Deck 10: Bony Thorax-Sternum and Ribs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Bony Thorax-Sternum and Ribs
1
The only bony connection between the shoulder girdle and the bony thorax is the acromioclavicular joint.
False
2
The widest aspect of the thorax generally occurs at the level of:
A) the eleventh and twelfth ribs.
B) T7.
C) the sternoclavicular joints.
D) the eighth or ninth ribs.
A) the eleventh and twelfth ribs.
B) T7.
C) the sternoclavicular joints.
D) the eighth or ninth ribs.
the eighth or ninth ribs.
3
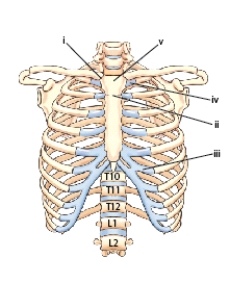
What is the name of the part labeled i in this figure?
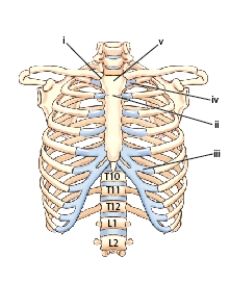
A) Facet for the first rib
B) Body
C) Sternoclavicular joint
D) Sternal angle

A) Facet for the first rib
B) Body
C) Sternoclavicular joint
D) Sternal angle
Sternoclavicular joint
4
At approximately what age does the xiphoid process become totally ossified?
A) 12 years old
B) 21 years old
C) 40 years old
D) The xiphoid process never becomes ossified.
A) 12 years old
B) 21 years old
C) 40 years old
D) The xiphoid process never becomes ossified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the erect adult bony thorax,the posterior portion of a typical rib is ____ higher or more superior to the anterior portion.
A) 1 to 2 inches (2.5 to 5 cm)
B) 3 to 5 inches (7.5 to 13 cm)
C) 6 to 8 inches (15 to 20 cm)
D) 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm)
A) 1 to 2 inches (2.5 to 5 cm)
B) 3 to 5 inches (7.5 to 13 cm)
C) 6 to 8 inches (15 to 20 cm)
D) 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is true about floating ribs?
A) They do not possess a head.
B) They do not possess a costovertebral joint.
C) They do not possess costocartilage.
D) They are ribs 10 through 12.
A) They do not possess a head.
B) They do not possess a costovertebral joint.
C) They do not possess costocartilage.
D) They are ribs 10 through 12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the joint classification and type of movement for the costotransverse joint?
A) Cartilaginous with diarthrodial (ginglymus) movement
B) Synovial with diarthrodial (plane) movement
C) Synovial with amphiarthrodial, limited movement
D) Cartilaginous with synarthrodial or no movement
A) Cartilaginous with diarthrodial (ginglymus) movement
B) Synovial with diarthrodial (plane) movement
C) Synovial with amphiarthrodial, limited movement
D) Cartilaginous with synarthrodial or no movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The tubercle portion of a typical rib connects the anterior end of the rib to the sternum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The structure labeled iii is costocartilage:
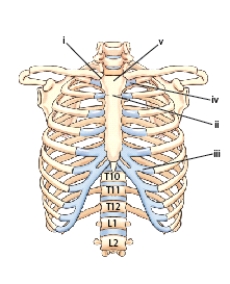
A) of the 10th rib.
B) portion of the first false rib.
C) of the last true rib.
D) of the sixth rib.

A) of the 10th rib.
B) portion of the first false rib.
C) of the last true rib.
D) of the sixth rib.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The xiphoid process corresponds to the vertebral level of:
A) T7.
B) T9-10.
C) T4-5.
D) L1-2.
A) T7.
B) T9-10.
C) T4-5.
D) L1-2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the name of the part labeled ii?
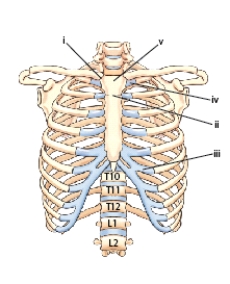
A) Xiphoid process
B) Body
C) Sternoclavicular joint
D) Sternal angle

A) Xiphoid process
B) Body
C) Sternoclavicular joint
D) Sternal angle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The suprasternal,manubrial,or jugular notch all correspond to the level of:
A) T2-3.
B) T1.
C) T4-5.
D) C7.
A) T2-3.
B) T1.
C) T4-5.
D) C7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the name of the part labeled iv?
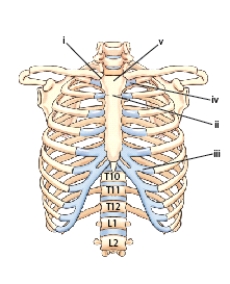
A) Facet for the sternum attachment
B) Head of the sternum
C) Facet for the second rib attachment
D) Costocartilage for the first rib attachment

A) Facet for the sternum attachment
B) Head of the sternum
C) Facet for the second rib attachment
D) Costocartilage for the first rib attachment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the primary term for the superior margin of the sternum?
A) Sternal notch
B) Manubrial notch
C) Suprasternal notch
D) Jugular notch
A) Sternal notch
B) Manubrial notch
C) Suprasternal notch
D) Jugular notch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following structures connects the anterior aspect of the ribs to the sternum?
A) Costocartilage
B) Sternal tendons
C) Costovertebral joints
D) Costotransverse joints
A) Costocartilage
B) Sternal tendons
C) Costovertebral joints
D) Costotransverse joints

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the name of the structure labeled v?
A) Head
B) Body
C) Manubrium
D) Xiphoid process

A) Head
B) Body
C) Manubrium
D) Xiphoid process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The sternal angle is a palpable landmark at the level of:
A) T4-5.
B) T2-3.
C) T7.
D) T9-10.
A) T4-5.
B) T2-3.
C) T7.
D) T9-10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following ribs is considered to be a false rib?
A) Seventh
B) First
C) Ninth
D) None of the above
A) Seventh
B) First
C) Ninth
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the joint classification and type of movement for the sternoclavicular joints?
A) Cartilaginous with diarthrodial (ginglymus) movement
B) Synovial with diarthrodial (gliding) movement
C) Synovial with amphiarthrodial, limited movement
D) Cartilaginous with synarthrodial or no movement
A) Cartilaginous with diarthrodial (ginglymus) movement
B) Synovial with diarthrodial (gliding) movement
C) Synovial with amphiarthrodial, limited movement
D) Cartilaginous with synarthrodial or no movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which pair of ribs attaches to the sternum at the level of the sternal angle?
A) First
B) Second
C) Third
D) Fourth and fifth
A) First
B) Second
C) Third
D) Fourth and fifth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following techniques is most effective in preventing lung markings from obscuring the sternum on an oblique projection?
A) Use a high kV.
B) Oblique as much as needed to not superimpose the sternum over the hilum region.
C) Decrease the source image receptor distance (SID) to magnify the sternum.
D) Use an orthostatic (breathing) technique.
A) Use a high kV.
B) Oblique as much as needed to not superimpose the sternum over the hilum region.
C) Decrease the source image receptor distance (SID) to magnify the sternum.
D) Use an orthostatic (breathing) technique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the recommended degree of obliquity for an RAO projection of the sternum for an asthenic type of patient?
A) 20°
B) 15°
C) 30°
D) 10°
A) 20°
B) 15°
C) 30°
D) 10°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the recommended SID for the lateral sternum position?
A) 40 inches (102 cm)
B) 44 inches (113 cm)
C) 46 inches (117 cm)
D) 60 to 72 inches (152 to 183 cm)
A) 40 inches (102 cm)
B) 44 inches (113 cm)
C) 46 inches (117 cm)
D) 60 to 72 inches (152 to 183 cm)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which two projections must be taken for an injury to the left posterior lower ribs?
A) AP and LPO
B) AP and RAO
C) PA and LPO
D) PA and RAO
A) AP and LPO
B) AP and RAO
C) PA and LPO
D) PA and RAO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The left anterior oblique (LAO)position of the sternum provides the best frontal image of the sternum with a minimal amount of distortion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following positions will best demonstrate the axillary portion of the left ribs?
A) AP
B) Posteroanterior (PA)
C) Left posterior oblique (LPO)
D) LAO
A) AP
B) Posteroanterior (PA)
C) Left posterior oblique (LPO)
D) LAO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Where is the CR centered for a PA projection of the sternoclavicular joints?
A) At the level of the vertebra prominens (T1)
B) At the level of the sternal angle (T4-5)
C) Three inches (7 cm) distal to vertebra prominens (T2-3)
D) At the level of the thyroid cartilage (T9)
A) At the level of the vertebra prominens (T1)
B) At the level of the sternal angle (T4-5)
C) Three inches (7 cm) distal to vertebra prominens (T2-3)
D) At the level of the thyroid cartilage (T9)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A recommended practice is to decrease the SID to less than 40 inches (102 cm)for the oblique sternum projection to increase the magnification and resultant unsharpness of overlying ribs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A right or left marker may be taped over the area of interest to indicate the location of the trauma to the ribs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which ribs are considered to be true ribs?
A) First and second ribs
B) First through seventh ribs
C) First through ninth ribs
D) 11th and 12th ribs
A) First and second ribs
B) First through seventh ribs
C) First through ninth ribs
D) 11th and 12th ribs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is true about radiography of ribs located above the diaphragm?
A) Suspend breathing upon inspiration.
B) Perform the study with the patient recumbent.
C) Use an analog kV range of 85 to 95.
D) Always include an anteroposterior (AP) projection as part of the routine.
A) Suspend breathing upon inspiration.
B) Perform the study with the patient recumbent.
C) Use an analog kV range of 85 to 95.
D) Always include an anteroposterior (AP) projection as part of the routine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which position can replace the RAO of the sternum if the patient cannot lie prone?
A) LAO
B) Left lateral decubitus
C) LPO
D) RPO
A) LAO
B) Left lateral decubitus
C) LPO
D) RPO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following positions will best demonstrate the axillary portion of the right ribs?
A) AP
B) PA
C) LAO
D) RAO
A) AP
B) PA
C) LAO
D) RAO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How much rotation and which oblique position are required to best demonstrate the left sternoclavicular joints?
A) 10° to 15° LAO
B) 35° to 45° LAO
C) 10° to 15° RAO
D) 5° to 10° RAO
A) 10° to 15° LAO
B) 35° to 45° LAO
C) 10° to 15° RAO
D) 5° to 10° RAO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which analog kV range is recommended for an AP study of the ribs found below the diaphragm?
A) 85 to 90 kV
B) 60 to 65 kV
C) 65 to 75 kV
D) 70 to 80 kV
A) 85 to 90 kV
B) 60 to 65 kV
C) 65 to 75 kV
D) 70 to 80 kV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following conditions may occur with trauma to the ribs?
A) Airway obstruction of the trachea
B) Pneumonia
C) Hemothorax
D) Pulmonary embolus
A) Airway obstruction of the trachea
B) Pneumonia
C) Hemothorax
D) Pulmonary embolus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Why is the RAO sternum preferred to the LAO position?
A) The RAO produces less magnification of the sternum.
B) The RAO projects the sternum over the shadow of the heart.
C) The RAO reduces dose to the thyroid gland.
D) The RAO projects the sternum away from the hilum and heart.
A) The RAO produces less magnification of the sternum.
B) The RAO projects the sternum over the shadow of the heart.
C) The RAO reduces dose to the thyroid gland.
D) The RAO projects the sternum away from the hilum and heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which two projections must be taken for an injury to the right anterior upper ribs?
A) PA and LAO
B) PA and RAO
C) AP and RAO
D) AP and LPO
A) PA and LAO
B) PA and RAO
C) AP and RAO
D) AP and LPO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which aspect of the rib articulates with the thoracic vertebral body?
A) Neck
B) Tubercles
C) Head
D) Facets
A) Neck
B) Tubercles
C) Head
D) Facets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The degree of rotation for the right anterior oblique (RAO)projection of the sternum is dependent on the size of the thoracic cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Multiple myeloma is seen often in the flat bones of the bony thorax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which condition of the sternum is often termed "funnel chest?"
A) Pectus excavatum
B) Flail chest
C) Pectus eruptus
D) Pectus deforminens
A) Pectus excavatum
B) Flail chest
C) Pectus eruptus
D) Pectus deforminens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A patient enters the ED with an injury to the left anterior lower ribs.Which of the following projections should be taken to demonstrate the involved area?
A) AP and LAO
B) PA and RAO
C) AP and LPO
D) PA and LAO
A) AP and LAO
B) PA and RAO
C) AP and LPO
D) PA and LAO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A radiograph of a lateral projection of the sternum reveals that the patient's ribs are superimposed over the sternum.What needs to be done to correct this problem during the repeat exposure?
A) Increase the SID.
B) Angle the CR 5° anterior.
C) Ensure that the patient is not rotated.
D) Increase the kV.
A) Increase the SID.
B) Angle the CR 5° anterior.
C) Ensure that the patient is not rotated.
D) Increase the kV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A PA radiograph of the sternoclavicular (SC)joints demonstrates unequal distance from the SC joints to the midline of the spine.The left SC joint is farther from the sternum than the right.What specific positioning error is present on this radiograph?
A) Slight right rotation (right side toward the image receptor)
B) Slight left rotation (left side toward the image receptor)
C) Tilt of the upper thorax
D) Excessive angulation of the CR
A) Slight right rotation (right side toward the image receptor)
B) Slight left rotation (left side toward the image receptor)
C) Tilt of the upper thorax
D) Excessive angulation of the CR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following conditions,if severe,requires a decrease adjustment of manual exposure factors?
A) Osteoblastic metastases
B) Osteomyelitis
C) Flail chest
D) None of the above
A) Osteoblastic metastases
B) Osteomyelitis
C) Flail chest
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A radiograph of an RAO sternum reveals that it is partially superimposed over the spine.What must be done to eliminate this problem during the repeat exposure?
A) Perform an LPO projection instead of an RAO.
B) Angle CR 5° to 10° laterally to the sternum.
C) Increase rotation of the body.
D) Increase kV.
A) Perform an LPO projection instead of an RAO.
B) Angle CR 5° to 10° laterally to the sternum.
C) Increase rotation of the body.
D) Increase kV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A radiograph of an RAO projection of the sternum demonstrates excessive lung markings obscuring the sternum.A 1-second exposure time and an orthostatic (breathing)technique were used.Which of the following will produce a more diagnostic image of the sternum?
A) Ensure that the patient is not breathing during the exposure.
B) Increase the exposure time; decrease the mA.
C) Decrease the kV; increase the mA or time.
D) Initiate exposure on deeper inspiration.
A) Ensure that the patient is not breathing during the exposure.
B) Increase the exposure time; decrease the mA.
C) Decrease the kV; increase the mA or time.
D) Initiate exposure on deeper inspiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The condition,flail chest,is most commonly caused by:
A) pneumothorax.
B) emphysema.
C) blunt trauma.
D) congenital heart defect.
A) pneumothorax.
B) emphysema.
C) blunt trauma.
D) congenital heart defect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Both bony and soft tissue anatomy may be evaluated by CT for pathology involving the sternum or the sternoclavicular joints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A young female patient from the emergency department (ED)is brought to radiology for rib examination.She is able to sit up or stand for the procedure.She indicates that the region of pain is to the right anterior-to-mid axillary region.Which rib projections should be performed to minimize the effective dose to this patient?
A) PA and RPO
B) AP and RPO
C) PA and RAO
D) PA and LAO
A) PA and RPO
B) AP and RPO
C) PA and RAO
D) PA and LAO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A patient enters the ED with trauma to the bony thorax.The initial radiographs reveal that there are fractured ribs and a possible pneumothorax of the left thorax.The physician orders a chest study to confirm the pneumothorax; however,the patient cannot stand.Which of the following positions would best demonstrate the pneumothorax?
A) Left lateral decubitus
B) Right lateral decubitus
C) Ventral decubitus
D) Dorsal decubitus
A) Left lateral decubitus
B) Right lateral decubitus
C) Ventral decubitus
D) Dorsal decubitus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Initial PA projections of the SC joints indicate a possible defect involving the left SC joint.The vertebral column is preventing a clear view of it.Which of the following projections will demonstrate the right SC joint without superimposition over the spine?
A) Horizontal beam lateral
B) LAO
C) RAO
D) Erect lateral projection
A) Horizontal beam lateral
B) LAO
C) RAO
D) Erect lateral projection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An ambulatory patient enters the ED with a possible injury to the right upper posterior ribs.Which of the following routines should be taken to demonstrate the involved area?
A) Erect PA and LPO
B) Erect AP and RPO
C) Recumbent AP and RPO
D) Erect PA and LAO
A) Erect PA and LPO
B) Erect AP and RPO
C) Recumbent AP and RPO
D) Erect PA and LAO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A patient enters the ED with blunt trauma to the sternum.The patient is in great pain and cannot lie prone on the table or stand erect.Which of the following routines would be best for the sternum examination in this situation?
A) RPO and lateral recumbent projections
B) AP and horizontal beam lateral projections
C) LPO and horizontal beam lateral projections
D) LPO and lateral recumbent projections
A) RPO and lateral recumbent projections
B) AP and horizontal beam lateral projections
C) LPO and horizontal beam lateral projections
D) LPO and lateral recumbent projections

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Fracture of adjacent ribs in two or more places with associated pulmonary injury is known as a(n)_____ rib fracture.
A) compound
B) flail chest
C) acute
D) compression
A) compound
B) flail chest
C) acute
D) compression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A congenital defect characterized by anterior protrusion of the lower sternum and xiphoid process is termed:
A) pectus excavatum.
B) flail chest.
C) pectus carinatum.
D) sternal protrusion.
A) pectus excavatum.
B) flail chest.
C) pectus carinatum.
D) sternal protrusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The radiographic appearance of the erosion of bony rib margins is a possible indication of:
A) osteomyelitis.
B) osteoblastic metastases.
C) spondylolysis.
D) osteolytic metastases.
A) osteomyelitis.
B) osteoblastic metastases.
C) spondylolysis.
D) osteolytic metastases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which disease or condition may be associated with postoperative complications of open heart surgery?
A) Spondylitis
B) Osteoblastic metastases
C) Osteomyelitis
D) Flail chest
A) Spondylitis
B) Osteoblastic metastases
C) Osteomyelitis
D) Flail chest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Both nuclear medicine and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)studies can be performed to evaluate metastatic rib lesions before conventional rib radiographic examination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following positioning considerations does NOT apply for a study of the lower ribs?
A) Perform positions recumbent.
B) Use a digital kV range between 65 and 70 kV.
C) Exposure on full expiration.
D) Both A and B are incorrect.
A) Perform positions recumbent.
B) Use a digital kV range between 65 and 70 kV.
C) Exposure on full expiration.
D) Both A and B are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the minimum number of ribs that must be demonstrated for a unilateral rib study above the diaphragm?
A) Ribs 1 through 6
B) Ribs 1 through 8
C) Ribs 1 through 10
D) All ribs must be demonstrated.
A) Ribs 1 through 6
B) Ribs 1 through 8
C) Ribs 1 through 10
D) All ribs must be demonstrated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A lateral projection of the sternum requires that respiration be suspended on expiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The use of 125 kV is recommended for AP and PA projections of the ribs to reduce skin dose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A radiograph of an RAO projection of the ribs demonstrates the left axillary ribs are foreshortened,whereas the right side is elongated.Which of the following is the most likely reason for this radiographic outcome?
A) The patient requires more rotation to the right.
B) An LAO was performed rather than the RAO position.
C) The technologist should have performed a PA projection to demonstrate the left axillary ribs, not an RAO.
D) CR angulation was incorrect.
A) The patient requires more rotation to the right.
B) An LAO was performed rather than the RAO position.
C) The technologist should have performed a PA projection to demonstrate the left axillary ribs, not an RAO.
D) CR angulation was incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A patient with metastatic disease in the ribs comes to radiology following a nuclear medicine scan.The radiologist orders a right,upper posterior rib study performed.Which of the following positioning factors should be followed for this specific study?
A) Perform positions erect if the patient's condition permits.
B) Exposure on full expiration.
C) Include the RPO position as part of the positioning routine.
D) Both A and C are correct.
A) Perform positions erect if the patient's condition permits.
B) Exposure on full expiration.
C) Include the RPO position as part of the positioning routine.
D) Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



