Deck 13: Mating Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/22
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Mating Systems
1
The Emlen and Oring model of the evolution of social mating systems is based on sexual conflict theory, which assumes which of the following?
A) Females typically invest more energy into offspring than do males.
B) Females typically are smaller than males.
C) Males and females typically differ in their lifetime number of mates.
D) Sperm competition is unimportant.
E) Sex-role reversed species do not exist.
A) Females typically invest more energy into offspring than do males.
B) Females typically are smaller than males.
C) Males and females typically differ in their lifetime number of mates.
D) Sperm competition is unimportant.
E) Sex-role reversed species do not exist.
A
2
In elephant seals, a male competes with other males while defending several females with whom he mates. What term best describes this social mating system?
A) Male aggressive polygynandry
B) Female passive polyandry
C) Female defense polygyny
D) Male dominance polygyny
E) Male-female plural breeding
A) Male aggressive polygynandry
B) Female passive polyandry
C) Female defense polygyny
D) Male dominance polygyny
E) Male-female plural breeding
C
3
In some hummingbirds, males compete for display sites on a lek. Females then visit the lek to select a mate. What term do Emlen and Oring use to refer to such a mating system?
A) Female defense polygyny
B) Female passive polyandry
C) Male aggressive polygynandry
D) Male dominance polygyny
E) Male-female plural breeding
A) Female defense polygyny
B) Female passive polyandry
C) Male aggressive polygynandry
D) Male dominance polygyny
E) Male-female plural breeding
D
4
What method did Leisler use to test the Emlen and Oring model of the evolution of mating systems in birds?
A) Knockout method
B) Experimental method
C) Observational method
D) QTL method
E) Comparative method
A) Knockout method
B) Experimental method
C) Observational method
D) QTL method
E) Comparative method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What association did Leisler find between mating system and habitat quality in the birds he studied?
A) Monogamy was prevalent in poor-quality habitats.
B) Polygyny was prevalent in xeric habitats.
C) Polygynandry was prevalent in mesic habitats.
D) Male dominance polygyny was predominant in medium-quality habitats.
E) Polyandry was predominant in high-quality habitats
A) Monogamy was prevalent in poor-quality habitats.
B) Polygyny was prevalent in xeric habitats.
C) Polygynandry was prevalent in mesic habitats.
D) Male dominance polygyny was predominant in medium-quality habitats.
E) Polyandry was predominant in high-quality habitats

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Social monogamy is rare in mammals but common in birds. What difference is hypothesized to explain this observation?
A) The mean body size
B) The need for biparental care
C) The mean body temperature
D) The average diet
E) The average brain size
A) The mean body size
B) The need for biparental care
C) The mean body temperature
D) The average diet
E) The average brain size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What study design was used by researchers to study mating systems in California mice and poison frogs?
A) Phylogenetic analysis of related species
B) Experimental addition of resources
C) Experimental addition of competitors
D) Experimental reduction in parental care
E) Correlations between habitat and mating system
A) Phylogenetic analysis of related species
B) Experimental addition of resources
C) Experimental addition of competitors
D) Experimental reduction in parental care
E) Correlations between habitat and mating system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which hypothesis can explain social monogamy in species without biparental care?
A) Mate competition
B) Polygyny threshold
C) Genetic quality
D) Public information
E) Territorial cooperation.
A) Mate competition
B) Polygyny threshold
C) Genetic quality
D) Public information
E) Territorial cooperation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
You discover a new species of bird and observe that males defend similar-sized territories early in the breeding season and that females then settle on these territories. On some male territories, only one female settles to breed, while on others, multiple females settle and breed. How would you best classify this social mating system?
A) Polygyny
B) Polyandry
C) Polgynandry
D) Promiscuity
E) Plural breeding
A) Polygyny
B) Polyandry
C) Polgynandry
D) Promiscuity
E) Plural breeding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the polygyny threshold model, why do some females mate polygynously when they have the opportunity to mate monogamously?
A) They experience reduced disease transmission.
B) They experience lower predation risk.
C) They obtain more resources.
D) They obtain greater care for their young.
E) They have lower energy requirements.
A) They experience reduced disease transmission.
B) They experience lower predation risk.
C) They obtain more resources.
D) They obtain greater care for their young.
E) They have lower energy requirements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What evidence suggests that carrion beetles exhibit resource defense polygyny?
A) A dominant male defends multiple carcasses.
B) A dominant male mate guards multiple females.
C) A subordinate male obtains multiple mates via a sneaker tactic.
D) A satellite male obtains multiple mates by remaining near a dominant male.
E) A dominant male mates with multiple females at a carcass.
A) A dominant male defends multiple carcasses.
B) A dominant male mate guards multiple females.
C) A subordinate male obtains multiple mates via a sneaker tactic.
D) A satellite male obtains multiple mates by remaining near a dominant male.
E) A dominant male mates with multiple females at a carcass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a necessary aspect of the hotspot hypothesis?
A) A male with a large nuptial gift
B) A high-quality male in the population
C) A location with ideal thermal properties
D) A location of high female activity
E) Females possess exaggerated secondary sexual traits
A) A male with a large nuptial gift
B) A high-quality male in the population
C) A location with ideal thermal properties
D) A location of high female activity
E) Females possess exaggerated secondary sexual traits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
You collect data at a lek and notice that a single male obtains over 70% of the matings that occur there. When he is experimentally removed, the remaining males move to different locations on the lek. What hypothesis best explains this observation?
A) Hamilton-Zuk hypothesis
B) Hotspot hypothesis
C) Mate competition hypothesis
D) Mate-guarding hypothesis
E) Hotshot hypothesis
A) Hamilton-Zuk hypothesis
B) Hotspot hypothesis
C) Mate competition hypothesis
D) Mate-guarding hypothesis
E) Hotshot hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is NOT true about sex-role reversed species?
A) Females produce smaller gametes than males.
B) Females often possess ornaments.
C) Males often provide higher levels of parental care than do females.
D) Polyandry is common.
E) Females often aggressively compete for males.
A) Females produce smaller gametes than males.
B) Females often possess ornaments.
C) Males often provide higher levels of parental care than do females.
D) Polyandry is common.
E) Females often aggressively compete for males.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is characteristic of a promiscuous mating system?
A) Both males and females have multiple sexual partners.
B) Pair bonds are formed early in the breeding season.
C) Individuals have a single sexual partner but mate repeatedly.
D) Young individuals have more sexual partners than do older individuals.
E) Extra-pair copulations commonly occur.
A) Both males and females have multiple sexual partners.
B) Pair bonds are formed early in the breeding season.
C) Individuals have a single sexual partner but mate repeatedly.
D) Young individuals have more sexual partners than do older individuals.
E) Extra-pair copulations commonly occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Extra-pair copulations do NOT occur in which mating system?
A) Extra-pair
B) Polygamous
C) Polyandrous
D) Promiscuous
E) Polygynandrous
A) Extra-pair
B) Polygamous
C) Polyandrous
D) Promiscuous
E) Polygynandrous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is NOT a proposed benefit of multi-male mating by females?
A) Reduced likelihood of infanticide
B) Reduced predation risk
C) Additional parental care for offspring
D) Increased genetic diversity of offspring
E) Increased genetic quality of offspring
A) Reduced likelihood of infanticide
B) Reduced predation risk
C) Additional parental care for offspring
D) Increased genetic diversity of offspring
E) Increased genetic quality of offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Common crossbills (Loxia curvirostra) are a socially and genetically monogamous bird whereas Gunnison's sage-grouse (Centrocercus minimus) form leks and are polygynous. What prediction can you make about the degree of variation in male mating success in these two species?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What feature distinguishes promiscuity from polygynandry (plural breeding). Describe one species that exhibits each breeding system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What two factors favor the evolution of monogamy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Explain why monogamy in reed warblers is favored in resource-poor environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
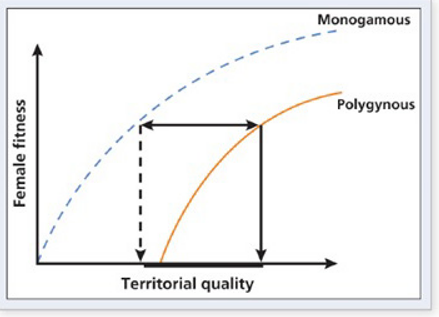
In the polygyny threshold model below, explain why the "Monogomous" line lies above the "Polygynous" line with respect to female fitness.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



