Deck 12: Neurons
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Neurons
1
The cablelike processes that convey electrical signals rapidly and faithfully from place to place in the body are called
A) cell bodies
B) dendrites
C) action potentials
D) axons
A) cell bodies
B) dendrites
C) action potentials
D) axons
C
2
Initiation of the action potential usually occurs _______ of the neuron.
A) in the cell body
B) on the dendrites
C) at the axon initial segment
D) on the axon
A) in the cell body
B) on the dendrites
C) at the axon initial segment
D) on the axon
C
3
Which statement about an animal's nervous system is true?
A) Neurotransmitter is released throughout the body via the blood.
B) Signal transmission rate is relatively slow.
C) Neurons form highly discrete lines of communication.
D) Action potential signals degrade over distance.
A) Neurotransmitter is released throughout the body via the blood.
B) Signal transmission rate is relatively slow.
C) Neurons form highly discrete lines of communication.
D) Action potential signals degrade over distance.
C
4
For a hormone to elicit a specific response from a cell, the cell must possess
A) a synapse.
B) a cell body.
C) dendrites specific to the hormone.
D) receptor proteins specific to the hormone.
A) a synapse.
B) a cell body.
C) dendrites specific to the hormone.
D) receptor proteins specific to the hormone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Compared to neural signaling, endocrine signaling is
A) faster and broadcast more discretely.
B) faster and broadcast more widely.
C) slower and broadcast more widely.
D) slower and broadcast more discretely.
A) faster and broadcast more discretely.
B) faster and broadcast more widely.
C) slower and broadcast more widely.
D) slower and broadcast more discretely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement about glial cells is true?
A) They integrate cell membrane potentials to enhance or inhibit action potentials.
B) They decrease the velocity of nerve-impulse propagation.
C) They help supply metabolic substrates to neurons.
D) They act as metabolic intermediaries between epithelial cells and neurons.
A) They integrate cell membrane potentials to enhance or inhibit action potentials.
B) They decrease the velocity of nerve-impulse propagation.
C) They help supply metabolic substrates to neurons.
D) They act as metabolic intermediaries between epithelial cells and neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement about the startle response of the cockroach is true?
A) Vibrations of hairs generate nerve impulses in sensory neurons.
B) Sound waves or air currents synapse with the filiform hairs.
C) Sensory neurons synapse with and excite the dorsal hollow spinal cord.
D) At the metathoracic ganglion, the interneurons synaptically inhibit leg motor neurons.
A) Vibrations of hairs generate nerve impulses in sensory neurons.
B) Sound waves or air currents synapse with the filiform hairs.
C) Sensory neurons synapse with and excite the dorsal hollow spinal cord.
D) At the metathoracic ganglion, the interneurons synaptically inhibit leg motor neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The separation of positive and negative charges constitutes
A) resistance.
B) an electric current.
C) a voltage.
D) capacitance.
A) resistance.
B) an electric current.
C) a voltage.
D) capacitance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which characteristic is not a factor in the Nernst Equation?
A) Capacitance
B) Temperature
C) The valence of the ion species
D) The ion concentrations on the two sides of the membrane
A) Capacitance
B) Temperature
C) The valence of the ion species
D) The ion concentrations on the two sides of the membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
According to the Nernst equation, which change will depolarize Vm, the membrane potential?
A) A decrease in temperature
B) An increase in the valence of the ion species involved
C) A decrease in the concentration of anions inside the membrane
D) A decrease in the electromotive force of the ion
A) A decrease in temperature
B) An increase in the valence of the ion species involved
C) A decrease in the concentration of anions inside the membrane
D) A decrease in the electromotive force of the ion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose there is a small patch of membrane from a mammalian muscle fiber, with a small volume of adjacent cytoplasm and extracellular fluid. Assume that the membrane is most permeable to K+. There are 110,000 cations and 110,000 anions in each fluid compartment. The membrane potential results from
A) only six pairs of ions sitting on the membrane.
B) the thousands of ions sitting on the membrane.
C) the overall difference intra- and extra cellular ion concentrations in the volume of cell.
D) movement of ions across the cell membrane.
A) only six pairs of ions sitting on the membrane.
B) the thousands of ions sitting on the membrane.
C) the overall difference intra- and extra cellular ion concentrations in the volume of cell.
D) movement of ions across the cell membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose there is a small patch of membrane from a mammalian muscle fiber, with a small volume of adjacent cytoplasm and extracellular fluid. Assume that the membrane is most permeable to K+. There are 110,000 cations and 110,000 anions in each fluid compartment. In the center of the cell
A) there would be a slight negative charge.
B) there would be a strong negative charge.
C) the overall charge neutrality would be maintained independently of the membrane potential.
D) there would be a slight positive charge.
A) there would be a slight negative charge.
B) there would be a strong negative charge.
C) the overall charge neutrality would be maintained independently of the membrane potential.
D) there would be a slight positive charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to the Goldman equation, the contribution of each ion to the membrane potential depends most on
A) its size.
B) its membrane permeability.
C) its activation energy.
D) the resting membrane potential.
A) its size.
B) its membrane permeability.
C) its activation energy.
D) the resting membrane potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a cell, the difference in ion concentration between the intracellular and extracellular fluids results from
A) active ion transport.
B) passive diffusion of ions.
C) bulk movements of intracellular and extracellular fluids.
D) both active ion transport and passive diffusion of ions.
A) active ion transport.
B) passive diffusion of ions.
C) bulk movements of intracellular and extracellular fluids.
D) both active ion transport and passive diffusion of ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which statement regarding the ions in intracellular and extracellular fluids in a standard animal cell is true?
A) Na+ leaks into the cell rapidly because its electrochemical gradient is large.
B) K+ leaks out of the cell slowly because the electrochemical gradient is small.
C) Cl- leaks into the cell rapidly because its electrochemical gradient is large.
D) Negatively charged proteins leak out of the cell slowly because their electrochemical gradient is small.
A) Na+ leaks into the cell rapidly because its electrochemical gradient is large.
B) K+ leaks out of the cell slowly because the electrochemical gradient is small.
C) Cl- leaks into the cell rapidly because its electrochemical gradient is large.
D) Negatively charged proteins leak out of the cell slowly because their electrochemical gradient is small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which statement about membrane capacitance is true?
A) It is in series with membrane resistance.
B) In a cell, the membrane separates only similarly charged ions.
C) It is measured in ohms.
D) It is a function of the permeability of the membrane.
A) It is in series with membrane resistance.
B) In a cell, the membrane separates only similarly charged ions.
C) It is measured in ohms.
D) It is a function of the permeability of the membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the figure shown.
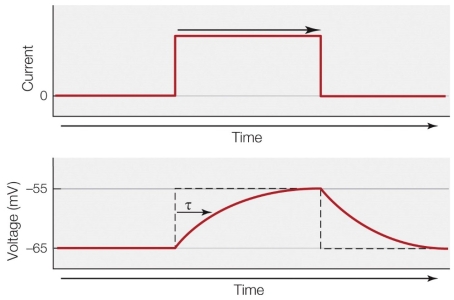 What is occurring at the membrane?
What is occurring at the membrane?
A) Depolarization
B) Hyperpolarization
C) Increase in resistance
D) Decrease in capacitance
 What is occurring at the membrane?
What is occurring at the membrane?A) Depolarization
B) Hyperpolarization
C) Increase in resistance
D) Decrease in capacitance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Refer to the figure shown.
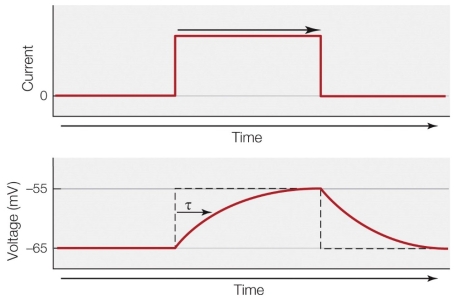 In the lower panel, the difference between the dashed line and the solid red line is due to
In the lower panel, the difference between the dashed line and the solid red line is due to
A) membrane resistance.
B) the fact that one represents a depolarization and the other represents a hyperpolarization.
C) the capacitive properties of the membrane.
D) the difference in applied voltage.
 In the lower panel, the difference between the dashed line and the solid red line is due to
In the lower panel, the difference between the dashed line and the solid red line is due toA) membrane resistance.
B) the fact that one represents a depolarization and the other represents a hyperpolarization.
C) the capacitive properties of the membrane.
D) the difference in applied voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which variable does not contribute to the passive electrical properties of a cell?
A) Membrane resistance
B) Membrane capacitance
C) The resting membrane current
D) The time constant
A) Membrane resistance
B) Membrane capacitance
C) The resting membrane current
D) The time constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the figure shown.
 In the figure, the _______ decreases with distance.
In the figure, the _______ decreases with distance.
A) graded potential
B) action potential
C) membrane current
D) membrane capacitance
 In the figure, the _______ decreases with distance.
In the figure, the _______ decreases with distance.A) graded potential
B) action potential
C) membrane current
D) membrane capacitance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
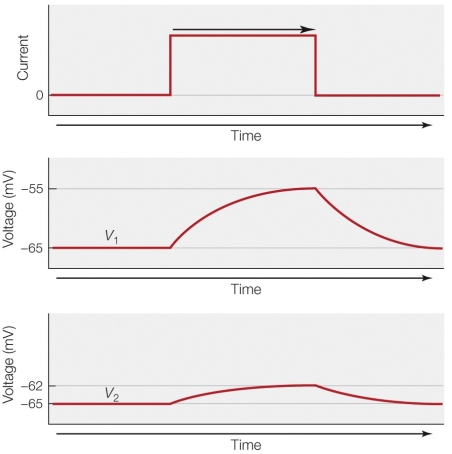
21
Refer to the figure shown.
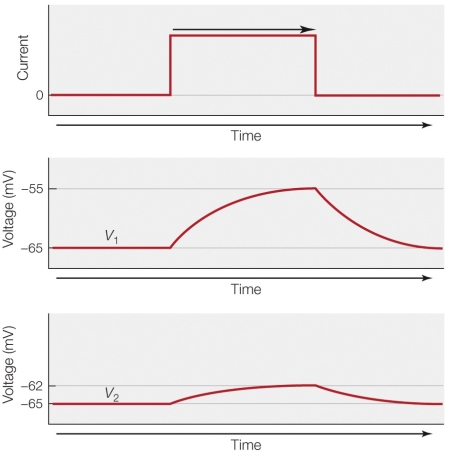 Which statement offers the best explanation for the difference between the middle panel and the lower panel?
Which statement offers the best explanation for the difference between the middle panel and the lower panel?
A) The membrane in the lower panel is producing a lower current.
B) There is a lower resistance in the lower panel at the point where voltage is measured.
C) There is a greater capacitance in the lower panel at the point where voltage is measured.
D) The membrane voltage measured in the lower panel is farther away from the current pulse.
 Which statement offers the best explanation for the difference between the middle panel and the lower panel?
Which statement offers the best explanation for the difference between the middle panel and the lower panel?A) The membrane in the lower panel is producing a lower current.
B) There is a lower resistance in the lower panel at the point where voltage is measured.
C) There is a greater capacitance in the lower panel at the point where voltage is measured.
D) The membrane voltage measured in the lower panel is farther away from the current pulse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Refer to the figure shown.
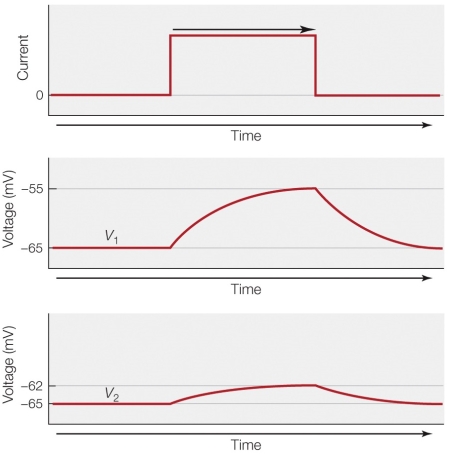 The properties shown in the figure can be measured in
The properties shown in the figure can be measured in
A) neurons.
B) neurons and pacemaker cells.
C) muscle cells.
D) neurons, pacemaker cells, and muscle cells
 The properties shown in the figure can be measured in
The properties shown in the figure can be measured inA) neurons.
B) neurons and pacemaker cells.
C) muscle cells.
D) neurons, pacemaker cells, and muscle cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which structure is most responsible for the all-or-none property of the action potential?
A) Myelin
B) Voltage-gated K+ channels
C) Voltage-gated Na+ channels
D) Leakage of K+ channels
A) Myelin
B) Voltage-gated K+ channels
C) Voltage-gated Na+ channels
D) Leakage of K+ channels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Refer to the figure shown.
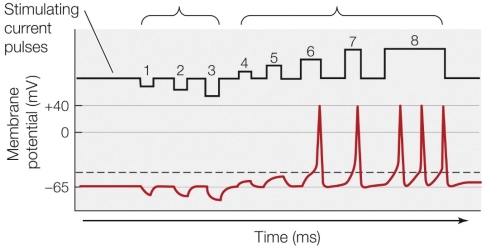 How many separate current pulses cause the membrane potential to reach the threshold?
How many separate current pulses cause the membrane potential to reach the threshold?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
 How many separate current pulses cause the membrane potential to reach the threshold?
How many separate current pulses cause the membrane potential to reach the threshold?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the figure shown.
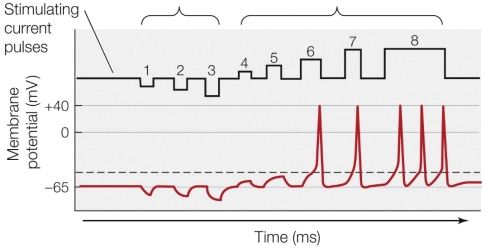 What would likely occur if stimulus 3 and 6 were performed simultaneously?
What would likely occur if stimulus 3 and 6 were performed simultaneously?
A) An action potential would likely occur.
B) An action potential would likely not occur.
C) Multiple action potentials would likely occur.
D) The threshold voltage would likely decrease.
 What would likely occur if stimulus 3 and 6 were performed simultaneously?
What would likely occur if stimulus 3 and 6 were performed simultaneously?A) An action potential would likely occur.
B) An action potential would likely not occur.
C) Multiple action potentials would likely occur.
D) The threshold voltage would likely decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure shown.
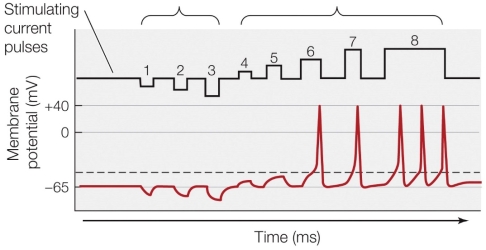 If stimulating current pulse 9 (not shown) was both stronger and longer than stimulating current pulse 8, then
If stimulating current pulse 9 (not shown) was both stronger and longer than stimulating current pulse 8, then
A) the train of action potentials would continue for the length of the stimulating current.
B) action potentials would increase in amplitude.
C) action potentials would first increase in frequency and then decrease.
D) the line at stimulus 9 would look exactly same as the line at stimulus 8.
 If stimulating current pulse 9 (not shown) was both stronger and longer than stimulating current pulse 8, then
If stimulating current pulse 9 (not shown) was both stronger and longer than stimulating current pulse 8, thenA) the train of action potentials would continue for the length of the stimulating current.
B) action potentials would increase in amplitude.
C) action potentials would first increase in frequency and then decrease.
D) the line at stimulus 9 would look exactly same as the line at stimulus 8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For an axon at resting membrane potential, the K+ leak channel is _______, the voltage-gated Na+ channel is _______, and the voltage-gated K+ channel is _______.
A) open; inactivated; closed
B) closed; inactivated; closed
C) open; inactivated; open
D) open; closed; closed
A) open; inactivated; closed
B) closed; inactivated; closed
C) open; inactivated; open
D) open; closed; closed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
During the falling phase of an action potential, the K+ leak channel on the axon is _______, the voltage-gated Na+ channel is _______, and the voltage-gated K+ channel is _______.
A) open; inactivated; closed
B) closed; inactivated; closed
C) open; inactivated; open
D) open; closed; closed
A) open; inactivated; closed
B) closed; inactivated; closed
C) open; inactivated; open
D) open; closed; closed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which statement about a voltage clamp of a neuron at 0 mV is true?
A) Once clamped, the membrane depolarizes then returns to resting potential.
B) Voltage-gated potassium channels open.
C) Apart from the initial current shift from the clamp, no other current is produced.
D) Voltage-gated sodium channels close
A) Once clamped, the membrane depolarizes then returns to resting potential.
B) Voltage-gated potassium channels open.
C) Apart from the initial current shift from the clamp, no other current is produced.
D) Voltage-gated sodium channels close

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which statement regarding the structure of the voltage-gated Na+ channels is false?
A) P loops mediate ion selectivity.
B) It has four domains with extensive sequence homology.
C) The channel protein changes its primary structure in response to membrane depolarization.
D) A cytoplasmic loop is thought to inactivate the channel by blocking the opening.
A) P loops mediate ion selectivity.
B) It has four domains with extensive sequence homology.
C) The channel protein changes its primary structure in response to membrane depolarization.
D) A cytoplasmic loop is thought to inactivate the channel by blocking the opening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the figure shown.
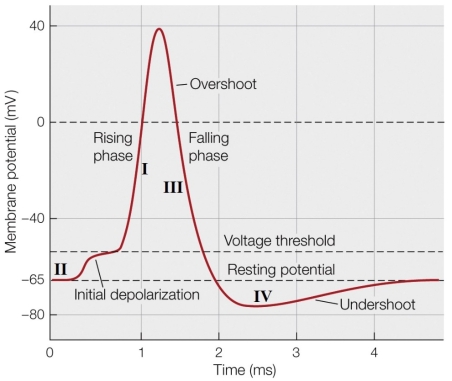 Which arrow best represents the point where the voltage-gated sodium channels are inactivated?
Which arrow best represents the point where the voltage-gated sodium channels are inactivated?
A) I
B) III
C) IV
D) III and IV
 Which arrow best represents the point where the voltage-gated sodium channels are inactivated?
Which arrow best represents the point where the voltage-gated sodium channels are inactivated?A) I
B) III
C) IV
D) III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Refer to the figure shown.
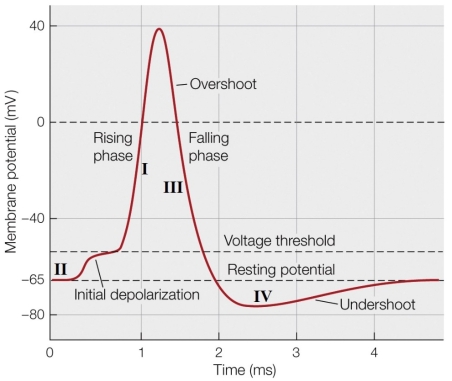 _______ channels are responsible for the undershoot at point D of the figure.
_______ channels are responsible for the undershoot at point D of the figure.
A) Voltage-gated sodium
B) Voltage-gated potassium
C) Ligand-gated potassium
D) Voltage-gated calcium
 _______ channels are responsible for the undershoot at point D of the figure.
_______ channels are responsible for the undershoot at point D of the figure.A) Voltage-gated sodium
B) Voltage-gated potassium
C) Ligand-gated potassium
D) Voltage-gated calcium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the figure shown.
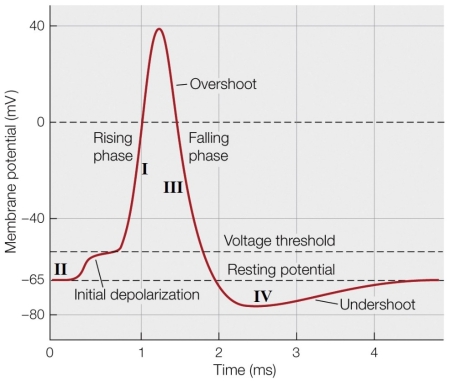 What occurs when the membrane is clamped at -100 mV?
What occurs when the membrane is clamped at -100 mV?
A) Voltage-gated ion channels behave in a similar manner as in the diagram.
B) Voltage-gated ion channels do not open at all.
C) There is a brief shift in ions and then a flat current at -100 mV.
D) Only ligand-gated channels work at this point.
 What occurs when the membrane is clamped at -100 mV?
What occurs when the membrane is clamped at -100 mV?A) Voltage-gated ion channels behave in a similar manner as in the diagram.
B) Voltage-gated ion channels do not open at all.
C) There is a brief shift in ions and then a flat current at -100 mV.
D) Only ligand-gated channels work at this point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which arrow best represents the point where permeability to sodium is the highest?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the figure shown.
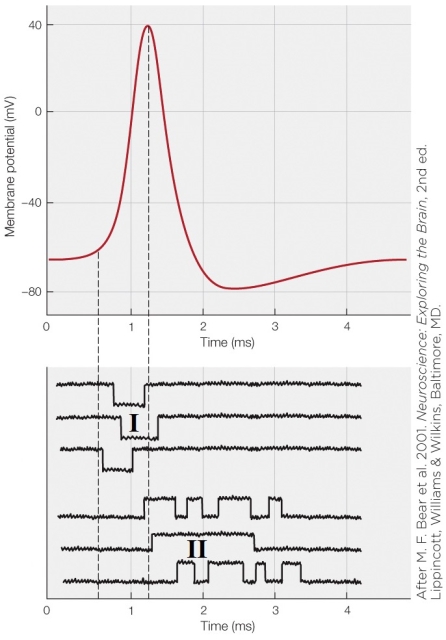 Which technique was used to collect the data in the bottom panel?
Which technique was used to collect the data in the bottom panel?
A) Patch-clamp
B) Voltage-clamp
C) Current-clamp
D) Hodgkin clamp
 Which technique was used to collect the data in the bottom panel?
Which technique was used to collect the data in the bottom panel?A) Patch-clamp
B) Voltage-clamp
C) Current-clamp
D) Hodgkin clamp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the figure shown.
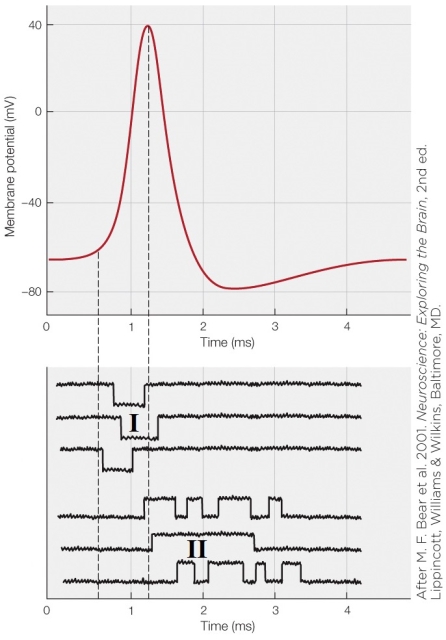 On the figure, I represents _______ currents through voltage-gated _______ channels.
On the figure, I represents _______ currents through voltage-gated _______ channels.
A) outward; Na+
B) inward; Na+
C) outward; K+
D) inward; K+
 On the figure, I represents _______ currents through voltage-gated _______ channels.
On the figure, I represents _______ currents through voltage-gated _______ channels.A) outward; Na+
B) inward; Na+
C) outward; K+
D) inward; K+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the figure shown.
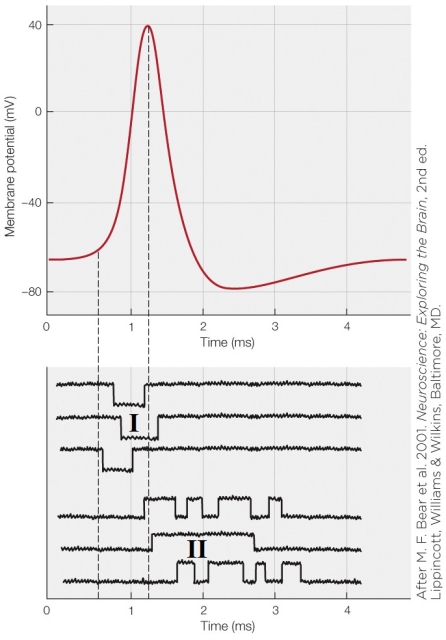 Why do the channels at II on the figure stay open longer than those at I?
Why do the channels at II on the figure stay open longer than those at I?
A) Channels at I are responding to a depolarization, whereas channels at II are responding to a hyperpolarization.
B) The depolarization is a faster event compared to the repolarization.
C) Channels at I are less sensitive to voltage compared to channels at II.
D) Channels at I become inactivated, whereas channels at II close due to membrane voltage.
 Why do the channels at II on the figure stay open longer than those at I?
Why do the channels at II on the figure stay open longer than those at I?A) Channels at I are responding to a depolarization, whereas channels at II are responding to a hyperpolarization.
B) The depolarization is a faster event compared to the repolarization.
C) Channels at I are less sensitive to voltage compared to channels at II.
D) Channels at I become inactivated, whereas channels at II close due to membrane voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the figure shown.
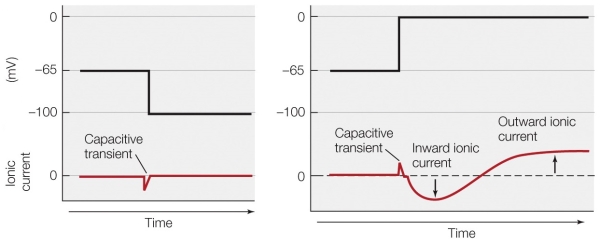 Which technique was used to collect the data shown in the figure?
Which technique was used to collect the data shown in the figure?
A) Patch-clamp
B) Hodgkin clamp
C) Current-clamp
D) Voltage-clamp
 Which technique was used to collect the data shown in the figure?
Which technique was used to collect the data shown in the figure?A) Patch-clamp
B) Hodgkin clamp
C) Current-clamp
D) Voltage-clamp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the figure shown.
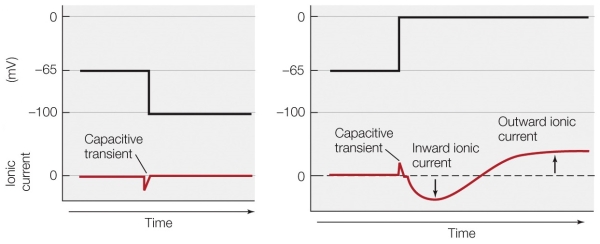 The treatment difference between the membranes shown in the graphs is that the membrane on the left is being _______, while the membrane on the right is being _______.
The treatment difference between the membranes shown in the graphs is that the membrane on the left is being _______, while the membrane on the right is being _______.
A) depolarized; depolarized in Na+-free seawater
B) hyperpolarized; hyperpolarized in an isoionic Na+ solution
C) hyperpolarized; depolarized
D) depolarized; hyperpolarized
 The treatment difference between the membranes shown in the graphs is that the membrane on the left is being _______, while the membrane on the right is being _______.
The treatment difference between the membranes shown in the graphs is that the membrane on the left is being _______, while the membrane on the right is being _______.A) depolarized; depolarized in Na+-free seawater
B) hyperpolarized; hyperpolarized in an isoionic Na+ solution
C) hyperpolarized; depolarized
D) depolarized; hyperpolarized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the figure shown.
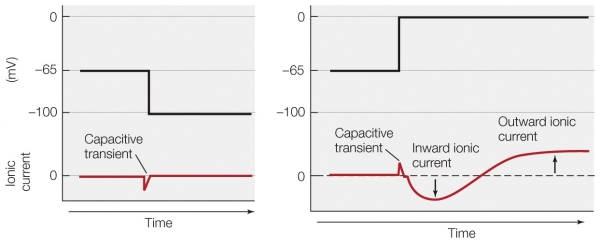 How would the trace on the right look if the neuron was soaking in tetraethylammonium (TEA)?
How would the trace on the right look if the neuron was soaking in tetraethylammonium (TEA)?
A) The inward ionic current would disappear.
B) The outward ionic current would disappear.
C) The trace would look exactly like the trace in the left panel.
D) The outward ionic current would be amplified.
 How would the trace on the right look if the neuron was soaking in tetraethylammonium (TEA)?
How would the trace on the right look if the neuron was soaking in tetraethylammonium (TEA)?A) The inward ionic current would disappear.
B) The outward ionic current would disappear.
C) The trace would look exactly like the trace in the left panel.
D) The outward ionic current would be amplified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A spiking neuron and a nonspiking neuron share which characteristic?
A) High concentration of voltage-gated Na+ channels at the axon hillock
B) A graded potential down the entire length of the axon
C) An action potential down the entire length of the axon
D) Neurotransmitter secretion based on a change in membrane potential
A) High concentration of voltage-gated Na+ channels at the axon hillock
B) A graded potential down the entire length of the axon
C) An action potential down the entire length of the axon
D) Neurotransmitter secretion based on a change in membrane potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How do nonspiking neurons function even though their depolarization signal significantly degrades with distance?
A) Voltage-gated Na+ channels are replaced by ligand-gated Na+ channels.
B) These neurons are very short, so there is no major signal decrement.
C) There are sufficient numbers of voltage-gated Na+ channels to convey the signal without major decrement.
D) Voltage-gated K+ channels compensate for the lack of voltage-gated Na+ channels.
A) Voltage-gated Na+ channels are replaced by ligand-gated Na+ channels.
B) These neurons are very short, so there is no major signal decrement.
C) There are sufficient numbers of voltage-gated Na+ channels to convey the signal without major decrement.
D) Voltage-gated K+ channels compensate for the lack of voltage-gated Na+ channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to the figure shown.
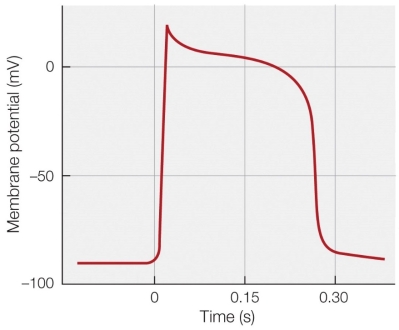 The figure depicts a
The figure depicts a
A) neuronal action potential.
B) cardiac action potential.
C) pacemaker potential.
D) graded potential.
 The figure depicts a
The figure depicts aA) neuronal action potential.
B) cardiac action potential.
C) pacemaker potential.
D) graded potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the figure shown.
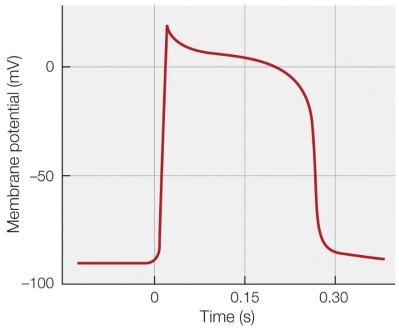 What is the best explanation for the plateau shown in the figure?
What is the best explanation for the plateau shown in the figure?
A) Voltage-gated Na+ channels remain open.
B) Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels remain open.
C) Voltage-gated K+ channels close.
D) Leaky K+ channels remain open.
 What is the best explanation for the plateau shown in the figure?
What is the best explanation for the plateau shown in the figure?A) Voltage-gated Na+ channels remain open.
B) Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels remain open.
C) Voltage-gated K+ channels close.
D) Leaky K+ channels remain open.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the figure shown.
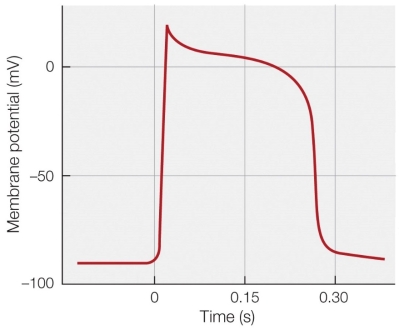 Which statement about ion permeability as shown in the figure is true?
Which statement about ion permeability as shown in the figure is true?
A) K+ permeability is at its lowest very close to the membrane potential peak.
B) K+ permeability is at its highest very close to the membrane potential peak.
C) Na+ permeability is at its lowest very close to the membrane potential peak.
D) Na+ permeability is at its highest very close to the membrane potential peak.
 Which statement about ion permeability as shown in the figure is true?
Which statement about ion permeability as shown in the figure is true?A) K+ permeability is at its lowest very close to the membrane potential peak.
B) K+ permeability is at its highest very close to the membrane potential peak.
C) Na+ permeability is at its lowest very close to the membrane potential peak.
D) Na+ permeability is at its highest very close to the membrane potential peak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The absolute refractory period of the action potential is best explained by
A) inactivated voltage-gated sodium channels.
B) closed voltage-gated sodium channels.
C) open slow calcium channels.
D) inactivated voltage-gated potassium channels.
A) inactivated voltage-gated sodium channels.
B) closed voltage-gated sodium channels.
C) open slow calcium channels.
D) inactivated voltage-gated potassium channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which statement about a local circuit in an axon is false?
A) Ions flow in intracellular fluid, carrying current to more distant parts of the membrane.
B) At the membrane, the ion movements change the distribution of charges on the membrane capacitance.
C) An ionic current completes the local circuit as cations move toward the locus of the action potential and anions move away.
D) Anions migrate into the membrane interior.
A) Ions flow in intracellular fluid, carrying current to more distant parts of the membrane.
B) At the membrane, the ion movements change the distribution of charges on the membrane capacitance.
C) An ionic current completes the local circuit as cations move toward the locus of the action potential and anions move away.
D) Anions migrate into the membrane interior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
_______ prevents bidirectional propagation of action potentials.
A) The inactivation of Na+ channels
B) A decrease in membrane resistance
C) Myelination
D) The K+ channel
A) The inactivation of Na+ channels
B) A decrease in membrane resistance
C) Myelination
D) The K+ channel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Conduction velocity shows _______ axon diameter.
A) a proportional relationship to
B) a proportional relationship to the square root of
C) an exponential relationship to
D) either a proportional relationship to, or a proportional relationship to the square root of
A) a proportional relationship to
B) a proportional relationship to the square root of
C) an exponential relationship to
D) either a proportional relationship to, or a proportional relationship to the square root of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Considering neurons in living systems, which variable affects conduction velocity the most?
A) Myelination
B) Temperature
C) Length
D) Diameter
A) Myelination
B) Temperature
C) Length
D) Diameter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Myelination by Schwann cells increases the velocity of action potential propagation by
A) increasing the resistance and decreasing the capacitance, allowing the action potential to "jump" over the myelinated area.
B) decreasing the resistance and increasing the capacitance, allowing the action potential to "jump" over the myelinated area.
C) increasing the resistance and increasing the capacitance, allowing the action potential to "jump" over the myelinated area.
D) increasing the diameter of the neuron.
A) increasing the resistance and decreasing the capacitance, allowing the action potential to "jump" over the myelinated area.
B) decreasing the resistance and increasing the capacitance, allowing the action potential to "jump" over the myelinated area.
C) increasing the resistance and increasing the capacitance, allowing the action potential to "jump" over the myelinated area.
D) increasing the diameter of the neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What are glial cells and how do they aid in the function of the nervous system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Describe the startle response in the cockroach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Compare and contrast current and voltage with respect to the cell membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Since the bulk solutions that make up the intracellular and extracellular fluids maintain charge neutrality, how does the cell produce membrane potentials?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Explain in mechanistic terms how the action potential is an all-or-none phenomenon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Compare and contrast the techniques of patch clamping and voltage clamping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What are the similarities and differences among the channels in the voltage-gated channel superfamily?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Explain in mechanistic terms why the action potential can travel a great distance along an axon without degrading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



