Deck 26: Microbial Ecology and Microbiomes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Microbial Ecology and Microbiomes
1
In April 2010 an oil rig blowout resulted in a major crude oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. How was the majority of the crude oil cleaned out of the Gulf?
A) Humans collected the oil from the surface of the water and along the coastline.
B) Artificial bioremediation, crude-oil eating microbes were poured into the ocean.
C) Natural bioremediation by microbes already present in the ocean.
D) Both human collection of oil and artificial bioremediation.
E) The crude oil still has not been cleaned up.
A) Humans collected the oil from the surface of the water and along the coastline.
B) Artificial bioremediation, crude-oil eating microbes were poured into the ocean.
C) Natural bioremediation by microbes already present in the ocean.
D) Both human collection of oil and artificial bioremediation.
E) The crude oil still has not been cleaned up.
C
2
Which of the following is the best definition of antagonism?
A) competition for limited resources
B) cooperation in utilization of resources
C) microbes living in the same environment without harming each other
D) microbes producing products that interfere with the growth of others
E) competition and producing products that interfere with growth
A) competition for limited resources
B) cooperation in utilization of resources
C) microbes living in the same environment without harming each other
D) microbes producing products that interfere with the growth of others
E) competition and producing products that interfere with growth
D
3
What is carbon fixation?
A) The conversion of dead organisms into fossil fuel.
B) The release of carbon dioxide by cellular respiration.
C) The conversion of carbon dioxide into organic molecules.
D) The storage of carbon compounds by heterotrophs.
E) The release of carbon dioxide by combustion.
A) The conversion of dead organisms into fossil fuel.
B) The release of carbon dioxide by cellular respiration.
C) The conversion of carbon dioxide into organic molecules.
D) The storage of carbon compounds by heterotrophs.
E) The release of carbon dioxide by combustion.
C
4
The use of microorganisms to clean a polluted environment is
A) bioremediation.
B) antagonism.
C) cooperation.
D) genetic engineering.
E) waste treatment.
A) bioremediation.
B) antagonism.
C) cooperation.
D) genetic engineering.
E) waste treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
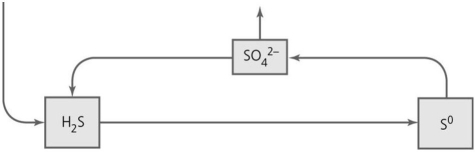 What type of reactions take place in the portion of the sulfur cycle indicated in the figure?
What type of reactions take place in the portion of the sulfur cycle indicated in the figure?A) oxidation-reduction
B) fermentation
C) dissimilation
D) denitrification
E) carbon fixation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A microbiome is composed of
A) biospheres.
B) microhabitats.
C) ecosystems.
D) populations
E) sets of guilds.
A) biospheres.
B) microhabitats.
C) ecosystems.
D) populations
E) sets of guilds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is nitrogen fixation?
A) the conversion of nitrate (NO₃⁻) into nucleic acids
B) the incorporation of ammonia (NH₃) into amino acids
C) the release of ammonia (NH₄⁻) from decomposing organic material
D) the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) into ammonia (NH₃)
E) the conversion of ammonia (NH₃) into ammonium ion (NH₄⁺)
A) the conversion of nitrate (NO₃⁻) into nucleic acids
B) the incorporation of ammonia (NH₃) into amino acids
C) the release of ammonia (NH₄⁻) from decomposing organic material
D) the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) into ammonia (NH₃)
E) the conversion of ammonia (NH₃) into ammonium ion (NH₄⁺)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What type(s) of microbial interactions take place in a microhabitat?
A) antagonism
B) cooperation
C) competition
D) antagonism and competition
E) a combination of antagonism, cooperation and competition
A) antagonism
B) cooperation
C) competition
D) antagonism and competition
E) a combination of antagonism, cooperation and competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The greatest diversity of the human microbiome is found
A) on the skin.
B) in the mouth.
C) in the intestine.
D) in the urinary system.
E) in the respiratory system.
A) on the skin.
B) in the mouth.
C) in the intestine.
D) in the urinary system.
E) in the respiratory system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is the conversion of ammonium ion⁺ into nitrogen gas (N₂)?
A) assimilation
B) anammox
C) nitrogen fixation
D) nitrification
E) denitrification
A) assimilation
B) anammox
C) nitrogen fixation
D) nitrification
E) denitrification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A guild is composed of
A) populations with similar metabolic activities.
B) microhabitats in a single location.
C) a single species.
D) microbiomes in a single zone.
E) ecosystems.
A) populations with similar metabolic activities.
B) microhabitats in a single location.
C) a single species.
D) microbiomes in a single zone.
E) ecosystems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is the CORRECT sequence of microbial associations from smallest to largest?
A) populations, guilds, communities, microhabitats, ecosystem
B) populations, communities, microhabitats, ecosystem, guilds
C) communities, microhabitats, ecosystem, guilds, populations
D) populations, communities, ecosystem, guilds, microhabitats
E) ecosystem, populations, communities, microhabitats, guilds
A) populations, guilds, communities, microhabitats, ecosystem
B) populations, communities, microhabitats, ecosystem, guilds
C) communities, microhabitats, ecosystem, guilds, populations
D) populations, communities, ecosystem, guilds, microhabitats
E) ecosystem, populations, communities, microhabitats, guilds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following oxidize H₂S to SO₄⁻², the form of sulfur animals use for their metabolism?
A) Beggiatoa
B) Desulfovibrio
C) purple sulfur bacteria
D) both Beggiatoa and purple sulfur bacteria
E) both Beggiatoa and Desulfovibrio
A) Beggiatoa
B) Desulfovibrio
C) purple sulfur bacteria
D) both Beggiatoa and purple sulfur bacteria
E) both Beggiatoa and Desulfovibrio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements concerning the phosphorus cycle in bacteria is TRUE?
A) The element cycles between different organic molecules.
B) It is the most important process for synthesizing proteins and nucleic acids.
C) The element alternates among several oxidative states.
D) The element changes from insoluble to soluble forms.
E) The element is converted to a gaseous state and is lost to the environment.
A) The element cycles between different organic molecules.
B) It is the most important process for synthesizing proteins and nucleic acids.
C) The element alternates among several oxidative states.
D) The element changes from insoluble to soluble forms.
E) The element is converted to a gaseous state and is lost to the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What nutrient most commonly contributes to eutrophication?
A) phosphorus
B) nitrite
C) sulfide
D) methane
E) iron oxides
A) phosphorus
B) nitrite
C) sulfide
D) methane
E) iron oxides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the source of the acidic pH of some mine runoff?
A) Iron ores are reduced by exposure to the atmosphere.
B) Pyrite is oxidized by exposure to the atmosphere and microbes.
C) Iron ores contain sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
D) Sulfur-containing ores are reduced by exposure to oxygen.
E) Hydrogen gas trapped in ore reacts with the atmosphere to produce hydrochloric acid (HCl).
A) Iron ores are reduced by exposure to the atmosphere.
B) Pyrite is oxidized by exposure to the atmosphere and microbes.
C) Iron ores contain sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
D) Sulfur-containing ores are reduced by exposure to oxygen.
E) Hydrogen gas trapped in ore reacts with the atmosphere to produce hydrochloric acid (HCl).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which form of sulfur can algae and plants use but not produce?
A) hydrogen sulfide (H₂S)
B) elemental sulfur (S⁰)
C) sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
D) sulfate (SO₄²⁻ )
E) both elemental sulfur and hydrogen sulfide
A) hydrogen sulfide (H₂S)
B) elemental sulfur (S⁰)
C) sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
D) sulfate (SO₄²⁻ )
E) both elemental sulfur and hydrogen sulfide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A ________ is a single species in an environment.
A) microhabitat
B) population
C) colony
D) biome
E) guild
A) microhabitat
B) population
C) colony
D) biome
E) guild

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The "greenhouse gas" methane is produced by
A) prokaryotes.
B) fungi.
C) algae.
D) animals.
E) both fungi and alga.
A) prokaryotes.
B) fungi.
C) algae.
D) animals.
E) both fungi and alga.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following best describes the roles of microorganisms in the carbon cycle?
A) primary producers
B) heterotrophs
C) decomposers
D) heterotrophs and decomposers
E) primary producers, heterotrophs and decomposers
A) primary producers
B) heterotrophs
C) decomposers
D) heterotrophs and decomposers
E) primary producers, heterotrophs and decomposers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which potential biological select agent currently has no natural source?
A) anthrax
B) arenaviruses
C) tularemia
D) epidemic typhus
E) smallpox
A) anthrax
B) arenaviruses
C) tularemia
D) epidemic typhus
E) smallpox

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following conditions will support the greatest diversity of microbes?
A) waterlogged with little mineral content
B) moderately moist soil with lots of organic compounds
C) alternating moist and dry with alkaline conditions
D) mostly dry soil with lots of organic compounds and acidic conditions
E) alternating moist and dry soil with high salt content
A) waterlogged with little mineral content
B) moderately moist soil with lots of organic compounds
C) alternating moist and dry with alkaline conditions
D) mostly dry soil with lots of organic compounds and acidic conditions
E) alternating moist and dry soil with high salt content

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The majority of the microbial carbon cycling activity will typically occur in
A) subsoil.
B) topsoil.
C) deep soil.
D) on the surface of the soil.
E) all depths of soil.
A) subsoil.
B) topsoil.
C) deep soil.
D) on the surface of the soil.
E) all depths of soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following sets of characteristics describes the highest level of threat potential from biological weapons?
A) a waterborne toxin that is easily introduced into public water supplies and does not replicate in humans
B) a pathogen of livestock transmitted by contact with infected animals but not infected people
C) a human pathogen easily produced as an aerosol and transmissible by respiratory aerosols
D) a pathogen of wheat that could be delivered using crop dusters
E) a microbe that can be introduced into food during packaging and withstands refrigerator temperatures but not typical cooking temperatures
A) a waterborne toxin that is easily introduced into public water supplies and does not replicate in humans
B) a pathogen of livestock transmitted by contact with infected animals but not infected people
C) a human pathogen easily produced as an aerosol and transmissible by respiratory aerosols
D) a pathogen of wheat that could be delivered using crop dusters
E) a microbe that can be introduced into food during packaging and withstands refrigerator temperatures but not typical cooking temperatures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following bacteria is a common soil contaminant that may cause disease in humans and is a biological select agent?
A) Aspergillus oryzae
B) Bacillus anthracis
C) Cyanobacteria
D) Lactoccocus cremoris
E) Streptomyces scabies
A) Aspergillus oryzae
B) Bacillus anthracis
C) Cyanobacteria
D) Lactoccocus cremoris
E) Streptomyces scabies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Metal ions are useful to organisms in the ________ form.
A) soluble
B) reduced
C) insoluble
D) oxidized
E) oxidized and insoluble
A) soluble
B) reduced
C) insoluble
D) oxidized
E) oxidized and insoluble

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Anaerobic organisms reside in the ________ zone of a lake.
A) limentic
B) benthic
C) littoral
D) profundal
E) both the littoral and the profundal
A) limentic
B) benthic
C) littoral
D) profundal
E) both the littoral and the profundal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which aquatic zone in a lake will have the highest nutrient levels and therefore the densest microbial populations?
A) the littoral zone
B) the limnetic zone
C) the profundal zone
D) the benthic zone
E) the sediment zone
A) the littoral zone
B) the limnetic zone
C) the profundal zone
D) the benthic zone
E) the sediment zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Soil contaminated with bird droppings may contain ________ which can cause respiratory disease in humans.
A) Agrobacterium tumifaciens
B) Clostridium tetani
C) Streptomyces scabies
D) Histoplasma capsulatum
E) Bacillus subtilis
A) Agrobacterium tumifaciens
B) Clostridium tetani
C) Streptomyces scabies
D) Histoplasma capsulatum
E) Bacillus subtilis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Biomining takes advantage of prokaryotes ability to ________ metals.
A) reduce
B) reduce the solubility of
C) oxidize
D) directly solubilize
E) bioaccumulate
A) reduce
B) reduce the solubility of
C) oxidize
D) directly solubilize
E) bioaccumulate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following disease agents has potential for both agroterrorism and bioterrorism?
A) smallpox
B) tularemia
C) plague
D) brucellosis
E) blight
A) smallpox
B) tularemia
C) plague
D) brucellosis
E) blight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What microbes thrive in waterlogged soil?
A) anaerobes
B) obligate aerobes
C) halophiles
D) thermophiles
E) bacteria capable of forming endospores
A) anaerobes
B) obligate aerobes
C) halophiles
D) thermophiles
E) bacteria capable of forming endospores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Why are Category B select agents considered lower risk biological agents?
A) They are less dangerous pathogens than Category A.
B) They may be difficult to disperse.
C) They cause disease in animals but not humans.
D) They are less dangerous pathogens and are more difficult to disperse.
E) Their threat potential is unknown.
A) They are less dangerous pathogens than Category A.
B) They may be difficult to disperse.
C) They cause disease in animals but not humans.
D) They are less dangerous pathogens and are more difficult to disperse.
E) Their threat potential is unknown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
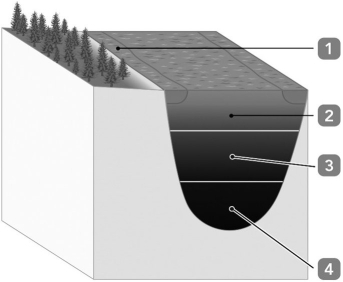 Green and purple sulfur bacteria will carry out anaerobic photosynthesis primarily in
Green and purple sulfur bacteria will carry out anaerobic photosynthesis primarily inA) zone 1.
B) zone 2.
C) zone 3.
D) zone 4.
E) both zones 1 and 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is a specific example of bioremediation?
A) the purification of water for drinking
B) the treatment of wastewater
C) the treatment of sludge
D) the degradation of crude oil spilled along the Alaska coastline
E) acid mine drainage
A) the purification of water for drinking
B) the treatment of wastewater
C) the treatment of sludge
D) the degradation of crude oil spilled along the Alaska coastline
E) acid mine drainage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Photoautotrophs reside in the ________ zone(s) of marine environments.
A) abyssal
B) limnetic
C) littoral
D) both limnetic and littoral
E) abyssal, limnetic and littoral
A) abyssal
B) limnetic
C) littoral
D) both limnetic and littoral
E) abyssal, limnetic and littoral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What pH conditions favor the growth of most bacteria?
A) pH 2
B) pH 5
C) pH 7
D) pH 9
E) Bacteria can grow at all ranges of pH.
A) pH 2
B) pH 5
C) pH 7
D) pH 9
E) Bacteria can grow at all ranges of pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following infectious diseases currently tops the list of bioterrorist threats?
A) anthrax
B) the plague
C) smallpox
D) botulism
E) cholera
A) anthrax
B) the plague
C) smallpox
D) botulism
E) cholera

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Where does the bulk of biogeochemical cycling occur?
A) in the air
B) in soil
C) in water
D) in the benthic zone
E) in both air and water
A) in the air
B) in soil
C) in water
D) in the benthic zone
E) in both air and water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following human diseases may result from exposure to soil containing the microbe responsible?
A) blastomycosis
B) giardiasis
C) crown gall disease
D) cryptosporidiosis
E) saxitoxin poisoning
A) blastomycosis
B) giardiasis
C) crown gall disease
D) cryptosporidiosis
E) saxitoxin poisoning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Acidic drainage from mine tailings is harmful to all life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
All the microbes in a community in one location constitute a(n) (biosphere/ecosystem/microbiome).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Members of a guild are metabolically related to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Cyanobacteria produce a cell type known as a (cyst/heterocyst/nodule) that protects nitrogenase from the exposure to oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Organic compounds are degraded to produce methane by (Archaea/fungi/Pseudomonas).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A biofilm is an example of (antagonism/competition/cooperation) among microbes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When runoff containing excessive nutrients enters streams and lakes it can result in an overgrowth of cyanobacteria and algae, a process known as
A) eutrophication.
B) oxidation.
C) fixation.
D) ammonification.
E) both ammonification and fixation.
A) eutrophication.
B) oxidation.
C) fixation.
D) ammonification.
E) both ammonification and fixation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Algae and protozoa in the soil are quite hardy, and therefore their abundance is not a useful indicator of environmental pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The interactions between microbes in a guild are constantly changing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is a nitrogen-fixing bacterium that forms associations with the roots of plants?
A) anaerobic Bacillus species
B) Clostridium species
C) Rhizobium species
D) Azotobacter species
E) cyanobacteria
A) anaerobic Bacillus species
B) Clostridium species
C) Rhizobium species
D) Azotobacter species
E) cyanobacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Most of the nitrogen in the environment is in the form of nitrogen gas, which is the form used by most organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A microbiome typically is a single population of organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Metals are cycled in the environment by microbes that (oxidize/reduce/solubilize) them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Anaerobic oxidation of (methane/rubisco/plastics) produces carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
During decomposition of amino acids, the amino groups undergo (ammonification/anammox/denitrification) and are converted to ammonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Bioremediation is the process of using organisms to clean up toxic, hazardous compounds by degrading them to less harmful substances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Only prokaryotes fix nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following would be most effective in reducing the amount of CO₂ in the atmosphere?
A) cyanobacteria
B) anaerobic microbes
C) heterotrophic organisms
D) fungi
E) nitrogen fixers
A) cyanobacteria
B) anaerobic microbes
C) heterotrophic organisms
D) fungi
E) nitrogen fixers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Bedrock does not contain microorganisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Without the activities of microorganisms, the functioning of earth's ecosystems would cease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Exposure to soil contaminated with rodent excrement may result in respiratory infection with (Coccidioides/Clostridium/Hantavirus).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Rivers typically lack a(n) (anaerobic/littoral/limnetic) zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The dengue and Ebola viruses cause hemorrhagic fevers. Evaluate their threat levels as select agents using the criteria in the textbook, and decide whether they pose significant risk as biological weapons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Smallpox is considered a serious potential biological weapon, whereas anthrax has been successfully used as one. Compare and contrast their potential with regard to the criteria for assessing biological threats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How do soil conditions impact the cycling of nitrogen during decomposition?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When one microbe's metabolic activities create favorable conditions for another microorganism, this is referred to as (competition/cooperation/facilitation).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A biological select agent spread by (aerosols/contact/ingestion) has a high threat level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The organic material found in topsoil is called (humus/peat/compost).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Some microbes can (dissimilate/oxidize/reduce) hydrogen sulfide to elemental sulfur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What are the levels of microbial associations in the environment? How do they relate to an ecosystem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The anthrax attack of fall 2001 was accomplished by mailing the agent in ordinary envelopes. This method of delivery took advantage of the ability of Bacillus anthracis to produce (aerosols/endospores/spores).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Eutrophication is primarily a result of (agricultural/industrial/urban) runoff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Compare and contrast carbon fixation and nitrogen fixation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



