Deck 11: Food, Energy, and Temperature at Work: The Lives of Mammals in Frigid Places
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Food, Energy, and Temperature at Work: The Lives of Mammals in Frigid Places
1
The biggest threat to a newborn reindeer's life upon birth is
A) its lack of camouflage.
B) the immediate risk of predation.
C) the significant temperature drop.
D) its lack of being able to move.
A) its lack of camouflage.
B) the immediate risk of predation.
C) the significant temperature drop.
D) its lack of being able to move.
C
2
In winter, reindeer have low energy costs because they
A) increase their heart rate.
B) change their behavior by constantly moving to warm up.
C) maintain different temperatures in different body parts.
D) hide in caves where the temperature is warmer.
A) increase their heart rate.
B) change their behavior by constantly moving to warm up.
C) maintain different temperatures in different body parts.
D) hide in caves where the temperature is warmer.
C
3
According to the experiment done by Nilssen et al. (1984), the resting metabolic rate in adult reindeer during winter
A) increases dramatically as the air temperature changes from -40°C to -20°C.
B) decreases significantly as the air temperature changes from 20°C to 40°C.
C) remains about the same as the air temperature changes from 0°C to 10°C.
D) decreases drastically as the air temperature changes from 0°C to 10°C.
A) increases dramatically as the air temperature changes from -40°C to -20°C.
B) decreases significantly as the air temperature changes from 20°C to 40°C.
C) remains about the same as the air temperature changes from 0°C to 10°C.
D) decreases drastically as the air temperature changes from 0°C to 10°C.
C
4
Oleic acid is _______ and contains _______ double bond(s).
A) monounsaturated; 1
B) monounsaturated; 2
C) polyunsaturated; 1
D) polyunsaturated; 2
A) monounsaturated; 1
B) monounsaturated; 2
C) polyunsaturated; 1
D) polyunsaturated; 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Fatty acids isolated from the distal limb of a reindeer would consist of
A) unsaturated fatty acids only.
B) some saturated fatty acids and some unsaturated fatty acids.
C) fatty acids that aggregate to form triglycerides.
D) more unsaturated than saturated fatty acids.
A) unsaturated fatty acids only.
B) some saturated fatty acids and some unsaturated fatty acids.
C) fatty acids that aggregate to form triglycerides.
D) more unsaturated than saturated fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement regarding microbes in reindeer rumen is false?
A) Microbes that digest fibers are less prevalent in summer communities than winter communities.
B) Microbes that digest cellulose are less prevalent in winter communities than summer communities.
C) Microbes that digest proteins are more prevalent in summer communities than winter communities.
D) Microbes that digest starch are more prevalent in summer communities than winter communities.
A) Microbes that digest fibers are less prevalent in summer communities than winter communities.
B) Microbes that digest cellulose are less prevalent in winter communities than summer communities.
C) Microbes that digest proteins are more prevalent in summer communities than winter communities.
D) Microbes that digest starch are more prevalent in summer communities than winter communities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In response to seasonal diets, the microbial community in reindeer will preferentially breakdown _______ in the winter.
A) chitin
B) fiber
C) protein
D) starch
A) chitin
B) fiber
C) protein
D) starch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Refer to the figure shown.
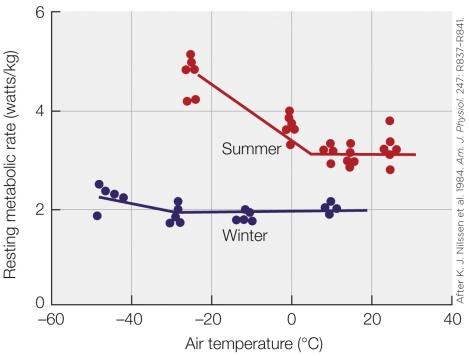 What is this figure showing?
What is this figure showing?
A) Maximum metabolic rate at various temperatures in summer-acclimatized and winter-acclimatized reindeer
B) Resting metabolic rate at various temperatures in summer-acclimatized and winter-acclimatized reindeer
C) Maximum metabolic rate at various temperatures in a northern species and southern species of reindeer
D) Resting metabolic rate at various temperatures in a northern species and southern species of reindeer
 What is this figure showing?
What is this figure showing?A) Maximum metabolic rate at various temperatures in summer-acclimatized and winter-acclimatized reindeer
B) Resting metabolic rate at various temperatures in summer-acclimatized and winter-acclimatized reindeer
C) Maximum metabolic rate at various temperatures in a northern species and southern species of reindeer
D) Resting metabolic rate at various temperatures in a northern species and southern species of reindeer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Refer to the figure shown.
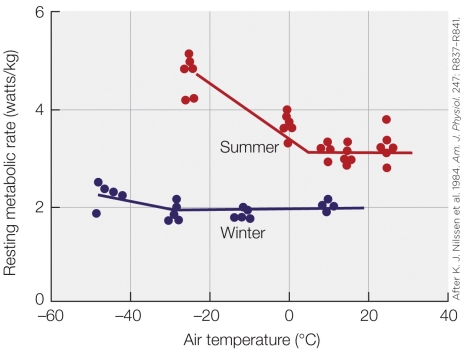 According to the figure, which animal is saving the most energy?
According to the figure, which animal is saving the most energy?
A) Summer-acclimatized reindeer at 10°C
B) Summer-acclimatized reindeer at -30°C
C) Winter-acclimatized reindeer at 10°C
D) Winter-acclimatized reindeer at -30°C
 According to the figure, which animal is saving the most energy?
According to the figure, which animal is saving the most energy?A) Summer-acclimatized reindeer at 10°C
B) Summer-acclimatized reindeer at -30°C
C) Winter-acclimatized reindeer at 10°C
D) Winter-acclimatized reindeer at -30°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to the figure shown.
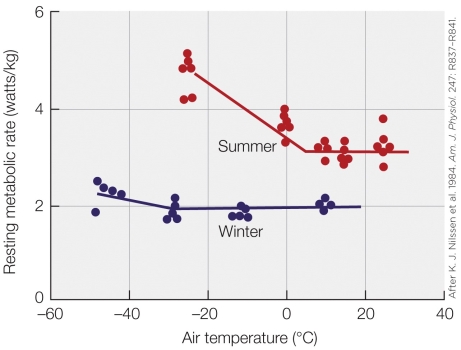 If animals in both groups of animals were exposed to progressively higher air temperatures than shown, and data collection from the experiment continued, what results would you expect to see?
If animals in both groups of animals were exposed to progressively higher air temperatures than shown, and data collection from the experiment continued, what results would you expect to see?
A) Both metabolic rates would remain flat.
B) Both metabolic rates would decrease, however, the summer-acclimatized reindeer would decrease first.
C) Both metabolic rates would increase, however, the winter-acclimatized reindeer would increase first.
D) Only the summer-acclimatized metabolic rates would decrease.
 If animals in both groups of animals were exposed to progressively higher air temperatures than shown, and data collection from the experiment continued, what results would you expect to see?
If animals in both groups of animals were exposed to progressively higher air temperatures than shown, and data collection from the experiment continued, what results would you expect to see?A) Both metabolic rates would remain flat.
B) Both metabolic rates would decrease, however, the summer-acclimatized reindeer would decrease first.
C) Both metabolic rates would increase, however, the winter-acclimatized reindeer would increase first.
D) Only the summer-acclimatized metabolic rates would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which animal has the highest mass-specific metabolic rate?
A) Summer-acclimatized reindeer at 10°C
B) Summer-acclimatized reindeer at -30°C
C) Winter-acclimatized reindeer at 10°C
D) Winter-acclimatized reindeer at -30°C
A) Summer-acclimatized reindeer at 10°C
B) Summer-acclimatized reindeer at -30°C
C) Winter-acclimatized reindeer at 10°C
D) Winter-acclimatized reindeer at -30°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Reindeer have low energy costs in cold environments because of their
A) skin.
B) pelage.
C) hypodermis.
D) antlers.
A) skin.
B) pelage.
C) hypodermis.
D) antlers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In winter, reindeer _______ is _______ thick.
A) fur; 3-4 cm
B) fur; 1-2 cm
C) skin; 3-4 cm
D) skin; 1-2 cm
A) fur; 3-4 cm
B) fur; 1-2 cm
C) skin; 3-4 cm
D) skin; 1-2 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
As the ambient temperature drops below zero, a newborn reindeer's resting metabolic rate
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) stays the same.
D) decreases first and then levels off.
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) stays the same.
D) decreases first and then levels off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a newborn reindeer's maximum rate of metabolic heat production is 10 watts/kg, its resting metabolic rate is _______ watts/kg.
A) 20
B) 10
C) 5
D) 15
A) 20
B) 10
C) 5
D) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which protein is found in brown fat?
A) UCP1
B) UCP2
C) UCP1 and UCP2
D) UCP1 and UCP3
A) UCP1
B) UCP2
C) UCP1 and UCP2
D) UCP1 and UCP3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which hormone was used to test for brown-fat function in newborn reindeer?
A) Thyroxine
B) Epinephrine
C) Cortisol
D) Testosterone
A) Thyroxine
B) Epinephrine
C) Cortisol
D) Testosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which marker is used to test for the presence of brown fat?
A) UCP1
B) Lactate dehydrogenase
C) UCP2
D) Hexokinase
A) UCP1
B) Lactate dehydrogenase
C) UCP2
D) Hexokinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In newborn humans, brown fat concentration is
A) high and remains high throughout growth.
B) low and remains low throughout growth.
C) high and declines as growth occurs.
D) low and increases as growth occurs.
A) high and remains high throughout growth.
B) low and remains low throughout growth.
C) high and declines as growth occurs.
D) low and increases as growth occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If you were to do an immunocytochemistry experiment on a newborn reindeer, a one-month-old reindeer, and a two-month-old reindeer to test for the presence of brown fat, your results would show a _______ amount of brown fat on the _______ compared to the _______-month old.
A) higher; newborn; one
B) lower; newborn; one
C) lower; newborn; two
D) higher; one-month-old; two
A) higher; newborn; one
B) lower; newborn; one
C) lower; newborn; two
D) higher; one-month-old; two

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The elevated rate of oxygen consumption response to norepinephrine in newborn reindeer has declined by _______ of age.
A) one week
B) one month
C) two months
D) one year
A) one week
B) one month
C) two months
D) one year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The major role of brown fat is to
A) warm the body by acting as insulation.
B) provide an energy source for muscle movement by storing lots of triglycerides.
C) warm the body by nonshivering mechanisms.
D) provide a source of fat for phospholipid synthesis.
A) warm the body by acting as insulation.
B) provide an energy source for muscle movement by storing lots of triglycerides.
C) warm the body by nonshivering mechanisms.
D) provide a source of fat for phospholipid synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If an adult animal had a lot of brown fat,
A) its metabolic rate would be higher at rest compared to an animal of the same size that does not have a lot of brown fat.
B) its metabolic rate would be lower during exercise compared to an animal of the same size that does not have a lot of brown fat.
C) it would facilitate the storage of high-energy triglycerides.
D) the metabolism of its brown fat cells would increase during exercise due to the release of cortisol.
A) its metabolic rate would be higher at rest compared to an animal of the same size that does not have a lot of brown fat.
B) its metabolic rate would be lower during exercise compared to an animal of the same size that does not have a lot of brown fat.
C) it would facilitate the storage of high-energy triglycerides.
D) the metabolism of its brown fat cells would increase during exercise due to the release of cortisol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which would have more brown fat, a lamb born in Palm Desert or one born in Alaska?
A) The lamb born in Alaska
B) The lamb born in Palm Desert
C) Both lambs will have an equal amount of brown fat
D) Neither; brown fat is not produced in sheep
A) The lamb born in Alaska
B) The lamb born in Palm Desert
C) Both lambs will have an equal amount of brown fat
D) Neither; brown fat is not produced in sheep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which newborn animal does not have brown fat?
A) Reindeer
B) Mice
C) Lamb
D) Piglet
A) Reindeer
B) Mice
C) Lamb
D) Piglet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Studies on domestic pigs have shown that the UCP1 gene is
A) duplicated.
B) mutated during the birthing process.
C) mutated by a deletion of 2 exons.
D) mutated by a deletion of 2 introns.
A) duplicated.
B) mutated during the birthing process.
C) mutated by a deletion of 2 exons.
D) mutated by a deletion of 2 introns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How do newborn piglets stay warm?
A) Very thick fur
B) Non-shivering thermogenesis
C) Shivering thermogenesis
D) Very thick layer of blubber
A) Very thick fur
B) Non-shivering thermogenesis
C) Shivering thermogenesis
D) Very thick layer of blubber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure shown.
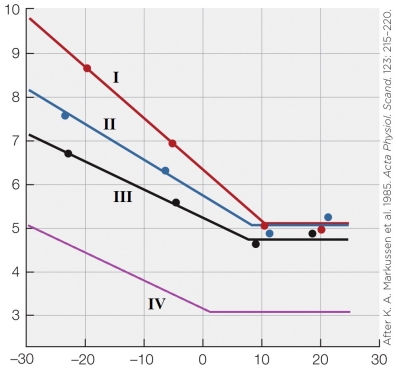 What does the figure show?
What does the figure show?
A) Changes in fur thickness as a function of temperature in four different species
B) Changes in metabolic rate as a function of temperature in different seasons
C) Changes in nonshivering thermogenesis as a function of temperature in different aged animals
D) Changes in metabolic rate as a function of temperature in different aged animals
 What does the figure show?
What does the figure show?A) Changes in fur thickness as a function of temperature in four different species
B) Changes in metabolic rate as a function of temperature in different seasons
C) Changes in nonshivering thermogenesis as a function of temperature in different aged animals
D) Changes in metabolic rate as a function of temperature in different aged animals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure shown.
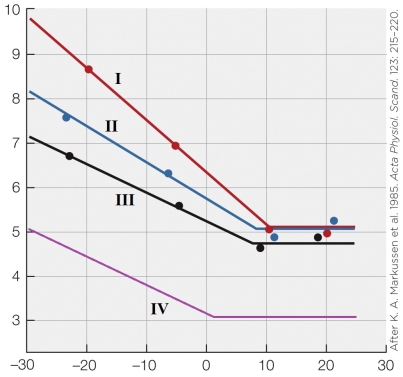 Which line most closely approximates an adult animal in the summer season?
Which line most closely approximates an adult animal in the summer season?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which line most closely approximates an adult animal in the summer season?
Which line most closely approximates an adult animal in the summer season?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Lambs born to shorn mothers _______ at birth compared to lambs born to unshorn mothers.
A) shiver more
B) engage in exercise more
C) have more brown fat
D) have less brown fat
A) shiver more
B) engage in exercise more
C) have more brown fat
D) have less brown fat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If near-term sheep fetuses with normal blood circulation are cooled inside the uteruses of their mothers,
A) brown fat is upregulated.
B) the fetus shivers.
C) fetal metabolic rate increases.
D) nothing happens.
A) brown fat is upregulated.
B) the fetus shivers.
C) fetal metabolic rate increases.
D) nothing happens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
One of the negative consequences to reindeer of rain falling in Arctic areas instead of snow is
A) rain is warmer than snow.
B) rain is more difficult to migrate through than snow.
C) rain freezes on the ground and ices in food plants.
D) rain freezes on the ground and compromises migration.
A) rain is warmer than snow.
B) rain is more difficult to migrate through than snow.
C) rain freezes on the ground and ices in food plants.
D) rain freezes on the ground and compromises migration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which animal will have the greatest amount of brown fat, relative to its body, at birth?
A) Lamb
B) Piglet
C) Mouse
D) Rat
A) Lamb
B) Piglet
C) Mouse
D) Rat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which will favor nonshivering thermoregulation at birth, a reindeer or a mouse?
A) The reindeer, because it is a larger mammal.
B) Both mice and reindeer use nonshivering thermogenesis at birth.
C) The mouse, because it is a small mammal.
D) The mouse, because it has to avoid predators.
A) The reindeer, because it is a larger mammal.
B) Both mice and reindeer use nonshivering thermogenesis at birth.
C) The mouse, because it is a small mammal.
D) The mouse, because it has to avoid predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which mammal would be most likely to maintain some brown fat as an adult?
A) Mouse
B) Beaver
C) Dog
D) Reindeer
A) Mouse
B) Beaver
C) Dog
D) Reindeer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which statement about white-footed mice newborns is false?
A) They are born in a highly protective habitat.
B) They can fully thermoregulate in isolation.
C) They do not have any fur covering their bodies.
D) They can keep warm by shivering in secluded underground burrows.
A) They are born in a highly protective habitat.
B) They can fully thermoregulate in isolation.
C) They do not have any fur covering their bodies.
D) They can keep warm by shivering in secluded underground burrows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is an advantage for small mammals, such as lemmings, in the winter?
A) They can escape the cold by huddling together.
B) They can thermoregulate to lower their core temperature when ambient temperatures are -30°C.
C) They can escape the cold by living under the snow.
D) They can keep warm because they grow a very thick pelage.
A) They can escape the cold by huddling together.
B) They can thermoregulate to lower their core temperature when ambient temperatures are -30°C.
C) They can escape the cold by living under the snow.
D) They can keep warm because they grow a very thick pelage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The single greatest option large-bodied mammals have to beat the cold environment is
A) migration.
B) daily torpor.
C) hibernation.
D) growing fur.
A) migration.
B) daily torpor.
C) hibernation.
D) growing fur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which animal is most likely to have the advantage of migration to a warmer region as winter approaches?
A) Adult white footed mouse
B) Lemming
C) Alpine marmot
D) Bighorn sheep
A) Adult white footed mouse
B) Lemming
C) Alpine marmot
D) Bighorn sheep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Based on the relationship of metabolic rate and body weight, an animal that weighs _______ kg as an adult is most likely to hibernate.
A) 4
B) 9
C) 10
D) 20
A) 4
B) 9
C) 10
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which animal has the lowest weight-specific metabolic rate?
A) Nonhibernating mouse
B) Small reindeer
C) Bear
D) Elephant
A) Nonhibernating mouse
B) Small reindeer
C) Bear
D) Elephant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An animal that weighs _______ will have the lowest weight-specific metabolic rate.
A) 100 g
B) 1000 g
C) 10 kg
D) 100 kg
A) 100 g
B) 1000 g
C) 10 kg
D) 100 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Physiologists have always pondered the relationship of body size to the evolution of hibernation. Based on evolutionary theory, an animal of that weighs _______ kg will have the least energy savings in hibernation.
A) 400
B) 300
C) 200
D) 100
A) 400
B) 300
C) 200
D) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which animal will have the highest weight-specific metabolic rate during hibernation?
A) Mouse
B) Marmot
C) Bear
D) All animals listed will have the same mass-specific metabolic rate during hibernation.
A) Mouse
B) Marmot
C) Bear
D) All animals listed will have the same mass-specific metabolic rate during hibernation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which hibernating animal will have the highest weight-specific metabolic rate in the summer?
A) Mouse
B) Marmot
C) Bear
D) All animals listed will have the same mass-specific metabolic rate in the summer.
A) Mouse
B) Marmot
C) Bear
D) All animals listed will have the same mass-specific metabolic rate in the summer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which animal does not hibernate?
A) Arctic ground squirrel
B) Reindeer
C) Alpine marmot
D) Hoary bat
A) Arctic ground squirrel
B) Reindeer
C) Alpine marmot
D) Hoary bat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Permafrost is
A) soil that thaws in the summer.
B) soil that never freezes.
C) soil that never melts throughout the year.
D) frost that never melts, (e.g., icebergs).
A) soil that thaws in the summer.
B) soil that never freezes.
C) soil that never melts throughout the year.
D) frost that never melts, (e.g., icebergs).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Ground squirrels that live in the Arctic Circle cannot burrow deeper than _______ m.
A) 0.1
B) 0.5
C) 0.8
D) 1
A) 0.1
B) 0.5
C) 0.8
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
During winter in the Arctic Circle, the temperature inside a ground squirrel hibernacula could reach as low as
A) -25°C.
B) -20°C.
C) -10°C.
D) 10°C.
A) -25°C.
B) -20°C.
C) -10°C.
D) 10°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The fat stored in animals prior to hibernation is in the form of
A) fatty acids.
B) glycerol.
C) triacylglycerols.
D) phospholipids.
A) fatty acids.
B) glycerol.
C) triacylglycerols.
D) phospholipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is most likely the cue for animals to begin to store nutrients in preparation for hibernation?
A) Changes in Earth's magnetic field
B) Decrease in length of daylight in the fall
C) Change in temperature in the spring
D) Change in temperature in the fall
A) Changes in Earth's magnetic field
B) Decrease in length of daylight in the fall
C) Change in temperature in the spring
D) Change in temperature in the fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Researchers have shown that animals that consume a diet rich in _______ can tolerate the lowest body temperature without being aroused from hibernation.
A) carbohydrates
B) protein
C) saturated fats
D) unsaturated fats
A) carbohydrates
B) protein
C) saturated fats
D) unsaturated fats

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When experimental animals are fed different diets and their subsequent hibernation times are measured, the animals that hibernate the most effectively are animals that were fed a _______ diet.
A) starchy
B) polyunsaturated fatty acid
C) mixed 75% saturated and 25% unsaturated fat
D) protein
A) starchy
B) polyunsaturated fatty acid
C) mixed 75% saturated and 25% unsaturated fat
D) protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When experimental animals are fed different diets and their body temperature is monitored during subsequent hibernation, the animals that tolerate the lowest body temperature without arousal are the animals that were fed a
A) carbohydrate-rich diet.
B) polyunsaturated fatty acids diet.
C) mixed diet of 65% saturated and 35% unsaturated fat.
D) protein diet.
A) carbohydrate-rich diet.
B) polyunsaturated fatty acids diet.
C) mixed diet of 65% saturated and 35% unsaturated fat.
D) protein diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When experimental animals are fed different diets and the length of each continuous hibernation bout at an ambient temperature of 5° C is measured, animals that have the shortest continuous hibernation bouts are the animals that have been fed a
A) carbohydrate-rich diet.
B) polyunsaturated fatty acids diet.
C) saturated fat diet.
D) protein-rich diet.
A) carbohydrate-rich diet.
B) polyunsaturated fatty acids diet.
C) saturated fat diet.
D) protein-rich diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which type of fat is important for calcium pump function in heart cells at low temperatures?
A) Saturated fatty acids
B) Triglycerides
C) Omega-3 fatty acids
D) Omega-6 fatty acids
A) Saturated fatty acids
B) Triglycerides
C) Omega-3 fatty acids
D) Omega-6 fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In ground squirrels, testosterone levels _______ during hibernation.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) stay the same
D) initially increase and then decrease
A) increase
B) decrease
C) stay the same
D) initially increase and then decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which statement about small hibernating mammals is true?
A) Their chances for survival increase during hibernation.
B) Their chances for survival decrease with hibernation.
C) Their chances of encountering a predator increase with hibernation.
D) Testosterone plasma levels increase during hibernation.
A) Their chances for survival increase during hibernation.
B) Their chances for survival decrease with hibernation.
C) Their chances of encountering a predator increase with hibernation.
D) Testosterone plasma levels increase during hibernation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In ground squirrels, males emerge before females because
A) males have more body mass and therefore can arouse sooner.
B) males have less brown fat and therefore cannot hibernate as long as females can.
C) the higher testosterone levels in males rouses them.
D) the testicles shrink during hibernation, so males emerge first to prepare to be successful mates.
A) males have more body mass and therefore can arouse sooner.
B) males have less brown fat and therefore cannot hibernate as long as females can.
C) the higher testosterone levels in males rouses them.
D) the testicles shrink during hibernation, so males emerge first to prepare to be successful mates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Refer to the figure shown.
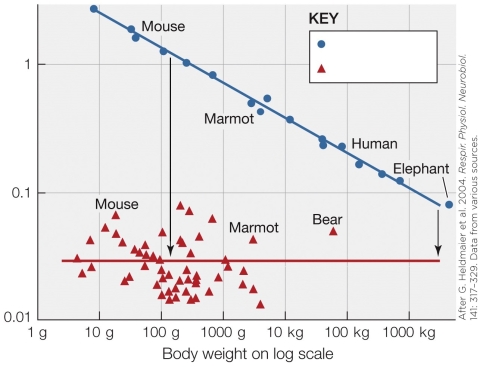 In the figure, what do the arrows represent?
In the figure, what do the arrows represent?
A) Energy savings per gram per hour during hibernation
B) The aerobic scope per gram per hour in relation to body mass
C) The winter season metabolic effect per gram per hour
D) The mass effect on cost of metabolism with winter fur insulation
 In the figure, what do the arrows represent?
In the figure, what do the arrows represent?A) Energy savings per gram per hour during hibernation
B) The aerobic scope per gram per hour in relation to body mass
C) The winter season metabolic effect per gram per hour
D) The mass effect on cost of metabolism with winter fur insulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Refer to the figure shown.
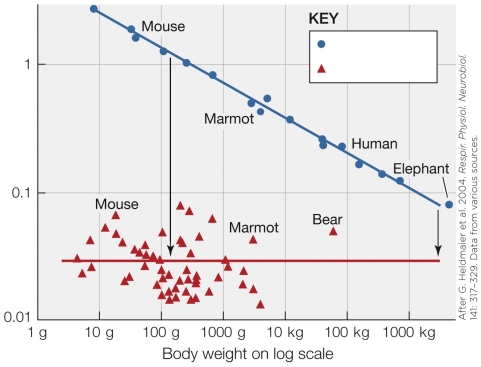 Which statement is not supported by data shown in the figure?
Which statement is not supported by data shown in the figure?
A) Larger animals save less energy during hibernation.
B) Smaller animals have higher nonhibernating metabolic rates.
C) There is no mass effect on metabolic rate in hibernating animals.
D) The larger the animal, the less likely they are to hibernate.
 Which statement is not supported by data shown in the figure?
Which statement is not supported by data shown in the figure?A) Larger animals save less energy during hibernation.
B) Smaller animals have higher nonhibernating metabolic rates.
C) There is no mass effect on metabolic rate in hibernating animals.
D) The larger the animal, the less likely they are to hibernate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the figure shown.
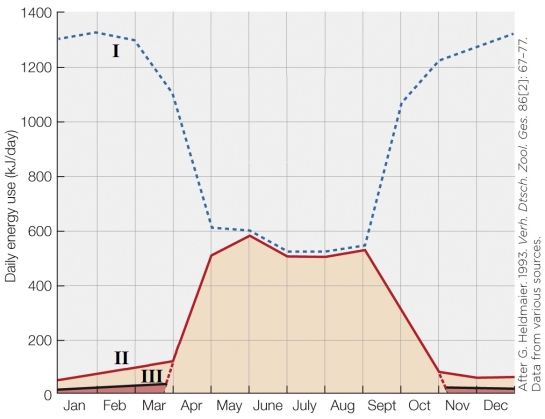 What is the most accurate title for this figure?
What is the most accurate title for this figure?
A) Annual cycle of energy use in alpine marmots
B) Annual metabolic rate cycling in ground squirrels
C) Hibernation frequency in alpine marmots
D) Hibernation effects on metabolic rate in ground squirrels
 What is the most accurate title for this figure?
What is the most accurate title for this figure?A) Annual cycle of energy use in alpine marmots
B) Annual metabolic rate cycling in ground squirrels
C) Hibernation frequency in alpine marmots
D) Hibernation effects on metabolic rate in ground squirrels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Refer to the figure shown.
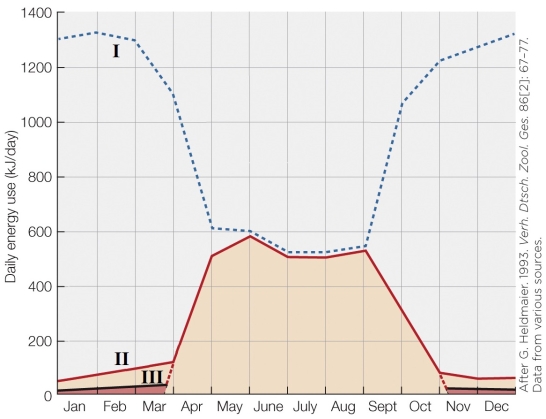 What best represents the actual cost savings of hibernation?
What best represents the actual cost savings of hibernation?
A) Line I
B) The difference between line I and line II
C) Line II
D) The difference between line II and line III
 What best represents the actual cost savings of hibernation?
What best represents the actual cost savings of hibernation?A) Line I
B) The difference between line I and line II
C) Line II
D) The difference between line II and line III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the figure shown.
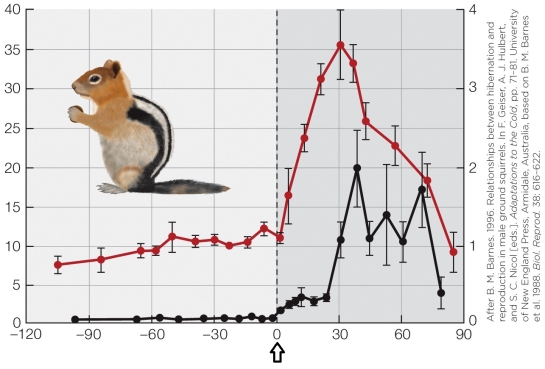 What is indicated by the arrow in the figure?
What is indicated by the arrow in the figure?
A) End of hibernation
B) Birth
C) Beginning of hibernation
D) Beginning of mating season
 What is indicated by the arrow in the figure?
What is indicated by the arrow in the figure?A) End of hibernation
B) Birth
C) Beginning of hibernation
D) Beginning of mating season

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the figure shown.
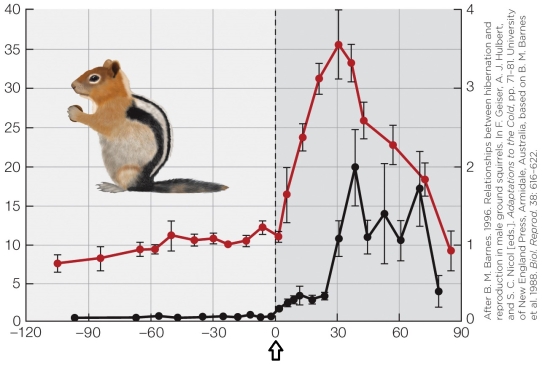 Which conclusion is best supported by the data in the figure?
Which conclusion is best supported by the data in the figure?
A) As temperature increases, testicle size and testosterone level increase.
B) Following birth, testicle size and testosterone level increase.
C) Following hibernation, both testosterone levels and testicle size increase.
D) Longer summer days increase testosterone levels and testicle size.
 Which conclusion is best supported by the data in the figure?
Which conclusion is best supported by the data in the figure?A) As temperature increases, testicle size and testosterone level increase.
B) Following birth, testicle size and testosterone level increase.
C) Following hibernation, both testosterone levels and testicle size increase.
D) Longer summer days increase testosterone levels and testicle size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An early hypothesis for arousal during hibernation was that animals
A) must wake up to metabolize glucose in their brains.
B) produce nitrogenous wastes and therefore must wake up to void.
C) must wake up because they need to move their muscles regularly.
D) must wake up and move because they need to circulate their blood.
A) must wake up to metabolize glucose in their brains.
B) produce nitrogenous wastes and therefore must wake up to void.
C) must wake up because they need to move their muscles regularly.
D) must wake up and move because they need to circulate their blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Explain the differences between brown fat and white fat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Describe the immunocytochemistry assay that was devised to test for brown fat in newborn reindeer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
It has been shown that fetuses inside the uterus do not rely on brown fat and only begin to rely on it after birth. Describe an experiment to test this conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Explain how body size relates to weight-specific metabolic rate in hibernating and nonhibernating animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Explain how technological advances have helped researchers record data pertaining to hibernation and other physiological mechanisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Explain how animals prepare for hibernation. Include the cues that trigger preparation, the type of nutrients stored, and the specific location of storage molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Explain social hibernation using a specific animal example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Explain the significance of social hibernation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Explain how certain animals undergo synchrony in their hibernation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which hypotheses for arousal during hibernation are currently popular?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



