Deck 9: The Energetics of Aerobic Activity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/72
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: The Energetics of Aerobic Activity
1
The metabolic rate of a young adult human is greatest while
A) walking at 4 miles per hour.
B) bicycling at 13 miles per hour.
C) running at 10 miles per hour.
D) crawl swimming at 2 miles per hour.
A) walking at 4 miles per hour.
B) bicycling at 13 miles per hour.
C) running at 10 miles per hour.
D) crawl swimming at 2 miles per hour.
C
2
Foraging birds typically fuel this activity by
A) anaerobic mechanisms.
B) aerobic mechanisms.
C) an equal mixture of aerobic and anaerobic mechanisms.
D) an equal mixture of aerobic mechanisms and the phosphagen system.
A) anaerobic mechanisms.
B) aerobic mechanisms.
C) an equal mixture of aerobic and anaerobic mechanisms.
D) an equal mixture of aerobic mechanisms and the phosphagen system.
B
3
Studies on energy costs of routine daily activity of animals focus on aerobic ATP production because
A) ATP requirements of routine daily living are mostly met aerobically.
B) ATP requirements of routine daily living are mostly met anaerobically.
C) animals generate ATP aerobically during the day.
D) all activities of interest use ATP generated aerobically.
A) ATP requirements of routine daily living are mostly met aerobically.
B) ATP requirements of routine daily living are mostly met anaerobically.
C) animals generate ATP aerobically during the day.
D) all activities of interest use ATP generated aerobically.
A
4
A monitor placed on or in a study animal that stores data is called a
A) telemetric device.
B) data logger.
C) motor driven treadmill.
D) deuterium infusing device.
A) telemetric device.
B) data logger.
C) motor driven treadmill.
D) deuterium infusing device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A monitor placed on or in a study animal that transmits data is called a
A) telemetric device.
B) data logger.
C) motor driven treadmill.
D) deuterium infusing device.
A) telemetric device.
B) data logger.
C) motor driven treadmill.
D) deuterium infusing device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In an experiment in which an animal is injected with deuterium and oxygen-18 (D218O method) and then released into the wild, which of the following trends would you expect to see from measurements taken after a period of rest and again after a period of exercise?
A) CO2 production will be higher during exercise than at rest.
C) CO2 production will be equal during exercise and at rest.
D) O2 production will be higher during exercise than at rest.
E) O2 production will be equal during exercise than at rest.
A) CO2 production will be higher during exercise than at rest.
C) CO2 production will be equal during exercise and at rest.
D) O2 production will be higher during exercise than at rest.
E) O2 production will be equal during exercise than at rest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which behavior represents the smallest component per unit time of the average daily metabolic rate (ADMR)?
A) An animal chasing a prey
B) An animal avoiding a predator
C) An animal sleeping in the shade
D) An animal standing guard
A) An animal chasing a prey
B) An animal avoiding a predator
C) An animal sleeping in the shade
D) An animal standing guard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If an animal spends 3 hours a day chasing a prey (49 kJ/hr) and 20 hours a day resting (using 15 kJ/hr), its total daily cost of behavior in kJ is
A) 147 kJ/day.
B) 153 kJ/day.
C) 300 kJ/day.
D) 447 kJ/day.
A) 147 kJ/day.
B) 153 kJ/day.
C) 300 kJ/day.
D) 447 kJ/day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If an animal spends 3 hours a day running away from a predator and 20 hours a day resting (using 20 kJ/hr), the total daily cost of behavior is 700 kJ. The kJ spent per hour running away from a predator is _______ kJ/hr.
A) 60
B) 100
C) 300
D) 400
A) 60
B) 100
C) 300
D) 400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If an animal spends 6 hours a day chasing prey (50 kJ/hr) and 18 hours a day resting (10 kJ/hr), its average hourly cost of behavior is _______ kJ/hr.
A) 20
B) 24
C) 30
D) 50
A) 20
B) 24
C) 30
D) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The average daily metabolic rate (ADMR) refers to the amount of energy expended _______ in their natural habitat.
A) during routine lives of animals
B) during strenuous physical activities of animals
C) in animals chasing prey
D) in animals avoiding a predator
A) during routine lives of animals
B) during strenuous physical activities of animals
C) in animals chasing prey
D) in animals avoiding a predator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The relationship between average daily metabolic rate (ADMR) per unit of body weight and body size is a(n)
A) inverse proportion.
B) direct proportion.
C) J-shaped curve.
D) U-shaped curve.
A) inverse proportion.
B) direct proportion.
C) J-shaped curve.
D) U-shaped curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which animal would display a U-shaped curve of oxygen consumption per unit of time relative to speed?
A) Sockeye salmon
B) Kangaroo
C) Ground squirrel
D) Magpie
A) Sockeye salmon
B) Kangaroo
C) Ground squirrel
D) Magpie

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Based on the study done by Taylor et al. (1970), the animal whose rate of oxygen consumption relative to its running speed creates a linear plot is a
A) lizard.
B) magpie.
C) trout.
D) ground squirrel.
A) lizard.
B) magpie.
C) trout.
D) ground squirrel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
As a human runs faster, her metabolic rate
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) stays the same.
D) decreases first and then increases.
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) stays the same.
D) decreases first and then increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which rate would allow an animal to continue walking for the longest period of time?
A) 15 kJ/min
B) 20 kJ/min
C) 25 kJ/min
D) 30 kJ/min
A) 15 kJ/min
B) 20 kJ/min
C) 25 kJ/min
D) 30 kJ/min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The speed that _______ the cost of transport is the speed that _______ the distance that can be traveled with a given amount of energy.
A) maximizes; maximizes
B) sustains; maximizes
C) minimizes; maximizes
D) minimizes; minimizes
A) maximizes; maximizes
B) sustains; maximizes
C) minimizes; maximizes
D) minimizes; minimizes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which rate would be most advantageous for a fish trying to swim for the longest period of time?
A) 1 m/h
B) 2 m/h
C) 3 m/h
D) 4 m/h
A) 1 m/h
B) 2 m/h
C) 3 m/h
D) 4 m/h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For animals of any given body size, engaging in their primary form of locomotion, which activity would be the most energetically costly to cover a long distance?
A) Walking
B) Running at a high speed
C) Swimming (in fish)
D) Flying (in birds)
A) Walking
B) Running at a high speed
C) Swimming (in fish)
D) Flying (in birds)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For animals of any given body size, engaging in their primary form of locomotion, which is the least energetically costly way to cover a long distance?
A) Walking
B) Running at a high speed
C) Swimming (in fish)
D) Flying (in birds)
A) Walking
B) Running at a high speed
C) Swimming (in fish)
D) Flying (in birds)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Comparing animals that share a single primary mode of locomotion, large bodied species will cover distances at a _______ weight-specific cost than small bodied species.
A) lower
B) slightly higher
C) higher
D) much higher
A) lower
B) slightly higher
C) higher
D) much higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An animal weighing _______ kg can cover the greatest distance before running out of fat (assuming all the animals have the same proportion of body fat).
A) 100
B) 200
C) 300
D) 500
A) 100
B) 200
C) 300
D) 500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which animal covers the largest distance at the lowest weight-specific cost?
A) Millipede
B) Mouse
C) Dog
D) Horse
A) Millipede
B) Mouse
C) Dog
D) Horse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which organism would have the lowest cost of transport?
A) Duck
B) Fish
C) Goose
D) Human
A) Duck
B) Fish
C) Goose
D) Human

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which statement regarding an individual riding a bike and a running individual is true?
A) The individual cyclist will have less cost of transport than the runner.
B) The runner will have less cost of transport than the cyclist.
C) Both individuals will have the same cost of energy.
D) The runner will have more cost of energy during the first ten minutes and then he will have less.
A) The individual cyclist will have less cost of transport than the runner.
B) The runner will have less cost of transport than the cyclist.
C) Both individuals will have the same cost of energy.
D) The runner will have more cost of energy during the first ten minutes and then he will have less.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure shown.
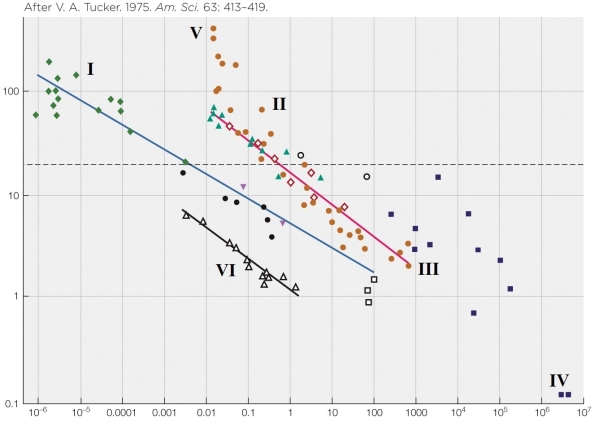 Choose the most appropriate label for the x axis.
Choose the most appropriate label for the x axis.
A) Body weight (kg) on a log scale
B) Body weight (g)
C) Body weight (g) on a log scale
D) Speed (m/s)
 Choose the most appropriate label for the x axis.
Choose the most appropriate label for the x axis.A) Body weight (kg) on a log scale
B) Body weight (g)
C) Body weight (g) on a log scale
D) Speed (m/s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the figure shown.
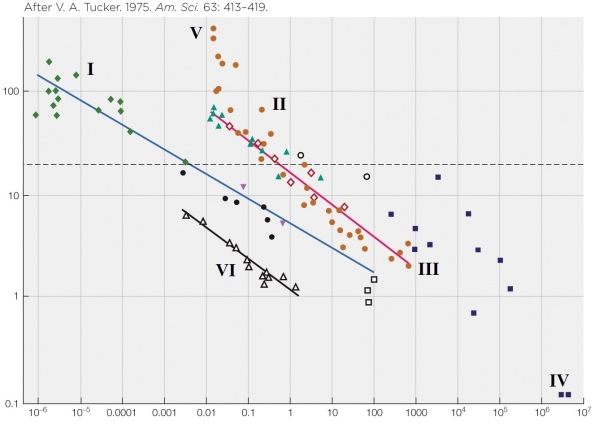 Choose the most appropriate units for the y axis.
Choose the most appropriate units for the y axis.
A) J/m•s
B) J/h•g
C) J/m•kg
D) J/g•h
 Choose the most appropriate units for the y axis.
Choose the most appropriate units for the y axis.A) J/m•s
B) J/h•g
C) J/m•kg
D) J/g•h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure shown.
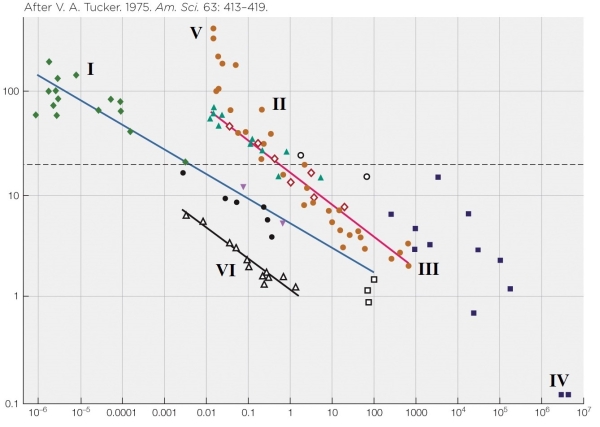 A horse would most likely be indicated by which data point?
A horse would most likely be indicated by which data point?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 A horse would most likely be indicated by which data point?
A horse would most likely be indicated by which data point?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure shown.
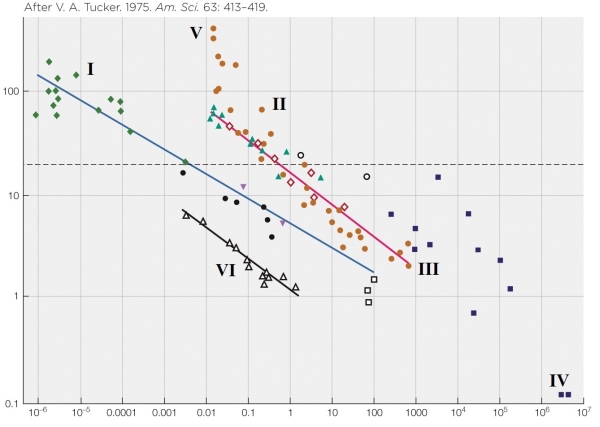 If you were to plot a mouse on this figure, where would the data point go?
If you were to plot a mouse on this figure, where would the data point go?
A) Close to I
B) Close to III
C) Close to VI
D) Close to V
 If you were to plot a mouse on this figure, where would the data point go?
If you were to plot a mouse on this figure, where would the data point go?A) Close to I
B) Close to III
C) Close to VI
D) Close to V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Energy production is highly correlated with the amount of
A) food consumed.
B) oxygen consumed.
C) water excreted.
D) carbohydrates used.
A) food consumed.
B) oxygen consumed.
C) water excreted.
D) carbohydrates used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If animal A has a V̇O2max of 22.4 ml/g•h and animal B has a V̇O2max of 24 ml/ g•h,
A) animal A can produce more energy.
B) animal B can produce more energy.
C) both animals can produce the same amount of energy.
D) animal A can produce more energy if it is bigger.
A) animal A can produce more energy.
B) animal B can produce more energy.
C) both animals can produce the same amount of energy.
D) animal A can produce more energy if it is bigger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
V̇O2max refers to an animal's
A) capacity to use fat as a source of energy.
B) maximum oxygen consumption.
C) maximum oxygen usage.
D) maximum energy production.
A) capacity to use fat as a source of energy.
B) maximum oxygen consumption.
C) maximum oxygen usage.
D) maximum energy production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Of the following values, an exercise requiring _______ of V̇O2max is the most strenuous.
A) 45%
B) 55%
C) 65%
D) 75%
A) 45%
B) 55%
C) 65%
D) 75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which animal will have the fastest rate of aerobic ATP production per unit of body mass?
A) Lizard
B) Monkey
C) Salamander
D) They will all have the same rate
A) Lizard
B) Monkey
C) Salamander
D) They will all have the same rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
According to the study done by Lindstedt (1991), which animal has the highest V̇O2max?
A) Horse
B) Dog
C) Fox
D) Pronghorn
A) Horse
B) Dog
C) Fox
D) Pronghorn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which animal will have the fastest rate of aerobic ATP production per unit of body mass?
A) Lizard
B) Monkey
C) Salamander
D) They will all have the same rate
A) Lizard
B) Monkey
C) Salamander
D) They will all have the same rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
According to the study done by Lindstedt (1991), which animal has the highest V̇O2max?
A) Horse
B) Dog
C) Fox
D) Pronghorn
A) Horse
B) Dog
C) Fox
D) Pronghorn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Assuming the same body size, an individual who is _______ years old would have the lowest V̇O2max.
A) 35
B) 40
C) 50
D) 55
A) 35
B) 40
C) 50
D) 55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Assuming individuals of the same body size, a person who is _______ years old would have the most difficulty performing an exercise that requires 65% V̇O2max.
A) 35
B) 40
C) 50
D) 55
A) 35
B) 40
C) 50
D) 55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Assuming individuals of the same body size, one who is at _______ would have the lowest V̇O2max.
A) sea level
B) 500 feet above sea level
C) 1000 feet above sea level
D) 1500 feet above sea level
A) sea level
B) 500 feet above sea level
C) 1000 feet above sea level
D) 1500 feet above sea level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The symmorphosis hypothesis states that
A) the circulatory system is the "weakest link."
B) V̇O2max is the maximal amount of oxygen consumed.
C) all systems have the same limitations when it comes to oxygen transport.
D) the consumed amount of oxygen is correlated with the amount of ATP produced.
A) the circulatory system is the "weakest link."
B) V̇O2max is the maximal amount of oxygen consumed.
C) all systems have the same limitations when it comes to oxygen transport.
D) the consumed amount of oxygen is correlated with the amount of ATP produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
According to many physiologists, the _______ system is considered to be the "weakest link" regarding V̇O2max.
A) circulatory
B) nervous
C) muscular
D) digestive
A) circulatory
B) nervous
C) muscular
D) digestive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When comparing the difference in V̇O2max and resting O2 consumption at the same temperature, we are referring to the
A) symmorphosis.
B) aerobic scope of activity.
C) aerobic expansibility.
D) aerobic capacity.
A) symmorphosis.
B) aerobic scope of activity.
C) aerobic expansibility.
D) aerobic capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
According to the symmorphosis hypothesis, the skeletal system
A) and the circulatory system have the same capability regarding oxygen consumption.
B) has a higher capability regarding oxygen consumption compared to the circulatory system.
C) has a lower capability regarding oxygen consumption compared to the circulatory system.
D) has a lower capability regarding oxygen consumption compared to the pulmonary system.
A) and the circulatory system have the same capability regarding oxygen consumption.
B) has a higher capability regarding oxygen consumption compared to the circulatory system.
C) has a lower capability regarding oxygen consumption compared to the circulatory system.
D) has a lower capability regarding oxygen consumption compared to the pulmonary system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When looking at the ratio of V̇O2max to resting O2 consumption at the same temperature, we are referring to
A) symmorphosis.
B) aerobic scope of activity.
C) aerobic expansibility.
D) aerobic capacity.
A) symmorphosis.
B) aerobic scope of activity.
C) aerobic expansibility.
D) aerobic capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If an organism has a resting oxygen consumption of 1mL/g•h, and its V̇O2max is 10 mL/g•h, its aerobic scope of activity will be _______ mL/g•h.
A) 9
B) 10
C) 0.1
D) 11
A) 9
B) 10
C) 0.1
D) 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If an organism has a resting oxygen consumption of 1mL/g•h, and its V̇O2max is 10 mL/g•h, its aerobic expansibility will be
A) 0.1.
B) 0.1 mL/g•h.
C) 10 mL/g•h.
D) 10.
A) 0.1.
B) 0.1 mL/g•h.
C) 10 mL/g•h.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If an organism has a resting oxygen consumption of 1mL/g•h, and its aerobic expansibility is 10, its V̇O2max will be
A) 0.1.
B) 0.1 mL/g•h.
C) 10 mL/g•h.
D) 10.
A) 0.1.
B) 0.1 mL/g•h.
C) 10 mL/g•h.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If an organism has a V̇O2max of 5 mL/g•h, and its aerobic expansibility is 5, its resting oxygen consumption will be
A) 1.
B) 1 mL/g•h.
C) 10 mL/g•h.
D) 10.
A) 1.
B) 1 mL/g•h.
C) 10 mL/g•h.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If an organism has a V̇O2max of 10mL/g•h, and its aerobic scope of activity is 8 mL/g•h, its resting oxygen consumption will be _______ mL/g•h.
A) 2
B) 8
C) 0.1
D) 18
A) 2
B) 8
C) 0.1
D) 18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If a human has a V̇O2max of 2.5 ml O2/kg•min, his O2 consumption at rest is about _______ O2/kg•min.
A) 0.025
B) 0.25
C) 2.5
D) 20
A) 0.025
B) 0.25
C) 2.5
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a human has a resting O2 consumption of 10 mL/kg•min, her V̇O2max consumption is _______ mL O2/kg•min.
A) 1
B) 10
C) 100
D) 250
A) 1
B) 10
C) 100
D) 250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A pronghorn can run for a longer period of time than a cheetah because a pronghorn
A) is adapted to aerobic respiration during running while the cheetah relies on anaerobic cellular respiration.
B) achieves faster speeds than the cheetah does.
C) has stronger sprinting skeletal muscles than the cheetah does.
D) more glycogen in its muscles than the cheetah does.
A) is adapted to aerobic respiration during running while the cheetah relies on anaerobic cellular respiration.
B) achieves faster speeds than the cheetah does.
C) has stronger sprinting skeletal muscles than the cheetah does.
D) more glycogen in its muscles than the cheetah does.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An athlete weighs 70 kg. His V̇O2max is 30 mL/kg•min. After 6 months of regular endurance training, his V̇O2max could be as high as _______ mL/kg•min.
A) 10
B) 19
C) 39
D) 100
A) 10
B) 19
C) 39
D) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An untrained sedentary person has a V̇O2max measured at 40 mL/kg•min. After 10 weeks of intense endurance training, this person's aerobic performance has improved. A reasonable measurement of this person's V̇O2max would be _______ mL/kg•min.
A) 40
B) 48
C) 80
D) 100
A) 40
B) 48
C) 80
D) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Individual A has a V̇O2max of 30 mL O2/kg•min. Individual B has a V̇O2max of 60 mL O2/kg•min. If both individuals are competing in a soccer activity, who will be able compete for a longer period of time?
A) Individual A because he has a lower V̇O2max.
B) Individual B because he has a higher V̇O2max.
C) Both individuals will get tired at the same time.
D) Individual A because he has a higher capacity to produce ATP.
A) Individual A because he has a lower V̇O2max.
B) Individual B because he has a higher V̇O2max.
C) Both individuals will get tired at the same time.
D) Individual A because he has a higher capacity to produce ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which activity requires the highest V̇O2max?
A) Long distance running
B) Canoeing
C) Ice hockey
D) Cross-country skiing
A) Long distance running
B) Canoeing
C) Ice hockey
D) Cross-country skiing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Compared to wild animals, humans have _____ average daily metabolic rates (ADMRs) when compared to basal metabolic rates.
A) higher
B) lower
C) similar
D) more variable
A) higher
B) lower
C) similar
D) more variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which one of the following activities has the highest average daily metabolic rate as a ratio of resting metabolic rate?
A) Humans hiking
B) 22-day Tour de France race
C) Gray seals nursing pups
D) Perching birds rearing young
A) Humans hiking
B) 22-day Tour de France race
C) Gray seals nursing pups
D) Perching birds rearing young

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Prior to migration, birds tend to accumulate
A) ATP.
B) muscle.
C) muscle glycogen.
D) fat.
A) ATP.
B) muscle.
C) muscle glycogen.
D) fat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which is the optimal temperature for bumblebees to fly at?
A) 15°C
B) 20°C
C) 25°C
D) 30°C
A) 15°C
B) 20°C
C) 25°C
D) 30°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of the following is not a major factor in bumblebee energetics?
A) Environmental temperature
B) Internal body temperature
C) Cost of ATP production
D) Flight time
A) Environmental temperature
B) Internal body temperature
C) Cost of ATP production
D) Flight time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain in detail how metabolism is studied in running animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What are some specific characteristics of the relationship between the metabolic cost per unit time and the speed of locomotion in swimming, running, and flying animals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the significance of V̇O2max in metabolism studies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the relationship between V̇O2max and aging? What effect does the change in V̇O2max have on the type of exercise performed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What are the physiological causes of the limits of oxygen consumption?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose at a particular body temperature, a fish has a resting oxygen consumption rate of 0.05 mL/g•h and an aerobic expansibility of 6. What is its aerobic scope?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Explain how V̇O2max changes with endurance training.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the fuel that birds store and use to meet their energy needs during migration? How are birds able to use this energy source?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In birds, what is the advantage of using proteins as a source of energy during migration?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Bumblebees require a specific flight muscle temperature to fly. What is this temperature and how do bumblebees maintain it during flight and while hovering between flowers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



