Deck 5: Transport of Solutes and Water
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Transport of Solutes and Water
1
Choose the most accurate definition of equilibrium.
A) The state of minimum capacity to do work when energy is slowly added to the system.
B) The state of maximum capacity to do work when energy is slowly added to the system.
C) The state of minimum capacity to do work under locally prevailing conditions.
D) The state of maximum capacity to do work under locally prevailing conditions.
A) The state of minimum capacity to do work when energy is slowly added to the system.
B) The state of maximum capacity to do work when energy is slowly added to the system.
C) The state of minimum capacity to do work under locally prevailing conditions.
D) The state of maximum capacity to do work under locally prevailing conditions.
C
2
The movement of an amino acid across the intestinal epithelial membrane in the direction of equilibrium
A) is passive transport.
B) is active transport.
C) could be either passive or active transport.
D) is neither passive or active transport.
A) is passive transport.
B) is active transport.
C) could be either passive or active transport.
D) is neither passive or active transport.
C
3
Transporter proteins on freshwater fish gills transport sodium and chloride
A) in exactly the same manner as any single animal cell.
B) into the animal from the surrounding water.
C) out of the animal and into the surrounding water.
D) in the direction of equilibrium.
A) in exactly the same manner as any single animal cell.
B) into the animal from the surrounding water.
C) out of the animal and into the surrounding water.
D) in the direction of equilibrium.
B
4
The process of _______ arises from the molecular agitation that exists in all systems above absolute zero and the tendency for such agitation to carry more molecules out of regions of relatively high concentration than into these regions.
A) facilitated diffusion
B) active transport
C) diffusion
D) osmosis
A) facilitated diffusion
B) active transport
C) diffusion
D) osmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Outward diffusion of a substance from an animal cell increases the concentration of that substance around the outer surface of the cell. If this process continues,
A) the rate of diffusion will increase.
B) the rate of diffusion will decrease.
C) the rate of diffusion will remain the same.
D) active transport will be initiated.
A) the rate of diffusion will increase.
B) the rate of diffusion will decrease.
C) the rate of diffusion will remain the same.
D) active transport will be initiated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Outward diffusion of a substance from an animal cell increases the concentration of that substance around the outer surface of the cell. This surface is called the
A) boundary layer.
B) bulk solution of the cell.
C) region of backup diffusion.
D) low-concentration region.
A) boundary layer.
B) bulk solution of the cell.
C) region of backup diffusion.
D) low-concentration region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the Fick diffusion equation, if the units of D are cm2 ∙ s‒1, which of the following best represents the units for J?
A) Moles ∙ cm‒2 ∙ s‒1
B) M ∙ cm ∙ s
C) Moles ∙ sec‒1
D) M ∙ cm2 ∙ s
A) Moles ∙ cm‒2 ∙ s‒1
B) M ∙ cm ∙ s
C) Moles ∙ sec‒1
D) M ∙ cm2 ∙ s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When X increases in the Fick diffusion equation, J
A) also increases.
B) decreases.
C) remains the same.
D) can increase or decrease.
A) also increases.
B) decreases.
C) remains the same.
D) can increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to the Fick diffusion equation, which letter represents permeability?
A) J
B) Permeability is integrated into D
C) Permeability is integrated into C1 - C2
D) X
A) J
B) Permeability is integrated into D
C) Permeability is integrated into C1 - C2
D) X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to the figure shown.
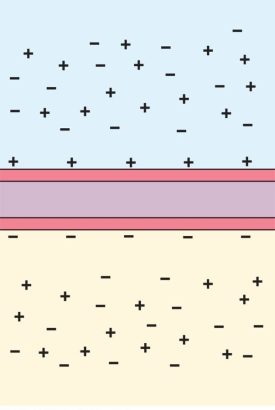 In the figure, the areas far above and far below the membrane denote
In the figure, the areas far above and far below the membrane denote
A) a boundary layer.
B) the bulk solution of the cell and extracellular fluid.
C) capacitance.
D) a net negative charge.
 In the figure, the areas far above and far below the membrane denote
In the figure, the areas far above and far below the membrane denoteA) a boundary layer.
B) the bulk solution of the cell and extracellular fluid.
C) capacitance.
D) a net negative charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Refer to the figure shown.
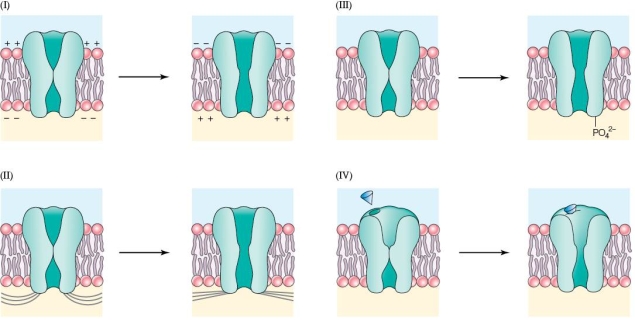 Which panel in the figure shows a voltage-gated channel?
Which panel in the figure shows a voltage-gated channel?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which panel in the figure shows a voltage-gated channel?
Which panel in the figure shows a voltage-gated channel?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Refer to the figure shown.
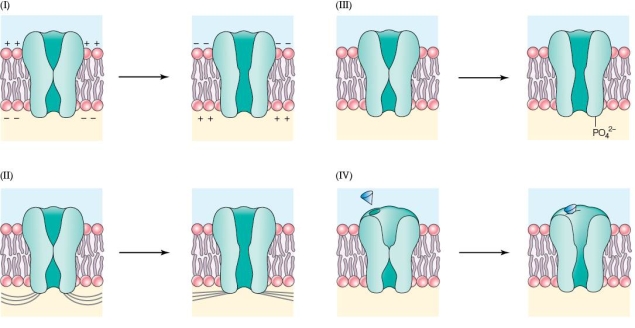 In which panel do the channels open and close based on chemical bonding?
In which panel do the channels open and close based on chemical bonding?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) Both III and IV
 In which panel do the channels open and close based on chemical bonding?
In which panel do the channels open and close based on chemical bonding?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) Both III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a change in the voltage of a cell membrane causes all the voltage-gated Na+ channels to open, the permeability of the cell membrane to Na+ has been
A) inhibited.
B) decreased.
C) increased.
D) unaffected.
A) inhibited.
B) decreased.
C) increased.
D) unaffected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A solution that has a concentration effect on diffusion that is equal but opposite to the electrical effect is said to be
A) in a steady state.
B) part of the Nernst equation.
C) in isoelectric balance.
D) in electrochemical equilibrium.
A) in a steady state.
B) part of the Nernst equation.
C) in isoelectric balance.
D) in electrochemical equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the animal cell, the overall concentration effects on Na+ diffusion cause Na+ to _______ the cell.
A) move into
B) move out of
C) remain inside
D) remain outside of
A) move into
B) move out of
C) remain inside
D) remain outside of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the animal cell, the overall electrical effects on Cl‒ diffusion cause Cl‒ to _______ the cell.
A) move into
B) remain equal on both sides of
C) remain inside
D) remain outside of
A) move into
B) remain equal on both sides of
C) remain inside
D) remain outside of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the animal cell, the combined concentration and electrical effects on K+ cause K+ to _______ the cell.
A) move into
B) leak out of
C) remain inside
D) remain outside of
A) move into
B) leak out of
C) remain inside
D) remain outside of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Among the ions outside and inside a typical living cell, which ion is furthest from electrochemical equilibrium?
A) Cl‒
B) Na+
C) K+
D) Mg2+
A) Cl‒
B) Na+
C) K+
D) Mg2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Refer to the figure shown.
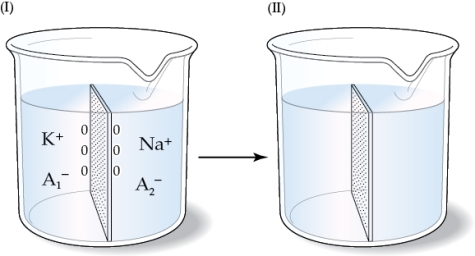 If the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable only to Na+, and the beaker on the left represents the initial state,
If the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable only to Na+, and the beaker on the left represents the initial state,
A) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, causing a net positive charge on the right side of the membrane.
B) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, causing a net negative charge on the right side of the membrane.
C) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, but there will be no separation of charges.
D) there will be no net movement of ions.
 If the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable only to Na+, and the beaker on the left represents the initial state,
If the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable only to Na+, and the beaker on the left represents the initial state,A) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, causing a net positive charge on the right side of the membrane.
B) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, causing a net negative charge on the right side of the membrane.
C) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, but there will be no separation of charges.
D) there will be no net movement of ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the figure shown.
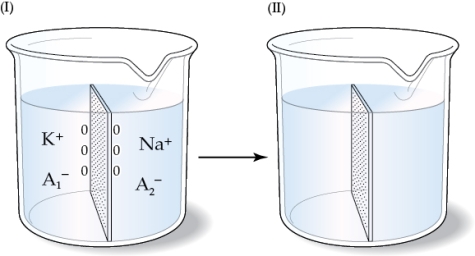 If the beaker on the left represents the initial state and the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable to K+ and Na+,
If the beaker on the left represents the initial state and the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable to K+ and Na+,
A) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, causing a net positive charge on the right side of the membrane.
B) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, causing a net negative charge on the right side of the membrane.
C) there will be no net movement of ions.
D) the movement of Na+ will be balanced by the movement of K+; therefore, there will be no net charge difference.
 If the beaker on the left represents the initial state and the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable to K+ and Na+,
If the beaker on the left represents the initial state and the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable to K+ and Na+,A) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, causing a net positive charge on the right side of the membrane.
B) Na+ will diffuse to the left side of the membrane, causing a net negative charge on the right side of the membrane.
C) there will be no net movement of ions.
D) the movement of Na+ will be balanced by the movement of K+; therefore, there will be no net charge difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the figure shown.
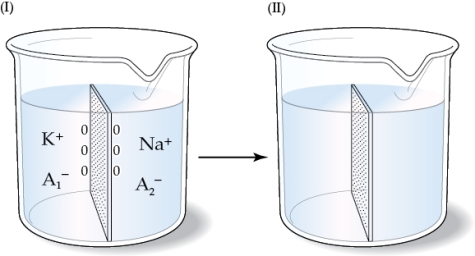 If the figure on the left represents the initial state and the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable only to Na+, which manipulation would cause a net negative charge on the left side of the membrane once the system comes to equilibrium?
If the figure on the left represents the initial state and the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable only to Na+, which manipulation would cause a net negative charge on the left side of the membrane once the system comes to equilibrium?
A) Making the membrane permeable only to water
B) Allowing the membrane to become permeable to K+ as well as to Na+
C) Tripling the amount of A2‒ and allowing the membrane to become permeable to A2‒
D) Tripling the amount of A1‒ and allowing the membrane to become permeable to A1‒
 If the figure on the left represents the initial state and the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable only to Na+, which manipulation would cause a net negative charge on the left side of the membrane once the system comes to equilibrium?
If the figure on the left represents the initial state and the membrane shown in the beakers is permeable only to Na+, which manipulation would cause a net negative charge on the left side of the membrane once the system comes to equilibrium?A) Making the membrane permeable only to water
B) Allowing the membrane to become permeable to K+ as well as to Na+
C) Tripling the amount of A2‒ and allowing the membrane to become permeable to A2‒
D) Tripling the amount of A1‒ and allowing the membrane to become permeable to A1‒

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The gills of freshwater fish present what challenges?
A) The gills of freshwater fish present no challenges.
B) The permeability of the gill tissue to water causes the fish to lose water.
C) The permeability of the gill tissue to ions causes the fish to gain ions from the water.
D) The permeability of the gill tissue to ions causes the fish to lose ions to the water.
A) The gills of freshwater fish present no challenges.
B) The permeability of the gill tissue to water causes the fish to lose water.
C) The permeability of the gill tissue to ions causes the fish to gain ions from the water.
D) The permeability of the gill tissue to ions causes the fish to lose ions to the water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which statement regarding facilitated diffusion is false?
A) Diffusion occurs in the direction of electrochemical equilibrium.
B) Solutes move faster with the protein facilitators than they would without them.
C) Protein facilitators change conformation with the help of ATP.
D) Solutes bind reversibly to the protein facilitators.
A) Diffusion occurs in the direction of electrochemical equilibrium.
B) Solutes move faster with the protein facilitators than they would without them.
C) Protein facilitators change conformation with the help of ATP.
D) Solutes bind reversibly to the protein facilitators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the intestine, glucose is brought into the cell membrane by
A) simple diffusion.
B) active transport.
C) facilitated diffusion.
D) osmosis.
A) simple diffusion.
B) active transport.
C) facilitated diffusion.
D) osmosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the figure shown.
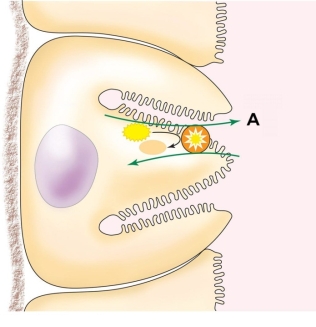 What type of process is shown in the figure?
What type of process is shown in the figure?
A) Simple diffusion
B) Facilitated diffusion
C) Active transport
D) Osmosis
 What type of process is shown in the figure?
What type of process is shown in the figure?A) Simple diffusion
B) Facilitated diffusion
C) Active transport
D) Osmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure shown.
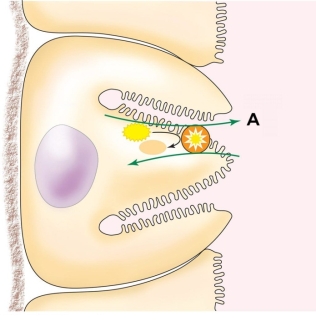 Which substance is mostly likely being pumped at A?
Which substance is mostly likely being pumped at A?
A) Na+
B) H+
C) K+
D) ATP
 Which substance is mostly likely being pumped at A?
Which substance is mostly likely being pumped at A?A) Na+
B) H+
C) K+
D) ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which process is electrogenic?
A) Glucose transport into the small intestine epithelium
B) Acid production in the stomach
C) The sodium‒potassium pump on a typical cell membrane
D) Sodium uptake in the freshwater fish gill
A) Glucose transport into the small intestine epithelium
B) Acid production in the stomach
C) The sodium‒potassium pump on a typical cell membrane
D) Sodium uptake in the freshwater fish gill

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure shown.
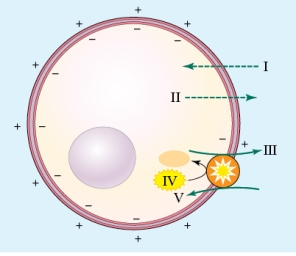 At what point in the figure is energy being used?
At what point in the figure is energy being used?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 At what point in the figure is energy being used?
At what point in the figure is energy being used?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure shown.
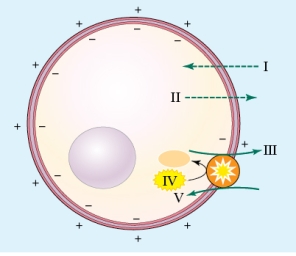 Which ion is moving into the cell via diffusion and where is it located?
Which ion is moving into the cell via diffusion and where is it located?
A) Na+ is diffusing into the cell at I.
B) K+ is diffusing into the cell at I.
C) K+ is diffusing into the cell at V.
D) Na+ is diffusing into the cell at V.
 Which ion is moving into the cell via diffusion and where is it located?
Which ion is moving into the cell via diffusion and where is it located?A) Na+ is diffusing into the cell at I.
B) K+ is diffusing into the cell at I.
C) K+ is diffusing into the cell at V.
D) Na+ is diffusing into the cell at V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the figure shown.
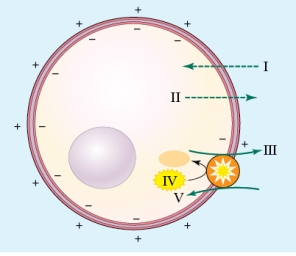 At which location(s) in the figure is K+ moving into or out of the cell?
At which location(s) in the figure is K+ moving into or out of the cell?
A) I
B) II
C) Both I and V
D) Both II and V
 At which location(s) in the figure is K+ moving into or out of the cell?
At which location(s) in the figure is K+ moving into or out of the cell?A) I
B) II
C) Both I and V
D) Both II and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
On the cell membrane, the Na+‒ K+ pump transports _______ in for every _______ that it transports out.
A) 3 Na+; 2 K+
B) 2 Na+; 3 K+
C) 3 K+; 2 Na+
D) 2 K+; 3 Na+
A) 3 Na+; 2 K+
B) 2 Na+; 3 K+
C) 3 K+; 2 Na+
D) 2 K+; 3 Na+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The molecular species that binds and unbinds to the Na+‒K+-ATPase, causing sodium and potassium to shuttle through it, is
A) PO42‒.
B) ATP.
C) Na+‒K+-ATPase.
D) ADP.
A) PO42‒.
B) ATP.
C) Na+‒K+-ATPase.
D) ADP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which statement about the transport of glucose into the gut epithelial cell through the apical membrane is true?
A) The glucose transporter on the apical membrane uses ATP-bond energy.
B) Glucose diffuses through the apical membrane using its own concentration gradient; therefore, it does not use any energy.
C) Na+ uses ATP-bond energy as it brings in glucose at the apical membrane.
D) ATP-bond energy is used at the Na+‒K+ pump in setting up the Na+ gradient.
A) The glucose transporter on the apical membrane uses ATP-bond energy.
B) Glucose diffuses through the apical membrane using its own concentration gradient; therefore, it does not use any energy.
C) Na+ uses ATP-bond energy as it brings in glucose at the apical membrane.
D) ATP-bond energy is used at the Na+‒K+ pump in setting up the Na+ gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Refer to the figure shown.
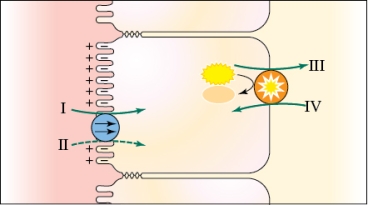 Which letter in the figure represents glucose?
Which letter in the figure represents glucose?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which letter in the figure represents glucose?
Which letter in the figure represents glucose?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the figure shown.
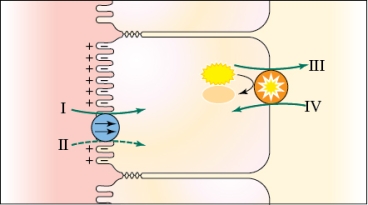 In the study of glucose transport, which pair of numerals in the figure represents the same ion?
In the study of glucose transport, which pair of numerals in the figure represents the same ion?
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) III and I
D) IV and II
 In the study of glucose transport, which pair of numerals in the figure represents the same ion?
In the study of glucose transport, which pair of numerals in the figure represents the same ion?A) I and II
B) II and III
C) III and I
D) IV and II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the figure shown.
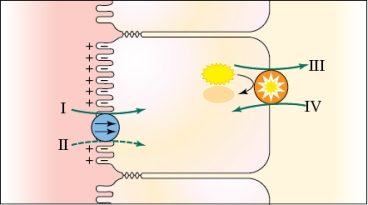 How does glucose cross the basolateral membrane?
How does glucose cross the basolateral membrane?
A) Via cotransport with Na+ at A
B) Via facilitated diffusion
C) Via active transport at C
D) Via simple diffusion
 How does glucose cross the basolateral membrane?
How does glucose cross the basolateral membrane?A) Via cotransport with Na+ at A
B) Via facilitated diffusion
C) Via active transport at C
D) Via simple diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the figure shown.
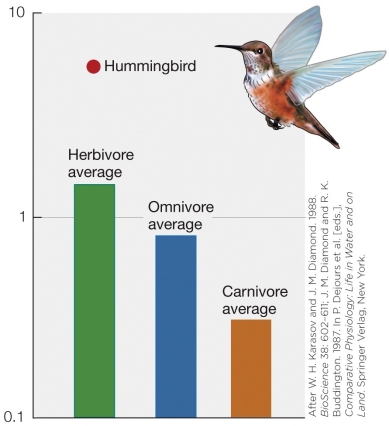 Which y-axis measurement would not be supported by the figure?
Which y-axis measurement would not be supported by the figure?
A) Total glucose uptake
B) Mass-specific metabolic rate
C) Glucose uptake per unit surface area of small intestine
D) Glucose uptake per gram of animal weight
 Which y-axis measurement would not be supported by the figure?
Which y-axis measurement would not be supported by the figure?A) Total glucose uptake
B) Mass-specific metabolic rate
C) Glucose uptake per unit surface area of small intestine
D) Glucose uptake per gram of animal weight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the figure shown.
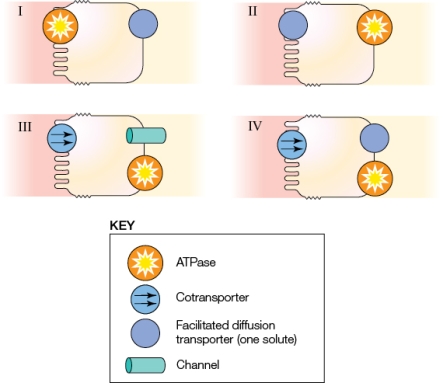 Which of the panels in the figure represents passive diffusion?
Which of the panels in the figure represents passive diffusion?
A) I and II
B) III
B) III and IV
D) I, II, and IV
 Which of the panels in the figure represents passive diffusion?
Which of the panels in the figure represents passive diffusion?A) I and II
B) III
B) III and IV
D) I, II, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the figure shown.
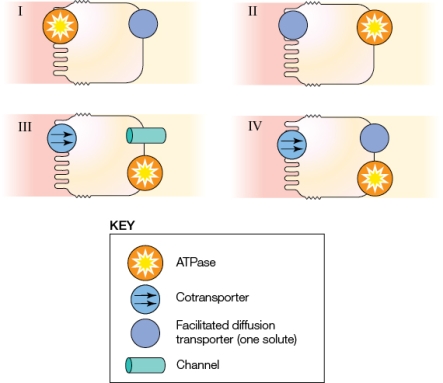 Which of the panels most accurately represents the mechanism for glucose transport at the epithelium?
Which of the panels most accurately represents the mechanism for glucose transport at the epithelium?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which of the panels most accurately represents the mechanism for glucose transport at the epithelium?
Which of the panels most accurately represents the mechanism for glucose transport at the epithelium?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements about ion transport in the typical freshwater fish gill is true?
A) Na+ and HCO3‒ are transported into the blood plasma.
B) Na+ and Cl‒ are transported into the water.
C) H+ and K+ are transported into the water.
D) Na+ and Cl‒ are transported into the blood plasma
A) Na+ and HCO3‒ are transported into the blood plasma.
B) Na+ and Cl‒ are transported into the water.
C) H+ and K+ are transported into the water.
D) Na+ and Cl‒ are transported into the blood plasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which statement regarding channels and transporters is false?
A) Multiple molecular forms of channel and transporter proteins are common.
B) Channel and transporter proteins have rapid turnover on the plasma membrane.
C) Channel and transporter proteins are subject to covalent and noncovalent modulation.
D) Channel and transporter proteins can be inserted into or retrieved from the plasma membrane.
A) Multiple molecular forms of channel and transporter proteins are common.
B) Channel and transporter proteins have rapid turnover on the plasma membrane.
C) Channel and transporter proteins are subject to covalent and noncovalent modulation.
D) Channel and transporter proteins can be inserted into or retrieved from the plasma membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The number of dissolved entities per unit of volume defines
A) colligative properties.
B) osmotic pressure.
C) osmolarity.
D) ultrafiltration.
A) colligative properties.
B) osmotic pressure.
C) osmolarity.
D) ultrafiltration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The osmotic pressure of a solution is _______ to the concentration of dissolved entities.
A) approximately proportional
B) specific
C) exponentially related
D) not related
A) approximately proportional
B) specific
C) exponentially related
D) not related

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A 1-M solution of Na2SO4 has _______ a 1-M solution of glucose.
A) one-third the osmolarity of
B) twice the osmolarity of
C) three times the osmolarity of
D) the same osmolarity as
A) one-third the osmolarity of
B) twice the osmolarity of
C) three times the osmolarity of
D) the same osmolarity as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A 1-osmolar solution has _______ dissolved entities per liter.
A) 1 kg of
B) 1 dalton of
C) 1.0 × 1023 independent
D) 6.022 × 1023 independent
A) 1 kg of
B) 1 dalton of
C) 1.0 × 1023 independent
D) 6.022 × 1023 independent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Most marine invertebrates typically have internal fluids of
A) 1 mOsm.
B) 1 Osm.
C) 10 Osm.
D) 300 mOsm.
A) 1 mOsm.
B) 1 Osm.
C) 10 Osm.
D) 300 mOsm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Most terrestrial vertebrates typically have internal fluids of approximately
A) 1 mOsm.
B) 1 Osm.
C) 10 Osm.
D) 300 mOsm.
A) 1 mOsm.
B) 1 Osm.
C) 10 Osm.
D) 300 mOsm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A 1-M solution of serum albumin (66,000 daltons) has _______ a 1-M solution of urea (66 daltons).
A) one-thousandth the osmolarity of
B) twice the osmolarity of
C) one thousand times the osmolarity of
D) the same osmolarity as
A) one-thousandth the osmolarity of
B) twice the osmolarity of
C) one thousand times the osmolarity of
D) the same osmolarity as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the figure shown. Assume that the two pistons have the same mass and move without friction, the center membrane in the diagram is permeable only to water, and solutes are shaded according to concentration (the darker the shading, the higher the concentration).
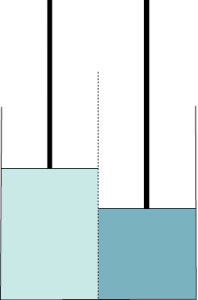 If the diagram represents the starting condition, what will occur as the solutions achieve equilibrium?
If the diagram represents the starting condition, what will occur as the solutions achieve equilibrium?
A) The left piston will move up.
B) The solutes will move but the pistons will not.
C) The right piston will move up.
D) The solutes will move to the left.
 If the diagram represents the starting condition, what will occur as the solutions achieve equilibrium?
If the diagram represents the starting condition, what will occur as the solutions achieve equilibrium?A) The left piston will move up.
B) The solutes will move but the pistons will not.
C) The right piston will move up.
D) The solutes will move to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the figure shown. Assume that the two pistons have the same mass and move without friction, the center membrane in the diagram is permeable only to water, and solutes are shaded according to concentration (the darker the shading, the higher the concentration).
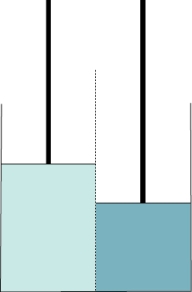 If a piston moved up because of water movement, could it be physically pushed back down to force water through the membrane?
If a piston moved up because of water movement, could it be physically pushed back down to force water through the membrane?
A) Yes, the physical pressure would oppose the osmotic pressure.
B) No, solutes would oppose the physical pressure.
D) Yes, and this would generate more charge on the membrane.
E) Yes, but only if the membrane were permeable to the solute.
 If a piston moved up because of water movement, could it be physically pushed back down to force water through the membrane?
If a piston moved up because of water movement, could it be physically pushed back down to force water through the membrane?A) Yes, the physical pressure would oppose the osmotic pressure.
B) No, solutes would oppose the physical pressure.
D) Yes, and this would generate more charge on the membrane.
E) Yes, but only if the membrane were permeable to the solute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Refer to the figure shown. Assume that the two pistons have the same mass and move without friction, the center membrane in the diagram is permeable only to water, and solutes are shaded according to concentration (the darker the shading, the higher the concentration).
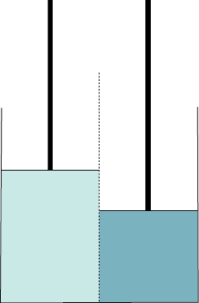 The piston on the left would move upward if the membrane were permeable to only _______ and the solution on the left was _______ and the solution on the right was _______.
The piston on the left would move upward if the membrane were permeable to only _______ and the solution on the left was _______ and the solution on the right was _______.
A) Na+; 1 M Na+; 3 M Cl‒
B) Cl‒; 1 M Cl‒; 3 M Na+
C) water and Na+; 2 M Cl‒; 3 M Na+
D) Ca2+; 1 M Na+; 3 M Ca2+
 The piston on the left would move upward if the membrane were permeable to only _______ and the solution on the left was _______ and the solution on the right was _______.
The piston on the left would move upward if the membrane were permeable to only _______ and the solution on the left was _______ and the solution on the right was _______.A) Na+; 1 M Na+; 3 M Cl‒
B) Cl‒; 1 M Cl‒; 3 M Na+
C) water and Na+; 2 M Cl‒; 3 M Na+
D) Ca2+; 1 M Na+; 3 M Ca2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which statement regarding osmosis is true?
A) Water cannot be described in terms of concentration.
B) Osmotic pressure is inversely proportional to temperature.
C) Large concentration gradients across cell membranes can generate osmotic pressure.
D) Osmosis applies only to the movement of salts.
A) Water cannot be described in terms of concentration.
B) Osmotic pressure is inversely proportional to temperature.
C) Large concentration gradients across cell membranes can generate osmotic pressure.
D) Osmosis applies only to the movement of salts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The passive transport of water across a membrane is called
A) facilitated diffusion.
B) diffusion.
C) osmosis.
D) osmotic pressure.
A) facilitated diffusion.
B) diffusion.
C) osmosis.
D) osmotic pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When two solutions exchange water by osmosis, water always moves
A) from the solution with the lower osmotic pressure to the one with the higher osmotic pressure.
B) from the solution with the higher osmotic pressure to the one with the lower osmotic pressure.
C) via facilitated diffusion.
D) from the lowest water concentration to the highest water concentration.
A) from the solution with the lower osmotic pressure to the one with the higher osmotic pressure.
B) from the solution with the higher osmotic pressure to the one with the lower osmotic pressure.
C) via facilitated diffusion.
D) from the lowest water concentration to the highest water concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If you were to drop a mammalian red blood cell into a 10 mOsm solution, the red cell would _______ in this _______ solution.
A) shrivel; hyposmotic
B) swell and burst; hyposmotic
C) swell and burst; hyperosmotic
D) shrivel; hyperosmotic
A) shrivel; hyposmotic
B) swell and burst; hyposmotic
C) swell and burst; hyperosmotic
D) shrivel; hyperosmotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Channel mediated water transport defines a type of
A) active transport specific to aquaporins.
B) passive diffusion specific to aquaporins.
C) facilitated diffusion specific to aquaporins.
D) active transport generally seen in most cells.
A) active transport specific to aquaporins.
B) passive diffusion specific to aquaporins.
C) facilitated diffusion specific to aquaporins.
D) active transport generally seen in most cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Choose the situation that would generate the greatest amount of hydrostatic pressure.
A) 1-M glucose solution interacting with a 2-M NaCl solution
B) 1-M glucose solution
C) 2-M NaCl solution
D) 2-M glucose solution interacting with a 1-M NaCl solution
A) 1-M glucose solution interacting with a 2-M NaCl solution
B) 1-M glucose solution
C) 2-M NaCl solution
D) 2-M glucose solution interacting with a 1-M NaCl solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Discuss how a boundary layer forms outside of a cell and how it can impede further diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The inside of a typical animal cell is negatively charged. Therefore, it makes sense that Na+ diffuses into the cell if there are channels that allow it to do so. Considering K+ has the same charge as Na+, why will it diffuse out of the cell if there are channels that allow it to do so?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Discuss the electrochemical equilibrium of Cl‒ across a typical animal cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In what way does facilitated diffusion resemble simple diffusion as well as active transport?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Briefly describe how the Na+‒K+-ATPase operates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Why is glucose transport through the apical membrane considered secondary active transport?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is meant by the "whole-epithelium" view of active ion transport? Provide an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Describe four ways in which channel and transporter proteins can be regulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Support or refute the following statement and provide evidence for your

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How can hydrostatic pressure develop from osmotic pressure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



