Deck 2: Why We Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Why We Trade
1
A simplified examination of a specific process or phenomenon is provided by:
A) an outline.
B) policies.
C) economic models.
D) a GPS view.
A) an outline.
B) policies.
C) economic models.
D) a GPS view.
C
2
A key characteristic of economic models is their:
A) variables.
B) equations.
C) simplicity.
D) detail.
A) variables.
B) equations.
C) simplicity.
D) detail.
C
3
The opportunity cost of an economic model is known as the:
A) measurement of time.
B) variables that can be included.
C) measurement of money and time.
D) exclusion of real-world complications.
A) measurement of time.
B) variables that can be included.
C) measurement of money and time.
D) exclusion of real-world complications.
D
4
Which model represents how households and businesses interact with each other?
A) production possibilities
B) global flow
C) economic flow
D) circular flow
A) production possibilities
B) global flow
C) economic flow
D) circular flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The resource market is comprised of:
A) labor and business.
B) labor and natural resources.
C) business and natural resources.
D) business and government.
A) labor and business.
B) labor and natural resources.
C) business and natural resources.
D) business and government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the circular flow model, people usually work for _____ in the _____ market.
A) goods and services; resource
B) goods and services; product
C) money; product
D) money; resource
A) goods and services; resource
B) goods and services; product
C) money; product
D) money; resource

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the circular flow model, people usually use money for _____ in the _____ market.
A) goods and services; resource
B) goods and services; product
C) money; product
D) money; resource
A) goods and services; resource
B) goods and services; product
C) money; product
D) money; resource

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Jeff Bezos, founder and CEO of Amazon, participates in the _____ market as he makes decisions regarding the use of factors of production used by Amazon.
A) technology
B) economic
C) resource
D) digital
A) technology
B) economic
C) resource
D) digital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Galina participates in the _____ market when she buys clothes in her local Macy's.
A) product
B) economic
C) resource
D) digital
A) product
B) economic
C) resource
D) digital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Goods and services are found in the _____ market.
A) resource
B) product
C) digital
D) government
A) resource
B) product
C) digital
D) government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Regarding the circular flow model, _____ is income to households and _____ to businesses.
A) revenue; money
B) spending; revenue
C) revenue; an expense
D) money; an expense
A) revenue; money
B) spending; revenue
C) revenue; an expense
D) money; an expense

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A simplified model that shows how households and businesses interact with one another in the product market and resource market is known as the:
A) basic economic model.
B) production possibilities model.
C) free trade model.
D) circular flow model.
A) basic economic model.
B) production possibilities model.
C) free trade model.
D) circular flow model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The economic model that depicts the maximum output that can be produced in an economy when resources are used efficiently is known as the:
A) circular flow model.
B) production possibilities frontier model.
C) opportunity cost model.
D) law of increasing costs.
A) circular flow model.
B) production possibilities frontier model.
C) opportunity cost model.
D) law of increasing costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The _____ is an economic model that shows the limit of what an economy can produce when all resources are used efficiently.
A) circular flow model
B) production possibilities frontier model
C) opportunity cost model
D) law of increasing costs
A) circular flow model
B) production possibilities frontier model
C) opportunity cost model
D) law of increasing costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The limits to what an economy can produce result from:
A) scarcity.
B) income.
C) production.
D) costs.
A) scarcity.
B) income.
C) production.
D) costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
(Figure: Production Possibilities Frontier, PPF) Point B represents:
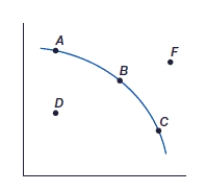
A) an inefficient use of resources.
B) an unattainable goal based on current resources.
C) the maximum use of resources.
D) a probable use of resources.

A) an inefficient use of resources.
B) an unattainable goal based on current resources.
C) the maximum use of resources.
D) a probable use of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
(Figure: Production Possibilities Frontier, PPF) Point D represents:
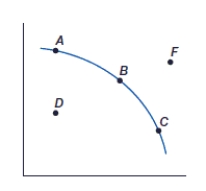
A) an inefficient use of resources.
B) an unattainable goal based on current resources.
C) the maximum use of resources.
D) a probable use of resources.

A) an inefficient use of resources.
B) an unattainable goal based on current resources.
C) the maximum use of resources.
D) a probable use of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
(Figure: Production Possibilities Frontier, PPF) Point F represents:
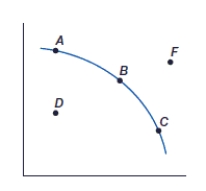
A) an inefficient use of resources.
B) an unattainable goal based on current resources.
C) the maximum use of resources.
D) a probable use of resources.

A) an inefficient use of resources.
B) an unattainable goal based on current resources.
C) the maximum use of resources.
D) a probable use of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
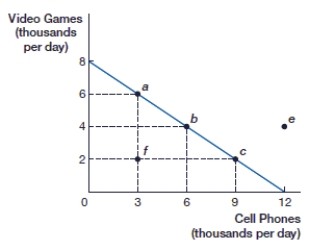
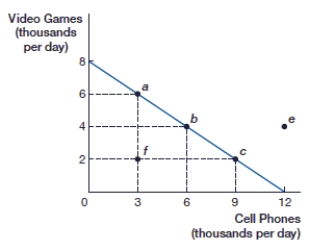
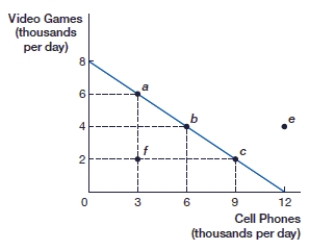
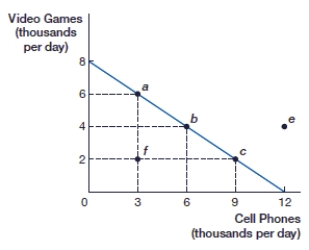
(Figure: Video Games and Cell Phones PPF) If this economy is producing 4,000 video games, what is the opportunity cost of 2,000 more video games?
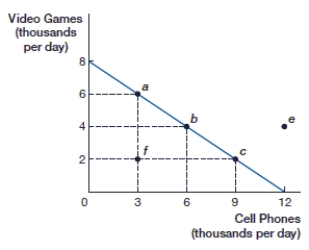
A) 1,000 cell phones
B) 3,000 cell phones
C) 6,000 cell phones
D) 9,000 cell phones

A) 1,000 cell phones
B) 3,000 cell phones
C) 6,000 cell phones
D) 9,000 cell phones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
(Figure: Video Games and Cell Phones PPF) If this economy is producing 2,000 video games, what is the opportunity cost of 2,000 more video games?
A) 1,000 cell phones
B) 2,000 cell phones
C) 3,000 cell phones
D) 9,000 cell phones

A) 1,000 cell phones
B) 2,000 cell phones
C) 3,000 cell phones
D) 9,000 cell phones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
(Figure: Video Games and Cell Phones PPF) If this economy is producing at point f, how many cell phones are being produced?
A) 1,000
B) 3,000
C) 6,000
D) 9,000

A) 1,000
B) 3,000
C) 6,000
D) 9,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
(Figure: Video Games and Cell Phones PPF) If this economy is producing at point f, how many video games are being produced?
A) 2,000
B) 3,000
C) 6,000
D) 9,000

A) 2,000
B) 3,000
C) 6,000
D) 9,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
(Figure: Video Games and Cell Phones PPF) If this economy is specializing in cell phones, how many video games are being produced?
A) 8,000
B) 6,000
C) 4,000
D) 0

A) 8,000
B) 6,000
C) 4,000
D) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
(Figure: Video Games and Cell Phones PPF) At point b, this economy is producing _____ video games and _____ cell phones.
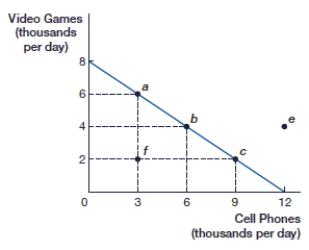
A) 2,000; 3,000
B) 3,000; 4,000
C) 4,000; 6,000
D) 8,000; 7,000

A) 2,000; 3,000
B) 3,000; 4,000
C) 4,000; 6,000
D) 8,000; 7,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
_____ cost is what is given up in order to acquire or do something else.
A) Opportunity
B) Marginal
C) Maximum
D) Minimum
A) Opportunity
B) Marginal
C) Maximum
D) Minimum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
(Figure: Cars and Watches PPF) What is the opportunity cost of moving from point C to point D?
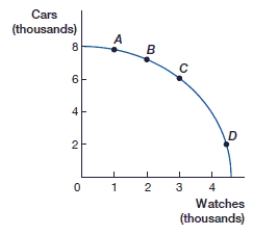
A) 1,000 watches
B) 2,000 watches
C) 3,000 cars
D) 4,000 cars

A) 1,000 watches
B) 2,000 watches
C) 3,000 cars
D) 4,000 cars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
(Figure: Cars and Watches PPF 2) What is the opportunity cost of moving from point B to point C?
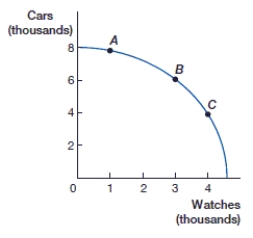
A) 1,000 cars
B) 2,000 cars
C) 1,000 watches
D) 2,000 watches

A) 1,000 cars
B) 2,000 cars
C) 1,000 watches
D) 2,000 watches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The bowed-out, concave shape of the production possibilities frontier is explained by the:
A) circular flow model.
B) law of increasing costs.
C) theory of marginal cost.
D) maximization model.
A) circular flow model.
B) law of increasing costs.
C) theory of marginal cost.
D) maximization model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When operating on the production possibilities frontier, producing more of one good generally results in less of the other good due to the:
A) opportunity cost.
B) changing technology.
C) theory of marginal cost.
D) maximization model.
A) opportunity cost.
B) changing technology.
C) theory of marginal cost.
D) maximization model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Obtaining the maximum possible output with a given set of resources or obtaining output for the lowest possible cost is known as:
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Minimizing production costs per unit is also known as:
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Obtaining the maximum well-being from producing the right set of goods and services is known as:
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Efficiency in the distribution and allotment of goods and services is known as:
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Ensuring that the optimal mix of goods and services is produced is known as:
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Maximizing output or minimizing waste is known as:
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.
A) allocative efficiency.
B) allocative effectiveness.
C) productive efficiency.
D) productive effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A sustained increase in the amount of goods and services produced is known as:
A) allocative efficiency.
B) productive efficiency.
C) minimizing opportunity costs.
D) economic growth.
A) allocative efficiency.
B) productive efficiency.
C) minimizing opportunity costs.
D) economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Sources of economic growth include:
A) innovation, investments in physical capital, and improvements in human capital.
B) new technology, changes in the unemployment rate, and changes in the exchange rate.
C) investments in physical capital, changes in the unemployment rate, and changes in the exchange rate.
D) changes in the exchange rate, improvements in human capital, and changes in the unemployment rate.
A) innovation, investments in physical capital, and improvements in human capital.
B) new technology, changes in the unemployment rate, and changes in the exchange rate.
C) investments in physical capital, changes in the unemployment rate, and changes in the exchange rate.
D) changes in the exchange rate, improvements in human capital, and changes in the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The introduction of the Apple iPhone in 2007 was an example of:
A) investment in physical capital.
B) innovation and technology.
C) investment in human capital.
D) innovation in manufacturing.
A) investment in physical capital.
B) innovation and technology.
C) investment in human capital.
D) innovation in manufacturing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A firm is considering opening a manufacturing plant in rural West Virginia. In analyzing costs, the firm has determined that labor in the area does not have the skill set to enable the firm to operate effectively. If it selects the West Virginia site, the firm will be faced with the additional cost of training employees. This is an example of:
A) investments in physical capital.
B) innovation and technology.
C) investments in human capital.
D) innovation in manufacturing.
A) investments in physical capital.
B) innovation and technology.
C) investments in human capital.
D) innovation in manufacturing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
(Figure: Cars and Bicycles PPF 1) This figure shows:
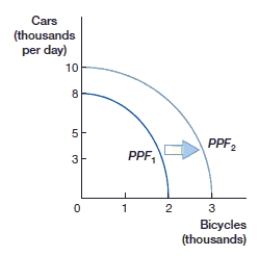
A) economic stagnation.
B) economic growth.
C) a stagnant economy.
D) a reduction in economic efficiency.

A) economic stagnation.
B) economic growth.
C) a stagnant economy.
D) a reduction in economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following may cause an economy's production possibilities frontier (PPF) to shift to the left?
A) The country's workforce increases its training and education.
B) Businesses in the country increase their investment in machinery and equipment.
C) Income taxes are reduced.
D) A massive earthquake and tsunami damage much of the country's infrastructure.
A) The country's workforce increases its training and education.
B) Businesses in the country increase their investment in machinery and equipment.
C) Income taxes are reduced.
D) A massive earthquake and tsunami damage much of the country's infrastructure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following may cause an economy's production possibilities frontier (PPF) to shift to the right?
A) The government is overthrown in a coup.
B) Businesses in the country increase their investment in machinery and equipment.
C) Income taxes are raised.
D) A massive earthquake and tsunami damage much of the country's infrastructure.
A) The government is overthrown in a coup.
B) Businesses in the country increase their investment in machinery and equipment.
C) Income taxes are raised.
D) A massive earthquake and tsunami damage much of the country's infrastructure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
_____ is the concentration on the production of a single good.
A) Efficiency
B) Opportunity
C) Comparative advantage
D) Specialization
A) Efficiency
B) Opportunity
C) Comparative advantage
D) Specialization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Comparative advantage is defined in terms of:
A) efficiency.
B) absolute advantage.
C) opportunity cost.
D) specialization.
A) efficiency.
B) absolute advantage.
C) opportunity cost.
D) specialization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
(Exhibit: Opportunity Cost) Video game production increases from 15,000 games to 20,000 games. In this economy, what is the opportunity cost?
A) 5,000 video games
B) 10,000 video games
C) 5,000 cell phones
D) 10,000 cell phones
A) 5,000 video games
B) 10,000 video games
C) 5,000 cell phones
D) 10,000 cell phones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
(Exhibit: Opportunity Cost) Video game production increases from 35,000 games to 50,000 games. In this economy, what is the opportunity cost?
A) 20,000 video games
B) 150,000 video games
C) 20,000 cell phones
D) 15,000 cell phones
A) 20,000 video games
B) 150,000 video games
C) 20,000 cell phones
D) 15,000 cell phones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
David can wash four cars in one hour or cut two lawns. Ralph can wash three cars in one hour or cut two lawns. David's opportunity cost for cutting one lawn is _____ car washes, and Ralph's opportunity cost for cutting one lawn is _____ car washes.
A) 2; 1.5
B) 4; 3.5
C) 1.5; 2
D) 3.5; 4
A) 2; 1.5
B) 4; 3.5
C) 1.5; 2
D) 3.5; 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
(Exhibit: Determining Comparative Advantage) Eric has a lower opportunity cost for:
A) baking bread.
B) baking a cake.
C) neither bread nor cake.
D) both bread and cake.
A) baking bread.
B) baking a cake.
C) neither bread nor cake.
D) both bread and cake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
(Exhibit: Determining Comparative Advantage) Daisy has a lower opportunity cost for:
A) baking bread.
B) baking a cake.
C) neither bread nor cake.
D) both bread and cake.
A) baking bread.
B) baking a cake.
C) neither bread nor cake.
D) both bread and cake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
(Exhibit: Determining Comparative Advantage) Who has a comparative advantage in baking bread?
A) Eric
B) Daisy
C) neither Eric nor Daisy
D) both Eric and Daisy
A) Eric
B) Daisy
C) neither Eric nor Daisy
D) both Eric and Daisy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
(Exhibit: Determining Comparative Advantage) Who has a comparative advantage in baking cakes?
A) Eric
B) Daisy
C) neither Eric nor Daisy
D) both Eric and Daisy
A) Eric
B) Daisy
C) neither Eric nor Daisy
D) both Eric and Daisy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
_____ is the ability to produce more of a product than a trading partner can.
A) Efficiency
B) Absolute advantage
C) Comparative advantage
D) Specialization
A) Efficiency
B) Absolute advantage
C) Comparative advantage
D) Specialization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
(Exhibit: Determining Comparative Advantage) Who has an absolute advantage in baking cakes?
A) Eric
B) Daisy
C) neither Eric nor Daisy
D) both Eric and Daisy
A) Eric
B) Daisy
C) neither Eric nor Daisy
D) both Eric and Daisy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
(Exhibit: Determining Comparative Advantage) Who has an absolute advantage in baking bread?
A) Eric
B) Daisy
C) neither Eric nor Daisy
D) both Eric and Daisy
A) Eric
B) Daisy
C) neither Eric nor Daisy
D) both Eric and Daisy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Gains from trade are based on _____ rather than:
A) opportunity cost; specialization.
B) comparative advantage; absolute advantage.
C) absolute advantage; specialization.
D) specialization; comparative advantage.
A) opportunity cost; specialization.
B) comparative advantage; absolute advantage.
C) absolute advantage; specialization.
D) specialization; comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Gains from trade are based on:
A) opportunity cost.
B) comparative advantage.
C) money.
D) absolute advantage.
A) opportunity cost.
B) comparative advantage.
C) money.
D) absolute advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When trade occurs on the basis of ____, both sides win.
A) comparative advantage
B) absolute advantage
C) price
D) revenue
A) comparative advantage
B) absolute advantage
C) price
D) revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What enables an economy to consume beyond the production possibilities frontier (PPF)?
A) comparative advantage
B) absolute advantage
C) trade
D) growth
A) comparative advantage
B) absolute advantage
C) trade
D) growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The opening of markets to foreign trade that leads to an increasing interdependence of world economies is known as:
A) globalization.
B) internationalism.
C) protectionism.
D) growth.
A) globalization.
B) internationalism.
C) protectionism.
D) growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
McDonald's has locations in more than 100 countries. This is an example of:
A) globalization.
B) internationalism.
C) trade.
D) growth.
A) globalization.
B) internationalism.
C) trade.
D) growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Boeing, a U.S. aircraft manufacturing company, has suppliers from countries such as Germany, Japan, and Italy. This is an example of:
A) globalization.
B) internationalism.
C) trade.
D) growth.
A) globalization.
B) internationalism.
C) trade.
D) growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Goods and services that are produced domestically and sold in a foreign country are:
A) high-value goods only.
B) exports.
C) imports.
D) low-value goods only.
A) high-value goods only.
B) exports.
C) imports.
D) low-value goods only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suzy purchases shoes in Boise, Idaho, that were made in Italy. These shoes are:
A) a high-value good.
B) an export.
C) an import.
D) a low-value good.
A) a high-value good.
B) an export.
C) an import.
D) a low-value good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Ford Motor Company, a U.S. firm, sells cars in Europe that were made in the United States. This is NOT an example of:
A) imports to the U.S.
B) imports to Europe.
C) exports from the U.S.
D) globalization.
A) imports to the U.S.
B) imports to Europe.
C) exports from the U.S.
D) globalization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The main export of Canada is:
A) transport equipment.
B) clothing and shoes.
C) motor vehicles and parts.
D) capital goods.
A) transport equipment.
B) clothing and shoes.
C) motor vehicles and parts.
D) capital goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The main export of Mexico is:
A) transport equipment.
B) clothing and shoes.
C) motor vehicles and parts.
D) capital goods.
A) transport equipment.
B) clothing and shoes.
C) motor vehicles and parts.
D) capital goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Another name for net exports is:
A) international trade.
B) trade surplus.
C) trade balance.
D) net imports.
A) international trade.
B) trade surplus.
C) trade balance.
D) net imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
_____ occurs when a country imports more than it exports.
A) No international trade
B) A trade surplus
C) Positive trade
D) A trade deficit
A) No international trade
B) A trade surplus
C) Positive trade
D) A trade deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
_____ occurs when a country exports more than it imports.
A) No international trade
B) A trade surplus
C) Positive trade
D) A trade deficit
A) No international trade
B) A trade surplus
C) Positive trade
D) A trade deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The country of Davilena exported $900,000 in goods and services and imported $680,000 in goods and services. The country has a _____ of:
A) net trade; $1,580,000.
B) trade surplus; $220,000.
C) trade balance; $680,000.
D) trade deficit; $900,000.
A) net trade; $1,580,000.
B) trade surplus; $220,000.
C) trade balance; $680,000.
D) trade deficit; $900,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a country exports more than it imports, it has a _____ trade balance.
A) negative
B) positive
C) zero
D) unattainable
A) negative
B) positive
C) zero
D) unattainable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the _____ market, currencies are traded.
A) resource
B) foreign exchange
C) product
D) barter
A) resource
B) foreign exchange
C) product
D) barter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Maurice is traveling from the United States to China. He will need to exchange his _____ for _____.
A) dollars; yuan
B) yuan; pesos
C) pesos; yen
D) yen; dollars
A) dollars; yuan
B) yuan; pesos
C) pesos; yen
D) yen; dollars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Exchange rates determined by economic or market conditions are _____ rates.
A) fixed
B) pegged
C) currency
D) flexible
A) fixed
B) pegged
C) currency
D) flexible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
An adjustment in the exchange rate that makes one country's currency more valuable relative to another country's currency is known as:
A) an appreciation of the currency.
B) a depreciation of the currency.
C) a parity of the currency.
D) a devaluation of the currency.
A) an appreciation of the currency.
B) a depreciation of the currency.
C) a parity of the currency.
D) a devaluation of the currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An adjustment in the exchange rate that make one country's currency less valuable relative to another country's currency is known as:
A) an appreciation of the currency.
B) a depreciation of the currency.
C) a parity of the currency.
D) a devaluation of the currency.
A) an appreciation of the currency.
B) a depreciation of the currency.
C) a parity of the currency.
D) a devaluation of the currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Appreciation occurs when:
A) two currencies are pegged to each other.
B) two currencies are equal to each other.
C) that currency increases in value relative to another.
D) that currency decreases in value relative to another.
A) two currencies are pegged to each other.
B) two currencies are equal to each other.
C) that currency increases in value relative to another.
D) that currency decreases in value relative to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Depreciation occurs when:
A) two currencies are pegged to each other.
B) two currencies are equal to each other.
C) that currency increases in value relative to another.
D) that currency decreases in value relative to another.
A) two currencies are pegged to each other.
B) two currencies are equal to each other.
C) that currency increases in value relative to another.
D) that currency decreases in value relative to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Yesterday, the exchange rate for the U.S dollar and the euro was 1 euro for every $1.10. Today, it is 1 euro for every $1.20. Which currency is appreciating?
A) the euro
B) the U.S. dollar
C) both
D) neither
A) the euro
B) the U.S. dollar
C) both
D) neither

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Yesterday, the exchange rate for the U.S dollar and the euro was 1 euro for every $1.10. Today, it is 1 euro for every $1.20. Which currency is depreciating?
A) the euro
B) the U.S. dollar
C) both
D) neither
A) the euro
B) the U.S. dollar
C) both
D) neither

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



