Deck 13: Epidemiology and Disease Control
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/130
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Epidemiology and Disease Control
1
The definition of epidemiology includes the term "distribution." Which of the following best describes this term?
A) Frequency and determinants
B) Determinants and application
C) Frequency and pattern
D) Frequency and application
A) Frequency and determinants
B) Determinants and application
C) Frequency and pattern
D) Frequency and application
C
2
Characterizing the distribution of health-related states or events according to person, place, and time is part of:
A) descriptive epidemiology.
B) analytic epidemiology.
C) cohort study designs.
D) case control study designs.
E) experimental study designs.
A) descriptive epidemiology.
B) analytic epidemiology.
C) cohort study designs.
D) case control study designs.
E) experimental study designs.
A
3
Analytic epidemiology may involve which of the following?
A) Identifying who is most likely to develop a given disease
B) Identifying where the health problem lies
C) Identifying what the clinical characteristics are of the disease
D) Identifying why a certain group of people developed a given disease
E) Identifying when a disease is most likely to occur
A) Identifying who is most likely to develop a given disease
B) Identifying where the health problem lies
C) Identifying what the clinical characteristics are of the disease
D) Identifying why a certain group of people developed a given disease
E) Identifying when a disease is most likely to occur
D
4
Malaria being spread by mosquitoes is an example of which type of disease transmission?
A) Vehicle-borne
B) Zoonosis
C) Fomite-borne
D) Vector-borne
A) Vehicle-borne
B) Zoonosis
C) Fomite-borne
D) Vector-borne

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A sharp increase in a given disease is always classified as an epidemic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An outbreak of salmonella traced to chicken cooked and held at an improper temperature and served at a potluck supper is an example of which of the following?
A) Point source epidemic
B) Intermittent or continuous source epidemic
C) Propagated epidemic
D) Mixed epidemic
A) Point source epidemic
B) Intermittent or continuous source epidemic
C) Propagated epidemic
D) Mixed epidemic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Effectiveness of a program refers to which of the following?
A) The ability of a program to produce benefits among those who are offered the program
B) The ability of a program to produce a desired effect among those who participate
C) Both of these are correct.
A) The ability of a program to produce benefits among those who are offered the program
B) The ability of a program to produce a desired effect among those who participate
C) Both of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What was the primary cause of death in 1900?
A) Cancer
B) Heart disease
C) Pneumonia and influenza
D) Diabetes
A) Cancer
B) Heart disease
C) Pneumonia and influenza
D) Diabetes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The epidemiologic triangle is based on the communicable disease model and is useful in showing the interaction and interdependence of certain factors. Which of the following best describes the host?
A) Cause of the disease
B) Harbors a disease
C) Causes or allows disease transmission
D) Duration
A) Cause of the disease
B) Harbors a disease
C) Causes or allows disease transmission
D) Duration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
For each of the following interventions, choose the type of prevention that best describes it.
-Mammograms for early detection of breast cancer and surgical intervention if necessary
A) Primary prevention
B) Secondary prevention
C) Tertiary prevention
-Mammograms for early detection of breast cancer and surgical intervention if necessary
A) Primary prevention
B) Secondary prevention
C) Tertiary prevention

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For each of the following interventions, choose the type of prevention that best describes it.
-Physical therapy for stroke victims
A) Primary prevention
B) Secondary prevention
C) Tertiary prevention
-Physical therapy for stroke victims
A) Primary prevention
B) Secondary prevention
C) Tertiary prevention

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For each of the following interventions, choose the type of prevention that best describes it.
-Education about the hazards of cigarette smoking
A) Primary prevention
B) Secondary prevention
C) Tertiary prevention
-Education about the hazards of cigarette smoking
A) Primary prevention
B) Secondary prevention
C) Tertiary prevention

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
All of the following are activities that fall under completing the clinical picture of disease, EXCEPT:
A) identification of types of exposures capable of causing disease.
B) description of the pathologic changes that occur, the stage of subclinical disease, and the expected length of this subclinical phase of the disease.
C) identification of the types of symptoms that characterize the disease.
D) identification of probable outcomes (recovery, disability, or death) associated with different levels of the disease.
E) All of these fall under completing the clinical picture of disease.
A) identification of types of exposures capable of causing disease.
B) description of the pathologic changes that occur, the stage of subclinical disease, and the expected length of this subclinical phase of the disease.
C) identification of the types of symptoms that characterize the disease.
D) identification of probable outcomes (recovery, disability, or death) associated with different levels of the disease.
E) All of these fall under completing the clinical picture of disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Who introduced the terms epidemic and endemic?
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Who exposed his wife and children to cowpox?
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Who insisted that that observation should drive the study of disease?
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Who applied experimental methods to identify that oranges and lemons were effective remedies for scurvy?
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Who demonstrated that cholera could be transmitted through contaminated water?
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham
A) Hippocrates
B) James Lind
C) John Snow
D) Benjamin Jesty
E) Thomas Sydenham

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Chinese made the observation that if one had a weak strain of smallpox, one would not get a strong strain of smallpox later. This is situation is termed:
A) zoonosis.
B) necropsy.
C) cold and hot disease theory.
D) variolation.
E) atomic theory.
A) zoonosis.
B) necropsy.
C) cold and hot disease theory.
D) variolation.
E) atomic theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Edgar Sydenstricker's primary contribution was in the development of which of the following?
A) Germ theory
B) Atomic theory
C) Morbidity statistics
D) Mortality statistics
E) A smallpox vaccine
A) Germ theory
B) Atomic theory
C) Morbidity statistics
D) Mortality statistics
E) A smallpox vaccine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The primary cause of beriberi, rickets, and pellagra is which of the following?
A) Vitamin deficiency
B) Bacteria
C) Viruses
D) Environmental exposures
A) Vitamin deficiency
B) Bacteria
C) Viruses
D) Environmental exposures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Who found that people, not fomites, were the primary means of transmission of typhoid fever in his or her investigations in the early 1900s?
A) Mary Mallon
B) George Soper
C) Lemuel Shattuck
D) T.K. Takaki
A) Mary Mallon
B) George Soper
C) Lemuel Shattuck
D) T.K. Takaki

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Janet Lane-Claypon published results on the epidemiology of breast cancer. Which of the following study designs did she employ?
A) Case-control
B) Cohort
C) Experimental
D) Two of the above study designs
E) All of these study designs were used.
A) Case-control
B) Cohort
C) Experimental
D) Two of the above study designs
E) All of these study designs were used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Framingham study involved which type of study design?
A) Case-control
B) Cohort
C) Experimental
D) Two of the above study designs
E) All of these study designs were used.
A) Case-control
B) Cohort
C) Experimental
D) Two of the above study designs
E) All of these study designs were used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
John Graunt divided disease into two types and causes. What are these?
A) Infectious and noninfectious
B) Infectious and acute
C) Noninfectious and chronic
D) Pathogenic and photogenic
E) Acute and chronic
A) Infectious and noninfectious
B) Infectious and acute
C) Noninfectious and chronic
D) Pathogenic and photogenic
E) Acute and chronic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following refres to inanimate objects that serve a role in disease transmission?
A) Fomites
B) Vectors
C) Reservoirs
D) Carriers
A) Fomites
B) Vectors
C) Reservoirs
D) Carriers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Humans that contain, spread, or harbor an infectious organism are known as:
A) fomites.
B) vectors.
C) reservoirs.
D) carriers.
A) fomites.
B) vectors.
C) reservoirs.
D) carriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Can a pathogen cause cancer?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Pathogens include all of the following, EXCEPT:
A) a virus that produces disease.
B) a microorganism that produces disease.
C) a source of or cause of communicable disease.
D) a nonmicroscopic parasite capable of producing disease.
E) All of these are pathogens.
A) a virus that produces disease.
B) a microorganism that produces disease.
C) a source of or cause of communicable disease.
D) a nonmicroscopic parasite capable of producing disease.
E) All of these are pathogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The incubation period is equivalent to which of the following?
A) Stage of susceptibility
B) Stage of presymptomatic disease
C) Stage of clinical disease
D) Stage of recover, disability, or death
A) Stage of susceptibility
B) Stage of presymptomatic disease
C) Stage of clinical disease
D) Stage of recover, disability, or death

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Latency period is a term used in the context of which of the following?
A) Infectious disease
B) Infectious acute disease
C) Noninfectious communicable disease
D) Chronic disease
A) Infectious disease
B) Infectious acute disease
C) Noninfectious communicable disease
D) Chronic disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The science and study of the causes of disease and their mode of operation is referred to as:
A) zoonosis.
B) invasiveness.
C) virulence.
D) etiology.
A) zoonosis.
B) invasiveness.
C) virulence.
D) etiology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Diseases may be classified into general categories. Which of the following is not one of these categories?
A) Congenital and hereditary diseases
B) Allergies and inflammatory diseases
C) Degenerative diseases
D) Metabolic diseases
E) Mental diseases
A) Congenital and hereditary diseases
B) Allergies and inflammatory diseases
C) Degenerative diseases
D) Metabolic diseases
E) Mental diseases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An invading substance that stimulates the immune system is called a(n):
A) toxicity.
B) pathogen.
C) antigen.
D) None of these is correct.
A) toxicity.
B) pathogen.
C) antigen.
D) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
John Salk suggested that herd immunity required what level of immunity for polio in the population or group?
A) 50%
B) 75%
C) 85%
D) 95%
A) 50%
B) 75%
C) 85%
D) 95%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consider the following two populations
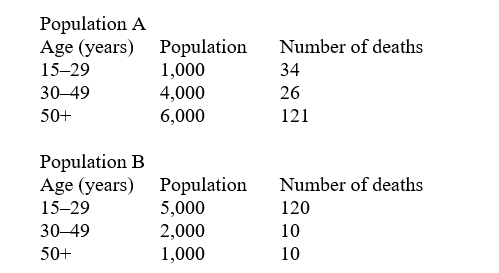
-What is the crude death rate ratio of population A to B?
A) 1.4
B) 1.2
C) 0.99
D) 0.94
E) None of these is correct.

-What is the crude death rate ratio of population A to B?
A) 1.4
B) 1.2
C) 0.99
D) 0.94
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the following two populations

-Age-adjust population B using population A as the standard (reference) population. Then, calculate the rate ratio of population A to B using this new age-adjusted rate. What is the rate ratio?
A) 1.4
B) 1.7
C) 2.2
D) None of these is correct.

-Age-adjust population B using population A as the standard (reference) population. Then, calculate the rate ratio of population A to B using this new age-adjusted rate. What is the rate ratio?
A) 1.4
B) 1.7
C) 2.2
D) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Consider the following two populations

-In what age group is the rate 30% greater in population A than B?
A) 15-29
B) 30-49
C) 50+

-In what age group is the rate 30% greater in population A than B?
A) 15-29
B) 30-49
C) 50+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the following two populations

-Which of the following descriptive study designs would you use if you wanted to collect exposure and disease data at the individual level and calculate prevalence estimates?
A) Case series
B) Ecologic
C) Cross-sectional
D) Prevalence is not estimated with any of these designs.

-Which of the following descriptive study designs would you use if you wanted to collect exposure and disease data at the individual level and calculate prevalence estimates?
A) Case series
B) Ecologic
C) Cross-sectional
D) Prevalence is not estimated with any of these designs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When several potential outcomes are being investigated for a given exposure, which observational study design is most appropriate?
A) Cross-sectional
B) Case-control
C) Cohort
D) Experimental
A) Cross-sectional
B) Case-control
C) Cohort
D) Experimental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Cancer screening is a form of primary prevention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following best describes a line listing?
A) A map that indicates the location of each case of a rare disease
B) A graphic representation of the frequency distribution of a variable
C) A histogram that shows the course of a disease outbreak
D) A visual display of the size of the different categories of a variable
E) None of these is correct.
A) A map that indicates the location of each case of a rare disease
B) A graphic representation of the frequency distribution of a variable
C) A histogram that shows the course of a disease outbreak
D) A visual display of the size of the different categories of a variable
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Match each of the following study types with the statement that best describes it.
-Aggregate data involved (i.e., no information is available for specific individuals)
A)ecologic study
B)case study
C) cross-sectional study
-Aggregate data involved (i.e., no information is available for specific individuals)
A)ecologic study
B)case study
C) cross-sectional study

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match each of the following study types with the statement that best describes it.
-Takes advantage of preexisting data
A)ecologic study
B)case study
C) cross-sectional study
-Takes advantage of preexisting data
A)ecologic study
B)case study
C) cross-sectional study

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match each of the following study types with the statement that best describes it.
-Useful for obtaining prevalence data
A)ecologic study
B)case study
C) cross-sectional study
-Useful for obtaining prevalence data
A)ecologic study
B)case study
C) cross-sectional study

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Match each of the following study types with the statement that best describes it.
-Qualitative descriptive research of the facts in chronological order
A)ecologic study
B)case study
C) cross-sectional study
-Qualitative descriptive research of the facts in chronological order
A)ecologic study
B)case study
C) cross-sectional study

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Match each of the following data types with the statement that best describes it.
-Number of cases in a defined area
A)nominal data
B)ordinal data
C) discrete data
D)continuous data
-Number of cases in a defined area
A)nominal data
B)ordinal data
C) discrete data
D)continuous data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match each of the following data types with the statement that best describes it.
-Outcome status
A)nominal data
B)ordinal data
C) discrete data
D)continuous data
-Outcome status
A)nominal data
B)ordinal data
C) discrete data
D)continuous data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Match each of the following data types with the statement that best describes it.
-Dose of radiation exposure
A)nominal data
B)ordinal data
C) discrete data
D)continuous data
-Dose of radiation exposure
A)nominal data
B)ordinal data
C) discrete data
D)continuous data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Match each of the following data types with the statement that best describes it.
-Low, medium, and high exposure status
A)nominal data
B)ordinal data
C) discrete data
D)continuous data
-Low, medium, and high exposure status
A)nominal data
B)ordinal data
C) discrete data
D)continuous data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following best describes the term "efficiency"?
A) The science and study of the causes of disease and their modes of operation
B) Ejection of the substance or metabolites from the body
C) The ability of a program to produce a desired effect among those who participate in the program compared with those who do not
D) The ability of a program to produce benefits among those who are offered the program
A) The science and study of the causes of disease and their modes of operation
B) Ejection of the substance or metabolites from the body
C) The ability of a program to produce a desired effect among those who participate in the program compared with those who do not
D) The ability of a program to produce benefits among those who are offered the program

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The definition of epidemiology involves all of the following, EXCEPT:
A) identification of determinants.
B) measuring the distribution of disease.
C) human populations.
D) application .
E) All of these are part of the definition of epidemiology.
A) identification of determinants.
B) measuring the distribution of disease.
C) human populations.
D) application .
E) All of these are part of the definition of epidemiology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is NOT an activity of descriptive epidemiology?
A) Monitoring health-related states or events over time
B) Monitoring potential exposures over time
C) Evaluating the effects of an assigned intervention on an outcome of interest
D) Understanding where and when the health problem is greatest
E) All of these are activities of descriptive epidemiology.
A) Monitoring health-related states or events over time
B) Monitoring potential exposures over time
C) Evaluating the effects of an assigned intervention on an outcome of interest
D) Understanding where and when the health problem is greatest
E) All of these are activities of descriptive epidemiology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A carrier contains, spreads, or harbors an infectious organism. Carriers may have different conditions or states. Which of the following defines a convalescent carrier?
A) Individual who has been exposed to and harbors a pathogen and who can spread the disease in different places or intervals
B) Individual who has been exposed to and harbors a pathogen, is in the beginning stages of the disease, is showing symptoms, and has the ability to transmit the disease
C) Individual who has been exposed to and harbors a pathogen, but has not become ill or shown any of the symptoms of the disease
D) Individual who has been exposed to and harbors a pathogen and who has done so for some time, but has recovered from the disease
E) Individual who harbors a pathogen and who, although in the recovery phase of the course of the disease, is still infectious
A) Individual who has been exposed to and harbors a pathogen and who can spread the disease in different places or intervals
B) Individual who has been exposed to and harbors a pathogen, is in the beginning stages of the disease, is showing symptoms, and has the ability to transmit the disease
C) Individual who has been exposed to and harbors a pathogen, but has not become ill or shown any of the symptoms of the disease
D) Individual who has been exposed to and harbors a pathogen and who has done so for some time, but has recovered from the disease
E) Individual who harbors a pathogen and who, although in the recovery phase of the course of the disease, is still infectious

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is NOT a possible reservoir for pathogens or infectious agents?
A) Animals or humans
B) Food
C) Feces
D) Organic matter
E) All of these are possible reservoirs.
A) Animals or humans
B) Food
C) Feces
D) Organic matter
E) All of these are possible reservoirs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following may cause cancer?
A) H. pylori bacterium
B) Human papillomavirus
C) Hepatitis C
D) Acute sun exposure
E) All of these have been linked to cancer.
A) H. pylori bacterium
B) Human papillomavirus
C) Hepatitis C
D) Acute sun exposure
E) All of these have been linked to cancer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The disease-evoking power of a pathogen is called its:
A) invasiveness.
B) variability.
C) virulence.
D) communicability.
A) invasiveness.
B) variability.
C) virulence.
D) communicability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The likelihood of a pathogen or agent to be transmitted from one infected person to another susceptible person is referred to as which of the following?
A) Communicability
B) Invasiveness
C) Variability
D) Virulence
A) Communicability
B) Invasiveness
C) Variability
D) Virulence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What are metabolic diseases?
A) A collective name that refers to a group of many diseases with one common characteristic: uncontrolled growth of mutated cells.
A) A lower level of mental, physical, or moral state than is normal
B) Diseases existing at birth, and often before birth, or that develop during the first month of life
C) Caused by the body reacting to an invasion of or injury by a foreign object or substance
D)d. Any of the diseases or disorders that disrupt the process of converting food to energy on a cellular level. Affects the ability of the cell to perform critical biochemical reactions that involve the processing or transport of proteins (amino acids), carbohydrates (sugars and starches), or lipids (fatty acids)
A) A collective name that refers to a group of many diseases with one common characteristic: uncontrolled growth of mutated cells.
A) A lower level of mental, physical, or moral state than is normal
B) Diseases existing at birth, and often before birth, or that develop during the first month of life
C) Caused by the body reacting to an invasion of or injury by a foreign object or substance
D)d. Any of the diseases or disorders that disrupt the process of converting food to energy on a cellular level. Affects the ability of the cell to perform critical biochemical reactions that involve the processing or transport of proteins (amino acids), carbohydrates (sugars and starches), or lipids (fatty acids)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The natural course of communicable disease involves a susceptible host; a point of exposure; a subclinical disease phase; the clinical disease phase; and a phase of recovery, disability, or death. Which phase is related to the incubation period?
A) Susceptibility phase
B) Subclinical phase
C) Clinical disease phase
D) Recovery, disability, or death phase
A) Susceptibility phase
B) Subclinical phase
C) Clinical disease phase
D) Recovery, disability, or death phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Active immunity is best described as which of the following?
A) The type of immunity that occurs when the body produces its own antibodies because of a specific invading substance
B) The type of immunity that involves the transfer of antibodies to one person that were produced by another person.
C) The type of immunity that can result from the introduction of already-produced antibodies by another host.
A) The type of immunity that occurs when the body produces its own antibodies because of a specific invading substance
B) The type of immunity that involves the transfer of antibodies to one person that were produced by another person.
C) The type of immunity that can result from the introduction of already-produced antibodies by another host.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Serial surveys involve which of the following?
A) Ecologic data
B) Cross-sectional data
C) Case-control data
D) Cohort data
A) Ecologic data
B) Cross-sectional data
C) Case-control data
D) Cohort data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What study design may be appropriate when it is not possible to estimate an effect on the individual level?
A) Case series
B) Cohort
C) Ecologic
D) Experimental
A) Case series
B) Cohort
C) Ecologic
D) Experimental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Public health surveillance refers to which of the following activities?
A) Public health monitoring
B) Interpretation and dissemination of systematically collected data
C) Ongoing collection and analysis of community health data
D) All of these activities are part of public health surveillance.
A) Public health monitoring
B) Interpretation and dissemination of systematically collected data
C) Ongoing collection and analysis of community health data
D) All of these activities are part of public health surveillance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following descriptive study designs can be useful for generating hypotheses?
A) Ecologic
B) Cross-sectional
C) Case study
D) All of these are correct.
A) Ecologic
B) Cross-sectional
C) Case study
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The geometric mean for the data 10, 10, 10, 100, 100, 1000, 10000 is:
A) 2.
B) 3.
C) 10.
D) 100.
E) 1000.
A) 2.
B) 3.
C) 10.
D) 100.
E) 1000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
All of the following are common measures of linear association between two discrete or continuous variables, EXCEPT:
A) relative risk.
B) correlation coefficient.
C) Spearman's rank correlation coefficient.
D) regression analysis (slope coefficient).
E) These are all common measures of linear association between two discrete or continuous variables.
A) relative risk.
B) correlation coefficient.
C) Spearman's rank correlation coefficient.
D) regression analysis (slope coefficient).
E) These are all common measures of linear association between two discrete or continuous variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Pearson correlation coefficient between two continuous variables is a potentially misleading measure under what which of the following conditions?
A) When outliers have a marked effect on the linear curve
B) When the sample size is large
C) When both variables involved are normally distributed
D) All of these can make this measure misleading.
A) When outliers have a marked effect on the linear curve
B) When the sample size is large
C) When both variables involved are normally distributed
D) All of these can make this measure misleading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is a substance that prompts the generation of antibodies and can cause an immune response?
A) Active immunity
B) Passive immunity
C) Antigen
A) Active immunity
B) Passive immunity
C) Antigen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How many of the following questions are reflected in descriptive epidemiology?
___ Who?
___ Why?
___ How?
___ What?
___ When?
___ Where?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
___ Who?
___ Why?
___ How?
___ What?
___ When?
___ Where?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Who evaluated the Bills of Mortality?
A) William Farr
B) John Graunt
C) Hippocrates
D) George Soper
A) William Farr
B) John Graunt
C) Hippocrates
D) George Soper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Who helped to establish the germ theory of disease?
A) James Lind
B) John Snow
C) Louis Pasteur
D) Florence Nightingale
A) James Lind
B) John Snow
C) Louis Pasteur
D) Florence Nightingale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following lacks independent metabolism?
A) Bacterium
B) Fungus
C) Virus
D) Parasite
A) Bacterium
B) Fungus
C) Virus
D) Parasite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the mean number of people in the household for the following data?
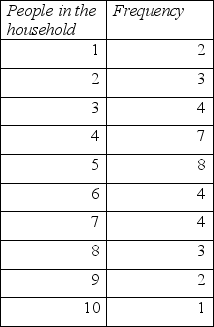
A) 5.6
B) 5.1
C) 3.8
D) None of these are correct.

A) 5.6
B) 5.1
C) 3.8
D) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A block-shaped pyramid indicates that the population is having high birth rate and a high death rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose in a given region that 15% of its population is younger than 15 and 10% is older than 65 years of age. What would the dependency ratio be?
A) 36
B) 50
C) 46
D) 33
A) 36
B) 50
C) 46
D) 33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following best defines a seasonal trend?
A) Represents periodic increases and decreases in the occurrence, interval, or frequency of a health-related state or event
B) Short-term fluctuations, usually brief and unexpected
C) Represents the long-term change in a health-related state or event
A) Represents periodic increases and decreases in the occurrence, interval, or frequency of a health-related state or event
B) Short-term fluctuations, usually brief and unexpected
C) Represents the long-term change in a health-related state or event

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the United States, the number of deaths from all causes was 70,663,474 for Whites, 9,692,906 for Blacks, and 1,125,108 for other racial groups for the combined years 2012-2016. The number of cancer deaths during this same time period was 15,533,648 for Whites, 1,946,813 for Blacks, and 249,591 for other racial groups. In which racial group is the proportional mortality ratio lowest?
A) Whites
B) Blacks
C) Other
A) Whites
B) Blacks
C) Other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following statistics is the most appropriate measure to use when investigating a disease outbreak?
A) Prevalence proportion
B) Mortality rate
C) Attack rate
D) Attributable risk percent
A) Prevalence proportion
B) Mortality rate
C) Attack rate
D) Attributable risk percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An age-adjusted rate is a weighted average of which of the following?
A) Age-specific rates
B) Point prevalence proportions
C) Attack rates
D) None of these is correct.
A) Age-specific rates
B) Point prevalence proportions
C) Attack rates
D) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 130 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



