Deck 8: The Skeletal System: Articulations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/131
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: The Skeletal System: Articulations
1
Which of the following is a function of synovial fluid?
A) acts as a shock absorber
B) prevents movement
C) channels the flow of blood
D) restricts joint movement
E) strengthens and reinforces the joint
A) acts as a shock absorber
B) prevents movement
C) channels the flow of blood
D) restricts joint movement
E) strengthens and reinforces the joint
A
2
The structure that surrounds a synovial joint is called (a)________.
A) meniscus
B) joint capsule
C) synovial membrane
D) bursa
E) fat pad
A) meniscus
B) joint capsule
C) synovial membrane
D) bursa
E) fat pad
B
3
Movement of joints may occur along how many possible axes of motion?
A) three
B) two
C) one
D) five
E) four
A) three
B) two
C) one
D) five
E) four
A
4
Damage to a joint so that it is slightly dislocated is called a ________.
A) luxation
B) subluxation
C) complete dislocation
D) separation
E) strain
A) luxation
B) subluxation
C) complete dislocation
D) separation
E) strain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a classification of a joint in which the bones are separated by a pad of fibrous cartilage?
A) ball and socket
B) gliding
C) pivot
D) symphysis
E) hinge
A) ball and socket
B) gliding
C) pivot
D) symphysis
E) hinge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Movement in the anterior-posterior plane that decreases the angle between the articulating elements is ________.
A) abduction
B) adduction
C) extension
D) rotation
E) flexion
A) abduction
B) adduction
C) extension
D) rotation
E) flexion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is the correct classification for the distal articulation between the tibia and fibula, and the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna?
A) gomphosis
B) suture
C) syndesmosis
D) synchondrosis
E) synostosis
A) gomphosis
B) suture
C) syndesmosis
D) synchondrosis
E) synostosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An accessory structure of a joint that may subdivide a synovial cavity, channel the flow of synovial fluid, or allow for variations in the shapes of the articular surfaces is a ________.
A) ligament
B) bursa
C) meniscus
D) fat pad
E) tendon
A) ligament
B) bursa
C) meniscus
D) fat pad
E) tendon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The type of joint formed by the joining of the diaphysis and each epiphysis is called a ________.
A) gomphosis
B) synchondrosis
C) synostosis
D) symphysis
E) suture
A) gomphosis
B) synchondrosis
C) synostosis
D) symphysis
E) suture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Small, synovial fluid-filled pockets in connective tissue are called ________.
A) tendons
B) intrinsic ligaments
C) fat pads
D) bursae
E) extrinsic ligaments
A) tendons
B) intrinsic ligaments
C) fat pads
D) bursae
E) extrinsic ligaments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A specialized form of fibrous synarthrosis that binds each tooth to the surrounding bony socket is a ________.
A) syndesmosis
B) symphysis
C) synchondrosis
D) gomphosis
E) synostosis
A) syndesmosis
B) symphysis
C) synchondrosis
D) gomphosis
E) synostosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Accessory structures found around the joint periphery, which provide packing material and fill spaces created when the joint cavity changes shape, are called ________.
A) fat pads
B) menisci
C) bursae
D) tendons
E) ligaments
A) fat pads
B) menisci
C) bursae
D) tendons
E) ligaments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A cartilaginous joint that permits slight movement is (a)________.
A) symphysis
B) synovial joint
C) synostosis
D) synchondrosis
E) gomphosis
A) symphysis
B) synovial joint
C) synostosis
D) synchondrosis
E) gomphosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following associations describes the shoulder joint?
A) uniaxial-hinge
B) biaxial-condyloid
C) triaxial-ball and socket
D) monaxial-hinge
E) None of the answers are correct.
A) uniaxial-hinge
B) biaxial-condyloid
C) triaxial-ball and socket
D) monaxial-hinge
E) None of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An example of angular motion away from the longitudinal axis of the body in the frontal plane is ________.
A) flexion
B) abduction
C) extension
D) rotation
E) adduction
A) flexion
B) abduction
C) extension
D) rotation
E) adduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following associations is most accurate?
A) synarthroses-slightly movable
B) amphiarthroses-freely movable
C) diarthroses-immovable
D) diarthroses-synovial
E) gomphoses-slightly movable
A) synarthroses-slightly movable
B) amphiarthroses-freely movable
C) diarthroses-immovable
D) diarthroses-synovial
E) gomphoses-slightly movable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A joint that permits free movement is called ________.
A) a synarthrosis
B) a synostosis
C) a diarthrosis
D) a synchondrosis
E) an amphiarthrosis
A) a synarthrosis
B) a synostosis
C) a diarthrosis
D) a synchondrosis
E) an amphiarthrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A fibrous synarthrosis joint that holds skull bones together is called (a)________.
A) suture
B) gomphosis
C) synchondrosis
D) synostosis
E) None of the answers are correct.
A) suture
B) gomphosis
C) synchondrosis
D) synostosis
E) None of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A dislocation, in which the articulating surfaces of a joint are forced entirely out of position, is called (a)________.
A) luxation
B) subluxation
C) congenital abnormality
D) symphysis
E) fracture
A) luxation
B) subluxation
C) congenital abnormality
D) symphysis
E) fracture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The first carpometacarpal joint and the wrist are ________ joints.
A) nonaxial
B) monoaxial
C) triaxial
D) quadaxial
E) biaxial
A) nonaxial
B) monoaxial
C) triaxial
D) quadaxial
E) biaxial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The condition called ________ may occur under severe compression, when the nucleus pulposus breaks through the annulus fibrosus.
A) rheumatoid arthritis
B) rheumatism
C) herniated disc
D) a sprain
E) None of the answers are correct.
A) rheumatoid arthritis
B) rheumatism
C) herniated disc
D) a sprain
E) None of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Intercarpal joints are ________.
A) ellipsoidal joints
B) hinge joints
C) plane joints
D) ball and socket joints
E) None of the answers are correct.
A) ellipsoidal joints
B) hinge joints
C) plane joints
D) ball and socket joints
E) None of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A painful condition associated with disc degeneration that affects the spinal nerves is called the ________.
A) bulging disc
B) herniated disc
C) intervertebral disc disease
D) sciata
E) ankylosing spondylitis
A) bulging disc
B) herniated disc
C) intervertebral disc disease
D) sciata
E) ankylosing spondylitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The joint that permits the greatest range of motion in the entire body is the ________.
A) hip
B) shoulder
C) knee
D) elbow
E) neck
A) hip
B) shoulder
C) knee
D) elbow
E) neck

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A joint that allows only rotational movements is called a ________.
A) circumductive joint
B) pivot joint
C) gliding joint
D) pronation joint
E) ball and socket
A) circumductive joint
B) pivot joint
C) gliding joint
D) pronation joint
E) ball and socket

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Moving a part of the body anteriorly in the horizontal plane is called ________.
A) flexion
B) opposition
C) retraction
D) protraction
E) extension
A) flexion
B) opposition
C) retraction
D) protraction
E) extension

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The ________ extends between the greater and lesser tubercles and holds the long head of the biceps brachii muscle in the intertubercular groove of the humerus.
A) coracoclavicular ligament
B) acromioclavicular ligament
C) glenohumeral ligament
D) transverse humeral ligament
E) coracoacromial ligament
A) coracoclavicular ligament
B) acromioclavicular ligament
C) glenohumeral ligament
D) transverse humeral ligament
E) coracoacromial ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The atlanto-axial joint is an example of a(n)________ joint.
A) gliding
B) pivot
C) saddle
D) ellipsoid
E) hinge
A) gliding
B) pivot
C) saddle
D) ellipsoid
E) hinge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The insertion of the ________ (an extracapsular structure of the temporomandibular joint)covers the posterior portion of the mylohyoid line.
A) lateral ligament
B) temporomandibular ligament
C) geniohyoid ligament
D) sphenomandibular ligament
E) stylomandibular ligament
A) lateral ligament
B) temporomandibular ligament
C) geniohyoid ligament
D) sphenomandibular ligament
E) stylomandibular ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The first carpometacarpal joint is an example of a/an ________.
A) hinge joint
B) ellipsoid joint
C) pivot joint
D) gliding joint
E) saddle joint
A) hinge joint
B) ellipsoid joint
C) pivot joint
D) gliding joint
E) saddle joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Pronation and supination occur at a/the ________.
A) humeroulnar joint
B) radio-ulnar joint
C) temporomandibular joint
D) glenohumeral joint
E) tibiofibular joint
A) humeroulnar joint
B) radio-ulnar joint
C) temporomandibular joint
D) glenohumeral joint
E) tibiofibular joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Joints between the superior and inferior articulating facets of adjacent vertebrae are called ________.
A) symphyses
B) gomphoses
C) synostoses
D) syndesmoses
E) zygapophysial joints
A) symphyses
B) gomphoses
C) synostoses
D) syndesmoses
E) zygapophysial joints

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
At the humeroradial joint, the ________ articulates with the head of the radius.
A) capitulum
B) greater tubercle
C) glenoid labrum
D) lesser tubercle
E) trochlea
A) capitulum
B) greater tubercle
C) glenoid labrum
D) lesser tubercle
E) trochlea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What movement occurs when the vertebral column bends to the side?
A) flexion
B) lateral flexion
C) abduction
D) elevation
E) adduction
A) flexion
B) lateral flexion
C) abduction
D) elevation
E) adduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is an example of angular motion?
A) depression
B) protraction
C) extension
D) eversion
E) opposition
A) depression
B) protraction
C) extension
D) eversion
E) opposition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
During a shoulder separation injury, which of the following structures is most likely to be damaged?
A) acromioclavicular ligament
B) coracohumeral ligament
C) coracoacromial ligament
D) sternoclavicular ligament
E) None of the answers are correct.
A) acromioclavicular ligament
B) coracohumeral ligament
C) coracoacromial ligament
D) sternoclavicular ligament
E) None of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The movement made at the proximal radioulnar joint when turning the palm of the hand upward is called ________.
A) extension
B) supination
C) flexion
D) retraction
E) pronation
A) extension
B) supination
C) flexion
D) retraction
E) pronation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which structure(s) , firmly attached to the superior border of the manubrium, prevents dislocation when the shoulder is depressed?
A) glenoid labrum
B) interclavicular ligament
C) anterior sternoclavicular ligament
D) costoclavicular ligament
E) glenohumeral ligament
A) glenoid labrum
B) interclavicular ligament
C) anterior sternoclavicular ligament
D) costoclavicular ligament
E) glenohumeral ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which ligament is often injured as a result of the repetitive, high-velocity motions involved in throwing?
A) radial collateral ligament
B) annular ligament
C) transverse humeral ligament
D) ulnar collateral ligament
E) coracoacromial ligament
A) radial collateral ligament
B) annular ligament
C) transverse humeral ligament
D) ulnar collateral ligament
E) coracoacromial ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The temporomandibular joint is ________.
A) amphiarthrotic
B) a symphysis
C) a gliding joint
D) actually made up of three separate joints
E) primarily a hinge joint
A) amphiarthrotic
B) a symphysis
C) a gliding joint
D) actually made up of three separate joints
E) primarily a hinge joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following are condylar joints in the foot that permit flexion/extension and abduction/adduction?
A) intertarsal joints
B) tarsometatarsal joints
C) metatarsophalangeal joints
D) interphalangeal joints
E) None of the answers are correct.
A) intertarsal joints
B) tarsometatarsal joints
C) metatarsophalangeal joints
D) interphalangeal joints
E) None of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Structures that compose the ankle joint include ________.
A) the distal articular surface of the tibia
B) the medial malleolus
C) the lateral malleolus of the fibula
D) the trochlea and lateral articular facets of the talus
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) the distal articular surface of the tibia
B) the medial malleolus
C) the lateral malleolus of the fibula
D) the trochlea and lateral articular facets of the talus
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A ligament that originates at the base of the coracoid process and inserts on the head of the humerus is the acromioclavicular ligament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The ________ crosses the acetabular notch in the hip joint.
A) transverse acetabular ligament
B) iliofemoral ligament
C) acetabular labrum
D) pubofemoral ligament
E) ischiofemoral ligament
A) transverse acetabular ligament
B) iliofemoral ligament
C) acetabular labrum
D) pubofemoral ligament
E) ischiofemoral ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is an intracapsular ligament that stabilizes the hip joint, and tightens only when the thigh is flexed and undergoing external rotation?
A) the iliofemoral ligament
B) the pubofemoral ligament
C) the ischiofemoral ligament
D) the transverse acetabular ligament
E) the ligament of the femoral head
A) the iliofemoral ligament
B) the pubofemoral ligament
C) the ischiofemoral ligament
D) the transverse acetabular ligament
E) the ligament of the femoral head

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Arthritis always involves damage to (the)________.
A) bony tissue
B) bursae
C) ligaments
D) articular cartilages
E) tendon sheaths
A) bony tissue
B) bursae
C) ligaments
D) articular cartilages
E) tendon sheaths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The cruciate ligaments attach to the ________ of the tibia.
A) condyles
B) epicondyles
C) anterior tuberosity
D) intercondylar area
E) linea aspera
A) condyles
B) epicondyles
C) anterior tuberosity
D) intercondylar area
E) linea aspera

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The metacarpophalangeal joints are ________ joints.
A) saddle
B) plane
C) hinge
D) gliding
E) condylar
A) saddle
B) plane
C) hinge
D) gliding
E) condylar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which structure(s) is/are attached to the anterior surface of the tibia?
A) tibial collateral ligament
B) popliteal ligament
C) anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
D) patellar ligament
E) fibular collateral ligament
A) tibial collateral ligament
B) popliteal ligament
C) anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
D) patellar ligament
E) fibular collateral ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
One of the thickenings in the anterior aspect of the capsule surrounding the shoulder joint is the glenohumeral ligament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The knee joint differs from other large, complex synovial joints of the body in which of the following features?
A) It is a hinge joint.
B) It is reinforced by ligaments.
C) It is rarely dislocated.
D) It is composed of two joints within a complex synovial capsule.
E) The knee joint does not differ from other joints.
A) It is a hinge joint.
B) It is reinforced by ligaments.
C) It is rarely dislocated.
D) It is composed of two joints within a complex synovial capsule.
E) The knee joint does not differ from other joints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following fractures are among the most dangerous seen in elderly people?
A) hip fractures
B) knee fractures
C) elbow fractures
D) ankle fractures
E) wrist fractures
A) hip fractures
B) knee fractures
C) elbow fractures
D) ankle fractures
E) wrist fractures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the knee structures function(s)to reinforce the medial and lateral surfaces of the joint, tighten only at full extension of the joint, and act to stabilize the joint?
A) patellar ligament
B) tibial and fibular collateral ligaments
C) popliteal ligaments
D) anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
E) iliofemoral ligament
A) patellar ligament
B) tibial and fibular collateral ligaments
C) popliteal ligaments
D) anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
E) iliofemoral ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Plantar flexion elevates the heel and plantar surface of the foot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The sphenomandibular ligament attaches the styloid process to the mandibular ramus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Ankylosing spondylitis is arthritis that affects the joints of the axial skeleton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
________ of the knee is preceded by unlocking of the knee.
A) Extension
B) Protraction
C) Opposition
D) Retraction
E) Flexion
A) Extension
B) Protraction
C) Opposition
D) Retraction
E) Flexion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which structure(s) connects the distal radius to the anterior surfaces of the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum?
A) dorsal radiocarpal ligament
B) ulnar collateral ligament
C) palmar radiocarpal ligament
D) radial collateral ligament
E) intercarpal ligament
A) dorsal radiocarpal ligament
B) ulnar collateral ligament
C) palmar radiocarpal ligament
D) radial collateral ligament
E) intercarpal ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The superficial ________ reinforce(s)the back of the knee joint.
A) anterior cruciate ligament
B) patellar ligaments
C) popliteal ligaments
D) medial collateral ligament
E) posterior cruciate ligament
A) anterior cruciate ligament
B) patellar ligaments
C) popliteal ligaments
D) medial collateral ligament
E) posterior cruciate ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The major weight-bearing articulation of the ankle is the ________ joint.
A) tibiocalcaneal
B) tibiotalar
C) tibiofibular
D) fibulocuboidal
E) fibulotalar
A) tibiocalcaneal
B) tibiotalar
C) tibiofibular
D) fibulocuboidal
E) fibulotalar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Figure 8.2
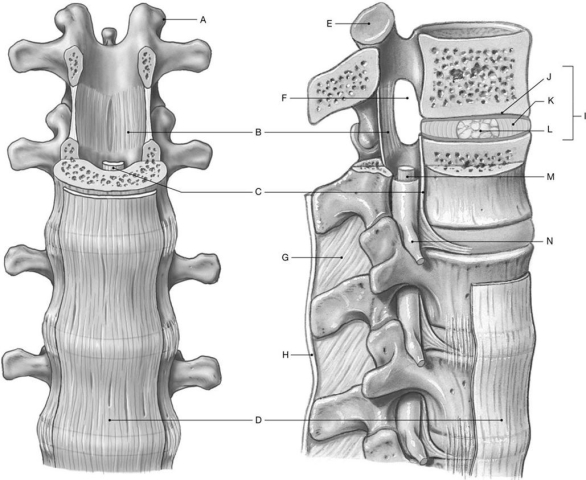
Using the above-referenced anterior view and lateral and sectional views of the intervertebral articulations, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label A.
A) Transverse process
B) Intervertebral foramen
C) Spinous process
D) Ligamentum flavum
E) Superior articular process

Using the above-referenced anterior view and lateral and sectional views of the intervertebral articulations, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label A.
A) Transverse process
B) Intervertebral foramen
C) Spinous process
D) Ligamentum flavum
E) Superior articular process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The radial collateral ligament extends from the styloid process of the radius to the medial surface of the scaphoid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 8.1
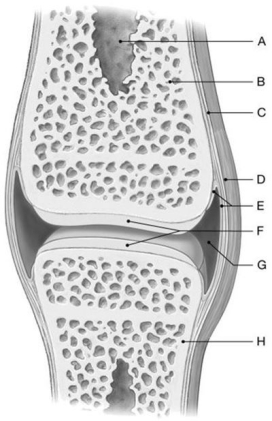
Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label C.
A) Endosteum
B) Synovial membrane
C) Joint capsule
D) Periosteum
E) Articular cartilage

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label C.
A) Endosteum
B) Synovial membrane
C) Joint capsule
D) Periosteum
E) Articular cartilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Figure 8.1

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label A.
A) Meniscus
B) Bursa
C) Articular cartilage
D) Medullary cavity
E) Joint capsule

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label A.
A) Meniscus
B) Bursa
C) Articular cartilage
D) Medullary cavity
E) Joint capsule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Figure 8.1

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label G.
A) Periosteum
B) Joint cavity
C) Medullary cavity
D) Compact bone
E) Articular cartilage

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label G.
A) Periosteum
B) Joint cavity
C) Medullary cavity
D) Compact bone
E) Articular cartilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Figure 8.1

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label E.
A) Periosteum
B) Articular cartilage
C) Endosteum
D) Medullary cavity
E) Synovial membrane

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label E.
A) Periosteum
B) Articular cartilage
C) Endosteum
D) Medullary cavity
E) Synovial membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Potts fracture involves the medial and lateral malleolus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Figure 8.2

Using the above-referenced anterior view and lateral and sectional views of the intervertebral articulations, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label B.
A) Posterior longitudinal ligament
B) Supraspinous ligament
C) Interspinous ligament
D) Anterior longitudinal ligament
E) Ligamentum flavum

Using the above-referenced anterior view and lateral and sectional views of the intervertebral articulations, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label B.
A) Posterior longitudinal ligament
B) Supraspinous ligament
C) Interspinous ligament
D) Anterior longitudinal ligament
E) Ligamentum flavum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What are the components of a synovial joint?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The ligament that ties the clavicle to the coracoid process to limit the relative motion between the clavicle and scapula is the coracoclavicular ligament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How does a syndesmosis differ from a symphysis, even though both are classified as amphiarthroses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Turn soles inward is called dorsiflexion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Figure 8.2

Using the above-referenced anterior view and lateral and sectional views of the intervertebral articulations, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label D.
A) Interspinous ligament
B) Anterior longitudinal ligament
C) Supraspinous ligament
D) Annulus fibrosus
E) Posterior longitudinal ligament

Using the above-referenced anterior view and lateral and sectional views of the intervertebral articulations, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label D.
A) Interspinous ligament
B) Anterior longitudinal ligament
C) Supraspinous ligament
D) Annulus fibrosus
E) Posterior longitudinal ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Figure 8.1

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label D.
A) Periosteum
B) Articular cartilage
C) Endosteum
D) Medullary cavity
E) Compact bone

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label D.
A) Periosteum
B) Articular cartilage
C) Endosteum
D) Medullary cavity
E) Compact bone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Why do human beings lose height as they reach old age?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 8.2

Using the above-referenced anterior view and lateral and sectional views of the intervertebral articulations, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label E.
A) Intervertebral disc
B) Superior articular facet
C) End plate
D) Transverse process
E) Inferior articular facet

Using the above-referenced anterior view and lateral and sectional views of the intervertebral articulations, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label E.
A) Intervertebral disc
B) Superior articular facet
C) End plate
D) Transverse process
E) Inferior articular facet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Why are the functional requirements of the lower limb joints different from those of the upper limb?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The head of the radius is held in place by the annular ligament and the quadrate ligament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How does the construction of the shoulder capsule contribute to the extensive range of motion of the shoulder joint?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Figure 8.1

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label F.
A) Endosteum
B) Articular cartilage
C) Periosteum
D) Compact bone
E) Medullary cavity

Using the above-referenced diagrammatic view of a simple articulation, identify the specified labeled items in each of the following questions.
Identify the structure(s) indicated by Label F.
A) Endosteum
B) Articular cartilage
C) Periosteum
D) Compact bone
E) Medullary cavity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



