Deck 3: The Biosphere
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: The Biosphere
1
Around 12,000 years ago, a sudden extinction occurred on the temperate grasslands of North America, during which most of the diverse large mammal species died out. A corresponding extinction did not occur on the African savanna, also a temperate grassland, and today it still has diverse herds of large mammals. What possible, but controversial, explanation is thought by some people to explain the North American extinction?
A) Declining habitat or food supply due to climate change
B) Arrival of humans in North America
C) Receding ice sheets, leading to a climate too warm to support megafauna
D) Expanding ice sheets, leading to a climate too cold to support megafauna
A) Declining habitat or food supply due to climate change
B) Arrival of humans in North America
C) Receding ice sheets, leading to a climate too warm to support megafauna
D) Expanding ice sheets, leading to a climate too cold to support megafauna
B
2
A biome contains sagebrush and many types of cacti, as well as rattlesnakes and jackrabbits. It has a hot, dry climate, and many microbes, including bacteria and archaea, that are adapted to live in extreme conditions. Which of these factors would be used to classify this biome?
A) Sagebrush and cacti
B) Rattlesnakes and jackrabbits
C) Hot, dry climate
D) Microbes adapted to extreme environments
A) Sagebrush and cacti
B) Rattlesnakes and jackrabbits
C) Hot, dry climate
D) Microbes adapted to extreme environments
A
3
A plant has the ability to grow from the base of its leaves, thereby keeping its reproductive buds under the surface and permitting high tolerance of climatic fluctuations. This plant most likely lives in a
A) deciduous forest.
B) temperate shrubland.
C) grassland.
D) tropical rainforest.
A) deciduous forest.
B) temperate shrubland.
C) grassland.
D) tropical rainforest.
C
4
A biome extends across several continents. Parts of the biome on the different continents can be best identified by the
A) growth forms of its plants.
B) amount of disturbance.
C) types of megafauna present.
D) average temperatures.
A) growth forms of its plants.
B) amount of disturbance.
C) types of megafauna present.
D) average temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Deciduous trees would most likely be found in which of these forest types?
A) Boreal forest
B) Tropical rainforest
C) Temperate evergreen forest
D) Temperate shrubland and woodland
A) Boreal forest
B) Tropical rainforest
C) Temperate evergreen forest
D) Temperate shrubland and woodland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If climate change causes a tropical rainforest to receive somewhat less rainfall, it will most likely become
A) temperate evergreen forest.
B) boreal forest.
C) savanna.
D) temperate deciduous forest.
A) temperate evergreen forest.
B) boreal forest.
C) savanna.
D) temperate deciduous forest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If climate change causes a boreal forest to be a little warmer and a little wetter, it will most likely become
A) temperate evergreen forest.
B) savanna.
C) tundra.
D) temperate deciduous forest.
A) temperate evergreen forest.
B) savanna.
C) tundra.
D) temperate deciduous forest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Refer to the figure.
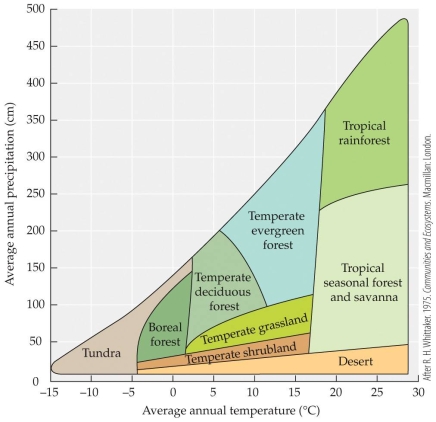
- The figure shows how biomes vary with temperature and precipitation. If the precipitation in Florida (largely temperate evergreen forest) increased to an average of 275 cm per year and the temperature warmed to an average of 19°C, how would that change the landscape?
A) All of Florida would be covered in evergreen forests.
B) Part of Florida would transition to a mix of grasslands and shrublands.
C) Florida would be covered in tropical seasonal forest with a small area of tropical rainforest.
D) All of Florida would be covered in tropical rainforest.

- The figure shows how biomes vary with temperature and precipitation. If the precipitation in Florida (largely temperate evergreen forest) increased to an average of 275 cm per year and the temperature warmed to an average of 19°C, how would that change the landscape?
A) All of Florida would be covered in evergreen forests.
B) Part of Florida would transition to a mix of grasslands and shrublands.
C) Florida would be covered in tropical seasonal forest with a small area of tropical rainforest.
D) All of Florida would be covered in tropical rainforest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Refer to the figure.
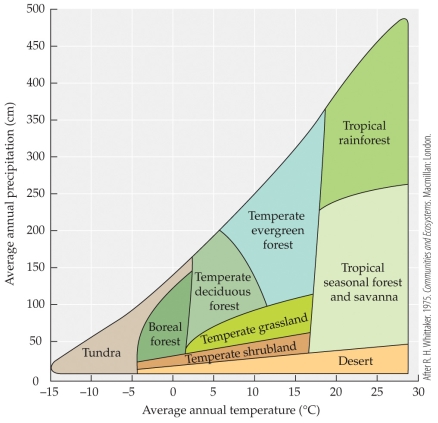
-The figure shows how biomes vary with temperature and precipitation. If the average temperature on Earth increased, what effect would this have on the distribution of boreal forests in the Northern Hemisphere?
A) Boreal forests would be able to grow further south than their present range.
B) Both northern and southern edges of the boreal forests would move northward.
C) The total global area covered by tundra would increase.
D) The distribution of boreal forests would not change.

-The figure shows how biomes vary with temperature and precipitation. If the average temperature on Earth increased, what effect would this have on the distribution of boreal forests in the Northern Hemisphere?
A) Boreal forests would be able to grow further south than their present range.
B) Both northern and southern edges of the boreal forests would move northward.
C) The total global area covered by tundra would increase.
D) The distribution of boreal forests would not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to the figure.
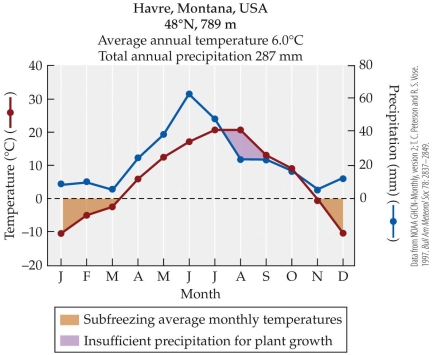 The figure is an example of a climate diagram, which gives average monthly temperatures and precipitation levels for a given location over a year. Using only the information in the climate diagram, which of the following conclusions can be drawn about the plant life at this location?
The figure is an example of a climate diagram, which gives average monthly temperatures and precipitation levels for a given location over a year. Using only the information in the climate diagram, which of the following conclusions can be drawn about the plant life at this location?
A) Plant life can grow here nearly all year, but is briefly limited by cold or drought.
B) Plant life can grow here for only about five months of the year.
C) Plant life can grow here for all twelve months of the year.
D) Plant life is not possible at this location due to extremes in temperature and rainfall.
 The figure is an example of a climate diagram, which gives average monthly temperatures and precipitation levels for a given location over a year. Using only the information in the climate diagram, which of the following conclusions can be drawn about the plant life at this location?
The figure is an example of a climate diagram, which gives average monthly temperatures and precipitation levels for a given location over a year. Using only the information in the climate diagram, which of the following conclusions can be drawn about the plant life at this location?A) Plant life can grow here nearly all year, but is briefly limited by cold or drought.
B) Plant life can grow here for only about five months of the year.
C) Plant life can grow here for all twelve months of the year.
D) Plant life is not possible at this location due to extremes in temperature and rainfall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Refer to the map.
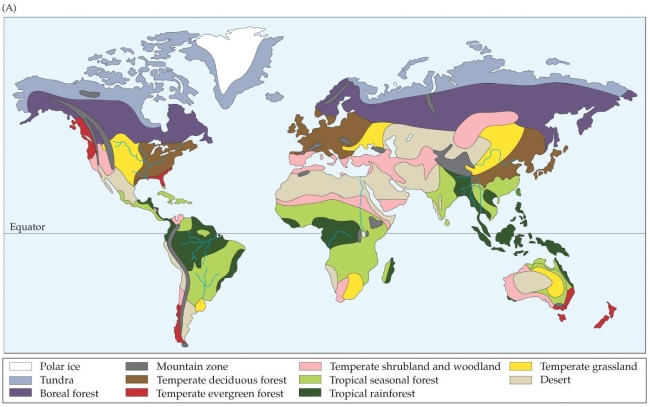 The map shows locations of biomes across the world. To which biome do New Zealand and the southeast section of Australia belong?
The map shows locations of biomes across the world. To which biome do New Zealand and the southeast section of Australia belong?
A) Tropical rainforest
B) Boreal forest
C) Temperate deciduous forest
D) Temperate evergreen forest
 The map shows locations of biomes across the world. To which biome do New Zealand and the southeast section of Australia belong?
The map shows locations of biomes across the world. To which biome do New Zealand and the southeast section of Australia belong?A) Tropical rainforest
B) Boreal forest
C) Temperate deciduous forest
D) Temperate evergreen forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Refer to the map.
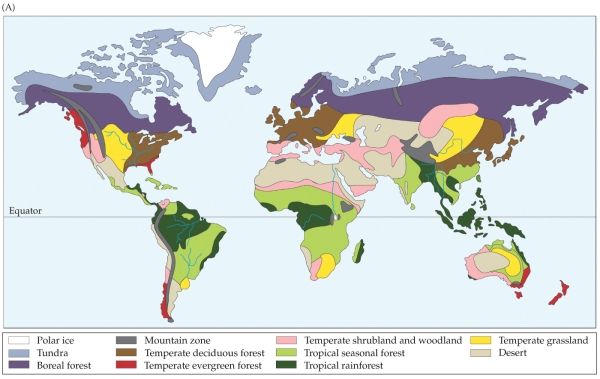 The map shows locations of biomes across the world. Going south from the Sahara Desert, you would most likely encounter which biome next?
The map shows locations of biomes across the world. Going south from the Sahara Desert, you would most likely encounter which biome next?
A) Tropical seasonal forest
B) Temperate shrubland and woodland
C) Tropical rainforest
D) Temperate grassland
 The map shows locations of biomes across the world. Going south from the Sahara Desert, you would most likely encounter which biome next?
The map shows locations of biomes across the world. Going south from the Sahara Desert, you would most likely encounter which biome next?A) Tropical seasonal forest
B) Temperate shrubland and woodland
C) Tropical rainforest
D) Temperate grassland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Refer to the figure.
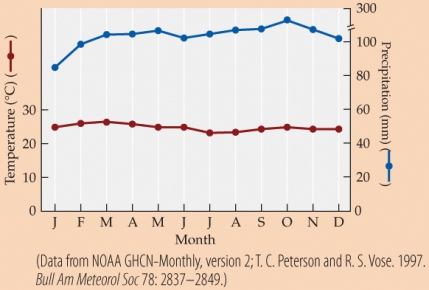 Based on the climate diagram, this location is likely in which biome?
Based on the climate diagram, this location is likely in which biome?
A) Tropical seasonal forest
B) Tropical rainforest
C) Temperate grassland
D) Temperate deciduous forest
 Based on the climate diagram, this location is likely in which biome?
Based on the climate diagram, this location is likely in which biome?A) Tropical seasonal forest
B) Tropical rainforest
C) Temperate grassland
D) Temperate deciduous forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Refer to the figure.
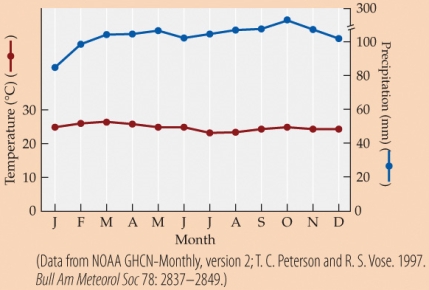 A plant requires a minimum of 50 mm of precipitation per month to grow. Its water requirements increase with increasing temperature, such that for every 1°C that the average monthly temperature is above freezing, it requires an additional 1 mm of precipitation. Based on the climate diagram, and assuming the weather reflects long-term climatic averages, this plant should be able to grow during how many months of the year?
A plant requires a minimum of 50 mm of precipitation per month to grow. Its water requirements increase with increasing temperature, such that for every 1°C that the average monthly temperature is above freezing, it requires an additional 1 mm of precipitation. Based on the climate diagram, and assuming the weather reflects long-term climatic averages, this plant should be able to grow during how many months of the year?
A) 6
B) 9
C) 11
D) 12
 A plant requires a minimum of 50 mm of precipitation per month to grow. Its water requirements increase with increasing temperature, such that for every 1°C that the average monthly temperature is above freezing, it requires an additional 1 mm of precipitation. Based on the climate diagram, and assuming the weather reflects long-term climatic averages, this plant should be able to grow during how many months of the year?
A plant requires a minimum of 50 mm of precipitation per month to grow. Its water requirements increase with increasing temperature, such that for every 1°C that the average monthly temperature is above freezing, it requires an additional 1 mm of precipitation. Based on the climate diagram, and assuming the weather reflects long-term climatic averages, this plant should be able to grow during how many months of the year?A) 6
B) 9
C) 11
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which biome contains only 11% of Earth's terrestrial vegetation cover, but is home to about half of Earth's species?
A) Tropical rainforest
B) Temperate grassland
C) Temperate deciduous forest
D) Tropical seasonal forest
A) Tropical rainforest
B) Temperate grassland
C) Temperate deciduous forest
D) Tropical seasonal forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The climate of a certain region is warm to hot, with little seasonal variation in temperature, but with a pronounced dry season. The vegetation is mostly grasses, but there are some shrubs and trees. This region is most likely a
A) desert.
B) tropical dry forest.
C) tropical savanna.
D) temperate grassland.
A) desert.
B) tropical dry forest.
C) tropical savanna.
D) temperate grassland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A biome in a tropical region gradually shifts from a tropical seasonal forest to a savanna. What environmental factor is most likely responsible for this change?
A) A gradual increase in average temperature
B) A gradual increase in average rainfall
C) Recurring fires set by humans
D) Removal of large grazing mammals
A) A gradual increase in average temperature
B) A gradual increase in average rainfall
C) Recurring fires set by humans
D) Removal of large grazing mammals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The blue candle cactus, found in Mexico's Chihuahuan Desert, and Euphorbia polyacantha, found in the Eastern Hemisphere, both have succulent upright stems and protective spines. These similar characteristics result from
A) convergence.
B) a close genetic relationship.
C) high water availability.
D) desertification.
A) convergence.
B) a close genetic relationship.
C) high water availability.
D) desertification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Refer to the figure.
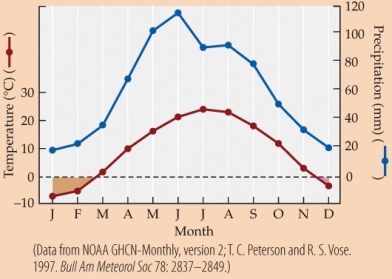
- Based on the climate diagram, this location is most likely in a
A) temperate evergreen forest.
B) seasonal tropical forest.
C) temperate grassland.
D) boreal forest.

- Based on the climate diagram, this location is most likely in a
A) temperate evergreen forest.
B) seasonal tropical forest.
C) temperate grassland.
D) boreal forest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the figure.
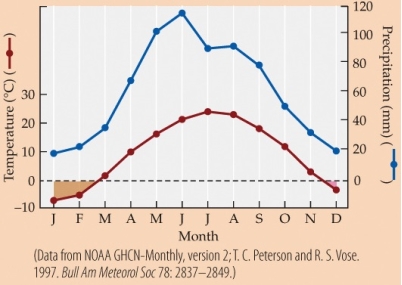
- Suppose that growing a plant requires at least 60 mm of precipitation and mean monthly temperatures between 5°C and 30°C. Based on the climate diagram, and assuming that the weather conforms to the long-term average, the plant should be able to grow during how many months of the year?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 10
D) 12

- Suppose that growing a plant requires at least 60 mm of precipitation and mean monthly temperatures between 5°C and 30°C. Based on the climate diagram, and assuming that the weather conforms to the long-term average, the plant should be able to grow during how many months of the year?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 10
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the figure.
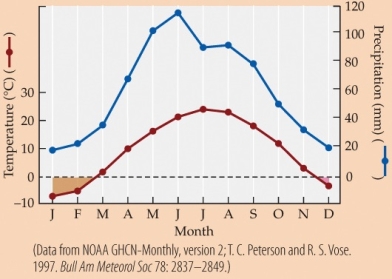
-Based on the climate diagram, precipitation is usually the highest in
A) January and February.
B) March and April.
C) May and June.
D) November and December.

-Based on the climate diagram, precipitation is usually the highest in
A) January and February.
B) March and April.
C) May and June.
D) November and December.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The temperate deciduous forest biome has been developed for agriculture for centuries. More recently, the tropical forest biome is undergoing the same transition to agriculture, but with less success. The most likely reason the tropical forest biome has adapted less well to agriculture is that this biome, compared to the deciduous forest biome, has
A) less precipitation.
B) lower soil fertility.
C) lower temperatures.
D) more pronounced seasons.
A) less precipitation.
B) lower soil fertility.
C) lower temperatures.
D) more pronounced seasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A forest is located at about 4°N latitude, has moderate precipitation, and grows on nutrient-poor soils. At intervals, the forest is subject to fires, which help it persist. This is most likely which kind of forest?
A) Tropical rainforest
B) Temperate deciduous forest
C) Temperate evergreen forest
D) Boreal forest
A) Tropical rainforest
B) Temperate deciduous forest
C) Temperate evergreen forest
D) Boreal forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Refer to the figure.
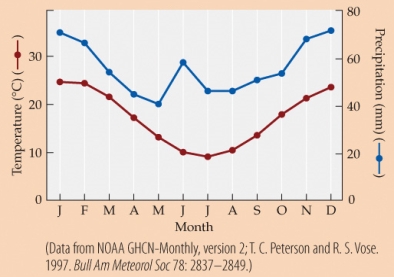
- According to the climate diagram, the highest temperatures and the most precipitation at this location occur during which months, respectively?
A) January; January
B) January; July
C) April; January
D) July; July

- According to the climate diagram, the highest temperatures and the most precipitation at this location occur during which months, respectively?
A) January; January
B) January; July
C) April; January
D) July; July

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the figure.
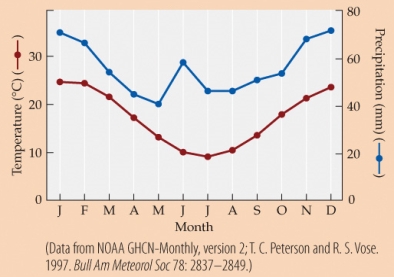
-Suppose that growing a plant requires an average of 10 mm of precipitation plus 1 mm of precipitation for every degree the average monthly temperature exceeds freezing. The plant also requires an average monthly temperature above freezing. Based on the climate diagram, and assuming that the temperature conforms to the long-term climatic average, during how many months of the year should the plant be able to grow?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 10
D) 12

-Suppose that growing a plant requires an average of 10 mm of precipitation plus 1 mm of precipitation for every degree the average monthly temperature exceeds freezing. The plant also requires an average monthly temperature above freezing. Based on the climate diagram, and assuming that the temperature conforms to the long-term climatic average, during how many months of the year should the plant be able to grow?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 10
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Boreal forests most likely consist of conifers because conifers
A) require the dry soil present in areas with permafrost.
B) are better equipped than angiosperms to withstand cold climates.
C) such as pines and firs can only grow in areas where permafrost is present.
D) require large areas to grow, and the boreal forest covers the most land area of any biome.
A) require the dry soil present in areas with permafrost.
B) are better equipped than angiosperms to withstand cold climates.
C) such as pines and firs can only grow in areas where permafrost is present.
D) require large areas to grow, and the boreal forest covers the most land area of any biome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The primary difference between tundra and boreal forest is that
A) the tundra generally lacks permafrost.
B) trees are the dominant vegetation in boreal forests but not in tundra.
C) nearly all tundra areas are very dry, whereas boreal forests are wet.
D) herds of caribou and musk oxen live in boreal forests but not in tundra.
A) the tundra generally lacks permafrost.
B) trees are the dominant vegetation in boreal forests but not in tundra.
C) nearly all tundra areas are very dry, whereas boreal forests are wet.
D) herds of caribou and musk oxen live in boreal forests but not in tundra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the figure.
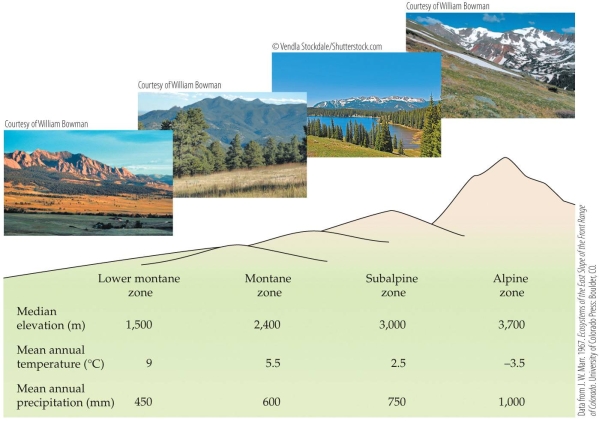 Based on the figure, how does the climate change as one moves from the alpine to the subalpine to the montane zone of a mountain?
Based on the figure, how does the climate change as one moves from the alpine to the subalpine to the montane zone of a mountain?
A) Both temperature and precipitation increase.
B) Both temperature and precipitation decrease.
C) Temperature increases and precipitation decreases.
D) Temperature decreases and precipitation increases.
 Based on the figure, how does the climate change as one moves from the alpine to the subalpine to the montane zone of a mountain?
Based on the figure, how does the climate change as one moves from the alpine to the subalpine to the montane zone of a mountain?A) Both temperature and precipitation increase.
B) Both temperature and precipitation decrease.
C) Temperature increases and precipitation decreases.
D) Temperature decreases and precipitation increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which condition is more likely to occur in tundra than in tropical alpine locales?
A) Very high wind speeds
B) High partial pressures of carbon dioxide
C) High solar radiation
D) Extremely hot temperatures
A) Very high wind speeds
B) High partial pressures of carbon dioxide
C) High solar radiation
D) Extremely hot temperatures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the map.
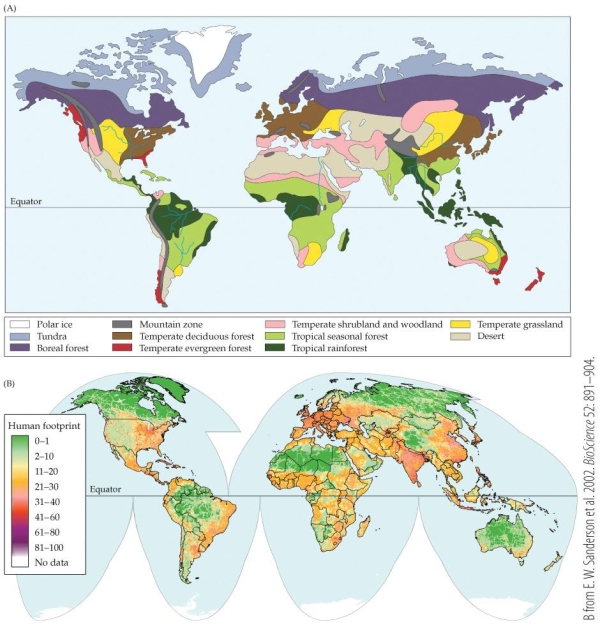 Part B on the map shows the alteration of terrestrial biomes by human activities (i.e., the "human footprint"), with green representing the least human impact and purple-red representing the most. According to the map, which biome is overall least altered by human activity world-wide?
Part B on the map shows the alteration of terrestrial biomes by human activities (i.e., the "human footprint"), with green representing the least human impact and purple-red representing the most. According to the map, which biome is overall least altered by human activity world-wide?
A) Deserts
B) Tropical rainforests
C) Tundra
D) Tropical seasonal forest
 Part B on the map shows the alteration of terrestrial biomes by human activities (i.e., the "human footprint"), with green representing the least human impact and purple-red representing the most. According to the map, which biome is overall least altered by human activity world-wide?
Part B on the map shows the alteration of terrestrial biomes by human activities (i.e., the "human footprint"), with green representing the least human impact and purple-red representing the most. According to the map, which biome is overall least altered by human activity world-wide?A) Deserts
B) Tropical rainforests
C) Tundra
D) Tropical seasonal forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the map.
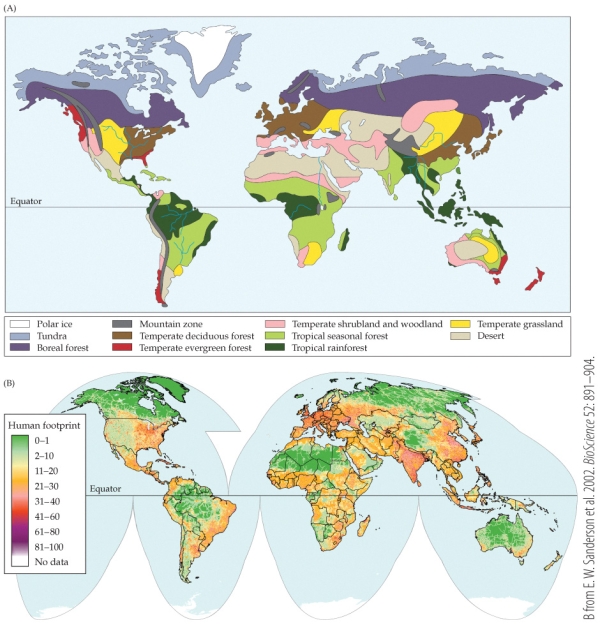 Part B on the map shows the alteration of terrestrial biomes by human activities (i.e., the "human footprint"), with green representing the least human impact and purple-red representing the most. Rank the following countries with respect to how much human activity has altered their native biomes (from most to least impact): India, United States, and Russia.
Part B on the map shows the alteration of terrestrial biomes by human activities (i.e., the "human footprint"), with green representing the least human impact and purple-red representing the most. Rank the following countries with respect to how much human activity has altered their native biomes (from most to least impact): India, United States, and Russia.
A) India > United States > Russia
B) India > Russia > United States
C) United States > Russia > India
D) United States > India > Russia
 Part B on the map shows the alteration of terrestrial biomes by human activities (i.e., the "human footprint"), with green representing the least human impact and purple-red representing the most. Rank the following countries with respect to how much human activity has altered their native biomes (from most to least impact): India, United States, and Russia.
Part B on the map shows the alteration of terrestrial biomes by human activities (i.e., the "human footprint"), with green representing the least human impact and purple-red representing the most. Rank the following countries with respect to how much human activity has altered their native biomes (from most to least impact): India, United States, and Russia.A) India > United States > Russia
B) India > Russia > United States
C) United States > Russia > India
D) United States > India > Russia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Livestock grazing in deserts and desert margins is likely to result in all of these changes to the environment except
A) erosion.
B) increased plant cover.
C) salinization of soils.
D) further desertification.
A) erosion.
B) increased plant cover.
C) salinization of soils.
D) further desertification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A factor that makes temperate grassland biomes particularly well suited for conversion into agricultural land is their
A) frequency of fires.
B) inability to support forests.
C) high level of soil organic matter.
D) generally low level of precipitation.
A) frequency of fires.
B) inability to support forests.
C) high level of soil organic matter.
D) generally low level of precipitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Assuming that the concept of a river continuum is correct, how would a second-, third-, and fourth-order river be ranked, in terms of the importance of terrestrial vegetation as a food source for the organisms within it?
A) Fourth order > third order > second order
B) Third order > second order > fourth order
C) Second order > fourth order > third order
D) Second order > third order > fourth order
A) Fourth order > third order > second order
B) Third order > second order > fourth order
C) Second order > fourth order > third order
D) Second order > third order > fourth order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider both the particle size on the stream bottom and the number of rooted and floating macrophytes in a higher-order stream, such as the Mississippi River, compared to a small first-order source stream of the Mississippi. The river would have
A) smaller particle size and fewer macrophytes.
B) smaller particle size and more macrophytes.
C) larger particle size and fewer macrophytes.
D) larger particle size and more macrophytes.
A) smaller particle size and fewer macrophytes.
B) smaller particle size and more macrophytes.
C) larger particle size and fewer macrophytes.
D) larger particle size and more macrophytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the figure.
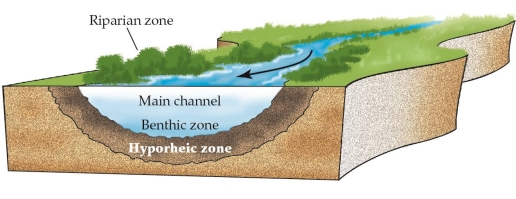 Invertebrates that consume detritus would most likely be found in which zone of the river ecosystem?
Invertebrates that consume detritus would most likely be found in which zone of the river ecosystem?
A) Riparian zone
B) Main channel
C) Benthic zone
D) Hyporheic zone
 Invertebrates that consume detritus would most likely be found in which zone of the river ecosystem?
Invertebrates that consume detritus would most likely be found in which zone of the river ecosystem?A) Riparian zone
B) Main channel
C) Benthic zone
D) Hyporheic zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Compare the surface area-to-volume ratios and the nutrient levels, respectively, in deep lakes as opposed to shallow lakes.
a. Deep lakes have lower surface-to-volume ratios and fewer nutrients.
b. Deep lakes have lower surface-to-volume ratios and more nutrients.
c. Deep lakes have similar surface-to-volume ratios, and fewer nutrients.
d. Deep lakes have higher surface-to-volume ratios and more nutrients.
Textbook Reference: 3.2 Biological zones in freshwater ecosystems are associated with the velocity, depth, temperature, clarity, and chemistry of the water
a. Deep lakes have lower surface-to-volume ratios and fewer nutrients.
b. Deep lakes have lower surface-to-volume ratios and more nutrients.
c. Deep lakes have similar surface-to-volume ratios, and fewer nutrients.
d. Deep lakes have higher surface-to-volume ratios and more nutrients.
Textbook Reference: 3.2 Biological zones in freshwater ecosystems are associated with the velocity, depth, temperature, clarity, and chemistry of the water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which organisms can only be found in the photic zone of any aquatic ecosystem?
A) Zooplankton
B) Phytoplankton
C) Fungi
D) Larger animals, like fish
A) Zooplankton
B) Phytoplankton
C) Fungi
D) Larger animals, like fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The coldest part of a large lake is usually in which zone?
A) Benthic
B) Littoral
C) Pelagic
D) Photic
A) Benthic
B) Littoral
C) Pelagic
D) Photic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
One characteristic of freshwater ecosystems, as compared with terrestrial ecosystems, is that freshwater ecosystems
A) are defined by the animals they contain as well as the plants.
B) show more variability in temperature.
C) occupy more surface area.
D) have been less affected by human impact.
A) are defined by the animals they contain as well as the plants.
B) show more variability in temperature.
C) occupy more surface area.
D) have been less affected by human impact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A river is being subjected to a variety of human-generated activities that are decreasing its ability to support life. Of these various activities, the one least likely to decrease water clarity is
A) addition of sewage.
B) addition of fertilizer runoff.
C) increased sediment input.
D) introduction of exotic species.
A) addition of sewage.
B) addition of fertilizer runoff.
C) increased sediment input.
D) introduction of exotic species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A researcher finds that the physical environment at a certain location alternates between marine and terrestrial with the rise and fall of the tides. A stable substratum provides an anchor against the pounding tides for a diverse array of organisms. Organisms that live there, especially those that are sessile, usually have high tolerance for changes in salinity, temperature, and desiccation. This area is most likely a(n)
A) estuary.
B) sandy shore.
C) rocky intertidal zone.
D) pelagic zone.
A) estuary.
B) sandy shore.
C) rocky intertidal zone.
D) pelagic zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A nearshore marine environment is located in a tropical area, and is home to salt-tolerant evergreen trees and animals including manatees and crab-eating monkeys. This environment is most likely a(an)
A) estuary.
B) salt marsh.
C) mangrove forest.
D) rocky intertidal zone.
A) estuary.
B) salt marsh.
C) mangrove forest.
D) rocky intertidal zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose corals had never evolved on Earth. What is one way in which Earth's oceans would likely be different today?
A) There would be more fish.
B) There would be fewer islands.
C) There would be no ocean algae.
D) Ocean ecosystems would be more diverse.
A) There would be more fish.
B) There would be fewer islands.
C) There would be no ocean algae.
D) Ocean ecosystems would be more diverse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the figure.
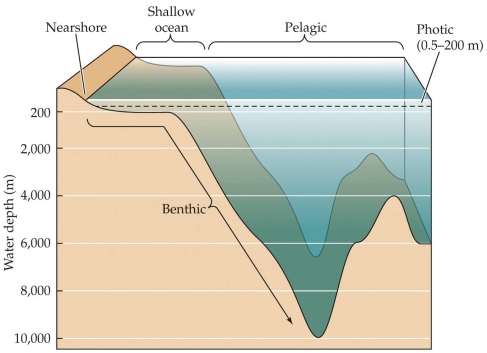 Organisms in the ocean that live on detritus are most likely to live in which zone, shown in the figure?
Organisms in the ocean that live on detritus are most likely to live in which zone, shown in the figure?
A) Nearshore
B) Shallow ocean
C) Photic zone
D) Benthic zone
 Organisms in the ocean that live on detritus are most likely to live in which zone, shown in the figure?
Organisms in the ocean that live on detritus are most likely to live in which zone, shown in the figure?A) Nearshore
B) Shallow ocean
C) Photic zone
D) Benthic zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Animals in the ocean's photic zone are likely to be more abundant and more diverse because of high levels of which factor present at this level?
A) Light
B) Pressure
C) Predation
D) Detritus
A) Light
B) Pressure
C) Predation
D) Detritus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The most likely way to halt or limit coral bleaching, or loss of a coral's symbiotic algal partner, would be to
A) decrease sediment runoff into coral reefs.
B) halt or slow global warming.
C) move coral reefs to deeper water.
D) designate all coral reefs as protected areas.
A) decrease sediment runoff into coral reefs.
B) halt or slow global warming.
C) move coral reefs to deeper water.
D) designate all coral reefs as protected areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following results, if found to be true, would provide evidence against the overkill hypothesis as the cause of extinction of North American megafauna?
A) Selective extinction of large animals, particularly mammals
B) The spread of diseases carried by humans and possibly dogs
C) Butchering sites containing spearheads and bones of now-extinct animals
D) Correlation between extinctions and arrival of humans on several continents
A) Selective extinction of large animals, particularly mammals
B) The spread of diseases carried by humans and possibly dogs
C) Butchering sites containing spearheads and bones of now-extinct animals
D) Correlation between extinctions and arrival of humans on several continents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Using deserts and forests as examples, explain why plant growth forms are better than other factors, such as climate, for characterizing biomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the figure.
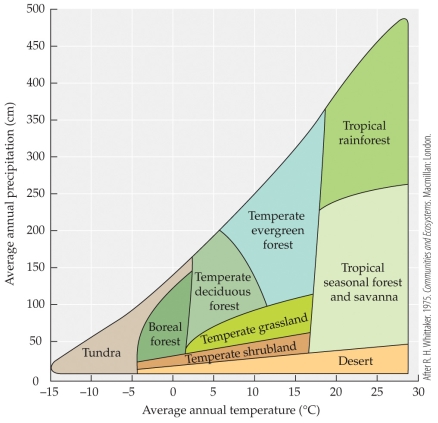 Using tundra, tropical rainforest, and temperate deciduous forest as examples, explain how the interaction of temperature and precipitation affects the location of biomes.
Using tundra, tropical rainforest, and temperate deciduous forest as examples, explain how the interaction of temperature and precipitation affects the location of biomes.
 Using tundra, tropical rainforest, and temperate deciduous forest as examples, explain how the interaction of temperature and precipitation affects the location of biomes.
Using tundra, tropical rainforest, and temperate deciduous forest as examples, explain how the interaction of temperature and precipitation affects the location of biomes.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A seasonal tropical forest has existed for centuries in Africa. Recently, large herds of mammals including elephants, wildebeests, and zebras, are moving into the area. They are seeking food, driven north by recurring droughts in their original habitats. How will the incursion of these large grazers likely affect the biome?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Boreal forests are the predominant biome between about 50 and 65°N latitude. Above this, tundra predominates. What is the major difference between the plant forms in these two biomes, and what is the major cause of this difference? How is the relationship between these two biomes likely to change as climate change continues?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Over the centuries, the human use of fire has altered the location and composition of biomes around the world. Explain how this has happened, giving specific examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the Amazon rainforest in August 2019, there were 80,000 human-caused fires burning in Brazil, an increase of 80 percent compared to 2018. Around the world, tropical rainforests are rapidly disappearing, as humans cut or burn them to provide lumber and agricultural land. Discuss the relationship of this loss of rainforests to climate change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Mississippi River flows from its headwaters, Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, to the Mississippi Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. As climate change has progressed, many areas along the river have seen increasingly heavy rainfall, which has increased the flow rate of the river. How would the increased flow rate affect the amounts of detritus and sediment that are carried by the river along its course? How would this change affect river life?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In Lake Tahoe, located in California and Nevada, algal growth historically occurred down to more than 100 meters. But since about 1960, increased human activity has caused a change in the lake; algal photosynthesis now occurs only down to between 40 and 60 m. What changes in the lake could account for this change in the depth of the photic zone?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose changing climatic conditions cause ocean currents to shift. This causes a large and sudden increase in deposition of sand in shallow waters that previously had a rocky bottom and supported a large kelp bed. What effect would this change have on kelp populations, and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The calcium carbonate skeletons of corals make up the physical structure of coral reefs. These skeletons provide a habitat for a diverse array of organisms and support a highly productive ecosystem. As more carbon dioxide enters the oceans and dissolves to form carbonic acid, the pH of the oceans becomes more acidic. This increasing ocean acidification decreases the ability of corals to build skeletons and construct reefs. If ocean acidification continues, how will it affect the diversity and productivity of coral reefs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A scientist studied the major plants in two different sites within a biome. He found many similarities in the plants in these two sites, including their growth forms and physiological responses. They were also very similar in their taxonomic classifications, with many being in the same genus. These similarities suggest that
A) the two sites are on the same continent.
B) the two sites are on different continents.
C) plants in a single biome are similar in all ways.
D) physical environment is more important than climate in defining biomes.
A) the two sites are on the same continent.
B) the two sites are on different continents.
C) plants in a single biome are similar in all ways.
D) physical environment is more important than climate in defining biomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Refer to the figure.
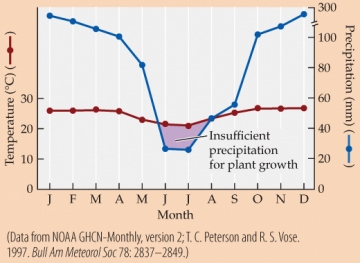
- Based on the climate diagram, the location is most likely in _______ biome, at around _______ latitude?
A) tropical seasonal forest; 20°S
B) tropical seasonal forest; 40°N
C) tropical rainforest; 5°N
D) tropical rainforest; 20°S

- Based on the climate diagram, the location is most likely in _______ biome, at around _______ latitude?
A) tropical seasonal forest; 20°S
B) tropical seasonal forest; 40°N
C) tropical rainforest; 5°N
D) tropical rainforest; 20°S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Refer to the figure.
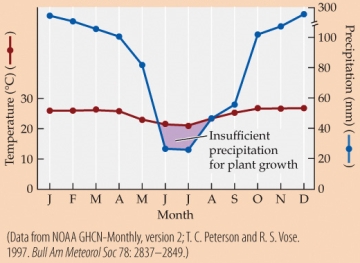
-Suppose that growing a plant requires at least 3 mm of precipitation for every 1°C that the average monthly temperature is above freezing. Based on the climate diagram and assuming that the weather conforms to the long-term average, this plant should be able to grow for about how many months of the year?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8

-Suppose that growing a plant requires at least 3 mm of precipitation for every 1°C that the average monthly temperature is above freezing. Based on the climate diagram and assuming that the weather conforms to the long-term average, this plant should be able to grow for about how many months of the year?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the figure.
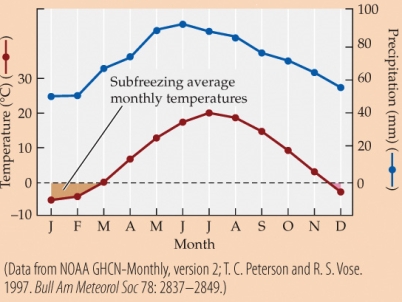 Based on the climate diagram, when would trees in this biome most likely drop their leaves?
Based on the climate diagram, when would trees in this biome most likely drop their leaves?
A) September
B) April
C) June
D) December
 Based on the climate diagram, when would trees in this biome most likely drop their leaves?
Based on the climate diagram, when would trees in this biome most likely drop their leaves?A) September
B) April
C) June
D) December

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Two sites of a biome both occur at a latitude of about 30°N. One site is in Mexico, the other in Ethiopia. Many of the plants at these two sites are succulents, with water-storing stems and many spines. The climate in this biome is most likely
A) hot and dry all year.
B) cold and dry all year.
C) seasonal, with hot and cold seasons.
D) seasonal, with wet and dry seasons.
A) hot and dry all year.
B) cold and dry all year.
C) seasonal, with hot and cold seasons.
D) seasonal, with wet and dry seasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the figure.
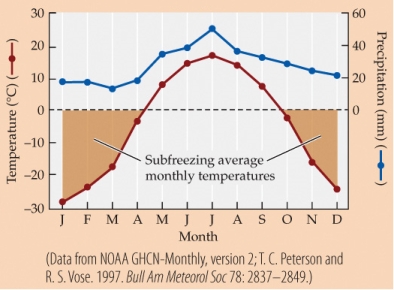 Suppose that trees in the boreal forest biome, a climate diagram for which is shown here, require at least 35 mm of average monthly precipitation to grow. The average growing season is 130 days per year. According to the climate diagram, growth in boreal forests is most likely limited by
Suppose that trees in the boreal forest biome, a climate diagram for which is shown here, require at least 35 mm of average monthly precipitation to grow. The average growing season is 130 days per year. According to the climate diagram, growth in boreal forests is most likely limited by
A) temperature only.
B) precipitation only.
C) both temperature and precipitation.
D) temperature in the winter and precipitation in the summer.
 Suppose that trees in the boreal forest biome, a climate diagram for which is shown here, require at least 35 mm of average monthly precipitation to grow. The average growing season is 130 days per year. According to the climate diagram, growth in boreal forests is most likely limited by
Suppose that trees in the boreal forest biome, a climate diagram for which is shown here, require at least 35 mm of average monthly precipitation to grow. The average growing season is 130 days per year. According to the climate diagram, growth in boreal forests is most likely limited byA) temperature only.
B) precipitation only.
C) both temperature and precipitation.
D) temperature in the winter and precipitation in the summer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A certain biome is characterized by sedges, forbs, grasses, low-growing shrubs, lichens, and mosses. Its growing season is short, but summer days are very long. Although precipitation is low, the soil is often wet. Alternate freezing and thawing of soil results in a pattern of polygons and pingos on the soil surface. This biome is most likely
A) tundra.
B) subalpine zone.
C) temperate evergreen forest.
D) boreal forest.
A) tundra.
B) subalpine zone.
C) temperate evergreen forest.
D) boreal forest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which factor most likely prevented the grasslands at the eastern edge of the Great Plains from becoming forest?
A) Insufficient precipitation
B) Frequent fires set by humans
C) Excessively low temperatures
D) Insufficient soil nutrients
A) Insufficient precipitation
B) Frequent fires set by humans
C) Excessively low temperatures
D) Insufficient soil nutrients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Certain fly larvae living in rivers consume detritus and can move most freely through fine particles. These fly larvae are most likely to be found in which part of the river?
A) Riffles
B) Benthic zone
C) Hyporheic zone
D) Open water
A) Riffles
B) Benthic zone
C) Hyporheic zone
D) Open water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Lake Baikal, in Siberia, is 5,200 feet (almost a mile) deep. Lake Erie, one of the U.S. Great Lakes has an average depth of 62 feet, and is 210 feet deep at its deepest point. What is the best comparison of the likely light penetration and nutrient levels in these two lakes?
A) Light will penetrate to the bottom of both lakes and nutrient levels will be high in both.
B) Light will penetrate to the bottom of Lake Baikal only, and nutrient levels will be high in Lake Baikal only.
C) Light will penetrate to the bottom of neither lake, but nutrient levels will be high in both.
D) Light will penetrate to the bottom of Lake Erie only, and nutrient levels will be high in Lake Erie only.
A) Light will penetrate to the bottom of both lakes and nutrient levels will be high in both.
B) Light will penetrate to the bottom of Lake Baikal only, and nutrient levels will be high in Lake Baikal only.
C) Light will penetrate to the bottom of neither lake, but nutrient levels will be high in both.
D) Light will penetrate to the bottom of Lake Erie only, and nutrient levels will be high in Lake Erie only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Seagrass beds form underwater meadows that are often closely associated with coral reefs. What is one likely reason for this association?
A) Corals feed mostly on seagrasses.
B) Seagrasses provide food, habitat, and stability for the coral reef ecosystem.
C) Corals provide a limestone substrate in which seagrass can root itself.
D) Seagrasses are more diverse than reefs; thus, they add to coral reef diversity.
A) Corals feed mostly on seagrasses.
B) Seagrasses provide food, habitat, and stability for the coral reef ecosystem.
C) Corals provide a limestone substrate in which seagrass can root itself.
D) Seagrasses are more diverse than reefs; thus, they add to coral reef diversity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A shallow region of the ocean (less than about 15 m) has a solid, rocky substrate. This would be an ideal substrate for which type of ocean vegetation?
A) Kelp
B) Seagrass
C) Sargassum
D) Mangrove forests
A) Kelp
B) Seagrass
C) Sargassum
D) Mangrove forests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A region of the ocean is very clear and filled with light, and most of its permanent inhabitants are phytoplankton and zooplankton. In some areas there are large floating algae, such as Sargassum. The region is frequently visited by a variety of nekton, including fishes, sea turtles, whales, and dolphins. Its overall biological density and diversity are relatively low. This region is most likely in
A) the deep benthic zone.
B) the deep pelagic zone.
C) the photic zone in the open ocean.
D) a nearshore estuary.
A) the deep benthic zone.
B) the deep pelagic zone.
C) the photic zone in the open ocean.
D) a nearshore estuary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A region along the U.S. East Coast has a variety of types of ecosystems. One of these ecosystems shows strong gradients in salinity, ranging from near freshwater levels to near ocean levels. Deposition of coastal sediments increases the nutrient levels of this ecosystem, enabling many fish to spend their larval stages here. This ecosystem is most likely a(an)
A) salt marsh.
B) rocky intertidal zone.
C) estuary.
D) sandy shore.
A) salt marsh.
B) rocky intertidal zone.
C) estuary.
D) sandy shore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Lake Merritt, near Oakland, California, is home to the first official wildlife refuge in the United States. Because it is a place where fresh water and the ocean meet, Lake Merritt should be classified not as a lake, but rather as a(n)
A) littoral zone.
B) pelagic zone.
C) estuary.
D) photic zone.
A) littoral zone.
B) pelagic zone.
C) estuary.
D) photic zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



