Deck 10: Market Power
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Market Power
1
Which one of the following type of markets has many identical firms selling the same goods or services?
A) monopoly
B) oligopoly
C) duopoly
D) perfect competition
A) monopoly
B) oligopoly
C) duopoly
D) perfect competition
D
2
If a firm has market power, then it has:
A) influence over the total quantity that consumers buy in that market.
B) influence over the price that it charges for its good or service.
C) no government regulation imposed on it.
D) no other firms competing with it in the market.
A) influence over the total quantity that consumers buy in that market.
B) influence over the price that it charges for its good or service.
C) no government regulation imposed on it.
D) no other firms competing with it in the market.
B
3
Firms in a perfectly competitive market have:
A) some control over the price that they can charge on their good.
B) no control over the price that they can charge.
C) no control over quantity that they can supply in the market.
D) no government regulations imposed on them.
A) some control over the price that they can charge on their good.
B) no control over the price that they can charge.
C) no control over quantity that they can supply in the market.
D) no government regulations imposed on them.
B
4
A firm will NOT have any market power if it operates in which one of the following types of markets?
A) monopoly
B) perfect competition
C) duopoly
D) oligopoly
A) monopoly
B) perfect competition
C) duopoly
D) oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the average total cost of a firm decreases with an increase in its output, then the firm experiences:
A) economies of scale.
B) economies of scope.
C) diseconomies of scale.
D) diseconomies of scope.
A) economies of scale.
B) economies of scope.
C) diseconomies of scale.
D) diseconomies of scope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Economies of scale refers to the situation where an increase in the output of a firm leads to a decrease in:
A) the total cost.
B) the total revenue.
C) average revenue.
D) the average cost.
A) the total cost.
B) the total revenue.
C) average revenue.
D) the average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If _____ in output causes _____ in average total cost, then a firm is said to be experiencing economies of scale.
A) an increase; an increase
B) a decrease; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) an increase; a decrease
A) an increase; an increase
B) a decrease; a decrease
C) a decrease; an increase
D) an increase; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following can give rise to economies of scale for a firm?
A) patents
B) high start-up costs
C) trademarks
D) copyrights
A) patents
B) high start-up costs
C) trademarks
D) copyrights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT a legal barrier that leads to market power?
A) economies of scale
B) patents
C) copyrights
D) trademarks
A) economies of scale
B) patents
C) copyrights
D) trademarks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is NOT a legal barrier to entry in a market?
A) patent
B) high start-up cost
C) copyright
D) trademark
A) patent
B) high start-up cost
C) copyright
D) trademark

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements about economies of scale is NOT true?
A) Economies of scale lead to markets with perfect competition.
B) Economies of scale do not result from patents and trademarks.
C) Economies of scale can arise in industries with high start-up costs.
D) Economies of scale can create markets where the optimal number of firms is one.
A) Economies of scale lead to markets with perfect competition.
B) Economies of scale do not result from patents and trademarks.
C) Economies of scale can arise in industries with high start-up costs.
D) Economies of scale can create markets where the optimal number of firms is one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the long-run average total costs of an industry decline with an increase in output, its market is:
A) perfectly competitive.
B) monopolistically competitive.
C) a natural monopoly.
D) a duopoly.
A) perfectly competitive.
B) monopolistically competitive.
C) a natural monopoly.
D) a duopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A natural monopoly arises when an increase in output in the long-run leads to:
A) a decrease in total cost.
B) an increase in total revenue.
C) a decrease in average total cost.
D) an increase in average revenue.
A) a decrease in total cost.
B) an increase in total revenue.
C) a decrease in average total cost.
D) an increase in average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which one of the following situations can create a natural monopoly?
A) A firm lobbies the government to block other firms from entering the market.
B) A firm innovates a new product and gains a patent over it.
C) A firm operates in an industry that requires very low start-up costs.
D) A firm operates in an industry that requires very high start-up costs.
A) A firm lobbies the government to block other firms from entering the market.
B) A firm innovates a new product and gains a patent over it.
C) A firm operates in an industry that requires very low start-up costs.
D) A firm operates in an industry that requires very high start-up costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a natural monopoly, the government regulations often require firms to price their goods at:
A) marginal cost.
B) total cost.
C) average total cost.
D) marginal revenue.
A) marginal cost.
B) total cost.
C) average total cost.
D) marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A monopolist faces a _____ demand curve.
A) downward-sloping
B) upward-sloping
C) horizontal
D) vertical
A) downward-sloping
B) upward-sloping
C) horizontal
D) vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A perfectly competitive firm faces a _____ demand curve, and a monopolist faces a _____ demand curve.
A) downward-sloping; horizontal
B) horizontal; vertical
C) vertical; horizontal
D) horizontal; downward-sloping
A) downward-sloping; horizontal
B) horizontal; vertical
C) vertical; horizontal
D) horizontal; downward-sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A perfectly competitive firm can sell _____ of output at a given market price; therefore, its demand curve is:
A) a fixed amount; vertical.
B) any amount; vertical.
C) a fixed amount; horizontal.
D) any amount; horizontal.
A) a fixed amount; vertical.
B) any amount; vertical.
C) a fixed amount; horizontal.
D) any amount; horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Because a monopolist must _____ price to sell additional output, its marginal revenue is _____ than the price.
A) decrease; lower
B) increase; lower
C) decrease; higher
D) increase; higher
A) decrease; lower
B) increase; lower
C) decrease; higher
D) increase; higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is FALSE for a monopoly firm?
A) Its marginal revenue is less than the price.
B) It faces a horizontal demand curve.
C) It can sell additional units of output by lowering the price.
D) Its marginal revenue can be negative.
A) Its marginal revenue is less than the price.
B) It faces a horizontal demand curve.
C) It can sell additional units of output by lowering the price.
D) Its marginal revenue can be negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
For a monopolist, which one of the following variables can take a negative value?
A) marginal cost
B) marginal revenue
C) average cost
D) average revenue
A) marginal cost
B) marginal revenue
C) average cost
D) average revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which one of the following statements is NOT true for a monopolist?
A) The marginal revenue can be negative.
B) The marginal revenue is equal to the price.
C) The marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve.
D) The marginal revenue falls as more quantity is sold.
A) The marginal revenue can be negative.
B) The marginal revenue is equal to the price.
C) The marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve.
D) The marginal revenue falls as more quantity is sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which one of the following statements is NOT true for a monopolist?
A) A monopolist is the only firm in a market.
B) A monopolist faces a downward-sloping demand.
C) The marginal revenue falls as more units are sold.
D) The price and marginal revenue are equal for a monopolist.
A) A monopolist is the only firm in a market.
B) A monopolist faces a downward-sloping demand.
C) The marginal revenue falls as more units are sold.
D) The price and marginal revenue are equal for a monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Use Figure: Demand for Gasoline. The figure shows the demand curve for gasoline in a small town that has only one provider, which therefore is a monopolist. What is the marginal revenue for the monopolist from increasing its sales from two gallons to three gallons?
Figure: Demand for Gasoline
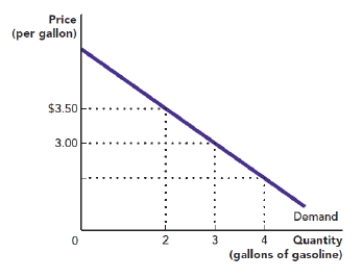
A) $1.00 per gallon
B) $1.50 per gallon
C) $2.00 per gallon
D) $2.50 per gallon
Figure: Demand for Gasoline

A) $1.00 per gallon
B) $1.50 per gallon
C) $2.00 per gallon
D) $2.50 per gallon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Use Figure: Demand for Gasoline. The figure shows the demand curve for gasoline in a small town that has only one provider, which therefore is a monopolist. The total revenue to the monopolist from selling three gallons is:
Figure: Demand for Gasoline
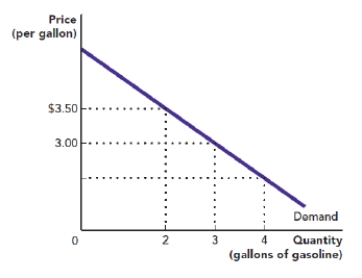
A) $7.
B) $9.
C) $10.
D) $11.
Figure: Demand for Gasoline

A) $7.
B) $9.
C) $10.
D) $11.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A monopolist maximizes profit at the point where the _____ of production is equal to:
A) marginal cost; price.
B) marginal cost; total revenue.
C) average total cost; price.
D) marginal cost; marginal revenue.
A) marginal cost; price.
B) marginal cost; total revenue.
C) average total cost; price.
D) marginal cost; marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose that the profit-maximizing price for a monopolist is $10 and the profit-maximizing quantity is 50 units. Further, the average total cost of producing 50 units is $8. The total profit for the monopolist in this scenario is:
A) $100.
B) $200.
C) $300.
D) $400.
A) $100.
B) $200.
C) $300.
D) $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose that the total profit earned by a monopolist $100. It also is known that the monopolist sells 50 units of output at a price of $10 per unit. Given this information, we can conclude that the average total cost of producing 50 units is:
A) $6.
B) $7.
C) $8.
D) $9.
A) $6.
B) $7.
C) $8.
D) $9.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose that a monopolist is operating at its profit-maximizing point where the profit per unit is $8. If the average total cost of production is $4, then what is the price charged by the monopolist?
A) $4
B) $8
C) $12
D) $16
A) $4
B) $8
C) $12
D) $16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose that a monopolist is operating at its profit-maximizing point. If the marginal cost of production at this point is $4, the average total cost is $6, and the profit per unit is $ 6, then the marginal revenue is _____, and the price charged by the monopolist is:
A) $6; $10.
B) $4; $6.
C) $6; $12.
D) $4; $12.
A) $6; $10.
B) $4; $6.
C) $6; $12.
D) $4; $12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose that a monopolist is operating at its profit-maximizing point. If the marginal revenue at this point is $4, the price is $12, and the profit per unit is $6, then the marginal cost is _____, and the average total cost is:
A) $4; $8.
B) $4; $6.
C) $6; $8.
D) $6; $6.
A) $4; $8.
B) $4; $6.
C) $6; $8.
D) $6; $6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose that a monopolist is operating at its profit-maximizing point by charging a price of $18 and selling 50 units of output. If the marginal revenue of the firm is $10 and the average total cost is $12, then the firm's marginal cost is _____, and the total profit is:
A) $10; $300.
B) $12; $300.
C) $10; $400.
D) $12; $400.
A) $10; $300.
B) $12; $300.
C) $10; $400.
D) $12; $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A monopolist's profit is maximized at the point where marginal cost is equal to:
A) price.
B) marginal revenue.
C) total revenue.
D) average revenue.
A) price.
B) marginal revenue.
C) total revenue.
D) average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
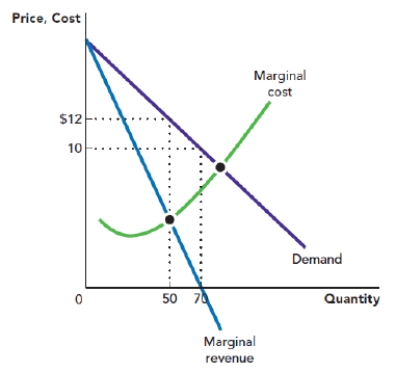
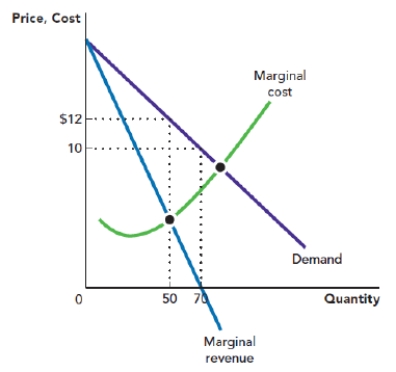
Use Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price. The figure depicts the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve that are facing a monopolist. The profit-maximizing price for the monopolist is _____, and the profit-maximizing quantity is _____ units.
Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price
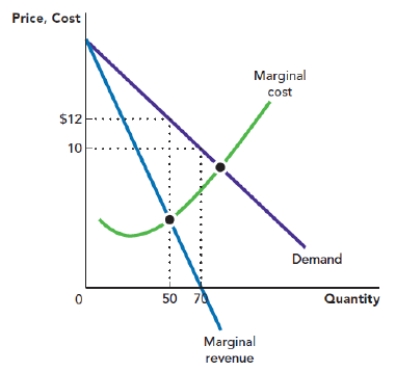
A) $12; 70
B) $10; 70
C) $12; 50
D) $10; 50
Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price

A) $12; 70
B) $10; 70
C) $12; 50
D) $10; 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Use Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price. The figure depicts the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Assume that the monopolist is operating at its profit-maximizing point. If the total profit of the monopolist is $200, then the total cost of production is:
Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price
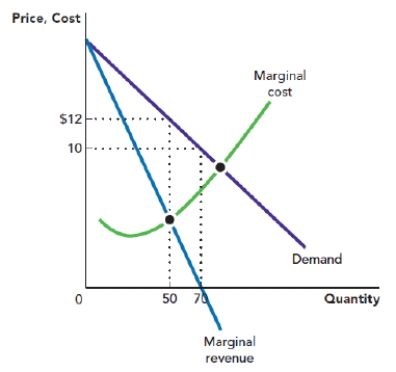
A) $200.
B) $300.
C) $400.
D) $500.
Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price

A) $200.
B) $300.
C) $400.
D) $500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price. The figure depicts the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Assume that the monopolist is operating at its profit-maximizing point. If the total profit of the monopolist is $200, then the average total cost of production is:
Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price
A) $5.
B) $6.
C) $7.
D) $8.
Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price

A) $5.
B) $6.
C) $7.
D) $8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price. The figure depicts the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Assume that the monopolist is operating at its profit-maximizing point. If the total profit of the monopolist is $200, then the profit per unit is:
Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price
A) $4.
B) $6.
C) $8.
D) $10.
Figure: Profit-Maximizing Quantity and Price

A) $4.
B) $6.
C) $8.
D) $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose that a monopoly firm is operating at its profit-maximizing point. The profit-maximizing price is $12, and the profit-maximizing quantity is 100 units. If the total profit of the monopolist is $400, then the average total cost of production is _____, and the profit per unit is:
A) $4; $8.
B) $8; $4.
C) $4; $4.
D) $8, $8.
A) $4; $8.
B) $8; $4.
C) $4; $4.
D) $8, $8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
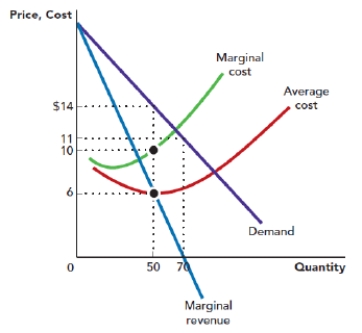
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization. The figure shows the demand, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are faced by a monopolist. The profit-maximizing price for the monopolist is _____, and the profit-maximizing quantity is _____ units.
Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization
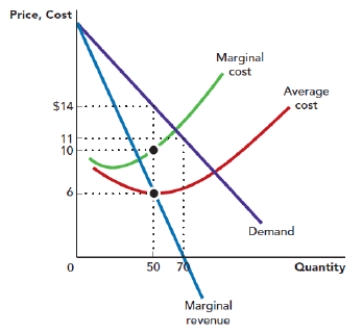
A) $14; 70
B) $14; 50
C) $10; 70
D) $10; 50
Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization

A) $14; 70
B) $14; 50
C) $10; 70
D) $10; 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are faced by a monopolist. Suppose that the firm is operating at its profit-maximizing point. The total revenue of the firm is _____, and the total cost of the firm is:
Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization
A) $700; $500.
B) $840; 700.
C) $700; $300.
D) $ 500; $700.
Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization

A) $700; $500.
B) $840; 700.
C) $700; $300.
D) $ 500; $700.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are faced by a monopolist. Suppose that the firm is operating at its profit-maximizing point. The profit per unit for the firm is_____, and the total profit is:
Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization
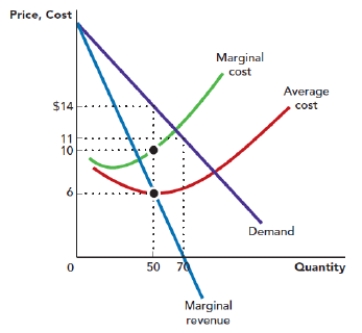
A) $4; $560.
B) $4; $280.
C) $8; $700.
D) $8; $400.
Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization

A) $4; $560.
B) $4; $280.
C) $8; $700.
D) $8; $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are faced by a monopolist. At what price level is the marginal revenue of the firm zero?
Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization
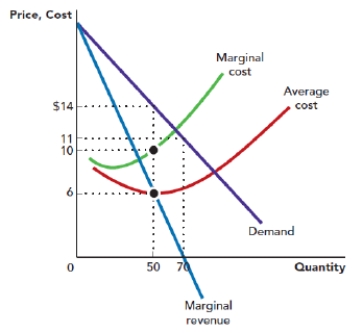
A) $6
B) $10
C) $11
D) $14
Figure: Monopoly Profit Maximization

A) $6
B) $10
C) $11
D) $14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Resource allocation is efficient from a societal standpoint if a good is produced until the_____ is equal to the _____ of production.
A) marginal revenue; marginal cost
B) price; marginal cost
C) price; average cost
D) marginal revenue; average cost
A) marginal revenue; marginal cost
B) price; marginal cost
C) price; average cost
D) marginal revenue; average cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Resource allocation is efficient from a societal standpoint if the price of a good is equal to the _____ cost of production.
A) marginal
B) average
C) total
D) variable
A) marginal
B) average
C) total
D) variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Because a monopolist charges a price that is ____ than marginal cost, a monopoly market allocates _____ resources to the production of a good than is socially optimal.
A) less; fewer
B) greater; fewer
C) less; more
D) greater; more
A) less; fewer
B) greater; fewer
C) less; more
D) greater; more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A perfectly competitive market produces a _____ level of output and charges a _____ price compared to a monopoly market.
A) higher; lower
B) lower; higher
C) higher; higher
D) lower; lower
A) higher; lower
B) lower; higher
C) higher; higher
D) lower; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Relative to a perfectly competitive market, a monopolist produces a_____ level of output and charges a _____ price.
A) higher; lower
B) higher; higher
C) lower; lower
D) lower; higher
A) higher; lower
B) higher; higher
C) lower; lower
D) lower; higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Based on this information, the profit-maximizing price for the firm is_____, and the profit-maximizing quantity is _____ units.
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss
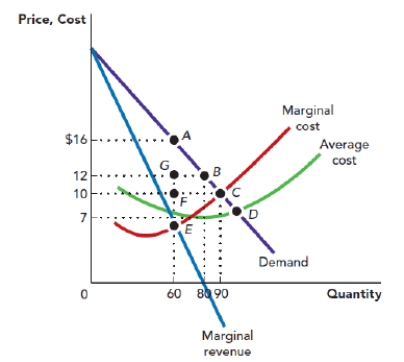
A) $16; 90
B) $16; 80
C) $10; 90
D) $16; 60
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss

A) $16; 90
B) $16; 80
C) $10; 90
D) $16; 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Suppose that the firm is operating at its profit-maximizing point. Given this, the profit per unit of the firm is:
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss

A) $9.
B) $6.
C) $5.
D) $4.
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss

A) $9.
B) $6.
C) $5.
D) $4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Suppose that the firm is operating at its profit-maximizing point. Given this, the total cost of producing the profit-maximizing level of output is:
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss
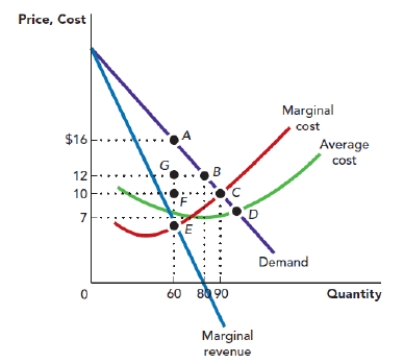
A) $960.
B) $900.
C) $600.
D) $420.
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss

A) $960.
B) $900.
C) $600.
D) $420.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Suppose that the firm is operating at its profit-maximizing point. Given this, the total revenue from selling the profit-maximizing level of output is:
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss
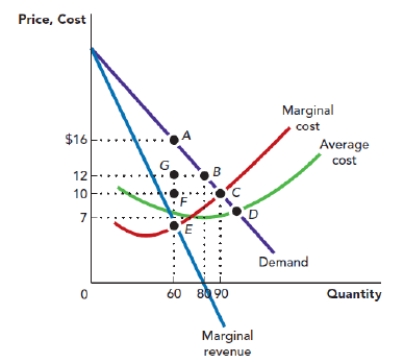
A) $960.
B) $900.
C) $600.
D) $420.
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss

A) $960.
B) $900.
C) $600.
D) $420.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Suppose that the firm is operating at its profit-maximizing point. Given this, the firm's profit per unit is _____, and the total profit is:
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss
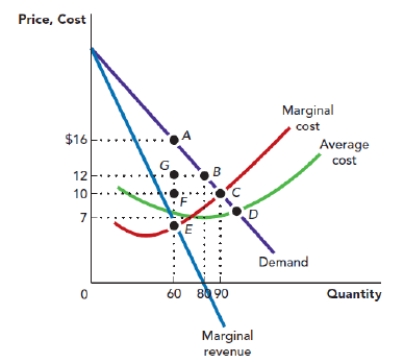
A) $9; $810.
B) $9; $720.
C) $9; $540.
D) $6; $540.
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss

A) $9; $810.
B) $9; $720.
C) $9; $540.
D) $6; $540.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Suppose that the firm is operating at its profit-maximizing point. Given this, the resulting deadweight loss to the society is given by the area:
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss
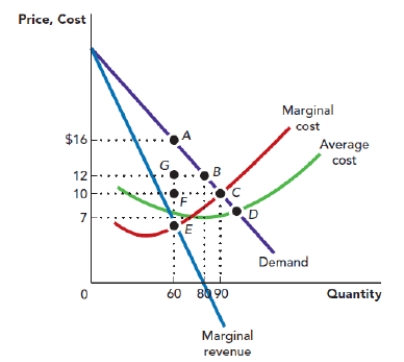
A) AGB.
B) ACF.
C) FCE.
D) ACE.
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss

A) AGB.
B) ACF.
C) FCE.
D) ACE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss. The figure shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and average total cost curve that are facing a monopolist. Suppose that the firm is NOT operating at the profit-maximization point and instead is operating at the socially optimal point. In this case, the firm must be producing _____ units of output and charging a price of:
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss
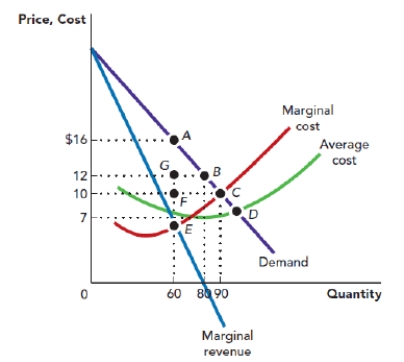
A) 60; $10.
B) 90; $10.
C) 60; $7.
D) 90; $7.
Figure: Monopoly Profit-Maximization and Deadweight Loss

A) 60; $10.
B) 90; $10.
C) 60; $7.
D) 90; $7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In which of the following scenarios would firms NOT be able to price discriminate?
A) Firms have some degree of market power.
B) Firms operate in a perfectly competitive market.
C) Firms are able to prevent resale of goods from one group to another.
D) Firms are able to identify customers with relatively elastic demand.
A) Firms have some degree of market power.
B) Firms operate in a perfectly competitive market.
C) Firms are able to prevent resale of goods from one group to another.
D) Firms are able to identify customers with relatively elastic demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements is true for a monopolist that practices perfect price discrimination?
A) It must operate in a perfectly competitive market.
B) It earns zero economic profit.
C) The price per unit is less than the marginal revenue of that unit.
D) Consumer surplus is zero in the market.
A) It must operate in a perfectly competitive market.
B) It earns zero economic profit.
C) The price per unit is less than the marginal revenue of that unit.
D) Consumer surplus is zero in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Price discrimination occurs when the same good is sold at different prices to different customers.
B) Consumer surplus is zero in the case of perfect price discrimination.
C) With price discrimination, customers with relatively elastic demand pay a higher price for the good.
D) Price discrimination is not possible in a perfectly competitive market.
A) Price discrimination occurs when the same good is sold at different prices to different customers.
B) Consumer surplus is zero in the case of perfect price discrimination.
C) With price discrimination, customers with relatively elastic demand pay a higher price for the good.
D) Price discrimination is not possible in a perfectly competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements is FALSE for a monopolist that practices perfect price discrimination?
A) The firm produces a socially optimal level of output.
B) The firm charges each customer according to its maximum willingness to pay.
C) The marginal revenue and demand curves are identical.
D) The firm earns zero economic profit.
A) The firm produces a socially optimal level of output.
B) The firm charges each customer according to its maximum willingness to pay.
C) The marginal revenue and demand curves are identical.
D) The firm earns zero economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is FALSE for a monopolist that practices perfect price discrimination?
A) The price per unit is the same as the marginal revenue per unit.
B) The firm faces a horizontal demand curve.
C) The firm produces a socially optimal level of output.
D) The firm charges each customer according to its maximum willingness to pay.
A) The price per unit is the same as the marginal revenue per unit.
B) The firm faces a horizontal demand curve.
C) The firm produces a socially optimal level of output.
D) The firm charges each customer according to its maximum willingness to pay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
By charging each customer according to its maximum willingness to pay, a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist leads to zero _____ in the market.
A) economic profit
B) producer surplus
C) consumer surplus
D) economic efficiency
A) economic profit
B) producer surplus
C) consumer surplus
D) economic efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose that a movie theater has a pricing policy where it charges a lower rate to students and a higher rate to everyone else. This is an example of:
A) a perfectly competitive market.
B) price discrimination.
C) legal barrier to entry.
D) duopoly.
A) a perfectly competitive market.
B) price discrimination.
C) legal barrier to entry.
D) duopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In which of the following types of markets does the business strategy of each firm affect the other firms in the market?
A) monopoly
B) monopolistic competition
C) perfect competition
D) oligopoly
A) monopoly
B) monopolistic competition
C) perfect competition
D) oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Economists use the tools of _____ theory to study behavior among economic agents whose decisions are interdependent.
A) auction
B) game
C) macro
D) social-choice
A) auction
B) game
C) macro
D) social-choice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following statements about oligopolies is FALSE?
A) The business strategy of one firm can affect the business of other firms.
B) Duopoly is an example of an oligopoly market.
C) Firms in the market do not have any market power.
D) Firms face a downward-sloping demand curve.
A) The business strategy of one firm can affect the business of other firms.
B) Duopoly is an example of an oligopoly market.
C) Firms in the market do not have any market power.
D) Firms face a downward-sloping demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of monopolistically competitive markets?
A) Firms can easily enter or exit the market.
B) Each firm in the market faces a horizontal demand curve.
C) Many firms are competing in the market.
D) The products that are sold by the different firms are not identical.
A) Firms can easily enter or exit the market.
B) Each firm in the market faces a horizontal demand curve.
C) Many firms are competing in the market.
D) The products that are sold by the different firms are not identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of monopolistically competitive markets?
A) Many firms compete in the market.
B) Firms can easily enter or exit the market.
C) Firms sell identical products.
D) Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
A) Many firms compete in the market.
B) Firms can easily enter or exit the market.
C) Firms sell identical products.
D) Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which one of the following statements is true about a monopolistically competitive market?
A) There are only two dominant firms in the market.
B) Each firm in the market faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
C) Firms in the market sell identical goods.
D) There are legal barriers to entry into the market.
A) There are only two dominant firms in the market.
B) Each firm in the market faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
C) Firms in the market sell identical goods.
D) There are legal barriers to entry into the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which one of the following statements is FALSE about a firm in a monopolistically competitive market at its long-run equilibrium?
A) It has zero economic profit per unit.
B) The price of its product equals the average total cost.
C) The price of its product equals the marginal cost.
D) Marginal revenue equals the marginal cost.
A) It has zero economic profit per unit.
B) The price of its product equals the average total cost.
C) The price of its product equals the marginal cost.
D) Marginal revenue equals the marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the long run, the price of a good that is sold by a monopolistically competitive firm is equal to the _____ cost of production.
A) marginal
B) total
C) average total
D) average variable
A) marginal
B) total
C) average total
D) average variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which one of the following statements is FALSE for a monopolistically competitive firm at its long-run equilibrium?
A) The price of its product equals the marginal cost.
B) The price of its product equals the average total cost.
C) The firm earns zero economic profit.
D) The marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A) The price of its product equals the marginal cost.
B) The price of its product equals the average total cost.
C) The firm earns zero economic profit.
D) The marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose that a firm in a monopolistically market charges $8 for its good and sells 100 units of output in the long-run. Given this, we can conclude that the total cost of production for the firm is _____ and the average cost of production is:
A) $800; $10.
B) $600; $12.
C) $800; $8.
D) $600; $8.
A) $800; $10.
B) $600; $12.
C) $800; $8.
D) $600; $8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that a firm in a monopolistically competitive market charges $10 for its good, sells 100 units of output, and has a marginal revenue of $6 in the long run. Given this, we can conclude that the marginal cost of production for the firm is _____ and the average cost of production is:
A) $6; $10.
B) $10; $6.
C) $8; $10.
D) $10; $8.
A) $6; $10.
B) $10; $6.
C) $8; $10.
D) $10; $8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose that a firm in a monopolistically competitive market is operating at its profit-maximizing point in the long run. The firm has a total cost of $800 and sells 50 units of output. Given this, we can conclude that the price of the good is _____ and the average total cost is:
A) $8; $16.
B) $16; $8.
C) $8; $8.
D) $16; $16.
A) $8; $16.
B) $16; $8.
C) $8; $8.
D) $16; $16.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose that a firm in a monopolistically competitive market is operating at its profit-maximizing point in the long run. The firm has a total revenue of $800 and sells 50 units of output. Given this, we can conclude that the average total cost of the firm is _____ and the price of the good is:
A) $8; $16.
B) $16; $8.
C) $16; $16.
D) $8; $8.
A) $8; $16.
B) $16; $8.
C) $16; $16.
D) $8; $8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose that a firm in a monopolistically competitive market is operating at its profit-maximizing point in the long run. The firm has a total revenue of $800, its marginal revenue is $10, and it sells 50 units of output. Given this, we can conclude that the average total cost of the firm is _____ and the marginal cost of production is:
A) $16; $16.
B) $16; $10.
C) $10; $16.
D) $10; $10.
A) $16; $16.
B) $16; $10.
C) $10; $16.
D) $10; $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose that a firm in a monopolistically competitive market is operating at its profit-maximizing point in the long run. The firm has a total revenue of $800, its marginal revenue is $10, and it sells 50 units of output. Given this, we can conclude that the price of the good is _____ and the marginal cost of production is:
A) $16; $16.
B) $10; $16.
C) $16; $10.
D) $10; $10.
A) $16; $16.
B) $10; $16.
C) $16; $10.
D) $10; $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose that a firm in a monopolistically competitive market is operating at its profit-maximizing point in the long run. The firm has an average total cost of $8 and produces 100 units of output. Given this, we can conclude that the total revenue of the firm is _____ and the price that it charges is:
A) $800; $10.
B) $600; $12.
C) $800; $8.
D) $600; $8.
A) $800; $10.
B) $600; $12.
C) $800; $8.
D) $600; $8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements is FALSE for a monopolistically competitive firm in the long run?
A) The price charged is equal to the average total cost of production.
B) It earns zero economic profit.
C) It produces a socially optimal level output.
D) The profit is maximized when marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.
A) The price charged is equal to the average total cost of production.
B) It earns zero economic profit.
C) It produces a socially optimal level output.
D) The profit is maximized when marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Relative to a perfectly competitive market, a monopolistically competitive market produces a_____ level of output and charges a _____ price.
A) higher; lower
B) higher; higher
C) lower; lower
D) lower; higher
A) higher; lower
B) higher; higher
C) lower; lower
D) lower; higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use Figure: Payoff Matrix Shell & BP I. The figure shows the payoff matrix where the hypothetical daily profits of BP and Shell (in millions of dollars) depend on each other's decision about whether to lower prices. Based on the payoffs, BP's dominant strategy is _____ the price, and Shell's dominant strategy is _____ the price.
Figure: Payoff Matrix Shell & BP I
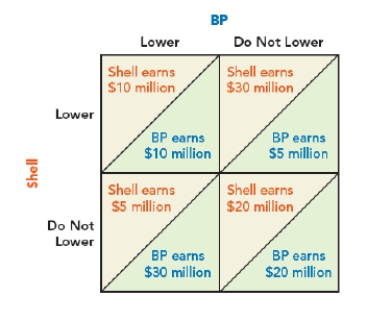
A) to lower; not to lower
B) not to lower; to lower
C) to lower; to lower
D) not to lower; not to lower
Figure: Payoff Matrix Shell & BP I

A) to lower; not to lower
B) not to lower; to lower
C) to lower; to lower
D) not to lower; not to lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



