Deck 2: The Nature of Science
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Nature of Science
1
According to the text, when students think of "scientists," they rarely think of
A) chemistry and physics.
B) white lab coats and test tubes.
C) research activities.
D) the formulation of theory.
A) chemistry and physics.
B) white lab coats and test tubes.
C) research activities.
D) the formulation of theory.
D
2
According to the authors of your textbook, the natural sciences and social sciences
A) have nothing in common.
B) share common philosophical and logical foundations.
C) differ primarily in how each defines the concept of "objectivity."
D) differ insofar as the natural sciences are based on empiricism, whereas the social sciences are not.
A) have nothing in common.
B) share common philosophical and logical foundations.
C) differ primarily in how each defines the concept of "objectivity."
D) differ insofar as the natural sciences are based on empiricism, whereas the social sciences are not.
B
3
The authors of the textbook take the position that
A) social research is fundamentally scientific.
B) the general scientific method may be applied to some social science topics but not to others.
C) the social sciences should model themselves after the natural sciences in terms of the structure of scientific theory but not in terms of the scientific "process."
D) the social sciences are less scientific than the natural sciences because they cannot be as objective.
A) social research is fundamentally scientific.
B) the general scientific method may be applied to some social science topics but not to others.
C) the social sciences should model themselves after the natural sciences in terms of the structure of scientific theory but not in terms of the scientific "process."
D) the social sciences are less scientific than the natural sciences because they cannot be as objective.
A
4
The most essential, defining "product" of science is
A) ideas in the form of principles and theories.
B) technological advances such as telecommunications, laser beams, and computer chips.
C) precise measurement and accurate prediction.
D) discoveries such as new planets, new organisms, and medical cures.
A) ideas in the form of principles and theories.
B) technological advances such as telecommunications, laser beams, and computer chips.
C) precise measurement and accurate prediction.
D) discoveries such as new planets, new organisms, and medical cures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is an example of a scientific question?
A) To what crimes should capital punishment apply?
B) Should clinical abortions be government funded?
C) Should intelligence tests be used in the schools?
D) Is political corruption a serious problem in the United States?
E) Why do women have abortions?
A) To what crimes should capital punishment apply?
B) Should clinical abortions be government funded?
C) Should intelligence tests be used in the schools?
D) Is political corruption a serious problem in the United States?
E) Why do women have abortions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not a rule about language usage in science?
A) One word, one concept.
B) Concepts must be linked to observable objects and events.
C) Concepts should stand the test of time.
D) Concepts should be judged by their usefulness.
A) One word, one concept.
B) Concepts must be linked to observable objects and events.
C) Concepts should stand the test of time.
D) Concepts should be judged by their usefulness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Social scientists have found consistent, substantial empirical support for the following proposition: As the size of a group increases, its complexity increases. This conclusion best represents a
A) theory.
B) law.
C) hypothesis.
D) concept.
E) paradigm.
A) theory.
B) law.
C) hypothesis.
D) concept.
E) paradigm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements is true of scientific theory?
A) Scientific theories can be proven logically.
B) There can be one and only one true theory of any social phenomenon.
C) Theories are less abstract than hypotheses.
D) Theories can be expressed as a logically interconnected set of propositions.
A) Scientific theories can be proven logically.
B) There can be one and only one true theory of any social phenomenon.
C) Theories are less abstract than hypotheses.
D) Theories can be expressed as a logically interconnected set of propositions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Freud's death wish is an example of
A) explanation without prediction.
B) prediction without explanation.
C) neither explanation nor prediction.
D) an objectively testable proposition.
A) explanation without prediction.
B) prediction without explanation.
C) neither explanation nor prediction.
D) an objectively testable proposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The ultimate goal of scientific inquiry is
A) the accumulation of facts.
B) the advancement of technology.
C) prediction and control.
D) hypothesis testing.
E) understanding.
A) the accumulation of facts.
B) the advancement of technology.
C) prediction and control.
D) hypothesis testing.
E) understanding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Scientific theories provide a sense of understanding by
A) introducing a unique set of concepts.
B) making accurate predictions.
C) describing the causal process that connects events.
D) connecting one set of generalizations to another.
A) introducing a unique set of concepts.
B) making accurate predictions.
C) describing the causal process that connects events.
D) connecting one set of generalizations to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which statement most accurately describes scientific knowledge or theory?
A) It is the best understanding that we have been able to produce thus far.
B) When perfected, it is a statement of what is ultimately real.
C) A theory is accepted as "scientific" when objective tests confirm its predictions.
D) Theory in a scientific discipline is essentially an inventory of the currently most accurate predictions.
A) It is the best understanding that we have been able to produce thus far.
B) When perfected, it is a statement of what is ultimately real.
C) A theory is accepted as "scientific" when objective tests confirm its predictions.
D) Theory in a scientific discipline is essentially an inventory of the currently most accurate predictions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The textbook describes science as both a product and a process. The "process" consists of
A) the development of scientific theory.
B) the continuous interaction of theory and data.
C) logical reasoning.
D) the application of precise scientific instruments.
A) the development of scientific theory.
B) the continuous interaction of theory and data.
C) logical reasoning.
D) the application of precise scientific instruments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The most accurate depiction of the scientific process is that it
A) always begins with theory and ends with research.
B) involves a continuous interplay between theory and data.
C) consists of the logical and empirical proof of hypotheses.
D) is an orderly procedure for making systematic observations.
A) always begins with theory and ends with research.
B) involves a continuous interplay between theory and data.
C) consists of the logical and empirical proof of hypotheses.
D) is an orderly procedure for making systematic observations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In his study Suicide, Durkheim
A) developed a comprehensive theory of suicide that included climatic, psychological, and social causes.
B) attempted to explain individual differences in types of suicide.
C) examined variation in suicide rates among different nations and groups.
D) did not produce a single finding that has stood the test of time.
A) developed a comprehensive theory of suicide that included climatic, psychological, and social causes.
B) attempted to explain individual differences in types of suicide.
C) examined variation in suicide rates among different nations and groups.
D) did not produce a single finding that has stood the test of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why is Durkheim's study Suicide a model of social scientific inquiry, even today?
A) It provided the first extensive quantitative analysis of suicide.
B) It presented the first truly scientific theory of suicide.
C) Virtually all of its predictions have been confirmed repeatedly by other investigators.
D) It showed how scientists use data to test theory and develop theories from data.
A) It provided the first extensive quantitative analysis of suicide.
B) It presented the first truly scientific theory of suicide.
C) Virtually all of its predictions have been confirmed repeatedly by other investigators.
D) It showed how scientists use data to test theory and develop theories from data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
To say that scientists follow principles of logical reasoning is to say that
A) logical proof is the primary means of verifying hypotheses.
B) logic provides the criteria for evaluating scientific reasoning.
C) scientists use logical rules to infer theory from observations or data.
D) logic suggests how to test scientific theory.
A) logical proof is the primary means of verifying hypotheses.
B) logic provides the criteria for evaluating scientific reasoning.
C) scientists use logical rules to infer theory from observations or data.
D) logic suggests how to test scientific theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the objective of logic or logical analysis?
A) to describe human thought processes
B) to facilitate creativity and imagination
C) to empirically validate scientific theory
D) to evaluate reasoning
A) to describe human thought processes
B) to facilitate creativity and imagination
C) to empirically validate scientific theory
D) to evaluate reasoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the primary difference between deductive and inductive logic?
A) the quality of the evidence supporting a conclusion
B) the certainty that a conclusion is true, based on the evidence
C) whether a conclusion can be drawn, based on the evidence
D) the closeness of the association between evidence and conclusion
A) the quality of the evidence supporting a conclusion
B) the certainty that a conclusion is true, based on the evidence
C) whether a conclusion can be drawn, based on the evidence
D) the closeness of the association between evidence and conclusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In valid deductive reasoning, if the evidence is true, the conclusion
A) may be true or false.
B) may be strong or weak.
C) must be true.
D) depends on the variety of supporting evidence.
A) may be true or false.
B) may be strong or weak.
C) must be true.
D) depends on the variety of supporting evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Someone studying homelessness finds that the first four homeless people he examines are mentally ill. He therefore concludes that all homeless people are mentally ill. What type(s) of reasoning is this?
A) deductive reasoning
B) inductive reasoning
C) neither deductive nor inductive reasoning
D) both deductive and inductive reasoning
A) deductive reasoning
B) inductive reasoning
C) neither deductive nor inductive reasoning
D) both deductive and inductive reasoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following sequences best describes the inductive logic of inquiry?
A) theory data hypothesis
B) data theory hypothesis
C) data empirical pattern theory
D) theory hypothesis data
E) empirical pattern hypothesis theory
A) theory data hypothesis
B) data theory hypothesis
C) data empirical pattern theory
D) theory hypothesis data
E) empirical pattern hypothesis theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following sequences best describes the deductive logic of inquiry?
A) theory data hypothesis
B) data theory hypothesis
C) data empirical pattern theory
D) theory hypothesis data
E) empirical pattern hypothesis theory
A) theory data hypothesis
B) data theory hypothesis
C) data empirical pattern theory
D) theory hypothesis data
E) empirical pattern hypothesis theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Scientists engage in deductive reasoning when they
A) show how a hypothesis follows from a theory.
B) infer empirical patterns from data.
C) formulate a theory to account for empirical patterns.
D) infer the validity of a theory from a set of data.
A) show how a hypothesis follows from a theory.
B) infer empirical patterns from data.
C) formulate a theory to account for empirical patterns.
D) infer the validity of a theory from a set of data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Based on the "mental alienation" theory of suicide, Durkheim argued that groups with higher rates of insanity will have higher rates of suicide. Women have higher rates of insanity than men. Therefore, women have higher rates of suicide than men. What type(s) of reasoning is this?
A) deductive reasoning
B) inductive reasoning
C) neither deductive nor inductive reasoning
D) both deductive and inductive reasoning
A) deductive reasoning
B) inductive reasoning
C) neither deductive nor inductive reasoning
D) both deductive and inductive reasoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to Durkheim's theory of suicide, the more socially integrated a group, the lower its suicide rate. Catholics are more socially integrated than Protestants. Therefore, the suicide rate is lower among Catholics than among Protestants. What type(s) of reasoning is this?
A) deductive reasoning
B) inductive reasoning
C) neither deductive nor inductive reasoning
D) both deductive and inductive reasoning
A) deductive reasoning
B) inductive reasoning
C) neither deductive nor inductive reasoning
D) both deductive and inductive reasoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Durkheim found that predominantly Catholic nations had lower suicide rates than predominantly Protestant nations, and that married people had lower suicide rates than single people. Noting that both Catholics and married people are more socially integrated than their counterparts, he theorized that the more socially integrated a group, the lower its suicide rate. What type(s) of reasoning is this?
A) deductive reasoning
B) inductive reasoning
C) neither deductive nor inductive reasoning
D) both deductive and inductive reasoning
A) deductive reasoning
B) inductive reasoning
C) neither deductive nor inductive reasoning
D) both deductive and inductive reasoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In a deductive argument the conclusion may be ___________, whereas in an inductive argument the conclusion is ___________.
A) true or false; more or less probable
B) valid; invalid
C) true or false; always true
D) valid or invalid; true or false
A) true or false; more or less probable
B) valid; invalid
C) true or false; always true
D) valid or invalid; true or false

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In contrast to deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning
A) is not based on empirical evidence.
B) involves conclusions that are more or less probable.
C) is less descriptive of human thought processes.
D) moves from general principles to particular conclusions.
E) should be avoided in science whenever possible.
A) is not based on empirical evidence.
B) involves conclusions that are more or less probable.
C) is less descriptive of human thought processes.
D) moves from general principles to particular conclusions.
E) should be avoided in science whenever possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When Durkheim formulated his theory of egoistic suicide from several established facts he used __________ ; when he showed how his theory explained the facts he used __________.
A) deductive reasoning; inductive reasoning.
B) deductive reasoning; valid reasoning.
C) valid reasoning; deductive reasoning
D) inductive reasoning; deductive reasoning
E) valid reasoning; inductive reasoning
A) deductive reasoning; inductive reasoning.
B) deductive reasoning; valid reasoning.
C) valid reasoning; deductive reasoning
D) inductive reasoning; deductive reasoning
E) valid reasoning; inductive reasoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An observer of street corner groups finds that more acts of vandalism are committed by same-sex groups than by mixed-sex groups. She speculates that the propensity to commit publicly deviant acts is a product of competition for recognition among peers of equal status. This is an example of
A) prediction without explanation.
B) deductive reasoning.
C) inductive reasoning.
D) hypothesis testing.
A) prediction without explanation.
B) deductive reasoning.
C) inductive reasoning.
D) hypothesis testing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
According to the deprivation theory of religiosity, people who are denied gratification within the secular society will be more likely to turn to the church as an alternative source of gratification. The United States is a male-dominated society in which women are denied the level of gratification enjoyed by men. Therefore, women will be more religious than men. This is an example of
A) logical inconsistency.
B) feminist reasoning.
C) deductive reasoning.
D) inductive reasoning.
A) logical inconsistency.
B) feminist reasoning.
C) deductive reasoning.
D) inductive reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The three key principles underlying scientific research are
A) observation, theory, experiment.
B) prediction, experiment, serendipity.
C) empiricism, objectivity, control.
D) deduction, induction, generalization.
A) observation, theory, experiment.
B) prediction, experiment, serendipity.
C) empiricism, objectivity, control.
D) deduction, induction, generalization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The principles of empiricism, objectivity, and control
A) are found in the social sciences but not in the natural sciences.
B) guide the collection and evaluation of scientific evidence.
C) are recent innovations in the scientific method.
D) complement intuition and revelation as ways of knowing in the social sciences.
A) are found in the social sciences but not in the natural sciences.
B) guide the collection and evaluation of scientific evidence.
C) are recent innovations in the scientific method.
D) complement intuition and revelation as ways of knowing in the social sciences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
According to the notion of empiricism, questions about the social world should be settled by resorting to
A) rational reflection.
B) logical reasoning.
C) careful, public discussion.
D) direct or indirect observation.
A) rational reflection.
B) logical reasoning.
C) careful, public discussion.
D) direct or indirect observation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which phrase best captures the meaning of "objectivity" as it applies to scientific inquiry?
A) Observational evidence that is completely free of bias.
B) Evidence that is not subject to interpretation.
C) Agreement among independent observers of the same event.
D) Agreement between scientists' observations and the external world.
A) Observational evidence that is completely free of bias.
B) Evidence that is not subject to interpretation.
C) Agreement among independent observers of the same event.
D) Agreement between scientists' observations and the external world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The revelation that Cyril Burt's data on the intelligence of identical twins reared apart were fraudulent demonstrates
A) that fraudulence is more likely to occur in the social than in the natural sciences.
B) how the public scrutiny of scientific research contributes to scientific "objectivity."
C) that social research findings should have no bearing on public policy.
D) some areas of social research tend to attract unethical scientists.
A) that fraudulence is more likely to occur in the social than in the natural sciences.
B) how the public scrutiny of scientific research contributes to scientific "objectivity."
C) that social research findings should have no bearing on public policy.
D) some areas of social research tend to attract unethical scientists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One "reality" of social scientific inquiry is that, in comparison with the natural sciences,
A) theoretical knowledge is less developed in the social sciences.
B) personal values and biases have a greater impact because social scientists are more passionate about their work.
C) the social sciences are more likely to involve collaborative research.
D) the social sciences seldom use methods to control for error and bias.
A) theoretical knowledge is less developed in the social sciences.
B) personal values and biases have a greater impact because social scientists are more passionate about their work.
C) the social sciences are more likely to involve collaborative research.
D) the social sciences seldom use methods to control for error and bias.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Theoretical knowledge is less developed in the social than in the natural sciences.
B) There is inevitably some degree of error in scientific prediction.
C) It is usually possible to eliminate the influence of personal values and biases in scientific work.
D) Some sociologists challenge the scientific conception of sociology and other social sciences.
A) Theoretical knowledge is less developed in the social than in the natural sciences.
B) There is inevitably some degree of error in scientific prediction.
C) It is usually possible to eliminate the influence of personal values and biases in scientific work.
D) Some sociologists challenge the scientific conception of sociology and other social sciences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which type of theoretical explanation is favored by qualitative researchers?
A) idiographic explanation
B) nomothetic explanation
C) universal explanation
D) abstract causal explanation
A) idiographic explanation
B) nomothetic explanation
C) universal explanation
D) abstract causal explanation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not among qualitative researchers' criticisms of using the natural sciences as a model for social scientific inquiry?
A) Knowledge is a social construction that differs from objective reality.
B) Explanations of the social world are limited by culture and time.
C) Human activities cannot be quantified.
D) Studying humans, as opposed to nonhuman objects, requires an understanding of the subjects' interpretations of the world.
A) Knowledge is a social construction that differs from objective reality.
B) Explanations of the social world are limited by culture and time.
C) Human activities cannot be quantified.
D) Studying humans, as opposed to nonhuman objects, requires an understanding of the subjects' interpretations of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The principal goal of science is to produce knowledge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The principal goal of science is the solution of technical and social problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In science, as in everyday language, it is acceptable for a concept to have multiple meanings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A concept is an idea or abstract notion usually communicated by words.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Explanation and prediction in science involve different forms of logical reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Theories provide a more general understanding than scientific laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
It is possible to have prediction without scientific understanding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The confirmation of a particular prediction is sufficient to prove a theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In science, evidence is always open to change through reinterpretation or possible contradiction by new evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Scientific knowledge is tentative and uncertain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Science is best defined as a step-by-step method of data collection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The scientific process always begins with theory and ends with data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Scientific inquiry always starts with data, from which theories are developed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Science involves both deductive and inductive reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In inductive reasoning, conclusions may go beyond the evidence at hand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Inductive reasoning generally represents a top-down process, moving from theory to hypothesis to data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In formulating a hypothesis from a theory, a researcher uses deductive reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Several theories may account for the same empirical patterns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Empirical evidence is observable to the researcher and others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Like many other intellectual endeavors, scientific inquiry relies on tradition, revelation, and intuition as sources of evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Objectivity in science basically boils down to agreement among independent observers of the same event.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The public nature of science safeguards scientific objectivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Theories must generate highly accurate predictions to be scientifically useful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Scientists may adhere to major theories for long periods in the face of much contradictory evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Qualitative researchers tend to reject the natural sciences as a model of social scientific inquiry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Qualitative researchers tend to assume that there is an objective reality that exists independent of the investigator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
According to the text, both nomothetic and idiographic explanations have a place in social scientific inquiry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The textbook describes science as a "product" and a "process." What is the essential defining product of science? What is the best overall description of the scientific process?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Describe how Durkheim used both deductive and inductive reasoning in his study of suicide. Be sure to give specific details of the study as these relate to each form of reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
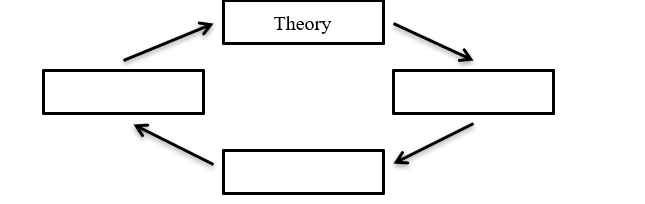
Below is an outline of a flowchart illustrating the scientific process. Fill in the boxes and then indicate whether each arrow in the diagram represents the application of deductive or inductive reasoning.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Because of the human element in science, some scholars believe that it is impossible to detect and eliminate sources of bias in scientific inquiry. Present a rebuttal to this criticism. Be sure to point out how biases and errors often are identifiable and correctable because the nature of scientific inquiry enables its own critique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What are the three epistemic assumptions of qualitative research that challenge the natural sciences model of social science? How do the textbook authors counter these challenges?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



