Deck 1: Biochemistry: an Introduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Biochemistry: an Introduction
1
The ultimate source of energy for life on earth is __________.
A) The sun
B) Geothermal heat
C) Carbohydrates
D) Fats
E) Other organisms
A) The sun
B) Geothermal heat
C) Carbohydrates
D) Fats
E) Other organisms
A
2
Which of the following is not a common component of biomolecules?
A) Carbon
B) Hydrogen
C) Oxygen
D) Nitrogen
E) Chlorine
A) Carbon
B) Hydrogen
C) Oxygen
D) Nitrogen
E) Chlorine
E
3
Which of the following is the basic structural unit of living organisms?
A) Nucleus
B) Cell membrane
C) Tissue
D) Cell
E) Cytoskeleton
A) Nucleus
B) Cell membrane
C) Tissue
D) Cell
E) Cytoskeleton
D
4
Which of the following is not an organelle?
A) Mitochondria
B) Chloroplast
C) Nucleus
D) Plasma membrane
E) Golgi complex
A) Mitochondria
B) Chloroplast
C) Nucleus
D) Plasma membrane
E) Golgi complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not a role played by carbohydrates in living cells?
A) Energy source
B) Structural support
C) Intercellular communication
D) Both A and B are correct
E) All are roles played by carbohydrates in living cells
A) Energy source
B) Structural support
C) Intercellular communication
D) Both A and B are correct
E) All are roles played by carbohydrates in living cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Metabolism is best defined as the _________.
A) Reactions of living cells
B) Reactions that synthesize large molecules in living cells
C) Reactions that degrade molecules in living cells
D) Conversion of food molecules to energy
E) Reactions that synthesize and degrade molecules in living cells
A) Reactions of living cells
B) Reactions that synthesize large molecules in living cells
C) Reactions that degrade molecules in living cells
D) Conversion of food molecules to energy
E) Reactions that synthesize and degrade molecules in living cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The average life span of a species is about ________years
A) One million
B) Ten million
C) Five hundred thousand
D) Five million
E) One hundred thousand
A) One million
B) Ten million
C) Five hundred thousand
D) Five million
E) One hundred thousand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not a waste product of living organisms
A) Carbon dioxide
B) Water
C) Urea
D) Ammonia
E) Glycine
A) Carbon dioxide
B) Water
C) Urea
D) Ammonia
E) Glycine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Biochemistry is defined as
A) The study of life processes
B) The study of the molecular basis of life
C) The study of living organisms
D) The study of organic compounds in living organisms
E) The study of living compounds
A) The study of life processes
B) The study of the molecular basis of life
C) The study of living organisms
D) The study of organic compounds in living organisms
E) The study of living compounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
One of the principal methods that organisms use to obtain energy from chemical bonds is by ___________.
A) Substitution reactions
B) Dehydration reactions
C) Oxidation/reduction reactions
D) Hydration reactions
E) Addition reactions
A) Substitution reactions
B) Dehydration reactions
C) Oxidation/reduction reactions
D) Hydration reactions
E) Addition reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The following is an example of which reaction class?
CH3Br + HSCH2CH(NH2)COOH CH3SCH2CH(NH2)COOH + Br- + H+
A) Substitution
B) Elimination
C) Addition
D) Isomerization
E) Oxidation/Reduction
CH3Br + HSCH2CH(NH2)COOH CH3SCH2CH(NH2)COOH + Br- + H+
A) Substitution
B) Elimination
C) Addition
D) Isomerization
E) Oxidation/Reduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The following is an example of which reaction class
HOOCCH=CHCOOH + H2O HOOCCH2CH(OH)COOH
A) Substitution
B) Elimination
C) Addition
D) Isomerization
E) Oxidation/Reduction
HOOCCH=CHCOOH + H2O HOOCCH2CH(OH)COOH
A) Substitution
B) Elimination
C) Addition
D) Isomerization
E) Oxidation/Reduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The following is an example of which reaction class?
CH3CH2OH CH3CHO + H2O
A) Substitution
B) Elimination
C) Addition
D) Isomerization
E) Oxidation/Reduction
CH3CH2OH CH3CHO + H2O
A) Substitution
B) Elimination
C) Addition
D) Isomerization
E) Oxidation/Reduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is not a component of nucleic acid?
A) Nucleotides
B) Glucose
C) Phosphate group
D) Purines
E) Pyrimidines
A) Nucleotides
B) Glucose
C) Phosphate group
D) Purines
E) Pyrimidines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The largest molecules in living organisms are _________.
A) proteins
B) lipids
C) nucleic acids
D) carbohydrates
E) steroids
A) proteins
B) lipids
C) nucleic acids
D) carbohydrates
E) steroids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
All of the following classes of compounds are lipids except _______.
A) fats
B) sterols
C) fatty acids
D) phosphoglycerides
E) nucleotides
A) fats
B) sterols
C) fatty acids
D) phosphoglycerides
E) nucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following classes of biomolecules are the most abundant in nature?
A) Lipids
B) Amino acids
C) Carbohydrates
D) Proteins
E) Nucleotides
A) Lipids
B) Amino acids
C) Carbohydrates
D) Proteins
E) Nucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the following molecule. Which arrow is pointing to a peptide bond? 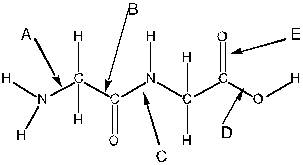
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The following molecule is an example of which single class of compounds?
CH3CH2CH(NH2)COOH
A) Amine
B) Acid
C) Ester
D) Amino acid
E) Alcohol
CH3CH2CH(NH2)COOH
A) Amine
B) Acid
C) Ester
D) Amino acid
E) Alcohol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The following molecule is an example of which class of compounds?
CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3
A) Hydrocarbon
B) Acid
C) Ester
D) Ether
E) Aldehyde
CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3
A) Hydrocarbon
B) Acid
C) Ester
D) Ether
E) Aldehyde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The following molecule is an example of which class of compounds?
CH3CH2CH2COOH
A) Hydrocarbon
B) Acid
C) Alcohol
D) Aldehyde
E) Ketone
CH3CH2CH2COOH
A) Hydrocarbon
B) Acid
C) Alcohol
D) Aldehyde
E) Ketone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The chemical properties of organic molecules are determined by specific arrangements of atoms called _____________.
A) Structure
B) Bonds
C) Functional groups
D) Radicals
E) Molecules
A) Structure
B) Bonds
C) Functional groups
D) Radicals
E) Molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following classes of compounds make up most of the mass of an organism?
A) Amino acids
B) Proteins
C) Lipids
D) Carbohydrates
E) Water
A) Amino acids
B) Proteins
C) Lipids
D) Carbohydrates
E) Water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not a basic element of life?
A) Phosphorous
B) Hydrogen
C) Nitrogen
D) Oxygen
E) All of the above are basic elements of life
A) Phosphorous
B) Hydrogen
C) Nitrogen
D) Oxygen
E) All of the above are basic elements of life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Most biomolecules can be considered to be derivatives of
A) Amino acids
B) Carbohydrates
C) Fats
D) Hydrocarbons
E) Alcohols
A) Amino acids
B) Carbohydrates
C) Fats
D) Hydrocarbons
E) Alcohols

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following amino acids contain a hydrophobic side chain
A) Leucine
B) Arginine
C) Glutamine
D) Glutamic acid
E) Aspartic acid
A) Leucine
B) Arginine
C) Glutamine
D) Glutamic acid
E) Aspartic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following small molecules do not form biopolymers
A) Amino acids
B) Sugars
C) Fatty acids
D) Nucleotides
E) C and D
A) Amino acids
B) Sugars
C) Fatty acids
D) Nucleotides
E) C and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Choose the amino acid that can function as a neurotransmitter
A) Glutamic acid
B) Alanine
C) Tyrosine
D) Lysine
E) Cysteine
A) Glutamic acid
B) Alanine
C) Tyrosine
D) Lysine
E) Cysteine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A constant source of _______ is required for maintenance of a cell's ordered state.
A) Heat
B) Oxygen
C) Energy
D) Stimulus
E) Water
A) Heat
B) Oxygen
C) Energy
D) Stimulus
E) Water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is not true of life?
A) Life is cellular
B) Life is information based
C) Life is complex and dynamic
D) All living things produce energy using mitochondria
E) Life adapts and evolves
A) Life is cellular
B) Life is information based
C) Life is complex and dynamic
D) All living things produce energy using mitochondria
E) Life adapts and evolves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following classes of compounds contain the same functional group as an ester?
A) Amino acids
B) Fatty acids
C) Carbohydrates
D) Proteins
E) Fats
A) Amino acids
B) Fatty acids
C) Carbohydrates
D) Proteins
E) Fats

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not a component of DNA
A) Uracil
B) Adenine
C) Cytosine
D) Guanidine
E) Thymine
A) Uracil
B) Adenine
C) Cytosine
D) Guanidine
E) Thymine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The sum total of all reactions of an organism is called
A) Life
B) Metabolism
C) Biosynthesis
D) Anabolism
E) Energetics
A) Life
B) Metabolism
C) Biosynthesis
D) Anabolism
E) Energetics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is not characteristic of an autopoietic system?
A) Autonomous
B) Self-organizing
C) Self-maintaining
D) Intelligent
E) B and D
A) Autonomous
B) Self-organizing
C) Self-maintaining
D) Intelligent
E) B and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The assumption that a complete understanding of a living organism can be obtained solely by investigating all of its components is called _________.
A) Systems biology
B) Reductionism
C) Emergence
D) Robustness
E) Feedback control
A) Systems biology
B) Reductionism
C) Emergence
D) Robustness
E) Feedback control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is not a core principle of systems biology?
A) Emergence
B) Robustness
C) Redundancy
D) Modularity
E) Limit of resolution
A) Emergence
B) Robustness
C) Redundancy
D) Modularity
E) Limit of resolution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The field of study associated with the investigation of gene expression patterns is called:
A) Proteomics
B) Bioinformatics
C) Genomics
D) Functional genomics
E) Synomics
A) Proteomics
B) Bioinformatics
C) Genomics
D) Functional genomics
E) Synomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is not an example of a macromolecule?
A) Nucleic acid
B) Protein
C) Polysaccharide
D) Enzyme
E) Amino acid
A) Nucleic acid
B) Protein
C) Polysaccharide
D) Enzyme
E) Amino acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is not considered a class of small biomolecule?
A) Amino acid
B) Sugar
C) Nucleic Acid
D) Fatty acid
E) Nucleotide
A) Amino acid
B) Sugar
C) Nucleic Acid
D) Fatty acid
E) Nucleotide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The functional group present in the following molecule is called: 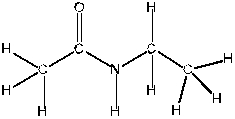
A) Amine
B) Ketone
C) Amide
D) Ester
E) Acid

A) Amine
B) Ketone
C) Amide
D) Ester
E) Acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The majority of Earth's species belong to which of the following classifications?
A) Eukaryotes
B) Prokaryotes
C) Viruses
D) Mammals
E) Archea
A) Eukaryotes
B) Prokaryotes
C) Viruses
D) Mammals
E) Archea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The conversion of earths atmosphere from anerobic to aerobic was due to the development of _________________ by cyanobacteria.
A) Photosynthesis
B) Metabolism
C) Chemosynthesis
D) Oxidation of iron
E) Fixation of nitrogen as cyanide
A) Photosynthesis
B) Metabolism
C) Chemosynthesis
D) Oxidation of iron
E) Fixation of nitrogen as cyanide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The largest mass extinction also known as the great dying was called the
A) Cenezoic extinction
B) Permian extinction
C) Mesozoic event
D) Great ice age
E) The great plague
A) Cenezoic extinction
B) Permian extinction
C) Mesozoic event
D) Great ice age
E) The great plague

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The most prominent function of RNA is
A) Energy source
B) Nutrient source
C) Protein synthesis
D) Structural elements
E) B and C
A) Energy source
B) Nutrient source
C) Protein synthesis
D) Structural elements
E) B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An organism's entire set of DNA is called
A) Genome
B) Genetic sequence
C) Polynucleotide sequence
D) Gene
E) Inheritance
A) Genome
B) Genetic sequence
C) Polynucleotide sequence
D) Gene
E) Inheritance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The major function of carbohydrates is
A) Catalysts and structural elements
B) Energy sources and structural elements
C) Genetic information
D) Protein synthesis
E) Insulation
A) Catalysts and structural elements
B) Energy sources and structural elements
C) Genetic information
D) Protein synthesis
E) Insulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is meant by the term biomolecule?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is meant by the term metabolism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is meant by the term hydrophobic?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is meant by the term sugar?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why is DNA sometimes referred to as the double helix?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Identify the functional groups in the following molecule.
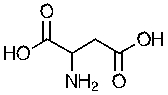


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Identify the functional group in the following molecule.
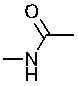


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Name four classes of small biomolecules. In what larger biomolecules are they found?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What are the functions of fatty acids?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What are two functions of nucleotides?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Compare the features of an airplane autopilot system with a biological system in terms of robustness, control mechanisms and redundancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How do plants dispose of waste products?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
To what major class of biomolecules does the following molecule belong?
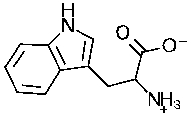


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
To what major class of biomolecules does the following molecule belong?
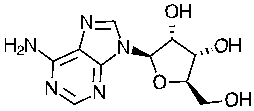


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What are the primary functions of metabolism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Compare and contrast the general features of human-designed complex systems and living systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Biochemistry and molecular biology are often thought of as very similar fields. In what ways do they differ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Humans synthesize most of the cholesterol required for cell membranes and for the synthesis of vitamin D and steroid hormones. What would you expect to happen if a person's diet is high in cholesterol. Provide a reason for your response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
DNA structure must be stable because it acts as an organism's repository of genetic information. However, it is equally important that DNA is not completely stable. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe the significance of the phrase "robust yet fragile".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Comment on the statement that carbon is not the most abundant element in the body by weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Why do anabolic processes consume energy and catabolic processes release energy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Comment on the statement that a species whose organisms are composed of exceptionally robust systems will most likely become extinct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When insulin binds to the insulin receptor, information is exchanged. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



