Deck 2: Molecules and Cells in Animal Physiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Molecules and Cells in Animal Physiology
1
How does venom permit a slow-moving predator to feed on prey capable of high-speed escape?
A) Venom disrupts sensory systems such that the prey can no longer detect the predator.
B) Venom disrupts the ability of the prey to digest food and thus have the energy to escape.
C) Venom shuts down the ability of the prey to move very far.
D) Venom confuses the prey such that it may run back in the direction of the predator.
A) Venom disrupts sensory systems such that the prey can no longer detect the predator.
B) Venom disrupts the ability of the prey to digest food and thus have the energy to escape.
C) Venom shuts down the ability of the prey to move very far.
D) Venom confuses the prey such that it may run back in the direction of the predator.
C
2
Why have many venomous animals evolved venoms that break down phospholipids?
A) Phospholipids are an important component of venom.
B) Phospholipids are important in sensing predators.
C) Phospholipids are the key to muscular contraction.
D) Phospholipids are the fundamental structure of all cell membranes and intracellular membranes.
A) Phospholipids are an important component of venom.
B) Phospholipids are important in sensing predators.
C) Phospholipids are the key to muscular contraction.
D) Phospholipids are the fundamental structure of all cell membranes and intracellular membranes.
D
3
Which molecule is part of a cell membrane?
A) Cholesterol
B) Ubiquitin
C) Cyclic AMP
D) Calmodulin
A) Cholesterol
B) Ubiquitin
C) Cyclic AMP
D) Calmodulin
A
4
A molecule that consists of a polar portion and a nonpolar portion is said to be
A) hydrophilic.
B) hydrophobic.
C) an integral protein.
D) amphipathic.
A) hydrophilic.
B) hydrophobic.
C) an integral protein.
D) amphipathic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A saturated hydrocarbon tends to
A) be more liquid at colder temperatures compared to an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
B) be more solid at colder temperatures compared to an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
C) contain many double bonds.
D) contain fewer carbon-carbon bonds compared to an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
A) be more liquid at colder temperatures compared to an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
B) be more solid at colder temperatures compared to an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
C) contain many double bonds.
D) contain fewer carbon-carbon bonds compared to an unsaturated hydrocarbon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Compared to fish found in lower temperature habitats, fish that inhabit higher temperatures tend to have more
A) saturated phospholipids in their brain synaptic membranes.
B) saturated phospholipids in their brain proteins.
C) unsaturated phospholipids in their brain synaptic membranes.
D) unsaturated phospholipids in their brain proteins.
A) saturated phospholipids in their brain synaptic membranes.
B) saturated phospholipids in their brain proteins.
C) unsaturated phospholipids in their brain synaptic membranes.
D) unsaturated phospholipids in their brain proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which membrane protein is responsible for the passive movement of K+ across the typical animal cell membrane?
A) Channel
B) Enzyme
C) Transporter
D) Receptor
A) Channel
B) Enzyme
C) Transporter
D) Receptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which molecule is a functional membrane protein?
A) Acetylcholine
B) Cholesterol
C) The Na+‒K+ pump
D) Calmodulin
A) Acetylcholine
B) Cholesterol
C) The Na+‒K+ pump
D) Calmodulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Choose a feature that is not common to all simple epithelia.
A) microvilli
B) basement membrane
C) nucleus in each cell
E) apical surface
A) microvilli
B) basement membrane
C) nucleus in each cell
E) apical surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A ring of _______ demarcates the apical surface of the cell from its lateral and basal surfaces.
A) tight junctions
B) septate junctions
C) gap junctions
E) microvilli
A) tight junctions
B) septate junctions
C) gap junctions
E) microvilli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is considered a communicating junction?
A) Gap junction
B) Tight junction
C) Septate junction
D) Desmosome
A) Gap junction
B) Tight junction
C) Septate junction
D) Desmosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a protein is denatured, which of the following structures is disrupted first?
A) Primary
B) Secondary
C) Tertiary
D) Quarternary
A) Primary
B) Secondary
C) Tertiary
D) Quarternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a protein in situ becomes partially denatured because of high temperature, the denaturation can be reversed by a
A) molecular chaperone.
B) proteasome.
C) ubiquitin.
D) peptidase.
A) molecular chaperone.
B) proteasome.
C) ubiquitin.
D) peptidase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following tags proteins for destruction?
A) Proteasome
B) Ubiquitin
C) Molecular chaperone
D) Heat-shock protein
A) Proteasome
B) Ubiquitin
C) Molecular chaperone
D) Heat-shock protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
How can amino acids in a protein be any closer to one another than their spaced positions in the linear string?
A) Many amino acids break their covalent bonds in the linear arrangement and form closer ionic bonding arrangements.
B) Amino acids in their linear primary structure are constantly breaking and reforming their covalent bonds. When they are not in a bonding arrangement, they can be closer to adjacent amino acids temporarily.
C) As amino acid chains fold into their tertiary structure, this commonly brings some amino acids closer together than their linear spaced positions.
D) Amino acids only form covalent bonds with one another and do not associate with one another at a distance closer than the covalent bond.
A) Many amino acids break their covalent bonds in the linear arrangement and form closer ionic bonding arrangements.
B) Amino acids in their linear primary structure are constantly breaking and reforming their covalent bonds. When they are not in a bonding arrangement, they can be closer to adjacent amino acids temporarily.
C) As amino acid chains fold into their tertiary structure, this commonly brings some amino acids closer together than their linear spaced positions.
D) Amino acids only form covalent bonds with one another and do not associate with one another at a distance closer than the covalent bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What drives the ATP protein machine?
A) Na+
B) The gradient of H+ across the membrane
C) ATP
D) The movement of electrons
A) Na+
B) The gradient of H+ across the membrane
C) ATP
D) The movement of electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why have many venomous animals evolved venoms that disrupt the gating mechanism of the voltage-gated sodium channel?
A) Disrupting the voltage-gated sodium channel would slow the prey's metabolism.
B) Disrupting the voltage-gated sodium channel would slow the prey's ability to manufacture ATP.
C) Disrupting the voltage-gated sodium channel would block oxygen transport.
D) Disrupting the voltage-gated sodium channel would disrupt the nervous system.
A) Disrupting the voltage-gated sodium channel would slow the prey's metabolism.
B) Disrupting the voltage-gated sodium channel would slow the prey's ability to manufacture ATP.
C) Disrupting the voltage-gated sodium channel would block oxygen transport.
D) Disrupting the voltage-gated sodium channel would disrupt the nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
_______ is(are) the specific set of processes by which complex chemical compounds are broken down to release energy, create smaller chemical building blocks, or prepare chemical constituents for elimination.
A) Metabolism
B) Catabolism
C) Anabolism
D) Biochemical reactions
A) Metabolism
B) Catabolism
C) Anabolism
D) Biochemical reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Per gram, the leopard frog can jump farther per jump compared to the western toad because the leopard frog
A) is insensitive to lactic acid.
B) tends to live in warmer climates.
C) has a higher aerobic capacity.
D) creates more lactic acid per unit time.
A) is insensitive to lactic acid.
B) tends to live in warmer climates.
C) has a higher aerobic capacity.
D) creates more lactic acid per unit time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which statement regarding enzymes is false?
A) All enzymes are catalysts.
B) Enzymes have substrates and products.
C) Enzymes speed chemical reactions.
D) All catalysts are enzymes.
A) All enzymes are catalysts.
B) Enzymes have substrates and products.
C) Enzymes speed chemical reactions.
D) All catalysts are enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which reaction is catalyzed by LDH?
A) Pyruvic acid + NADH2 → lactic acid + NAD
B) Pyruvic acid + NAD → pyruvic acid + NADH2
C) Pyruvic acid + NAD → lactic acid + NADH2
D) Lactic acid + NADH2 → pyruvic acid + NAD
A) Pyruvic acid + NADH2 → lactic acid + NAD
B) Pyruvic acid + NAD → pyruvic acid + NADH2
C) Pyruvic acid + NAD → lactic acid + NADH2
D) Lactic acid + NADH2 → pyruvic acid + NAD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The amount of substrate converted to product per unit of time is called the
A) turnover number.
B) saturated speed.
C) Vmax.
D) reaction velocity.
A) turnover number.
B) saturated speed.
C) Vmax.
D) reaction velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Turnover number (kcat) describes what property of an enzymatic reaction?
A) Activation energy
B) Catalytic effectiveness
C) Enzyme‒substrate affinity
D) The transition state
A) Activation energy
B) Catalytic effectiveness
C) Enzyme‒substrate affinity
D) The transition state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The likelihood that an enzyme will form a complex with the substrate during a collision is called the
A) catalytic effectiveness.
B) activation energy.
C) enzyme‒substrate affinity.
D) transition state.
A) catalytic effectiveness.
B) activation energy.
C) enzyme‒substrate affinity.
D) transition state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An enzymatic reaction is proceeding at subsaturation. Which of the following is not a means by which the enzymatic reaction can be increased?
A) Adding more substrate
B) Adding more enzyme
C) Increasing the catalytic effectiveness
D) Increasing the temperature
A) Adding more substrate
B) Adding more enzyme
C) Increasing the catalytic effectiveness
D) Increasing the temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure shown.
 Which of the following represent the best labels for the x axis and the y axis in the figure?
Which of the following represent the best labels for the x axis and the y axis in the figure?
A) x = Substrate concentration; y = Reaction velocity
B) x = Enzyme concentration; y = Reaction velocity
C) x = Time; y = Substrate concentration
D) x = Time; y = Enzyme‒substrate conversion rate
 Which of the following represent the best labels for the x axis and the y axis in the figure?
Which of the following represent the best labels for the x axis and the y axis in the figure?A) x = Substrate concentration; y = Reaction velocity
B) x = Enzyme concentration; y = Reaction velocity
C) x = Time; y = Substrate concentration
D) x = Time; y = Enzyme‒substrate conversion rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the figure shown.
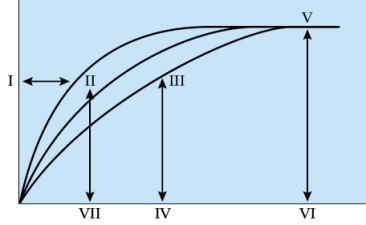 Which letter in the figure represents high affinity?
Which letter in the figure represents high affinity?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) V
 Which letter in the figure represents high affinity?
Which letter in the figure represents high affinity?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure shown.
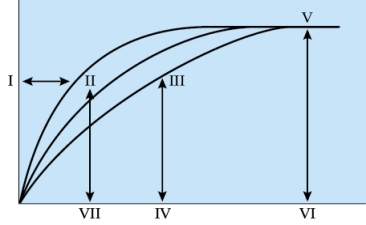 Which letter in the figure best represents the Vmax?
Which letter in the figure best represents the Vmax?
A) VI
B) I
C) III
D) V
 Which letter in the figure best represents the Vmax?
Which letter in the figure best represents the Vmax?A) VI
B) I
C) III
D) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure shown.
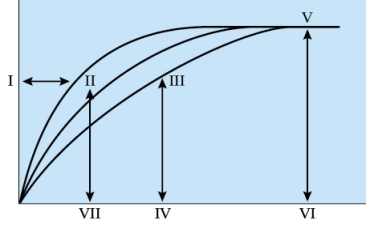 In the figure, which region best represents the Km of the highest affinity enzyme?
In the figure, which region best represents the Km of the highest affinity enzyme?
A) I
B) II
C) VII
D) IV
 In the figure, which region best represents the Km of the highest affinity enzyme?
In the figure, which region best represents the Km of the highest affinity enzyme?A) I
B) II
C) VII
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the figure shown.
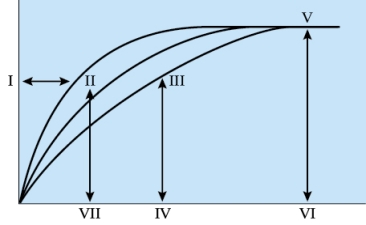 If more substrate is added to the reaction system of line C in the figure, what would be the most likely outcome?
If more substrate is added to the reaction system of line C in the figure, what would be the most likely outcome?
A) The curve of line C would shift toward line B.
B) The Vmax will increase.
C) Km will decrease.
D) The curve will remain the same.
 If more substrate is added to the reaction system of line C in the figure, what would be the most likely outcome?
If more substrate is added to the reaction system of line C in the figure, what would be the most likely outcome?A) The curve of line C would shift toward line B.
B) The Vmax will increase.
C) Km will decrease.
D) The curve will remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Human LDH-B4 and rat LDH-B4 are examples of
A) isozymes.
B) analogous enzymes.
C) isoenzymes.
D) interspecific enzyme homologs.
A) isozymes.
B) analogous enzymes.
C) isoenzymes.
D) interspecific enzyme homologs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An enzyme-encoding gene is considered to be _______ within a cell if the gene results in the synthesis of the encoded enzyme within that same cell.
A) promoted
B) induced
C) expressed
D) enhanced
A) promoted
B) induced
C) expressed
D) enhanced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
_______ enzymes are present in a tissue in relatively high and steady amounts regardless of conditions, whereas _______ enzymes are present at low levels (or not at all) in a tissue unless their synthesis is activated.
A) Inducible; constitutive
B) Promotable; constitutive
C) Constitutive; inducible
D) Expressed; promotable
A) Inducible; constitutive
B) Promotable; constitutive
C) Constitutive; inducible
D) Expressed; promotable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement regarding allosteric modulation is true?
A) The binding of an allosteric modulator follows the law of mass action.
B) The binding of an allosteric modulator is irreversible.
C) An allosteric modulator, when present, will always bind to the enzyme it modulates.
D) The binding of an allosteric modulator always increases the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
A) The binding of an allosteric modulator follows the law of mass action.
B) The binding of an allosteric modulator is irreversible.
C) An allosteric modulator, when present, will always bind to the enzyme it modulates.
D) The binding of an allosteric modulator always increases the catalytic activity of the enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is directly involved in covalent modulation?
A) The Na+‒K+ pump
B) Protein kinases
C) van der Waals interactions
D) Calcium
A) The Na+‒K+ pump
B) Protein kinases
C) van der Waals interactions
D) Calcium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the figure shown.
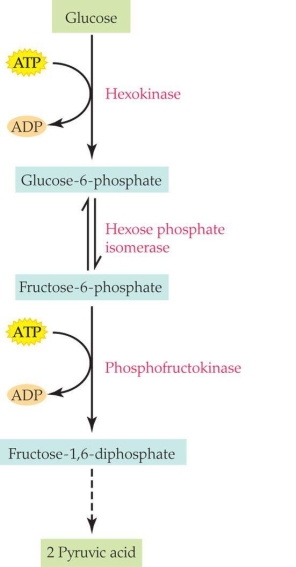 How many different enzymes are catalyzing reactions?
How many different enzymes are catalyzing reactions?
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five
 How many different enzymes are catalyzing reactions?
How many different enzymes are catalyzing reactions?A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the figure shown.
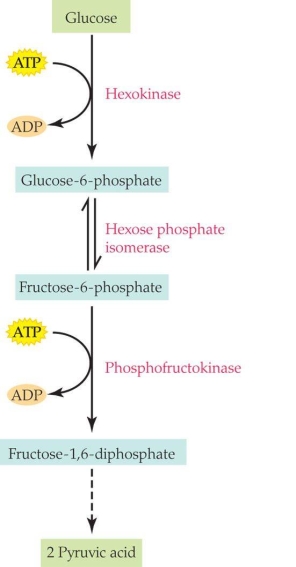 According to the figure, a high number of products from the Kreb's cycle could act as _______ and result in _______ of the overall reaction.
According to the figure, a high number of products from the Kreb's cycle could act as _______ and result in _______ of the overall reaction.
A) covalent modulators; inhibition
B) covalent modulators; acceleration
C) allosteric modulators; inhibition
D) allosteric modulators; acceleration
 According to the figure, a high number of products from the Kreb's cycle could act as _______ and result in _______ of the overall reaction.
According to the figure, a high number of products from the Kreb's cycle could act as _______ and result in _______ of the overall reaction.A) covalent modulators; inhibition
B) covalent modulators; acceleration
C) allosteric modulators; inhibition
D) allosteric modulators; acceleration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A protein kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of another protein kinase, which in turn catalyzes the phosphorylation of a third protein kinase. This series of multiple enzyme sequences is an excellent example of
A) amplification.
B) a rate-limiting reaction.
C) inducing enzymes.
D) allosteric regulation.
A) amplification.
B) a rate-limiting reaction.
C) inducing enzymes.
D) allosteric regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The _______ is(are) directly responsible for the amplifying effects during a second messenger cascade.
A) receptors
B) substrates
C) enzymes
D) cell membrane
A) receptors
B) substrates
C) enzymes
D) cell membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the figure shown.
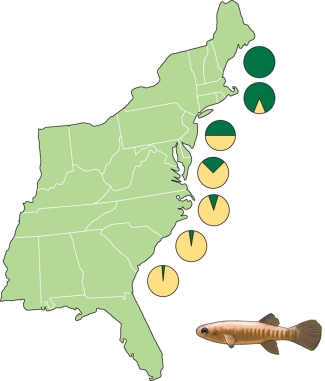 Which abiotic factor most likely explains the data in the figure?
Which abiotic factor most likely explains the data in the figure?
A) LDH expression
B) Allele frequencies
C) Temperature
D) Predation
 Which abiotic factor most likely explains the data in the figure?
Which abiotic factor most likely explains the data in the figure?A) LDH expression
B) Allele frequencies
C) Temperature
D) Predation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Refer to the figure shown.
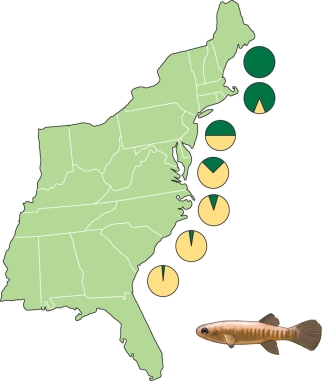 The figure shows the
The figure shows the
A) frequency distribution of two predators on killifish.
B) frequency distribution of two different alleles of the gene for LDH.
C) frequency distribution of two main diets of killifish.
D) temperature tolerance of two subtypes of killifish.
 The figure shows the
The figure shows theA) frequency distribution of two predators on killifish.
B) frequency distribution of two different alleles of the gene for LDH.
C) frequency distribution of two main diets of killifish.
D) temperature tolerance of two subtypes of killifish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the figure shown.
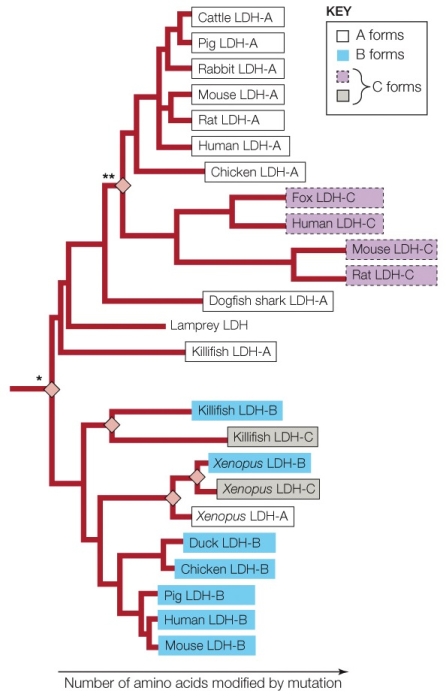 What is the best explanation for why mammalian and fish LDH-C enzymes are shown to be so distantly related?
What is the best explanation for why mammalian and fish LDH-C enzymes are shown to be so distantly related?
A) Many separate gene duplication events created the C version of LDH.
B) The tree is based on LDH-A relationships, so it does not accurately show how closely related the LHD-C versions are to one another.
C) The enzymes were named before the actual evolutionary relationships were known.
D) The tree is separated based on animal phyla, not LDH.
 What is the best explanation for why mammalian and fish LDH-C enzymes are shown to be so distantly related?
What is the best explanation for why mammalian and fish LDH-C enzymes are shown to be so distantly related?A) Many separate gene duplication events created the C version of LDH.
B) The tree is based on LDH-A relationships, so it does not accurately show how closely related the LHD-C versions are to one another.
C) The enzymes were named before the actual evolutionary relationships were known.
D) The tree is separated based on animal phyla, not LDH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to the figure shown.
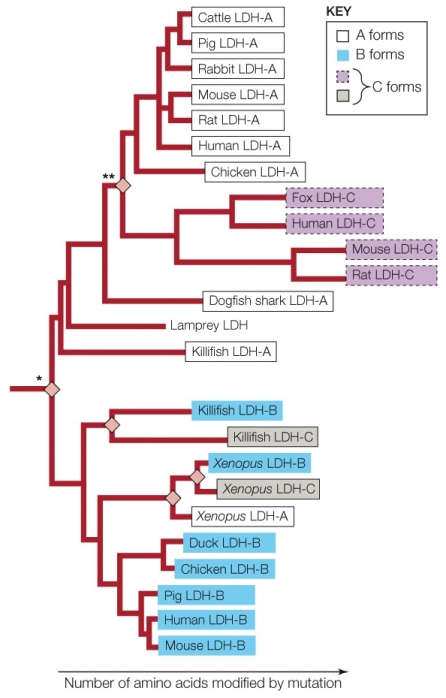 The diamonds refer to
The diamonds refer to
A) genetic divergence.
B) gene duplication.
C) mutations.
D) speciation.
 The diamonds refer to
The diamonds refer toA) genetic divergence.
B) gene duplication.
C) mutations.
D) speciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In rats, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity per gram of liver significantly increases at birth and remains at this higher level for the life of the animal. This is an example of enzymatic change that takes place over a(n) _______ time frame.
A) acute
B) chronic
C) evolutionary
D) developmental
A) acute
B) chronic
C) evolutionary
D) developmental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The process of absorbing preexisting light and re-emitting it at longer wavelengths is called
A) bioluminescence.
B) reflection.
C) chromatophoration.
D) fluorescence.
A) bioluminescence.
B) reflection.
C) chromatophoration.
D) fluorescence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The ability of animals to change color in seconds or minutes depends on the function of
A) photocytes.
B) chromatophores.
C) photoproteins.
D) luciferin.
A) photocytes.
B) chromatophores.
C) photoproteins.
D) luciferin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Intracellular modification of activity in response to an external signal is an example of
A) transduction.
B) transformation.
C) conversion.
D) covalent modulation.
A) transduction.
B) transformation.
C) conversion.
D) covalent modulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Extracellular signaling molecules initiate their actions on a cell by binding with certain protein molecules of the cell called
A) ligands.
B) peripheral proteins.
C) integral proteins.
D) receptors.
A) ligands.
B) peripheral proteins.
C) integral proteins.
D) receptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following statements regarding the ligand-gated receptor is false?
A) The naturally occurring ligand can cause the associated protein channel to open.
B) The naturally occurring ligand should bind irreversibly to the receptor until it breaks down.
C) A similarly shaped foreign ligand can attach to the receptor and block the naturally occurring ligand from binding.
D) A ligand can attach to the receptor and activate an intracellular catalytic site on the same molecule.
A) The naturally occurring ligand can cause the associated protein channel to open.
B) The naturally occurring ligand should bind irreversibly to the receptor until it breaks down.
C) A similarly shaped foreign ligand can attach to the receptor and block the naturally occurring ligand from binding.
D) A ligand can attach to the receptor and activate an intracellular catalytic site on the same molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Receptor proteins can bring about all of the following cellular actions except
A) reinforcing the structure of the membrane.
B) opening a protein channel on the membrane.
C) activating an enzyme on the intracellular surface.
D) combining with a ligand to initiate transcription.
A) reinforcing the structure of the membrane.
B) opening a protein channel on the membrane.
C) activating an enzyme on the intracellular surface.
D) combining with a ligand to initiate transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The α-conotoxin injected into fish by the cone snail binds to and therefore blocks receptor sites on the muscle membrane. This prevents a(n)
A) enzyme from being activated.
B) G protein from being activated.
C) channel from opening into the nucleus.
D) channel from opening.
A) enzyme from being activated.
B) G protein from being activated.
C) channel from opening into the nucleus.
D) channel from opening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which reaction does not directly produce an amplification?
A) Activation of a G protein by an activated receptor
B) Formation of cyclic AMP by catalyzing action of adenylyl cyclase
C) Activation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase by active cAMP-dependent protein kinase
D) Opening of a ligand-gated channel on the membrane
A) Activation of a G protein by an activated receptor
B) Formation of cyclic AMP by catalyzing action of adenylyl cyclase
C) Activation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase by active cAMP-dependent protein kinase
D) Opening of a ligand-gated channel on the membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which substance is considered a second messenger?
A) IP3-gated calcium channel
B) Calcium
C) Epinephrine
D) Adenylyl cyclase
A) IP3-gated calcium channel
B) Calcium
C) Epinephrine
D) Adenylyl cyclase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
As a second messenger, calcium typically binds to
A) calmodulin, and the complex activates protein kinases.
B) a G protein to activate general second messengers.
C) cyclic AMP to activate cAMP-dependent protein kinases.
D) inositol triphosphate to activate the endoplasmic reticulum.
A) calmodulin, and the complex activates protein kinases.
B) a G protein to activate general second messengers.
C) cyclic AMP to activate cAMP-dependent protein kinases.
D) inositol triphosphate to activate the endoplasmic reticulum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Steroid hormones bind to _______ and ultimately cause _______.
A) specific intracellular membrane proteins; the opening of ion channels
B) specific intracellular receptor proteins; gene expression
C) specific extracellular receptor proteins; the opening of ion channels
D) specific extracellular membrane proteins; gene expression
A) specific intracellular membrane proteins; the opening of ion channels
B) specific intracellular receptor proteins; gene expression
C) specific extracellular receptor proteins; the opening of ion channels
D) specific extracellular membrane proteins; gene expression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Provide a specific example of how a membrane protein can be categorized as more than one functional type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Describe what it means for a phospholipid to be amphipathic and how this feature is paramount in the formation of the membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Describe how epithelial cells control the transport of substances between the apical and basal sides and thus between different body regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Define the law of mass action and apply it to a real biochemical reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Compare and contrast the factors affecting the rate of an enzymatic reaction in a substrate that is subsaturated and one that is saturated or at Vmax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe how amplification works in the cell and why it is important.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How does the killifish demonstrate the present-day operation of evolutionary forces?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Compare and contrast bioluminescence and fluorescence and describe the light production of the hydromedusan jellyfish (Aequorea victoria).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
List and briefly describe the four types of receptor proteins involved in cell signaling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Describe how a simple ion such as calcium is used as a second messenger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



