detects pheromones and other chemical signals.
B) It integrates the olfactory information before sending it to the brain.
C) It interacts with the olfactory system to amplify the signal.
D) It detects chemicals from greater distances than olfaction does.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure shown.
 The sensory process shown in the figure is
The sensory process shown in the figure is
A) the bitter taste response.
B) the vomeronasal mechanism.
C) vertebrate olfaction.
D) insect vision.
 The sensory process shown in the figure is
The sensory process shown in the figure isA) the bitter taste response.
B) the vomeronasal mechanism.
C) vertebrate olfaction.
D) insect vision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure shown.
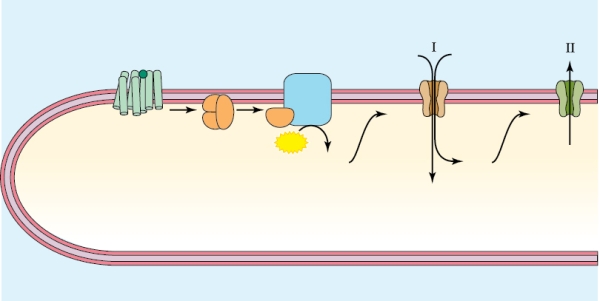 Which key best represents the ion movement shown in the figure?
Which key best represents the ion movement shown in the figure?
A) I = Na+ and Ca2+; II = Cl-
B) I = K+; II = Cl‒
C) I = Na+ and Cl‒; II = Ca2+
D) I = Ca2+; II = K+
 Which key best represents the ion movement shown in the figure?
Which key best represents the ion movement shown in the figure?A) I = Na+ and Ca2+; II = Cl-
B) I = K+; II = Cl‒
C) I = Na+ and Cl‒; II = Ca2+
D) I = Ca2+; II = K+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the figure shown.
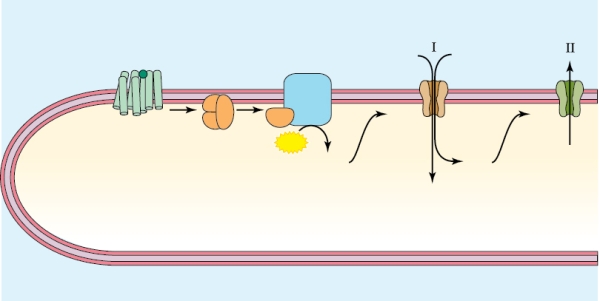 What is the resulting electrical event on the membrane as shown in the figure?
What is the resulting electrical event on the membrane as shown in the figure?
A) Hyperpolarization
B) Depolarization at I, hyperpolarization at II
C) Hyperpolarization at I, depolarization at II
D) Depolarization
 What is the resulting electrical event on the membrane as shown in the figure?
What is the resulting electrical event on the membrane as shown in the figure?A) Hyperpolarization
B) Depolarization at I, hyperpolarization at II
C) Hyperpolarization at I, depolarization at II
D) Depolarization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the mechanism of vertebrate olfaction, a G protein activates the enzyme
A) cGMP phosphodiesterase.
B) phospholipase C.
C) adenylyl cyclase.
D) transducin.
A) cGMP phosphodiesterase.
B) phospholipase C.
C) adenylyl cyclase.
D) transducin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which statement best describes the ion movement on the cilium of the olfactory receptor cell in vertebrate olfaction?
A) Na+ enters the cell and K+ leaves the cell.
B) Cl‒ moves out of the cell.
C) Na+ and Ca2+ enter the cell.
D) Na+ and Ca2+ move into the cell and Cl‒ moves out of the cell.
A) Na+ enters the cell and K+ leaves the cell.
B) Cl‒ moves out of the cell.
C) Na+ and Ca2+ enter the cell.
D) Na+ and Ca2+ move into the cell and Cl‒ moves out of the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is the most common evolved feature of eyes?
A) A lens
B) A retina
C) Similar genes regulating eye development
D) A rhodopsin-based photoreceptor cell
A) A lens
B) A retina
C) Similar genes regulating eye development
D) A rhodopsin-based photoreceptor cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For terrestrial vertebrates, the greatest amount of refraction occurs
A) at the interface between the air and the cornea.
B) in the aqueous humor.
C) in the lens.
D) in the vitreous humor.
A) at the interface between the air and the cornea.
B) in the aqueous humor.
C) in the lens.
D) in the vitreous humor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The molecule that absorbs light is called a
A) photoreceptor.
B) photochemical.
C) rhabdomere.
D) photopigment.
A) photoreceptor.
B) photochemical.
C) rhabdomere.
D) photopigment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which statement regarding the transduction mechanism in vision is true of both vertebrates and invertebrates?
A) G proteins activate cGMP phosphodiesterase.
B) Light triggers the conversion of cis retinal to trans retinal.
C) Cation channels are opened and Na+ enters the photoreceptor membrane.
D) Second messengers IP3 and DAG are synthesized.
A) G proteins activate cGMP phosphodiesterase.
B) Light triggers the conversion of cis retinal to trans retinal.
C) Cation channels are opened and Na+ enters the photoreceptor membrane.
D) Second messengers IP3 and DAG are synthesized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Phototransduction in Drosophila takes place on the membrane of the
A) microvilli of the retinular cell's rhabdomere.
B) ommatidium of the compound eye's retinular cell.
C) outer segment of the rod.
D) ommatidium's rhabdomere.
A) microvilli of the retinular cell's rhabdomere.
B) ommatidium of the compound eye's retinular cell.
C) outer segment of the rod.
D) ommatidium's rhabdomere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the figure shown.
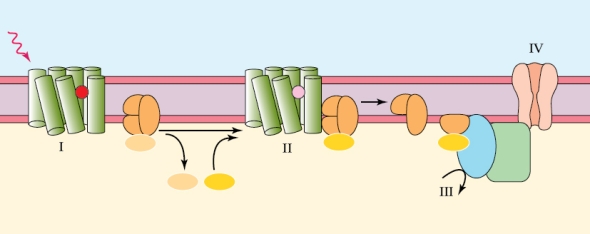 The animals that make use of the sensory mechanism shown in this figure are all
The animals that make use of the sensory mechanism shown in this figure are all
A) arthropods.
B) arthropods with compound eyes.
C) insects.
D) vertebrates.
 The animals that make use of the sensory mechanism shown in this figure are all
The animals that make use of the sensory mechanism shown in this figure are allA) arthropods.
B) arthropods with compound eyes.
C) insects.
D) vertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the figure shown.
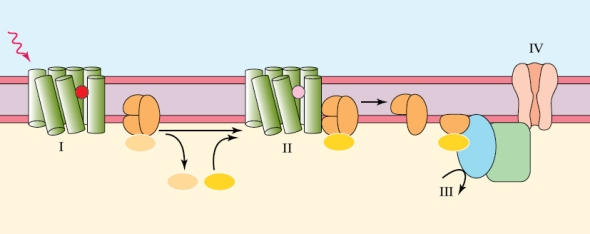 Which letter in the figure corresponds to activated opsin?
Which letter in the figure corresponds to activated opsin?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which letter in the figure corresponds to activated opsin?
Which letter in the figure corresponds to activated opsin?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the figure shown.
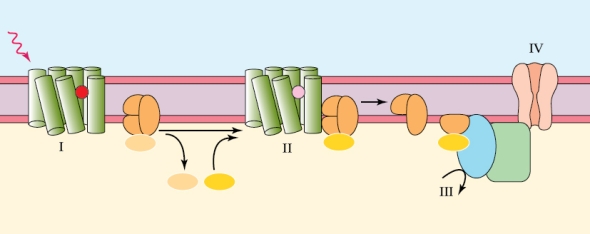 What the mechanism is occurring at IV in the figure?
What the mechanism is occurring at IV in the figure?
A) Second messengers have led to the opening of a K+ channel.
B) Second messengers have led to the opening of a Ca2+ channel.
C) Second messengers have led to the opening of a cation channel, causing depolarization.
D) G proteins open a sodium channel.
 What the mechanism is occurring at IV in the figure?
What the mechanism is occurring at IV in the figure?A) Second messengers have led to the opening of a K+ channel.
B) Second messengers have led to the opening of a Ca2+ channel.
C) Second messengers have led to the opening of a cation channel, causing depolarization.
D) G proteins open a sodium channel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Refer to the figure shown.
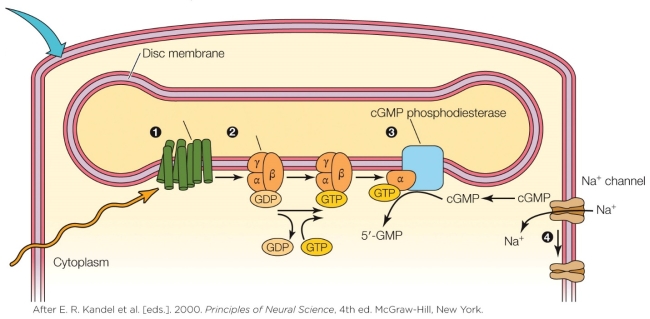 The sensory mechanism depicted in the figure is that of
The sensory mechanism depicted in the figure is that of
A) vertebrate vision.
B) invertebrate vision.
C) vertebrate sweet taste reception.
D) vertebrate olfaction.
 The sensory mechanism depicted in the figure is that of
The sensory mechanism depicted in the figure is that ofA) vertebrate vision.
B) invertebrate vision.
C) vertebrate sweet taste reception.
D) vertebrate olfaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the figure shown.
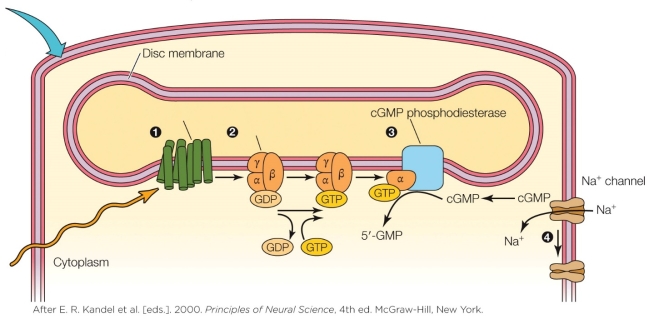 Which number in the figure corresponds to the location where an aldehyde is isomerized?
Which number in the figure corresponds to the location where an aldehyde is isomerized?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
 Which number in the figure corresponds to the location where an aldehyde is isomerized?
Which number in the figure corresponds to the location where an aldehyde is isomerized?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to the figure shown.
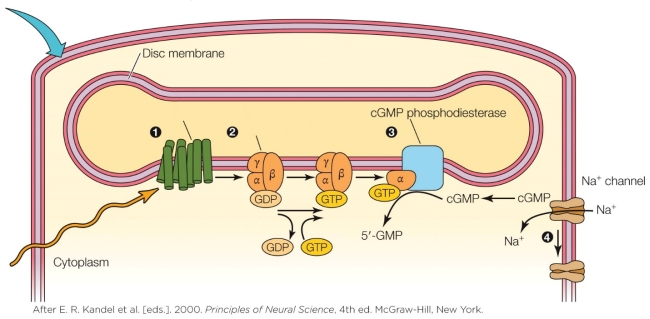 Which statement regarding the regeneration of rhodopsin in vertebrates is false?
Which statement regarding the regeneration of rhodopsin in vertebrates is false?
A) All-trans retinol is re-isomerized back to all-cis retinol.
B) Regeneration of rhodopsin is enzymatic.
C) All-trans retinal becomes unbound from the opsin protein.
D) An added photon is necessary to change all-trans retinal back to all-cis retinal.
 Which statement regarding the regeneration of rhodopsin in vertebrates is false?
Which statement regarding the regeneration of rhodopsin in vertebrates is false?A) All-trans retinol is re-isomerized back to all-cis retinol.
B) Regeneration of rhodopsin is enzymatic.
C) All-trans retinal becomes unbound from the opsin protein.
D) An added photon is necessary to change all-trans retinal back to all-cis retinal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What would occur at location number 4 in the figure in the absence of light?
A) cGMP would detach itself from the sodium channels, causing them to close.
B) cGMP attached to the sodium channels would cause them to open.
C) Darkness would inactivate rhodopsin by isomerizing retinal from cis to trans.
D) Darkness would inactivate rhodopsin by isomerizing retinal from trans to cis.
A) cGMP would detach itself from the sodium channels, causing them to close.
B) cGMP attached to the sodium channels would cause them to open.
C) Darkness would inactivate rhodopsin by isomerizing retinal from cis to trans.
D) Darkness would inactivate rhodopsin by isomerizing retinal from trans to cis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What happens in the vertebrate rod in the absence of light?
A) Rhodopsin is activated.
B) cGMP is converted back to 5ʹ-GMP.
C) cGMP dissociates from Na+ channels.
D) cGMP opens Na+ channels.
A) Rhodopsin is activated.
B) cGMP is converted back to 5ʹ-GMP.
C) cGMP dissociates from Na+ channels.
D) cGMP opens Na+ channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which statement best describes the vertebrate mechanism that operates on the outer segment cell membrane of the rod in the presence of light?
A) cGMP detaches from the sodium channels, causing them to close.
B) cGMP that is attached to the sodium channels causes them to open.
C) Light activates rhodopsin by isomerizing retinal from cis to trans.
D) Light activates rhodopsin by isomerizing retinal from trans to cis.
A) cGMP detaches from the sodium channels, causing them to close.
B) cGMP that is attached to the sodium channels causes them to open.
C) Light activates rhodopsin by isomerizing retinal from cis to trans.
D) Light activates rhodopsin by isomerizing retinal from trans to cis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the dark, a cone membrane of a fish will be
A) relatively depolarized.
B) relatively hyperpolarized.
C) at zero mV.
D) photochemically fluctuating.
A) relatively depolarized.
B) relatively hyperpolarized.
C) at zero mV.
D) photochemically fluctuating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Refer to the figure shown.
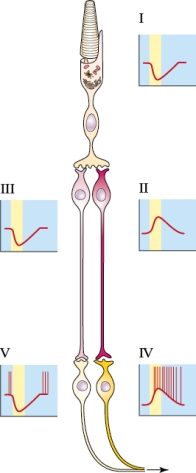 The light in the figure is entering
The light in the figure is entering
A) from the bottom.
B) from the top.
C) from the right.
D) by diffusion from all directions.
 The light in the figure is entering
The light in the figure is enteringA) from the bottom.
B) from the top.
C) from the right.
D) by diffusion from all directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the figure shown.
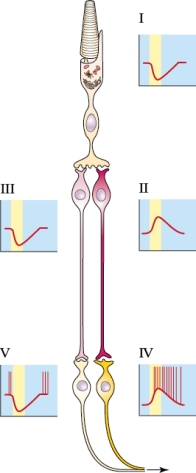 Which letter in the figure best represents only a depolarizing graded potential in the presence of light.
Which letter in the figure best represents only a depolarizing graded potential in the presence of light.
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which letter in the figure best represents only a depolarizing graded potential in the presence of light.
Which letter in the figure best represents only a depolarizing graded potential in the presence of light.A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the figure shown.
 According to the letters in the figure, light inducing (activating) an on-center response would proceed through which of the following sequences?
According to the letters in the figure, light inducing (activating) an on-center response would proceed through which of the following sequences?
A) I → II → III → V → IV
B) I → II → IV
C) I → III → V
D) I → II → V
 According to the letters in the figure, light inducing (activating) an on-center response would proceed through which of the following sequences?
According to the letters in the figure, light inducing (activating) an on-center response would proceed through which of the following sequences?A) I → II → III → V → IV
B) I → II → IV
C) I → III → V
D) I → II → V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
_______ cells are the output of the retina.
A) Amacrine
B) Horizontal
C) Bipolar
D) Ganglion
A) Amacrine
B) Horizontal
C) Bipolar
D) Ganglion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Refer to the figure shown.
 The figure shows the activity of _______ cells.
The figure shows the activity of _______ cells.
A) bipolar
B) horizontal
C) cone
D) ganglion
 The figure shows the activity of _______ cells.
The figure shows the activity of _______ cells.A) bipolar
B) horizontal
C) cone
D) ganglion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Refer to the figure shown.
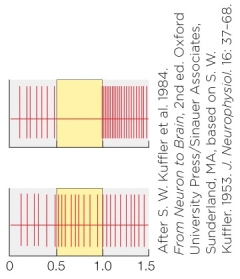 If the top panel (activity trace) of the figure is the result of light shining in the center of the receptive field, which of the following is true?
If the top panel (activity trace) of the figure is the result of light shining in the center of the receptive field, which of the following is true?
A) The entire receptive field has been inhibited.
B) Central illumination has increased activity.
C) This is likely an off-center cell response.
D) This is likely an on-center cell response.
 If the top panel (activity trace) of the figure is the result of light shining in the center of the receptive field, which of the following is true?
If the top panel (activity trace) of the figure is the result of light shining in the center of the receptive field, which of the following is true?A) The entire receptive field has been inhibited.
B) Central illumination has increased activity.
C) This is likely an off-center cell response.
D) This is likely an on-center cell response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the figure shown.
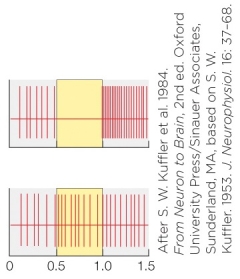 The bottom panel of the figure depicts _______ illumination of an _______ cell.
The bottom panel of the figure depicts _______ illumination of an _______ cell.
A) central; on-center
B) diffuse; on-center
C) peripheral; on-center
D) central; off-center
 The bottom panel of the figure depicts _______ illumination of an _______ cell.
The bottom panel of the figure depicts _______ illumination of an _______ cell.A) central; on-center
B) diffuse; on-center
C) peripheral; on-center
D) central; off-center

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The area of the retina within which the membrane potential of a particular neuron can be influenced by light is called the
A) on-center area.
B) straight-through area.
C) outer plexiform layer.
D) receptive field.
A) on-center area.
B) straight-through area.
C) outer plexiform layer.
D) receptive field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Choose the best explanation for mammals not being able to process the color reddish green.
A) Mammals are actually able to process the color reddish green.
B) Red-green opponent cells lack center-surround antagonism.
C) Red-green opponent ganglion cells have concentric antagonistic receptive fields but are also color-opponent.
D) Green cone cells are inhibited by red light.
A) Mammals are actually able to process the color reddish green.
B) Red-green opponent cells lack center-surround antagonism.
C) Red-green opponent ganglion cells have concentric antagonistic receptive fields but are also color-opponent.
D) Green cone cells are inhibited by red light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Bees have ultraviolet light sensitivity because
A) of a photoreceptors with maximum sensitivity to 340 nm wavelengths.
B) of a photoreceptors with maximum sensitivity to 440 nm wavelengths.
C) of a photoreceptors with maximum sensitivity to 560 nm wavelengths.
D) of the aggregate response of the photoreceptors with maximum sensitivities at 340 nm, 440 nm, and 560 nm wavelengths.
A) of a photoreceptors with maximum sensitivity to 340 nm wavelengths.
B) of a photoreceptors with maximum sensitivity to 440 nm wavelengths.
C) of a photoreceptors with maximum sensitivity to 560 nm wavelengths.
D) of the aggregate response of the photoreceptors with maximum sensitivities at 340 nm, 440 nm, and 560 nm wavelengths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Explain the principle of labeled lines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What are the four different ways a sensory receptor cell can be classified?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How does the transduction mechanism work in a stretch (mechano-) receptor?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe the process of adaptation as it relates to mechanoreceptors in mammalian skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How could the statocyst of a lobster be manipulated experimentally to cause the lobster to behave as if Earth's gravity were the opposite of its true gravity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain how the hair cells transduce sound intensity and frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A blowfly can taste with its feet. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How would you test whether an olfactory receptor cell responds to an odor?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast vertebrate and invertebrate transduction in photoreception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Explain how hyperpolarization of a vertebrate cone will eventually be transduced into a train of action potentials sent to the brain via the optic nerve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



