Deck 5: The Rise of Rome and Its Republic, 753-44 B.C.E
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: The Rise of Rome and Its Republic, 753-44 B.C.E
1
How did the patron-client system benefit both parties as well as Roman society as a whole?
Answer would ideally include the following. A patron was a man of superior status who could offer financial and political assistance to persons of lower status, who became his clients. In return, these individuals owed him duties, which could range from supporting him in a political contest to loaning him money for his daughter's dowry. The patron-client relationship was a long-lasting, mutually beneficial one, and, although the patron-client system institutionalized the hierarchical nature of Roman society, it also encouraged social stability through its structure of intertwined obligations.
2
In which ways did Cornelia, mother of Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus, personify the Roman ideal of female virtue?
Answer would ideally include the following. Cornelia was the wife of a distinguished Roman citizen. She bore twelve children, of whom only three survived. She devoted herself to raising her children and teaching them Roman values, as well as overseeing and managing her husband's property. Her devotion to her family was such that after her husband died and the king of Egypt proposed to her, she refused him so that she could continue to manage the family estate and educate her children. Although Cornelia also became famous for her intellectual gifts, as demonstrated in her letters, she exemplified the virtuous Roman matron who put raising good citizens and providing for her family before her own social advancement.
3
The Romans were a culture that borrowed heavily from the Greeks and the Etruscans. What specific cultural modalities did Romans borrow from each civilization? What did they eschew from these groups?
Answer would ideally include the following. From their northern neighbors, the Etruscans, the Romans borrowed many cultural forms, including musical instruments, religious rituals, and lictors (attendants who walked before the highest officials carrying the fasces, a bundle of rods surrounding an ax, which symbolized the officials' right to command and punish), and the rituals of divination, by which the gods' will was determined by viewing the organs of slaughtered animals. From the Greeks, the Romans borrowed the Greek deities, literature, art, and architectural styles. One Greek concept that the Romans particularly despised was the lack of military unity.
4
How did the Roman republican system ensure that consuls would have sufficient experience to fulfill their duties?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How did Rome convince many of their vanquished foes in Italy to willingly accept Roman domination?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
With regard to the Second Punic War, and the outcome at Cannae in particular, one could call Hannibal the general who won the battle but lost the war. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Although the Romans finally won the Punic Wars, why were the hard-won victories ultimately disastrous for the soldiers and their families?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Gaius Marius (c. 157-86 B.C.E.) changed Roman history when he reformed the army entrance requirements. Explain Marius's rise to power and the influence of his reform on the nature of the Roman army.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What were Julius Caesar's policies as dictator, and did some of those policies need reforms? Why was Julius Caesar assassinated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Define the nature of religion and morality in the Roman republic; explain how each was both a private matter and a public factor of social and political stability. What moral values did the Romans esteem, and how were humans expected to behave vis-à-vis the gods?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the Roman republic, the highest officials were known as consuls. Consuls were elected each year and were expected to command the army. How did the Romans ensure that the elected consuls would be sufficiently experienced to carry out such an important task? Explain in detail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why did the Romans expand nearly continuously throughout the Mediterranean world until the first century B.C.E.? What factors enabled this expansion? Please detail the stages of Roman expansion in your response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Discuss the cultural relationship between Greece and Rome after Greece became a Roman province. Explain the Hellenization of Roman culture. Did Greek culture affect Roman literature and the arts?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The expansion of Rome increased the disparity between rich and poor because the elites gained wealth and increased their estates through the spoils of war, while the soldiers, all of whom were small landholders, were unable to maintain their farms while they were away at war and often lost their land altogether. How did the Gracchus brothers and Gaius Marius try to remedy this situation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What did Roman citizens believe they would receive in return for their honor of the gods?
A) Immense wealth
B) Divine support
C) Material gains
D) Absolute freedom
A) Immense wealth
B) Divine support
C) Material gains
D) Absolute freedom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What did Roman morality primarily emphasize?
A) A personal relationship with the gods
B) Virtue, faithfulness, and respect
C) Power, status, and wealth
D) Democracy, equality, and generosity
A) A personal relationship with the gods
B) Virtue, faithfulness, and respect
C) Power, status, and wealth
D) Democracy, equality, and generosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following traits were highly esteemed in the early Roman republic (509-287 B.C.E.)?
A) Ingenuity and creativity
B) Fidelity and perseverance
C) Ambition and personal independence
D) Egalitarianism and concern for the less fortunate
A) Ingenuity and creativity
B) Fidelity and perseverance
C) Ambition and personal independence
D) Egalitarianism and concern for the less fortunate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Roman concept of authority was based on the belief that
A) in an egalitarian society, authority could be earned only through virtuous living and charity toward others.
B) society had to be hierarchical to be just.
C) emperors were the perfect embodiment of patriarchal authority.
D) women and men should share responsibilities and power equally.
A) in an egalitarian society, authority could be earned only through virtuous living and charity toward others.
B) society had to be hierarchical to be just.
C) emperors were the perfect embodiment of patriarchal authority.
D) women and men should share responsibilities and power equally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What institution of the early Roman republic was based on a network of relationships characterized by mutual obligations?
A) The office of tribune
B) The Centuriate Assembly
C) Co-consulship
D) The patron-client system
A) The office of tribune
B) The Centuriate Assembly
C) Co-consulship
D) The patron-client system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Patria potestas referred to the right of the father to hold formal power over which of the following?
A) His children and his slaves
B) His wife and children
C) His wife and her family
D) His wife and children and his slaves
A) His children and his slaves
B) His wife and children
C) His wife and her family
D) His wife and children and his slaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What Roman woman of the second century B.C.E. gained fame for having turned down a marriage offer from King Ptolemy VIII of Egypt and giving birth to two leading politicians, Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus?
A) Lucretia
B) Cornelia
C) Tullia
D) Alexandria
A) Lucretia
B) Cornelia
C) Tullia
D) Alexandria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How did the status of wealthy Roman women differ from that of most Greek women in the Classical Age?
A) Roman women had a slightly higher status, since they not only managed their households but also were able to play an indirect but important role in politics.
B) Roman women enjoyed a higher social status and were even allowed to work as actresses and musicians in public settings.
C) Roman women suffered a lower status, since they generally were not allowed to buy, sell, or inherit property.
D) There was little or no difference; in neither society were women permitted to control the household or to serve in public life.
A) Roman women had a slightly higher status, since they not only managed their households but also were able to play an indirect but important role in politics.
B) Roman women enjoyed a higher social status and were even allowed to work as actresses and musicians in public settings.
C) Roman women suffered a lower status, since they generally were not allowed to buy, sell, or inherit property.
D) There was little or no difference; in neither society were women permitted to control the household or to serve in public life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following subjects was considered most important for an elite Roman boy's education and preparation for adulthood?
A) Military training
B) Philosophy
C) Management skills
D) Rhetoric
A) Military training
B) Philosophy
C) Management skills
D) Rhetoric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The chastity of the Vestal Virgins was meant to
A) prove their worthiness of the gods' attentions.
B) symbolize the security and stability of the Roman family and by extension the Roman republic itself.
C) signify the priestesses' proximity to divinity, making all Romans closer to the gods.
D) preserve legends of virtuous females such as the Sabine women and the Roman matron Lucretia.
A) prove their worthiness of the gods' attentions.
B) symbolize the security and stability of the Roman family and by extension the Roman republic itself.
C) signify the priestesses' proximity to divinity, making all Romans closer to the gods.
D) preserve legends of virtuous females such as the Sabine women and the Roman matron Lucretia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What was the primary function of the gods in Roman religion?
A) To judge each Roman as either fit or unfit for a happy afterlife
B) To guard Rome's safety and prosperity
C) To serve as models of proper and virtuous behavior
D) To maintain the power of the mos maiorum
A) To judge each Roman as either fit or unfit for a happy afterlife
B) To guard Rome's safety and prosperity
C) To serve as models of proper and virtuous behavior
D) To maintain the power of the mos maiorum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why did the Romans occasionally seek the help of foreign deities?
A) They hoped to win the hearts of future trading partners who lived abroad.
B) They believed that turning to foreign gods would make it easier to conquer new territories.
C) They had little other recourse in times of desperation and need.
D) They sought to forge new dynastic alliances by adopting foreign gods.
A) They hoped to win the hearts of future trading partners who lived abroad.
B) They believed that turning to foreign gods would make it easier to conquer new territories.
C) They had little other recourse in times of desperation and need.
D) They sought to forge new dynastic alliances by adopting foreign gods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Why did Rome's most prominent men seek the post of pontifex maximus ("greatest bridge-builder")?
A) It paid the highest salary of any position, even more than consul or senator.
B) It would give them the power to appoint senators and the opportunity to build a political following.
C) It allowed the officeholder to claim aristocratic status, regardless of his class at birth.
D) It bestowed increased political power, since the officeholder was the head of state religion.
A) It paid the highest salary of any position, even more than consul or senator.
B) It would give them the power to appoint senators and the opportunity to build a political following.
C) It allowed the officeholder to claim aristocratic status, regardless of his class at birth.
D) It bestowed increased political power, since the officeholder was the head of state religion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Freed slaves in the Roman republic could not hold elective office or serve in the army,
A) but their children possessed citizenship without any limitations.
B) and often as a result they emigrated to nations that gave them more rights.
C) making them a dangerous source of civil discontent.
D) unless they accumulated enough wealth to qualify as equestrians or equites.
A) but their children possessed citizenship without any limitations.
B) and often as a result they emigrated to nations that gave them more rights.
C) making them a dangerous source of civil discontent.
D) unless they accumulated enough wealth to qualify as equestrians or equites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Roman Senate was originally created as a(n)
A) elected body that could veto any measures proposed by the executive branch.
B) group of twenty-five men whose purpose was to advise the assemblies.
C) council of distinguished men whose purpose was to advise and consult with the king.
D) group of ten men constituted to negotiate the assimilation of the Sabines into the Roman community.
A) elected body that could veto any measures proposed by the executive branch.
B) group of twenty-five men whose purpose was to advise the assemblies.
C) council of distinguished men whose purpose was to advise and consult with the king.
D) group of ten men constituted to negotiate the assimilation of the Sabines into the Roman community.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why was Rome's geography perfect for territorial expansion?
A) Rome's winters featured prolonged cold periods that killed the mosquitos that spread malaria.
B) Rome's location at the edge of the Atlantic Ocean meant that it could expand easily into northern and western Europe.
C) Located far from the active seismic zones in the Mediterranean, Rome was free of natural disasters.
D) Rome possessed a river, fertile farmland, and a port on the Mediterranean.
A) Rome's winters featured prolonged cold periods that killed the mosquitos that spread malaria.
B) Rome's location at the edge of the Atlantic Ocean meant that it could expand easily into northern and western Europe.
C) Located far from the active seismic zones in the Mediterranean, Rome was free of natural disasters.
D) Rome possessed a river, fertile farmland, and a port on the Mediterranean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is supported by this map?
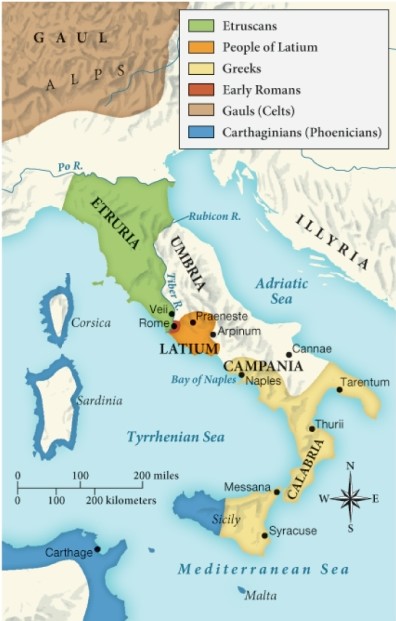
A) In ancient Italy, Rome had very little control over territory.
B) Ancient Italy was largely run by the Carthaginians.
C) Most of ancient Italy was dominated by Roman influence.
D) The Gauls had a significant influence on ancient Italian culture.

A) In ancient Italy, Rome had very little control over territory.
B) Ancient Italy was largely run by the Carthaginians.
C) Most of ancient Italy was dominated by Roman influence.
D) The Gauls had a significant influence on ancient Italian culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What customs and practices did the Romans adopt from the Etruscans?
A) Political models, including democracy and oligarchy
B) Deities, including Jupiter and Mars
C) Ceremonial features, including musical instruments and religious rituals
D) Architectural styles and models of poetry
A) Political models, including democracy and oligarchy
B) Deities, including Jupiter and Mars
C) Ceremonial features, including musical instruments and religious rituals
D) Architectural styles and models of poetry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Why did the Roman aristocrats create a republican system of government and not a monarchy?
A) They were committed to a government in which all citizens were participants.
B) They distrusted eastern Mediterranean empires such as the Persian Empire and wanted to avoid emulating them in any way.
C) They had come to believe that it was necessary to share power between adult male citizens.
D) They had learned from Greek political theorists about the evils and abuses of monarchy.
A) They were committed to a government in which all citizens were participants.
B) They distrusted eastern Mediterranean empires such as the Persian Empire and wanted to avoid emulating them in any way.
C) They had come to believe that it was necessary to share power between adult male citizens.
D) They had learned from Greek political theorists about the evils and abuses of monarchy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The tale of the rape of Lucretia reflects which of the following?
A) The author's disgust with the decline in Roman morals following the Punic Wars
B) The Romans' tradition of incorporating local tribes into their dominions as citizens
C) The belief that this outrage led the morally virtuous Romans to overthrow the monarchy and establish a republican government
D) One of the major issues in the struggle of the orders, which was the fact that patricians were permitted to mistreat any plebeian, including virtuous matrons such as Lucretia
A) The author's disgust with the decline in Roman morals following the Punic Wars
B) The Romans' tradition of incorporating local tribes into their dominions as citizens
C) The belief that this outrage led the morally virtuous Romans to overthrow the monarchy and establish a republican government
D) One of the major issues in the struggle of the orders, which was the fact that patricians were permitted to mistreat any plebeian, including virtuous matrons such as Lucretia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following finally ended the struggle of the orders, a political power struggle between Rome's most aristocratic families (the patricians) and the rest of Rome's citizens (the plebeians)?
A) The plebeians learned to manipulate the patronage system and influence patrons to legislate in favor of plebeian interests.
B) In 451 B.C.E., the ban on marriage between plebeians and patricians was lifted.
C) The patricians agreed to make plebeians eligible for membership in the Roman Senate.
D) In 287 B.C.E., the plebeians won the right to draft and pass laws in their own assembly.
A) The plebeians learned to manipulate the patronage system and influence patrons to legislate in favor of plebeian interests.
B) In 451 B.C.E., the ban on marriage between plebeians and patricians was lifted.
C) The patricians agreed to make plebeians eligible for membership in the Roman Senate.
D) In 287 B.C.E., the plebeians won the right to draft and pass laws in their own assembly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What was the main tactic used by the plebeians to force the patricians to make political and economic concessions?
A) They pressured the patricians by periodically refusing to perform military service.
B) They invaded patrician estates and freed their slaves.
C) They instructed their tribunes to veto every measure that the patricians strove to pass in the Tribal Assembly.
D) They rioted, destroying a significant part of the Roman forum.
A) They pressured the patricians by periodically refusing to perform military service.
B) They invaded patrician estates and freed their slaves.
C) They instructed their tribunes to veto every measure that the patricians strove to pass in the Tribal Assembly.
D) They rioted, destroying a significant part of the Roman forum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
According to this map, the security of Rome during the republic was largely based on which of the following?

A) Walls surrounding the major structures of the city
B) Heavy artillery to defend against invaders
C) Geographical features that acted as natural obstacles
D) The establishment of temples on the outskirts of the city

A) Walls surrounding the major structures of the city
B) Heavy artillery to defend against invaders
C) Geographical features that acted as natural obstacles
D) The establishment of temples on the outskirts of the city

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How did the office of tribune differ from most other political offices?
A) It was established to serve and protect the plebeian order, not all of society.
B) Former slaves who had served in the military could stand for election as tribunes.
C) It was the only official position in the Roman republic that had been retained from the era of the Roman monarchy.
D) Senators were eligible to be elected to the post.
A) It was established to serve and protect the plebeian order, not all of society.
B) Former slaves who had served in the military could stand for election as tribunes.
C) It was the only official position in the Roman republic that had been retained from the era of the Roman monarchy.
D) Senators were eligible to be elected to the post.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What was the most common reason for men to seek public office in the early Roman republic?
A) To increase their wealth through government contracts
B) To achieve status and glory through service to the republic
C) To benefit from the patron-client system
D) To move their families into the elite ranks of the nobles
A) To increase their wealth through government contracts
B) To achieve status and glory through service to the republic
C) To benefit from the patron-client system
D) To move their families into the elite ranks of the nobles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What specific function did the Roman Senate fulfill during the years of the Roman republic?
A) It drafted and passed legislation.
B) It advised and consulted with the highest republican officials.
C) It appointed consuls and tribunals.
D) It had formal veto power over the decisions of the assemblies.
A) It drafted and passed legislation.
B) It advised and consulted with the highest republican officials.
C) It appointed consuls and tribunals.
D) It had formal veto power over the decisions of the assemblies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What was the most important of the Roman assemblies, in which plebeians outnumbered patricians?
A) The Tribal Assembly
B) The Centuriate Assembly
C) The Plebeian Assembly
D) The Roman Assembly
A) The Tribal Assembly
B) The Centuriate Assembly
C) The Plebeian Assembly
D) The Roman Assembly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What did the term plebiscites originally refer to?
A) The geographical location of the Plebeian Assembly
B) Resolutions passed by the Plebeian Assembly
C) The powers invested in the three Roman assemblies
D) Resolutions approved by a direct popular vote of all Roman citizens
A) The geographical location of the Plebeian Assembly
B) Resolutions passed by the Plebeian Assembly
C) The powers invested in the three Roman assemblies
D) Resolutions approved by a direct popular vote of all Roman citizens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement most accurately describes the complex Roman legal system during the republic?
A) It was led by a supreme court that served as the ultimate arbiter on questions of law.
B) It evolved in response to protracted conflicts over power.
C) It changed significantly in the second century B.C.E. when state-appointed judges replaced juries in determining guilt and innocence in criminal trials.
D) Its power was derived from the emperors, who presided over all major trials.
A) It was led by a supreme court that served as the ultimate arbiter on questions of law.
B) It evolved in response to protracted conflicts over power.
C) It changed significantly in the second century B.C.E. when state-appointed judges replaced juries in determining guilt and innocence in criminal trials.
D) Its power was derived from the emperors, who presided over all major trials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Concerns about national security and a desire for wealth led the Romans to
A) undertake expansionist campaigns against their neighbors.
B) arrange foreign marriages in the hope of creating ties with their neighbors.
C) negotiate defensive treaties with all of Rome's major trading partners.
D) establish temples to all the major gods of the most powerful foreign nations.
A) undertake expansionist campaigns against their neighbors.
B) arrange foreign marriages in the hope of creating ties with their neighbors.
C) negotiate defensive treaties with all of Rome's major trading partners.
D) establish temples to all the major gods of the most powerful foreign nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
To consolidate its power on the Italian peninsula, republican Rome often required conquered neighboring peoples to
A) pay only moderate taxes.
B) become Roman citizens and serve in the Roman army.
C) provide military aid in times of war.
D) swear an oath of loyalty to Rome or else withdraw by crossing the Alps.
A) pay only moderate taxes.
B) become Roman citizens and serve in the Roman army.
C) provide military aid in times of war.
D) swear an oath of loyalty to Rome or else withdraw by crossing the Alps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
This map of the Roman roads demonstrates what about the Roman republic around 110 B.C.E.?
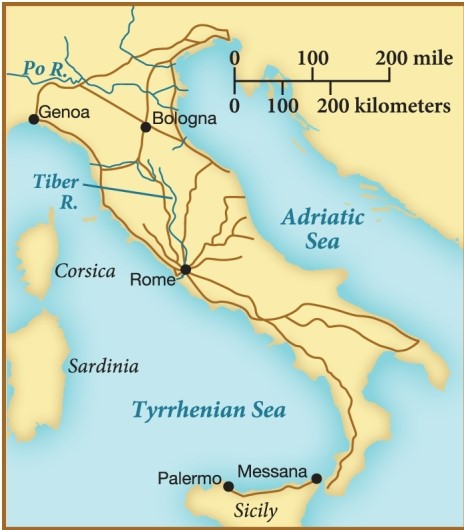
A) The republic functioned with a series of large nodes in its road systems.
B) Major seaports dotted Italy at this time period.
C) Romans, despite impressive engineering feats, could not develop effective bridges.
D) All roads led to Rome, the economic, political, and cultural capital.

A) The republic functioned with a series of large nodes in its road systems.
B) Major seaports dotted Italy at this time period.
C) Romans, despite impressive engineering feats, could not develop effective bridges.
D) All roads led to Rome, the economic, political, and cultural capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What triggered the First Punic War between Rome and Carthage?
A) A dispute over Sicily, where Rome wished to prevent Carthaginian troops from being too close to Roman territory
B) The march of Hannibal over the Alps and into the heart of Italy
C) A dispute over the establishment of Roman trading outposts in North Africa, which had historically been part of the Carthaginian sphere of influence
D) Roman outrage at Carthaginian practices of child sacrifice
A) A dispute over Sicily, where Rome wished to prevent Carthaginian troops from being too close to Roman territory
B) The march of Hannibal over the Alps and into the heart of Italy
C) A dispute over the establishment of Roman trading outposts in North Africa, which had historically been part of the Carthaginian sphere of influence
D) Roman outrage at Carthaginian practices of child sacrifice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following territories only came under Roman control between 133 B.C.E. and the death of Julius Caesar?
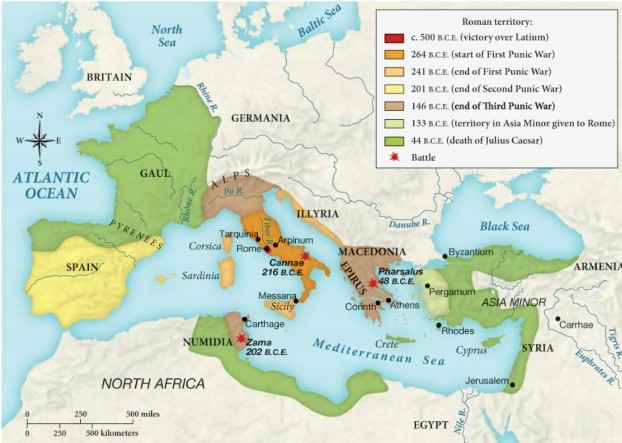
A) Illyria
B) Spain
C) Gaul
D) Macedonia

A) Illyria
B) Spain
C) Gaul
D) Macedonia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How did a Hellenistic king increase Roman power in 133 B.C.E.?
A) By offering his daughter as bride to the then-consul Scipio Africanus
B) By bequeathing his entire Asia Minor kingdom to Rome
C) By sending numerous legions to aid Rome in the Punic Wars against Carthage
D) By quelling the rebellious Greeks while Rome fought the Punic Wars
A) By offering his daughter as bride to the then-consul Scipio Africanus
B) By bequeathing his entire Asia Minor kingdom to Rome
C) By sending numerous legions to aid Rome in the Punic Wars against Carthage
D) By quelling the rebellious Greeks while Rome fought the Punic Wars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In mid-second century B.C.E., Cato wrote The Origins, which was
A) a religious epic about the creation of the world and the origins of the gods.
B) a political attack on the Senate for betraying republican ideals.
C) the first history of Rome written in Latin.
D) a defense of his family's rise to political power through hard work and public service.
A) a religious epic about the creation of the world and the origins of the gods.
B) a political attack on the Senate for betraying republican ideals.
C) the first history of Rome written in Latin.
D) a defense of his family's rise to political power through hard work and public service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why did Romans such as Cato in the second century B.C.E. distrust the influence of Greek ideas and culture on Rome?
A) They despised Alexander the Great and his legacy of conquest and brutality.
B) They scorned Greek culture as inferior to Roman culture.
C) They feared that Romans would adopt the Greek deities, who had nothing in common with Roman deities.
D) They believed that adopting Greek ways would weaken Roman power.
A) They despised Alexander the Great and his legacy of conquest and brutality.
B) They scorned Greek culture as inferior to Roman culture.
C) They feared that Romans would adopt the Greek deities, who had nothing in common with Roman deities.
D) They believed that adopting Greek ways would weaken Roman power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Why did so many farmers sink into debt or lose their land in the latter years of the Roman republic?
A) The small-scale farmers who made up the bulk of the army were taken away from their land and livestock by military campaigns for so long that their farms failed.
B) As Roman political leaders increasingly depended on military conquest to maintain their power, they raised taxes on farmers in order to support the army.
C) The devastation of a prolonged drought and damage to the land from wars and foreign armies left farmers unable to grow crops.
D) Farmers hoped for easily gotten spoils while in military service and resisted returning to their farms.
A) The small-scale farmers who made up the bulk of the army were taken away from their land and livestock by military campaigns for so long that their farms failed.
B) As Roman political leaders increasingly depended on military conquest to maintain their power, they raised taxes on farmers in order to support the army.
C) The devastation of a prolonged drought and damage to the land from wars and foreign armies left farmers unable to grow crops.
D) Farmers hoped for easily gotten spoils while in military service and resisted returning to their farms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How did many of the landless poor in the Roman countryside seek to better their condition in the second century B.C.E.?
A) They emigrated abroad, taking advantages of the opportunities opened up by Roman conquests throughout the Mediterranean.
B) They attacked the landed estates of the wealthy patricians in the countryside and burned down houses and crops.
C) They left the countryside altogether and resettled in Rome.
D) They helped lead slave revolts in an effort to topple the republic.
A) They emigrated abroad, taking advantages of the opportunities opened up by Roman conquests throughout the Mediterranean.
B) They attacked the landed estates of the wealthy patricians in the countryside and burned down houses and crops.
C) They left the countryside altogether and resettled in Rome.
D) They helped lead slave revolts in an effort to topple the republic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How did the Roman elites who profited from Rome's expansion undermine traditional Roman values?
A) By marrying wealthy foreign women and adopting their cultural norms
B) By using governmental posts in the provinces to extort fortunes from the local inhabitants
C) By creating private armies of mercenary soldiers that staged raids beyond Rome's borders
D) By building new temples to foreign gods to bring in wealth from believers
A) By marrying wealthy foreign women and adopting their cultural norms
B) By using governmental posts in the provinces to extort fortunes from the local inhabitants
C) By creating private armies of mercenary soldiers that staged raids beyond Rome's borders
D) By building new temples to foreign gods to bring in wealth from believers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How were the violent deaths of Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus a turning point in the history of the Roman republic?
A) Their deaths broke with the traditional taboo against political violence and introduced factions into Roman politics.
B) Their deaths saw the end of the democratic reforms enacted during the republic, which had given commoners the majority say in political life.
C) Their murder at the hands of senators convinced other senators that a strong, sole ruler was needed to prevent civil war.
D) Their murders made the landless commoners realize that they too could dictate policy through the threat of violence.
A) Their deaths broke with the traditional taboo against political violence and introduced factions into Roman politics.
B) Their deaths saw the end of the democratic reforms enacted during the republic, which had given commoners the majority say in political life.
C) Their murder at the hands of senators convinced other senators that a strong, sole ruler was needed to prevent civil war.
D) Their murders made the landless commoners realize that they too could dictate policy through the threat of violence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How did Gaius Marius's military conquests and election as consul represent a turning point in the Roman republic?
A) He was the first consul to have openly supported the Gracchus brothers in their quest for land reform.
B) He came from the equites class and not the patrician class, and his armies were more loyal to him than to the republic.
C) He was the first politician to urge the assassination of rival politicians.
D) He gave the plunder from his conquests to Julius Caesar, who used it to seize power.
A) He was the first consul to have openly supported the Gracchus brothers in their quest for land reform.
B) He came from the equites class and not the patrician class, and his armies were more loyal to him than to the republic.
C) He was the first politician to urge the assassination of rival politicians.
D) He gave the plunder from his conquests to Julius Caesar, who used it to seize power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What was the cause of the Social War that took place between 91 and 87 B.C.E.?
A) Rome's Italian allies demanded unrestricted Roman citizenship.
B) The Senate wanted to purge the social order of marriages between Romans and foreigners.
C) Rome's Italian allies wanted to sever their ties with Rome and establish independent states.
D) The patricians in Rome tried to undermine the tribunes and bar the plebeians from the assemblies.
A) Rome's Italian allies demanded unrestricted Roman citizenship.
B) The Senate wanted to purge the social order of marriages between Romans and foreigners.
C) Rome's Italian allies wanted to sever their ties with Rome and establish independent states.
D) The patricians in Rome tried to undermine the tribunes and bar the plebeians from the assemblies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What enraged the Roman consul Sulla just before his campaign against King Mithridates VI in Asia Minor?
A) His archrival Marius arranged a plebiscite that transferred the command of the campaign to himself.
B) The Senate denied him the extra troops and money he thought necessary to wage a successful campaign against Mithridates.
C) The priests of Jupiter declared that the omens were unfavorable and forbade Sulla to depart.
D) The other consul, Marius, was put in charge of a more important and potentially more lucrative campaign in Gaul.
A) His archrival Marius arranged a plebiscite that transferred the command of the campaign to himself.
B) The Senate denied him the extra troops and money he thought necessary to wage a successful campaign against Mithridates.
C) The priests of Jupiter declared that the omens were unfavorable and forbade Sulla to depart.
D) The other consul, Marius, was put in charge of a more important and potentially more lucrative campaign in Gaul.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What did the Roman generals Sulla (c. 138-78 B.C.E.), Pompey (106-48 B.C.E.), and Julius Caesar (100-44 B.C.E.) have in common?
A) Respect for Rome's republican traditions of loyal public service and incorruptibility, despite the temptations created by the plunder of war
B) An interest in destroying any remaining distinctions between patricians and plebeians in the army
C) A willingness to embroil Rome in civil wars to secure their own personal wealth and power
D) The ability to bring Romans together through the power of their oratory and their personal example
A) Respect for Rome's republican traditions of loyal public service and incorruptibility, despite the temptations created by the plunder of war
B) An interest in destroying any remaining distinctions between patricians and plebeians in the army
C) A willingness to embroil Rome in civil wars to secure their own personal wealth and power
D) The ability to bring Romans together through the power of their oratory and their personal example

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How did the general and politician Gnaeus Pompey shatter Roman tradition?
A) By appealing to the urban poor, whose numbers were swelling in Rome
B) By inflicting massive defeats upon Rome's enemies abroad
C) By demanding and receiving a consulship long before he had reached the legal age
D) By providing support for Sulla
A) By appealing to the urban poor, whose numbers were swelling in Rome
B) By inflicting massive defeats upon Rome's enemies abroad
C) By demanding and receiving a consulship long before he had reached the legal age
D) By providing support for Sulla

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The First Triumvirate of Pompey, Crassus, and Caesar formed in 60 B.C.E. when
A) the three men joined forces for an assault on Egypt.
B) Spartacus's slave army threatened to overrun Rome.
C) the Senate's challenge to Pompey forced him into a coalition with his two greatest rivals.
D) the Senate recognized that the empire had grown too large for only two consuls.
A) the three men joined forces for an assault on Egypt.
B) Spartacus's slave army threatened to overrun Rome.
C) the Senate's challenge to Pompey forced him into a coalition with his two greatest rivals.
D) the Senate recognized that the empire had grown too large for only two consuls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What factor enabled Julius Caesar to triumph in the civil war that lasted from 49 to 45 B.C.E.?
A) His love affair with Cleopatra ensured him the support of the Ptolemaic army in Egypt, which proved indispensable in defeating Pompey.
B) He wielded immense popular support, and his army remained loyal even in the most difficult of times.
C) He succeeded in engineering the deaths of his two leading rivals, Crassus and Pompey.
D) His daughter, Julia, who was placed in an arranged marriage with Caesar's rival Pompey, turned against her husband and had him assassinated.
A) His love affair with Cleopatra ensured him the support of the Ptolemaic army in Egypt, which proved indispensable in defeating Pompey.
B) He wielded immense popular support, and his army remained loyal even in the most difficult of times.
C) He succeeded in engineering the deaths of his two leading rivals, Crassus and Pompey.
D) His daughter, Julia, who was placed in an arranged marriage with Caesar's rival Pompey, turned against her husband and had him assassinated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Although Julius Caesar had won the civil war by 45 B.C.E. and appointed himself dictator, he preserved the appearance of traditional republican offices and elections
A) as a safeguard against the recurrence of civil war after his death.
B) because he always intended to restore faithful adherence to Roman traditions.
C) to dispel the fears of the Roman public that he would remain dictator for life.
D) in order to make his rule palatable by maintaining the forms of the Roman republic.
A) as a safeguard against the recurrence of civil war after his death.
B) because he always intended to restore faithful adherence to Roman traditions.
C) to dispel the fears of the Roman public that he would remain dictator for life.
D) in order to make his rule palatable by maintaining the forms of the Roman republic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following was a Roman client state by 44 B.C.E.?
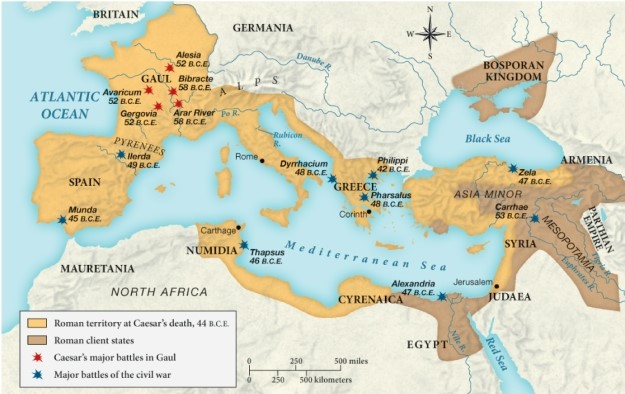
A) Germania
B) Mesopotamia
C) Britain
D) Mauretania

A) Germania
B) Mesopotamia
C) Britain
D) Mauretania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



