Deck 23: Empire, Industry, and Everyday Life, 1870-1890
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Empire, Industry, and Everyday Life, 1870-1890
1
Name four of the African commodities that were coveted by Europeans in 1880-1900, and explain the technologies that enabled Europeans to seize remote or dangerous territories that had these commodities.
Answer would ideally include the following. Europeans wanted access to trade for palm oil, metals, diamonds, cocoa, cotton, and rubber. Many of these commodities were difficult for Europeans to access until the late nineteenth century, when the development of quinine combated the threat of malaria, a disease that had killed many Europeans. New military technology, including improved breech-loading rifles and the machine gun, and the growth of railroads and the telegraph gave Europeans the technological superiority that allowed them to seize African territory from its native owners.
2
Describe the inroads that Russia made into Asia between the 1860s and the 1890s.
Answer would ideally include the following. For years, Russia absorbed small Muslim states in central Asia, including part of Afghanistan, and made inroads into Persia, China, and India. The building of the Trans-Siberian Railroad allowed Russia's government to have much better communications with Siberia and to begin to incorporate more fully parts of central and East Asia, and to begin to settle land-hungry peasants on Asian territory.
3
Briefly describe Japan's approach to modernization in terms of its economy and government.
Answer would ideally include the following. In its effort to transform into a modern industrialized nation, Japan embraced foreign trade and industry and adopted many processes and customs that were similar to nations in the West. Western dress became the rule at the imperial court, Japan's German-modeled constitution emphasized state authority over individual rights, and the state promoted economic development through the funding of railroads, shipyards, and banks. The Japanese government also supported entrepreneurs such as Iwasaki Yataro, the founder of Mitsubishi, in developing capital-intensive industries such as mining and shipping.
4
Briefly explain why late-nineteenth-century imperialism was not as beneficial to European politics and Europeans as it was generally supposed to be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why were the dramatic economic fluctuations that followed the crisis of 1873 different from the economic cycles before 1850, and how did governments attempt to deal with them?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Briefly describe how changes in the workplace provided jobs for educated women as well as how social changes increasingly allowed women to work outside the home.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why did increasingly fast-paced factory labor based on new technology create new problems for workers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How did scientific ideas influence new social reforms and organizations for social improvement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How did the Ballot Act of 1872 contribute to increasing agitation for home rule in Ireland?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Briefly describe the significance of Pan-Slavism in shaping the Balkan peninsula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What factors led to the development of the "new imperialism" in the late nineteenth century? In your answer, be sure to take into consideration the economic, political, and social aspects of the European quest for empire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How did the political and economic developments of the late nineteenth century affect women's roles in society? What new opportunities were women afforded and why? In what areas were they held back? In your answer, consider factors like the impact of imperialism, the revolution in business practices, the shift in consumption patterns, and the influence of mass politics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Social Darwinism, which applied evolutionary theory to the social sphere, gained authority in Europe in the late nineteenth century. Explain how Social Darwinist ideas influenced European social and political policies in the late nineteenth century. What was their connection to the growth of nationalism and imperialism, and what was their role in domestic social policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Discuss the ways in which industrialization promoted the growth of mass politics. How did industrialization promote the formation of working-class organizations? How did industrialization change the means by which people formed their opinions about issues and politicians, and how did it in turn change the way citizens made their concerns known to the government?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
How did the evolution of politics in Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Russia differ from that of western European nations from 1870 through 1890? Explain how the political climate impacted each nation economically and culturally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The demand for raw materials along with business that was brought on by industrialism led to a rise in
A) republicanism.
B) imperialism.
C) romanticism.
D) classicism.
A) republicanism.
B) imperialism.
C) romanticism.
D) classicism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why was Egypt an early and attractive target for European takeover in the age of imperialism?
A) The Egyptian state was weak, and Europeans felt there would be no resistance to their imperial expansion.
B) Egypt was a backward, unindustrialized country, so it provided a clean slate for Europeans to imprint their values.
C) Egypt's modernizing rulers had already built a thriving commercial and manufacturing center, and Egypt provided a convenient stopping point on the way to Asia.
D) Occupying Egypt gave Europeans easy access to the interior of central Africa, especially down the Nile corridor and through the Sudan.
A) The Egyptian state was weak, and Europeans felt there would be no resistance to their imperial expansion.
B) Egypt was a backward, unindustrialized country, so it provided a clean slate for Europeans to imprint their values.
C) Egypt's modernizing rulers had already built a thriving commercial and manufacturing center, and Egypt provided a convenient stopping point on the way to Asia.
D) Occupying Egypt gave Europeans easy access to the interior of central Africa, especially down the Nile corridor and through the Sudan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The French followed up their colonization of Algeria by occupying what territory?
A) The Sudan
B) The Congo
C) Cyprus
D) Tunisia
A) The Sudan
B) The Congo
C) Cyprus
D) Tunisia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Although cruelty abounded under imperialist rule, what European ruler was known for inflicting the worst atrocities?
A) Austrian emperor Francis Joseph
B) French emperor Napoleon III
C) Belgian king Leopold II
D) German kaiser William I
A) Austrian emperor Francis Joseph
B) French emperor Napoleon III
C) Belgian king Leopold II
D) German kaiser William I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the early 1880s, what touched off a scramble among European countries for colonies in Africa?
A) Britain and France began a race to claim Egypt.
B) Leopold of Belgium claimed a huge territory in the Congo region.
C) The Ottoman Empire posed a threat to the Suez Canal.
D) Great Britain and Germany clashed dangerously in Morocco.
A) Britain and France began a race to claim Egypt.
B) Leopold of Belgium claimed a huge territory in the Congo region.
C) The Ottoman Empire posed a threat to the Suez Canal.
D) Great Britain and Germany clashed dangerously in Morocco.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements is supported by this map?
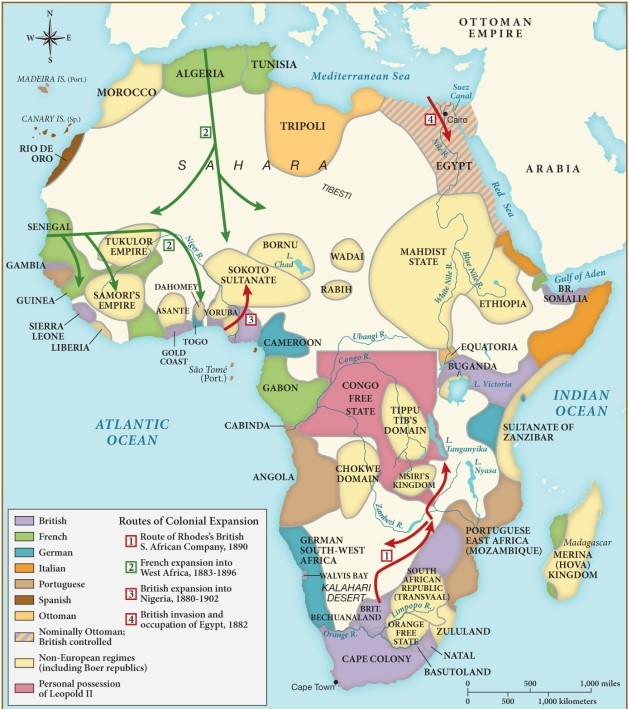
A) Most African colonies had gained independence from European powers by the 1890s.
B) By the 1890s, most of Africa was colonized by Germany and Italy.
C) The British were primarily concerned with securing territory along the coast of Africa at this time.
D) The French sought to expand further into the interior of West Africa in the 1890s.

A) Most African colonies had gained independence from European powers by the 1890s.
B) By the 1890s, most of Africa was colonized by Germany and Italy.
C) The British were primarily concerned with securing territory along the coast of Africa at this time.
D) The French sought to expand further into the interior of West Africa in the 1890s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What resulted from the Berlin conferences of 1884 and 1885 that determined European control of Africa?
A) A linear dissection of the continent that cut across indigenous boundaries of African ethnicities, a ban on the sale of alcohol, and limits on the flow of firearms to Africans
B) Britain and Germany taking control of huge amounts of territory while not allowing less powerful countries like France and Belgium to gain control of any important land
C) An agreement that dictated shared European responsibility for Africa, with Britain and France supplying civilian leaders and Germany and Russia supplying military forces
D) Further national feuding, as none of the nations could agree on territorial borders within Africa or how to resolve claims on places such as South Africa where multiple nations were involved
A) A linear dissection of the continent that cut across indigenous boundaries of African ethnicities, a ban on the sale of alcohol, and limits on the flow of firearms to Africans
B) Britain and Germany taking control of huge amounts of territory while not allowing less powerful countries like France and Belgium to gain control of any important land
C) An agreement that dictated shared European responsibility for Africa, with Britain and France supplying civilian leaders and Germany and Russia supplying military forces
D) Further national feuding, as none of the nations could agree on territorial borders within Africa or how to resolve claims on places such as South Africa where multiple nations were involved

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What ideology helped enable the expansion of European imperialism by using racist ideas of European superiority to justify the conversion of trade with Africans into conquest of their lands?
A) Marxism
B) Ethnocentrism
C) Social Darwinism
D) Positivism
A) Marxism
B) Ethnocentrism
C) Social Darwinism
D) Positivism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Indian National Congress, founded in 1885, was
A) a good example of the rise of mass politics in Europe's new colonies, especially among the new working classes.
B) an organization run by educated Indian elites who accepted aspects of British liberalism but occasionally challenged British rule.
C) a revolutionary organization that demanded a "free India," including the removal of all British personnel and interests.
D) an attempt by the British to offer the natives control of their own political system through self-rule.
A) a good example of the rise of mass politics in Europe's new colonies, especially among the new working classes.
B) an organization run by educated Indian elites who accepted aspects of British liberalism but occasionally challenged British rule.
C) a revolutionary organization that demanded a "free India," including the removal of all British personnel and interests.
D) an attempt by the British to offer the natives control of their own political system through self-rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Trans-Siberian Railroad played a key role in the expansion of what country into northern Asia?
A) Britain
B) Russia
C) France
D) China
A) Britain
B) Russia
C) France
D) China

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Based on this map, as Russia expanded its territory through 1900, it also
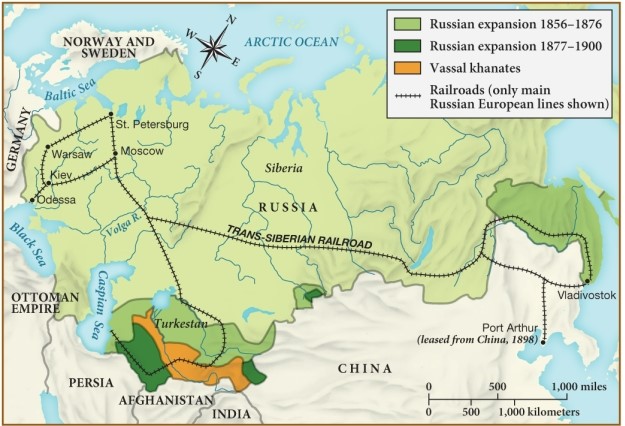
A) fortified its relationship with the Ottoman Empire.
B) decreased its industrial capacity.
C) expanded the lines of the Trans-Siberian Railroad.
D) established major cities in its eastern region.

A) fortified its relationship with the Ottoman Empire.
B) decreased its industrial capacity.
C) expanded the lines of the Trans-Siberian Railroad.
D) established major cities in its eastern region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
As part of its program for modernization, the Meiji government in Japan
A) gave overly favorable trade agreements to technologically advanced Western powers.
B) incurred the wrath and intractable resistance of its artisan and merchant classes.
C) sent students, entrepreneurs, and government officials to the West to gain knowledge of technology and industry.
D) received financial support from France and Great Britain.
A) gave overly favorable trade agreements to technologically advanced Western powers.
B) incurred the wrath and intractable resistance of its artisan and merchant classes.
C) sent students, entrepreneurs, and government officials to the West to gain knowledge of technology and industry.
D) received financial support from France and Great Britain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Many European advocates of imperialism believed that whites had a "civilizing mission"; what did this mission entail?
A) Demonstrating to their fellow Europeans the achievements of African and Asian cultures in art, literature, science, and technology
B) Teaching colonial subjects Enlightenment and liberal values such as the fundamental equality of all humans
C) Spreading superior European knowledge and culture to colonial subjects through education or even violence, if necessary
D) Ensuring the survival of the European race in Africa and Asia through selective breeding programs designed by Social Darwinists
A) Demonstrating to their fellow Europeans the achievements of African and Asian cultures in art, literature, science, and technology
B) Teaching colonial subjects Enlightenment and liberal values such as the fundamental equality of all humans
C) Spreading superior European knowledge and culture to colonial subjects through education or even violence, if necessary
D) Ensuring the survival of the European race in Africa and Asia through selective breeding programs designed by Social Darwinists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following was a major industrial innovation of the late nineteenth century?
A) Antibiotics
B) The spinning jenny
C) Interchangeable machine parts
D) Refrigeration
A) Antibiotics
B) The spinning jenny
C) Interchangeable machine parts
D) Refrigeration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The discovery of which medicine removed a roadblock to European conquest of Africa?
A) Quinine
B) Cola
C) Aspirin
D) Sodium bicarbonate
A) Quinine
B) Cola
C) Aspirin
D) Sodium bicarbonate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following two countries came to rival Britain in industrial strength?
A) Germany and the United States
B) France and Austria
C) Russia and Italy
D) Sweden and Spain
A) Germany and the United States
B) France and Austria
C) Russia and Italy
D) Sweden and Spain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following European countries was the slowest to industrialize?
A) Russia
B) Belgium
C) France
D) Austria-Hungary
A) Russia
B) Belgium
C) France
D) Austria-Hungary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
As industrialization advanced, the two problems that began to plague entrepreneurs most were skyrocketing start-up costs and
A) excessive state regulatory interference.
B) an outmoded stock market system.
C) the failure of consumption to keep pace with production.
D) a steep rise in workers' wages.
A) excessive state regulatory interference.
B) an outmoded stock market system.
C) the failure of consumption to keep pace with production.
D) a steep rise in workers' wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the late nineteenth century, industrialization tended to be capital intensive, which meant that
A) industries tended to mass themselves around capital cities.
B) companies were expected to produce high returns for their investors.
C) large amounts of money were needed to buy expensive machinery and equipment.
D) a handful of private banks made loans to the most profitable new industries.
A) industries tended to mass themselves around capital cities.
B) companies were expected to produce high returns for their investors.
C) large amounts of money were needed to buy expensive machinery and equipment.
D) a handful of private banks made loans to the most profitable new industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What major step did European governments take to raise investor confidence in the wake of the economic crisis of the 1870s?
A) They established government banks to finance industry.
B) They issued government guarantees for private investments in heavy industry.
C) They promoted an increased military presence in overseas colonies.
D) They passed new laws to create the limited liability corporation.
A) They established government banks to finance industry.
B) They issued government guarantees for private investments in heavy industry.
C) They promoted an increased military presence in overseas colonies.
D) They passed new laws to create the limited liability corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Why did many European countries abandon free-trade policies in the late nineteenth century?
A) As socialist and communist governments came to power across Europe, they rejected all liberal and capitalist economic ideas, which centered around free trade.
B) In an era of increasing national competition, governments saw free trade as a hindrance to the growth of nationalist sentiment among their citizens.
C) Free trade caused huge trade deficits that slowed job growth and increased social unrest, so governments had broad popular support to tax imports and prevent outside competition.
D) Amid the rush to extract resources from their new overseas territories, European governments and economists saw free-trade policies within Europe as obsolete.
A) As socialist and communist governments came to power across Europe, they rejected all liberal and capitalist economic ideas, which centered around free trade.
B) In an era of increasing national competition, governments saw free trade as a hindrance to the growth of nationalist sentiment among their citizens.
C) Free trade caused huge trade deficits that slowed job growth and increased social unrest, so governments had broad popular support to tax imports and prevent outside competition.
D) Amid the rush to extract resources from their new overseas territories, European governments and economists saw free-trade policies within Europe as obsolete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following factors was essential to the emergence of a "white-collar" service sector in the late 1800s?
A) The decline in manufacturing, due to the economic recession of the early 1870s
B) Compulsory primary school education, which allowed workers to acquire literacy and mathematical skills they could use in offices
C) The growing importance of labor unions and the rebellion of factory workers against the harsh working conditions imposed on them
D) The emergence of the consumption economy, and especially the department store, as salesgirls were needed to attract shoppers
A) The decline in manufacturing, due to the economic recession of the early 1870s
B) Compulsory primary school education, which allowed workers to acquire literacy and mathematical skills they could use in offices
C) The growing importance of labor unions and the rebellion of factory workers against the harsh working conditions imposed on them
D) The emergence of the consumption economy, and especially the department store, as salesgirls were needed to attract shoppers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Women's massive entry into the service sector in the late nineteenth century accelerated what social change?
A) The division of occupations into male and female categories
B) The acceptance of women into universities
C) The growth of bureaucracies, made possible by paying lower wages to women
D) Reform legislation in Britain and the United States aimed at achieving voting rights for women
A) The division of occupations into male and female categories
B) The acceptance of women into universities
C) The growth of bureaucracies, made possible by paying lower wages to women
D) Reform legislation in Britain and the United States aimed at achieving voting rights for women

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following did the most to stimulate the new consumer culture in the late nineteenth century?
A) Department stores and mail order catalogs
B) Radio advertising
C) Traveling salesmen
D) Designer fashion shows
A) Department stores and mail order catalogs
B) Radio advertising
C) Traveling salesmen
D) Designer fashion shows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is an example of how empire reshaped the daily lives of the European upper classes?
A) European women began emulating African and Asian styles of dress, as clothing styles like saris and African-inspired headdresses became items of high fashion.
B) Europeans imported servants from overseas colonies in large numbers to lend a sense of exoticism to their homes.
C) Wealthy Europeans decorated their homes with trophies of big-game hunting expeditions in Africa and Asia, as well as imperial treasures like Oriental carpets, furniture, and exotic plants.
D) Europeans began sending their children to overseas colonies for their education to make them more cosmopolitan and well rounded.
A) European women began emulating African and Asian styles of dress, as clothing styles like saris and African-inspired headdresses became items of high fashion.
B) Europeans imported servants from overseas colonies in large numbers to lend a sense of exoticism to their homes.
C) Wealthy Europeans decorated their homes with trophies of big-game hunting expeditions in Africa and Asia, as well as imperial treasures like Oriental carpets, furniture, and exotic plants.
D) Europeans began sending their children to overseas colonies for their education to make them more cosmopolitan and well rounded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In general, why did large numbers of emigrants depart from rural Ireland and Scandinavia?
A) The population was expanding so rapidly that these countries did not have enough jobs at which to employ the growing labor pool.
B) Because none of these countries was an independent, democratic state, people left to find more freedom.
C) American entrepreneurs who needed workers targeted these people and gave them large signing bonuses to emigrate.
D) These three areas lagged behind the rest of Europe in unionization and workers' rights.
A) The population was expanding so rapidly that these countries did not have enough jobs at which to employ the growing labor pool.
B) Because none of these countries was an independent, democratic state, people left to find more freedom.
C) American entrepreneurs who needed workers targeted these people and gave them large signing bonuses to emigrate.
D) These three areas lagged behind the rest of Europe in unionization and workers' rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What were the most frequent destinations for international migrants who left Europe seeking economic opportunity?
A) Europe's colonies in East Asia, including Indochina and Malaysia
B) North and South America, Australia, and New Zealand
C) European colonies in Africa, particularly South Africa
D) British-controlled India
A) Europe's colonies in East Asia, including Indochina and Malaysia
B) North and South America, Australia, and New Zealand
C) European colonies in Africa, particularly South Africa
D) British-controlled India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The establishment of maternal and child health centers and clinics was the result of
A) upper-class Christian women looking for an acceptable outlet for social activism.
B) the concern that the working classes would let their diseases go untreated and cause epidemics that would infect the upper classes.
C) the belief that working women had become "defeminized" by entering the public sphere and therefore needed instruction in caring for infants and children.
D) the Social Darwinist belief that such institutions would help the European "races" remain the most "fit" in an increasingly competitive world.
A) upper-class Christian women looking for an acceptable outlet for social activism.
B) the concern that the working classes would let their diseases go untreated and cause epidemics that would infect the upper classes.
C) the belief that working women had become "defeminized" by entering the public sphere and therefore needed instruction in caring for infants and children.
D) the Social Darwinist belief that such institutions would help the European "races" remain the most "fit" in an increasingly competitive world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What new organizations were established by educated reformers in the nineteenth century in an effort to understand and alleviate working-class poverty?
A) University study groups
B) Settlement houses
C) Workhouse reform boards
D) Artisan cooperatives
A) University study groups
B) Settlement houses
C) Workhouse reform boards
D) Artisan cooperatives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In 1893, the Fabian Society in Great Britain
A) helped found the Labour Party.
B) launched the suffragette movement.
C) helped bring home rule to Ireland.
D) brought Marxism to Britain.
A) helped found the Labour Party.
B) launched the suffragette movement.
C) helped bring home rule to Ireland.
D) brought Marxism to Britain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the 1880s, Dutch physician Aletta Jacobs opened the first clinic in Europe to provide
A) psychiatric care.
B) cosmetic surgery.
C) birth control for women.
D) no-cost pediatric care for the lower classes.
A) psychiatric care.
B) cosmetic surgery.
C) birth control for women.
D) no-cost pediatric care for the lower classes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following was manifested in the development of team sports and leisure activities like mountain climbing and bicycle touring in Europe?
A) An increasing disinterest in global affairs and a new focus on self-interest and the pursuit of wealth and happiness
B) The desire to foster class harmony through the promotion of activities that were accessible to everyone in the nation
C) The drive to increase national strength and promote imperial citizenship through the nation's exercise of raw power
D) The attempt to distract the working classes from union or political organizing, which many saw as dangerous to social order
A) An increasing disinterest in global affairs and a new focus on self-interest and the pursuit of wealth and happiness
B) The desire to foster class harmony through the promotion of activities that were accessible to everyone in the nation
C) The drive to increase national strength and promote imperial citizenship through the nation's exercise of raw power
D) The attempt to distract the working classes from union or political organizing, which many saw as dangerous to social order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following authors wrote a series of books that reflected his concerns about social decay?
A) Henrik Ibsen
B) Émile Zola
C) Karl Marx
D) William Morris
A) Henrik Ibsen
B) Émile Zola
C) Karl Marx
D) William Morris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How did nineteenth-century painters respond to the intense competition that arose from the development of the hugely popular camera?
A) They began painting pictures as true to life as possible to keep up with the new desire for the realistic images that photographs could produce.
B) They no longer painted portraits or landscapes, since photographs took over those markets completely, and instead focused almost entirely on copying Old Masters.
C) They altered their style, employing new and varying techniques to distinguish their art from the photographic realism of the camera.
D) They sought new professions, as the market for painting dropped off entirely and art schools began to close across Europe.
A) They began painting pictures as true to life as possible to keep up with the new desire for the realistic images that photographs could produce.
B) They no longer painted portraits or landscapes, since photographs took over those markets completely, and instead focused almost entirely on copying Old Masters.
C) They altered their style, employing new and varying techniques to distinguish their art from the photographic realism of the camera.
D) They sought new professions, as the market for painting dropped off entirely and art schools began to close across Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which major new artistic movement emerged from France in the 1800s and is best represented in the work of Claude Monet?
A) Impressionism
B) Realism
C) Surrealism
D) Romanticism
A) Impressionism
B) Realism
C) Surrealism
D) Romanticism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What features characterized the 1880s movement known as new unionism?
A) It featured nationwide unions with salaried managers who could organize a widespread general strike across the trades, focusing on common goals such as the eight-hour workday.
B) It was built around craft-based unions of skilled artisans, such as carpenters and painters, who focused on the issues that affected their particular craft.
C) It emerged out of working-class political parties throughout Europe and focused on organizing workers around political causes such as universal manhood suffrage.
D) It first organized as a movement dedicated to improving the conditions of female workers but later expanded to focus on the social conditions of all workers.
A) It featured nationwide unions with salaried managers who could organize a widespread general strike across the trades, focusing on common goals such as the eight-hour workday.
B) It was built around craft-based unions of skilled artisans, such as carpenters and painters, who focused on the issues that affected their particular craft.
C) It emerged out of working-class political parties throughout Europe and focused on organizing workers around political causes such as universal manhood suffrage.
D) It first organized as a movement dedicated to improving the conditions of female workers but later expanded to focus on the social conditions of all workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Of the working-class parties that developed out of socialism, which of the following was the largest after 1890?
A) The Socialist Party in France
B) The Labour Party in England
C) The Social Democratic Party in Germany
D) The Social Democratic Party in Sweden
A) The Socialist Party in France
B) The Labour Party in England
C) The Social Democratic Party in Germany
D) The Social Democratic Party in Sweden

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Second International (1889) was an organization that sought
A) cooperation among banks in various countries.
B) Marxist revolution.
C) cooperation among European nation-states in dividing up the African continent.
D) international peace through a system of mandatory negotiations over conflicts.
A) cooperation among banks in various countries.
B) Marxist revolution.
C) cooperation among European nation-states in dividing up the African continent.
D) international peace through a system of mandatory negotiations over conflicts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The new mass journalism of this period was characterized by
A) an increase in sensational stories in newspapers and an emphasis on spreading information quickly.
B) a broadening of the literary scope of newspapers, to keep up with the expansion of commercial fiction.
C) a migration of political opinions in newspapers toward the center, an increased desire for objectivity, and the abandonment of specific liberal, conservative, or socialist points of view.
D) a steep increase in newspaper prices to keep up with mounting wages and to boost profits for the new press barons.
A) an increase in sensational stories in newspapers and an emphasis on spreading information quickly.
B) a broadening of the literary scope of newspapers, to keep up with the expansion of commercial fiction.
C) a migration of political opinions in newspapers toward the center, an increased desire for objectivity, and the abandonment of specific liberal, conservative, or socialist points of view.
D) a steep increase in newspaper prices to keep up with mounting wages and to boost profits for the new press barons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is an example of the opening of the political process to wider participation in Europe?
A) The struggle of the Bonapartist, Orléanist, and Bourbon factions trying to destroy the Third Republic in France
B) William Gladstone's 1879 campaign to be prime minister of Great Britain
C) Bismarck's 1873 alliance with Austria-Hungary and Russia
D) The Berlin conferences of 1884 and 1885
A) The struggle of the Bonapartist, Orléanist, and Bourbon factions trying to destroy the Third Republic in France
B) William Gladstone's 1879 campaign to be prime minister of Great Britain
C) Bismarck's 1873 alliance with Austria-Hungary and Russia
D) The Berlin conferences of 1884 and 1885

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Irish politician Charles Stewart Parnell demanded British support for which controversial policy in return for Irish votes in Parliament?
A) Woman suffrage
B) An end to the ban on slavery
C) Irish home rule
D) A universal eight-hour workday
A) Woman suffrage
B) An end to the ban on slavery
C) Irish home rule
D) A universal eight-hour workday

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Why was the Third Republic so unstable despite its new democratic institutions?
A) Monarchist elements within society used the new mass journalism to undermine the authority of the legislature and of successive prime ministers.
B) Economic downturns, widespread corruption, and growing anti-Semitism, fueled by a highly partisan press, kept the republic on shaky ground.
C) After the Paris Commune, Marxism gained ground within France, and the working-class parties threatened France's political stability with constant strikes.
D) The Catholic church regained a loyal following and struck back against the Third Republic's secularizing policies.
A) Monarchist elements within society used the new mass journalism to undermine the authority of the legislature and of successive prime ministers.
B) Economic downturns, widespread corruption, and growing anti-Semitism, fueled by a highly partisan press, kept the republic on shaky ground.
C) After the Paris Commune, Marxism gained ground within France, and the working-class parties threatened France's political stability with constant strikes.
D) The Catholic church regained a loyal following and struck back against the Third Republic's secularizing policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Spain and Belgium abruptly awarded suffrage to all men in 1890 and 1893, respectively,
A) yet both countries remained monarchies.
B) and women received the right to vote soon after.
C) but Catholic leaders in both countries denounced the reform.
D) which led to significant governmental and social reforms in both countries.
A) yet both countries remained monarchies.
B) and women received the right to vote soon after.
C) but Catholic leaders in both countries denounced the reform.
D) which led to significant governmental and social reforms in both countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
According to this map, what is the likely relationship between the establishment of railways and canals and the territory of the city of Berlin?
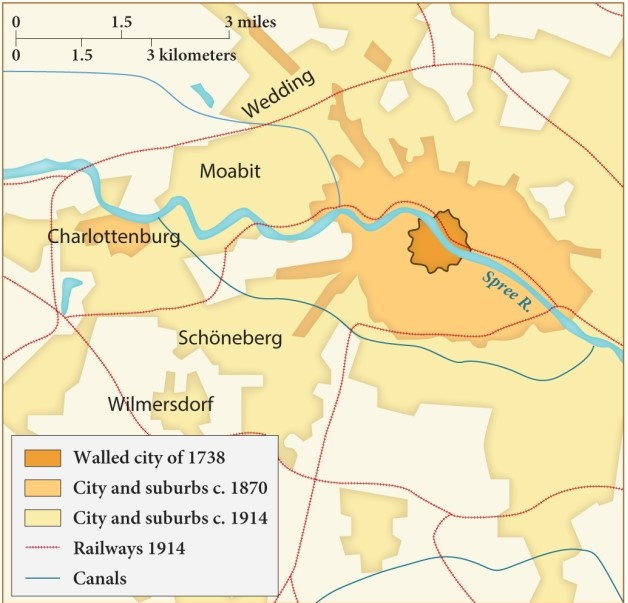
A) As railroad lines were built, much of Berlin contracted closer to the walled city of 1738.
B) More people could live comfortably within the walled city as railroads were established.
C) As more modes of transportation emerged, the limits of the city and suburbs expanded.
D) Canals were more effective than railways at expanding city limits.

A) As railroad lines were built, much of Berlin contracted closer to the walled city of 1738.
B) More people could live comfortably within the walled city as railroads were established.
C) As more modes of transportation emerged, the limits of the city and suburbs expanded.
D) Canals were more effective than railways at expanding city limits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What German institution did German chancellor Otto von Bismarck (1815-1898) attack in 1878, after the failure of his Kulturkampf?
A) The Catholic church
B) German Jews
C) All aspects of "American" culture
D) The Social Democratic Party
A) The Catholic church
B) German Jews
C) All aspects of "American" culture
D) The Social Democratic Party

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How did the Ottoman Empire change after 1878?
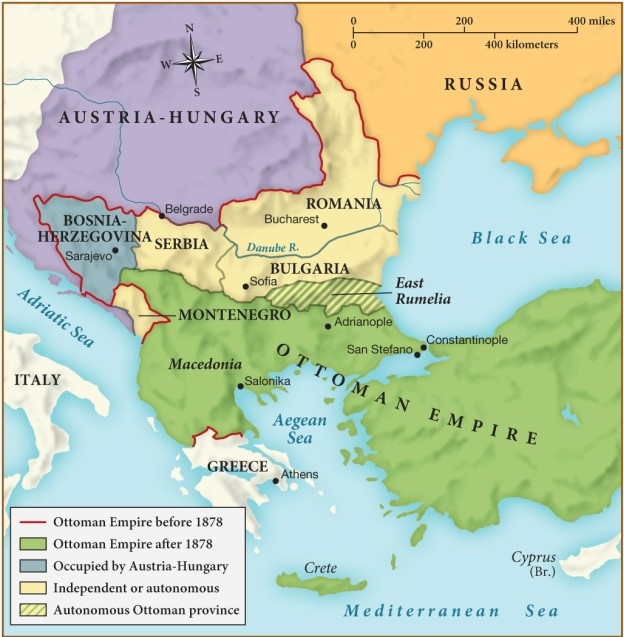
A) It was wiped out entirely by efforts at expansion from Austria-Hungary and Russia.
B) It decreased in size as Romania, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Bosnia-Herzegovina became their own territories.
C) It increased its territorial claims by occupying East Rumelia.
D) It gained access to critical trading posts in the Mediterranean, Aegean, and Black Seas.

A) It was wiped out entirely by efforts at expansion from Austria-Hungary and Russia.
B) It decreased in size as Romania, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Bosnia-Herzegovina became their own territories.
C) It increased its territorial claims by occupying East Rumelia.
D) It gained access to critical trading posts in the Mediterranean, Aegean, and Black Seas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What was one of the main purposes of the Dual Alliance forged by Germany and Austria-Hungary in 1879?
A) To pressure Russia to stop negotiations for a Franco-Russian military alliance
B) To strengthen the ties among the German-speaking lands of central Europe
C) To defend against Russian aggression, particularly in the Balkans
D) To intimidate the Pan-Slavic movement into scaling back its political agitation
A) To pressure Russia to stop negotiations for a Franco-Russian military alliance
B) To strengthen the ties among the German-speaking lands of central Europe
C) To defend against Russian aggression, particularly in the Balkans
D) To intimidate the Pan-Slavic movement into scaling back its political agitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The growth of revolutionary movements in Russia in the late nineteenth century resulted in which of the following events?
A) The expulsion of five million Jews from Russian territory
B) The assassination of Tsar Alexander II in a bomb attack
C) The destruction of the Russian naval fleet in the port at Vladivostok
D) The release of all political prisoners in Moscow
A) The expulsion of five million Jews from Russian territory
B) The assassination of Tsar Alexander II in a bomb attack
C) The destruction of the Russian naval fleet in the port at Vladivostok
D) The release of all political prisoners in Moscow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why did Kaiser William II dismiss Otto von Bismarck from the German government in 1890?
A) He became convinced that Bismarck not only hindered his nationalistic plans but also might prove to be a rival for power.
B) By that time, Bismarck was so old that his governing style was becoming capricious and worrisome.
C) William II opposed Bismarck's ideas about German nationalism and imperial expansion in East Africa.
D) William II opposed Bismarck's idea of uniting all German-speaking peoples in Europe by annexing Austria.
A) He became convinced that Bismarck not only hindered his nationalistic plans but also might prove to be a rival for power.
B) By that time, Bismarck was so old that his governing style was becoming capricious and worrisome.
C) William II opposed Bismarck's ideas about German nationalism and imperial expansion in East Africa.
D) William II opposed Bismarck's idea of uniting all German-speaking peoples in Europe by annexing Austria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
By 1890, which European nation claimed territory on each of the continents shown on this map?
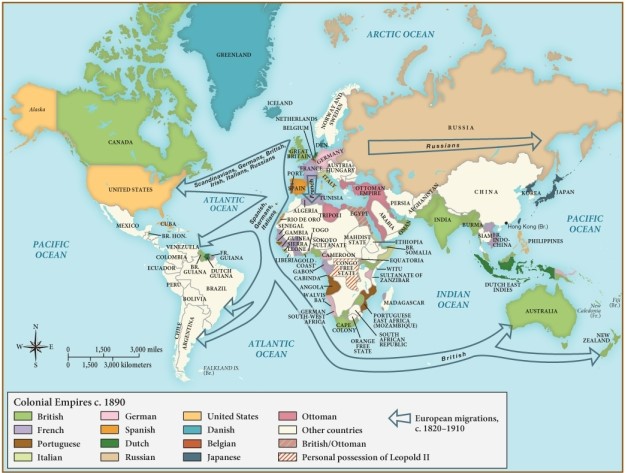
A) Great Britain
B) Russia
C) The United States
D) France

A) Great Britain
B) Russia
C) The United States
D) France

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



