Deck 7: Waveform Analysis and Application
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Waveform Analysis and Application
1
The respiratory therapist is taking care of a trauma patient with bilateral chest tubes for pneumothoraces. The inability to sustain adequate ventilation may be related to which of the following situations?
A) Obstructed chest tube
B) Increased airway resistance
C) Air trapping
D) Air leak

A) Obstructed chest tube
B) Increased airway resistance
C) Air trapping
D) Air leak
D
2
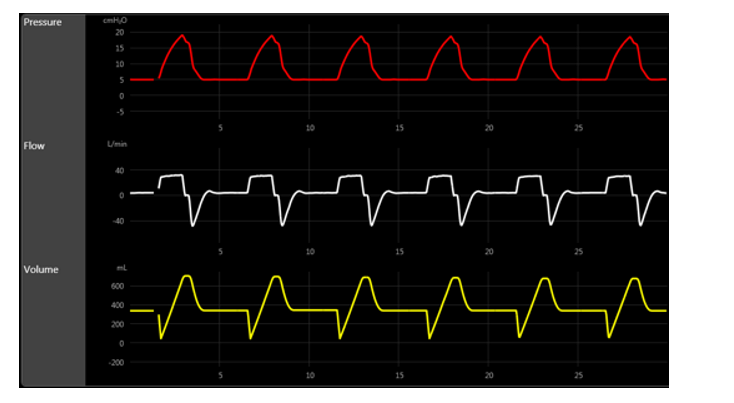
The scalars below are consistent with the presence of:
A) gas trapping.
B) slow rise time.
C) flow asynchrony.
D) positive response to bronchodilator.

A) gas trapping.
B) slow rise time.
C) flow asynchrony.
D) positive response to bronchodilator.
A
3
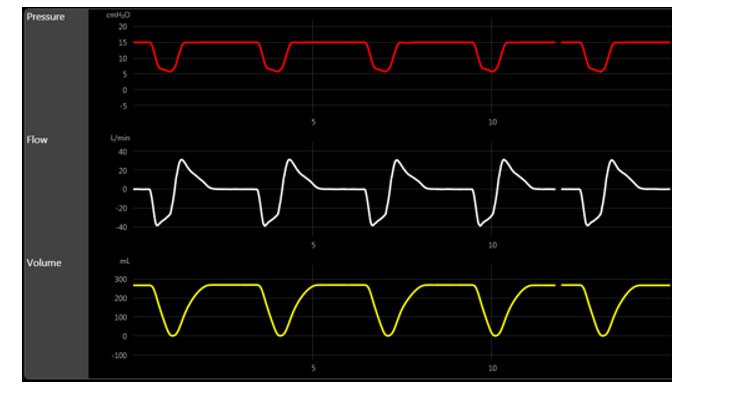
Based on the scenario displayed on the scalars below, which of the following maneuvers is indicated at this point?
A) Remove the expiratory filter to determine gas trapping
B) Inspiratory hold to measure plateau pressure
C) Expiratory hold to measure auto-PEEP
D) Increase the rise time

A) Remove the expiratory filter to determine gas trapping
B) Inspiratory hold to measure plateau pressure
C) Expiratory hold to measure auto-PEEP
D) Increase the rise time
C
4
How do you typically identify a patient-triggered breath (except when flow compensation is used)?
A) When the waveform changes to a different color
B) A pressure rise without a pressure deflection below the baseline
C) When the ventilator displays the letter "S" with the breath displayed
D) A pressure deflection below baseline right before a rise in pressure
A) When the waveform changes to a different color
B) A pressure rise without a pressure deflection below the baseline
C) When the ventilator displays the letter "S" with the breath displayed
D) A pressure deflection below baseline right before a rise in pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What happens to the waveform, PIP, and Pplat when compliance decreases?
A) Waveform size increases; difference in PIP and Pplat remains the same.
B) Waveform size increases; difference in PIP and Pplat decreases.
C) Waveform size decreases; difference in PIP and Pplat remains the same.
D) Waveform size increases; difference in PIP and Pplat increases.
A) Waveform size increases; difference in PIP and Pplat remains the same.
B) Waveform size increases; difference in PIP and Pplat decreases.
C) Waveform size decreases; difference in PIP and Pplat remains the same.
D) Waveform size increases; difference in PIP and Pplat increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The P-T and the F-T (with brief inspiratory hold) of a patient admitted for COPD exacerbation confirm the presence of:
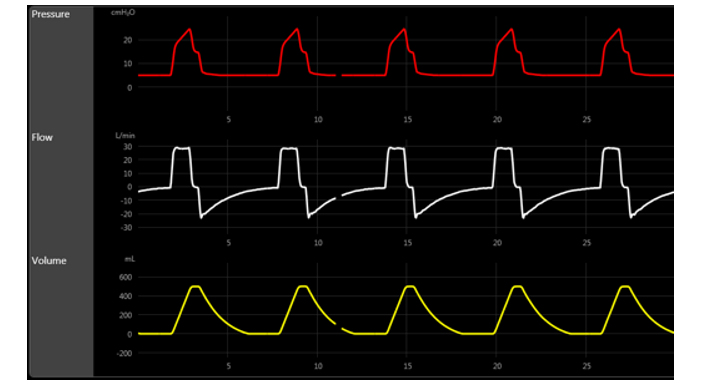
A) air leak.
B) cycling asynchrony.
C) air trapping.
D) increased airway resistance.

A) air leak.
B) cycling asynchrony.
C) air trapping.
D) increased airway resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The P-T of a patient displays a bump at the beginning of the initial inspiratory tracing. This change is consistent with:
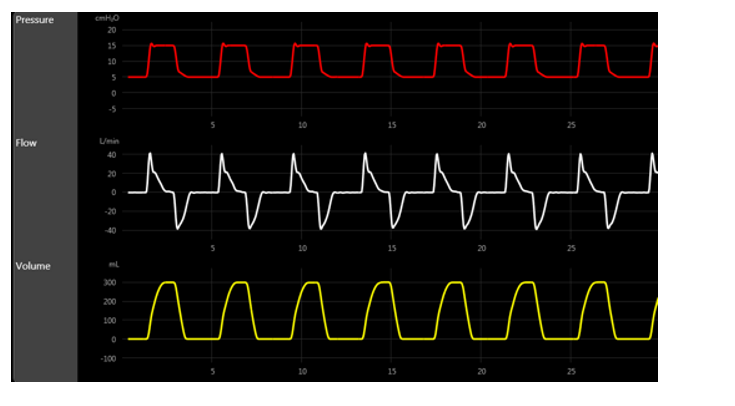
A) increased airway resistance.
B) fast rise time.
C) decreased lung compliance.
D) air trapping.

A) increased airway resistance.
B) fast rise time.
C) decreased lung compliance.
D) air trapping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The FVL of a patient with tracheoesophageal fistula indicates a leak of at least:
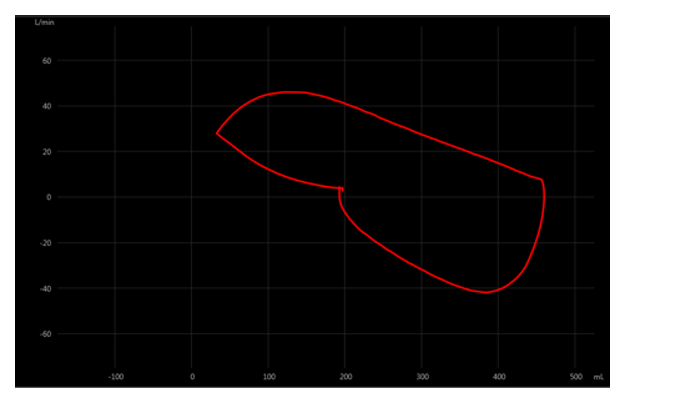
A) 50 mL.
B) 100 mL.
C) 150 mL.
D) 200 mL.

A) 50 mL.
B) 100 mL.
C) 150 mL.
D) 200 mL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When inspiratory flow takes longer to return to baseline, what does this indicate on a flow waveform?
A) Airway obstruction
B) Decreased alveolar compliance
C) Gas trapping
D) Air leak
A) Airway obstruction
B) Decreased alveolar compliance
C) Gas trapping
D) Air leak

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When expiratory flow takes longer to return to baseline, what does this indicate on a flow waveform?
A) Airway obstruction
B) Decreased alveolar compliance
C) Gas trapping
D) Air leak
A) Airway obstruction
B) Decreased alveolar compliance
C) Gas trapping
D) Air leak

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In order to assess improvement after administration of a bronchodilator, you should see:
A) lower mean airway pressures.
B) improved PEFR and shorter expiratory time.
C) decrease in Pplat.
D) improved PIFR and shorter inspiratory time.
A) lower mean airway pressures.
B) improved PEFR and shorter expiratory time.
C) decrease in Pplat.
D) improved PIFR and shorter inspiratory time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
On the first round of the evening, a critical care fellow is asking the respiratory therapist what mode of ventilation these scalars are more consistent with. The RT should answer: 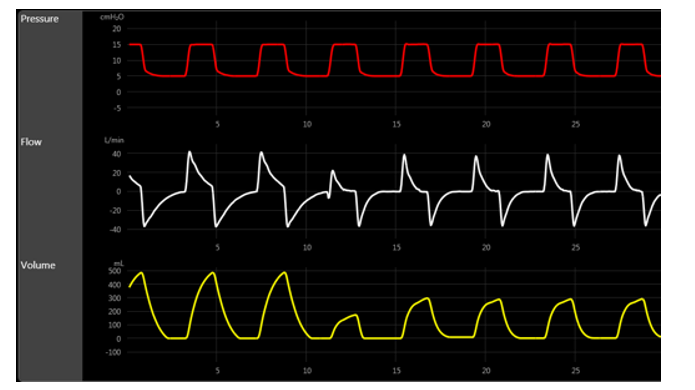
A) VAC.
B) PAC.
C) PRVC.
D) APRV.

A) VAC.
B) PAC.
C) PRVC.
D) APRV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
On a pressure-volume loop, what does beaking suggest?
A) Overdistention
B) Airway obstruction
C) Presence of airway secretions
D) Insufficient PEEP
A) Overdistention
B) Airway obstruction
C) Presence of airway secretions
D) Insufficient PEEP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An increase in airway resistance causes the pressure-volume loop to do what?
A) It causes it to widen.
B) It causes it to narrow.
C) It causes a shift upward.
D) It causes a shift to the middle.
A) It causes it to widen.
B) It causes it to narrow.
C) It causes a shift upward.
D) It causes a shift to the middle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What does a shift downward indicate on a PVL?
A) Decreased resistance
B) Decreased compliance
C) Trigger asynchrony
D) Overdistention
A) Decreased resistance
B) Decreased compliance
C) Trigger asynchrony
D) Overdistention

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
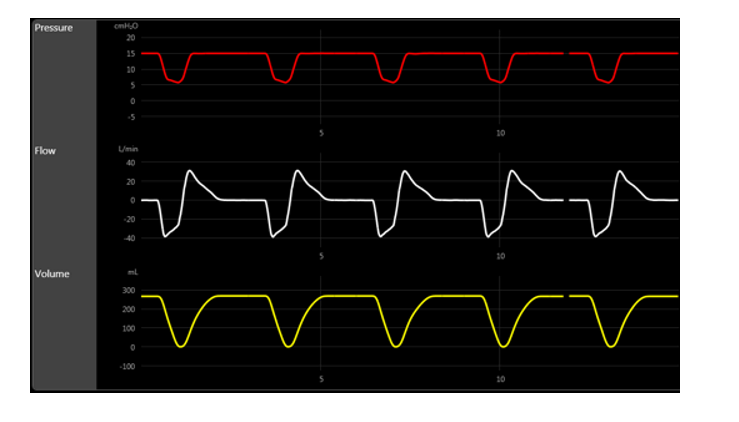
Which mode of ventilation is more consistent with the scalars below?
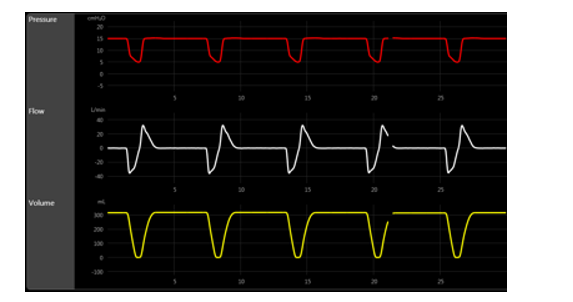
A) SIMV
B) APRV
C) PS
D) PAC

A) SIMV
B) APRV
C) PS
D) PAC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What do you do if the pressure deflection is greater than normal?
A) Change the mode of ventilation.
B) Increase the PEEP.
C) Decrease the sensitivity to make it easier to trigger.
D) Decrease the rise time.
A) Change the mode of ventilation.
B) Increase the PEEP.
C) Decrease the sensitivity to make it easier to trigger.
D) Decrease the rise time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What type of PVA does this P-T waveform represent?
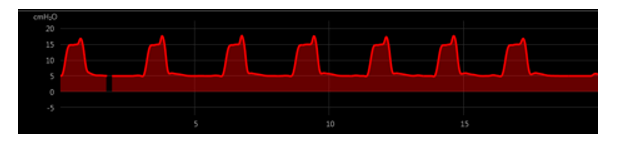
A) Trigger asynchrony
B) Flow asynchrony
C) Delayed cycling
D) Premature cycling

A) Trigger asynchrony
B) Flow asynchrony
C) Delayed cycling
D) Premature cycling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which waveform is most likely to determine a sensitivity setting problem?
A) Pressure-time
B) Flow-time
C) Volume-time
D) FVL
A) Pressure-time
B) Flow-time
C) Volume-time
D) FVL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which waveform is most likely to determine the beneficial effects of a bronchodilator treatment?
A) Pressure-time
B) Flow-time
C) Volume-time
D) PVL
A) Pressure-time
B) Flow-time
C) Volume-time
D) PVL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



