Deck 22: Politics and Culture of the Nation-State, 1850-1870
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Politics and Culture of the Nation-State, 1850-1870
1
How was Napoleon III able to maintain public support despite his authoritarian regime?
Answer would ideally include the following. Although he ruthlessly repressed any opposition, Napoleon III also promoted a strong economy and created public works programs and jobs. He played upon French nationalism by linking his own reign with that of his uncle, a time when France had been the most powerful country in Europe. He and his wife carefully cultivated an imperial style at court, which especially appealed to peasants, who were far more conservative than urban radicals, and through his international policies he sought to increase French power and acquire glory abroad. Napoleon III hoped that all Frenchmen would take pride in France's achievements and respect him as the man who had restored the country to greatness.
2
Who benefited most from the emancipation of Russian serfs, and why were they not truly "free" after 1861?
Answer would ideally include the following. The real beneficiaries of the end of serfdom were the landowners, who received the best land and, because the government was afraid of alienating them, also received compensation for any land they lost and for the loss of peasant labor. Former serfs, on the other hand, were not given land as part of their freedom; instead, it was distributed to the male elders of a community, who had the absolute right to allocate this land to individuals and direct the economic activity of the community. Further, even when peasants received their land allocation, it was not a free grant; they had to "redeem" or pay the government for the land they farmed.
3
How did Giuseppe Garibaldi and Camillo di Cavour both oppose and complement each other in the struggle for Italian unification?
Answer would ideally include the following. Camillo di Cavour was the prime minister of Piedmont-Sardinia in northern Italy, and through economic management, military reform, and careful international planning, he managed to make Piedmont the most powerful state in Italy. While Cavour was working from the north to bring all of Italy together under the king of Piedmont-Sardinia, the republican revolutionary Giuseppe Garibaldi (1807-1882) and his Red Shirts liberated Sicily and then invaded southern Italy. The two men opposed each other in terms of the type of post-unification government they envisioned, but they complemented each other by unifying the sections of Italy under their control. Ultimately, the forces of Cavour's monarch, King Victor Emmanuel, met Garibaldi's in Naples, where Garibaldi threw his support behind the king and agreed to the formation of the kingdom of Italy in 1861.
4
Describe Otto von Bismarck's approach to the unification and strengthening of Germany.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What was the Second Reform Bill of 1867, and why is it somewhat surprising that it was passed through Parliament under Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In what ways did educational innovations improve opportunities for women in the middle of the nineteenth century?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How did the Meiji Restoration in the 1860s show that Japan both accepted and rejected the West?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What was Karl Marx's concept of the "mode of production"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How did mid-nineteenth-century novelists such as Charles Dickens and George Eliot exemplify realism in their work?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What was the basic argument of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species (1859), and how did it become Social Darwinism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Describe France's foreign policy under Napoleon III, and explain how it brought an end to the concert of Europe (established in 1815).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Urban planners initiated radical changes in many European cities during the second half of the nineteenth century. Explain the origins, goals, and results of these urban renovations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In what ways was the Paris Commune of 1871 a reaction against the growing power of the nation-state? What other political questions were at stake? Be sure to describe the Commune's origins, aims, and conclusion in your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Who was Karl Marx? Explain Marxism and how it differed from the other sociopolitical doctrines of the time. How did Marx believe change would be achieved? Do you agree with Marx? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
How were natural and social sciences used to both challenge the social order and solve social problems in the mid-nineteenth century?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Who were the main targets of Louis-Napoleon Bonaparte (Napoleon III) during the nineteenth century?
A) Great Britain and Italy
B) Germany and Spain
C) Poland and Prussia
D) Russia and Austria
A) Great Britain and Italy
B) Germany and Spain
C) Poland and Prussia
D) Russia and Austria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why did France, under the rule of Napoleon III, help engineer the Crimean War?
A) To assert full control over trade routes in the Mediterranean
B) To gain colonies in Africa and the Americas
C) To reduce the dominance of Russia and Austria
D) To improve international relations with China
A) To assert full control over trade routes in the Mediterranean
B) To gain colonies in Africa and the Americas
C) To reduce the dominance of Russia and Austria
D) To improve international relations with China

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What were Napoleon III's main international goals?
A) Undermining the international authority of France's historic enemy, Great Britain, and taking back France's Caribbean colonies
B) Overcoming the containment of France imposed by the Congress of Vienna and living up to the Bonaparte name by acquiring international territory
C) Gaining territory in Africa and the Ottoman Empire in order to expand colonial settlement and promote French power overseas
D) Enforcing the settlement imposed by the Congress of Vienna, which was under threat from the Realpolitik visions of Prussian and Austrian leaders
A) Undermining the international authority of France's historic enemy, Great Britain, and taking back France's Caribbean colonies
B) Overcoming the containment of France imposed by the Congress of Vienna and living up to the Bonaparte name by acquiring international territory
C) Gaining territory in Africa and the Ottoman Empire in order to expand colonial settlement and promote French power overseas
D) Enforcing the settlement imposed by the Congress of Vienna, which was under threat from the Realpolitik visions of Prussian and Austrian leaders

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What did Napoleon III offer Maximilian, the brother of the Austrian emperor Francis Joseph?
A) His allegiance in a Franco-Austrian war against Russia
B) The chance to replace the former king of Spain, recently overthrown in a military coup
C) The imperial crown of Mexico
D) His support for Maximilian's plan to seize the imperial throne from his brother
A) His allegiance in a Franco-Austrian war against Russia
B) The chance to replace the former king of Spain, recently overthrown in a military coup
C) The imperial crown of Mexico
D) His support for Maximilian's plan to seize the imperial throne from his brother

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to this map, which of the following was likely one of Russia's goals during the Crimean War?
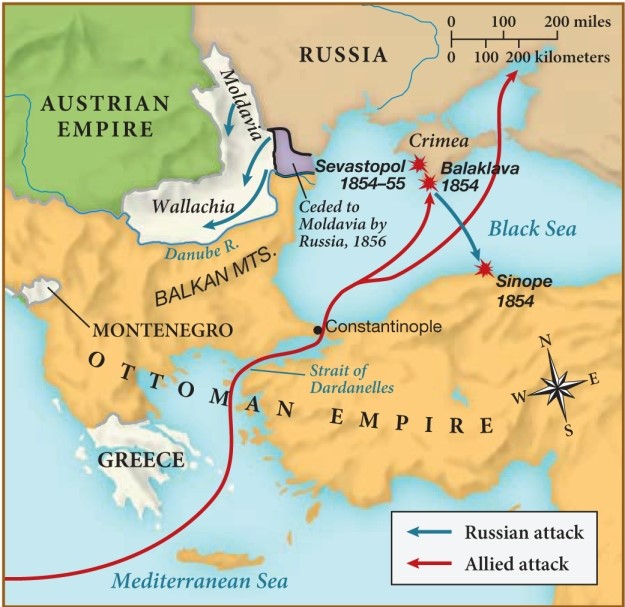
A) To take control of Greece
B) To establish trade routes in the Black Sea
C) To expand territorial control in the west and the southeast
D) To install a democratic government in the Austrian Empire

A) To take control of Greece
B) To establish trade routes in the Black Sea
C) To expand territorial control in the west and the southeast
D) To install a democratic government in the Austrian Empire

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Crimean War (1853-1856) accomplished Napoleon III's goal of
A) severing the alliance between the Austrian Habsburgs and Russia.
B) expanding French territory in the Balkans.
C) augmenting Prussia's power to further undermine Austria.
D) uniting the French people in nationalist support of his dictatorial regime.
A) severing the alliance between the Austrian Habsburgs and Russia.
B) expanding French territory in the Balkans.
C) augmenting Prussia's power to further undermine Austria.
D) uniting the French people in nationalist support of his dictatorial regime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the Crimean War of 1853-1856, Britain and France fought to achieve what geopolitical objective?
A) Saving Greece from the Ottoman Empire
B) Defending the Ottoman Empire from dismemberment by Russia
C) Protecting the Bulgarians from Austro-Hungarian massacres
D) Stopping Prussia from annexing parts of Denmark
A) Saving Greece from the Ottoman Empire
B) Defending the Ottoman Empire from dismemberment by Russia
C) Protecting the Bulgarians from Austro-Hungarian massacres
D) Stopping Prussia from annexing parts of Denmark

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For what did Florence Nightingale achieve fame in the mid-nineteenth century?
A) Her celebrated musical compositions
B) Her role in the movement for woman suffrage
C) Her work toward the abolition of slavery
D) Her pioneering work in the field of nursing
A) Her celebrated musical compositions
B) Her role in the movement for woman suffrage
C) Her work toward the abolition of slavery
D) Her pioneering work in the field of nursing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Alexander II's Great Reforms were intended to do what?
A) Give greater democracy to the people and thus avoid any upheaval
B) Preserve the social hierarchy and maintain the status quo in Russia
C) Act as a first step in giving proportional representation to ethnic groups within the state
D) Strengthen the power of the monarchy so much that no one would challenge the state
A) Give greater democracy to the people and thus avoid any upheaval
B) Preserve the social hierarchy and maintain the status quo in Russia
C) Act as a first step in giving proportional representation to ethnic groups within the state
D) Strengthen the power of the monarchy so much that no one would challenge the state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following was the most dramatic of Alexander II's Great Reforms?
A) The emancipation of almost fifty million serfs
B) The reform of the Russian military
C) The creation of zemstvos, or regional governing councils
D) The introduction of universal manhood suffrage
A) The emancipation of almost fifty million serfs
B) The reform of the Russian military
C) The creation of zemstvos, or regional governing councils
D) The introduction of universal manhood suffrage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What enduring obstacle prevented the development of a free, mobile labor force even after Alexander II's Great Reforms?
A) The policy of lengthy military conscription that kept men in the army for twenty-five years
B) The lack of sufficient infrastructure, especially roads and rail transport
C) The fact that the zemstvos often denied former serfs' requests for permission to move
D) The fact that former serfs remained tied to a system of communal landowning and decision making
A) The policy of lengthy military conscription that kept men in the army for twenty-five years
B) The lack of sufficient infrastructure, especially roads and rail transport
C) The fact that the zemstvos often denied former serfs' requests for permission to move
D) The fact that former serfs remained tied to a system of communal landowning and decision making

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
After uprisings by minority nationalist groups, Tsar Alexander II insisted that minorities in the Russian Empire adopt the Russian language and culture, a policy known as
A) assimilation.
B) Russification.
C) ethnic nationalization.
D) Slavic integration.
A) assimilation.
B) Russification.
C) ethnic nationalization.
D) Slavic integration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Who was the pragmatic prime minister of Piedmont-Sardinia whose Realpolitik vision of Italian unification led him to seek Napoleon III's assistance in overthrowing Austrian rule?
A) Giuseppe Garibaldi
B) Giuseppe Verdi
C) Camillo di Cavour
D) Vittorio Emmanuele
A) Giuseppe Garibaldi
B) Giuseppe Verdi
C) Camillo di Cavour
D) Vittorio Emmanuele

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to this map, what did the kingdom of Italy gain in 1870?
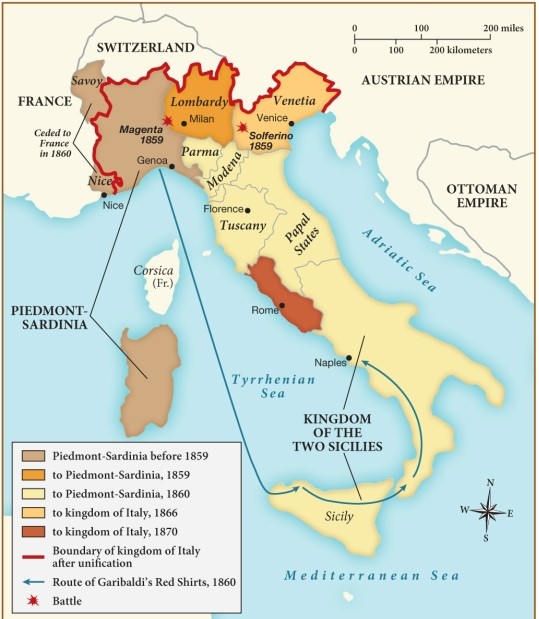
A) Rome
B) Full control of the Mediterranean Sea
C) Venice
D) Better trade routes

A) Rome
B) Full control of the Mediterranean Sea
C) Venice
D) Better trade routes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why was Italian unification in 1861 led by the kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia?
A) It had industry, a good economy, a strong army, and the backing of France.
B) The pope would work only with Prime Minister Camillo di Cavour and with no one else.
C) It was the home of Giuseppe Garibaldi and of most of his Red Shirts.
D) Its strategic location meant that unification would be impossible without its support.
A) It had industry, a good economy, a strong army, and the backing of France.
B) The pope would work only with Prime Minister Camillo di Cavour and with no one else.
C) It was the home of Giuseppe Garibaldi and of most of his Red Shirts.
D) Its strategic location meant that unification would be impossible without its support.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What frustrated Cavour's nationalist ambitions following the rout of the Austrians by Italian and French forces?
A) Napoleon signed a treaty with Austria granting Lombardy, but not Venetia, to Piedmont.
B) King Victor Emmanuel insisted that Cavour break his promises to the French.
C) Napoleon III compelled Victor Emmanuel to put his army under French command.
D) King Victor Emmanuel demanded that Cavour also liberate southern Italy.
A) Napoleon signed a treaty with Austria granting Lombardy, but not Venetia, to Piedmont.
B) King Victor Emmanuel insisted that Cavour break his promises to the French.
C) Napoleon III compelled Victor Emmanuel to put his army under French command.
D) King Victor Emmanuel demanded that Cavour also liberate southern Italy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How did Giuseppe Garibaldi help derail Napoleon III's plan to prevent Italian unification?
A) He convinced the Austrian government that Napoleon was acting in bad faith in his deal to grant them Venetia, and they backed out of the agreement and exited Italy.
B) He signed a secret agreement with Otto von Bismarck, in which Prussia would assist in unifying Italy in exchange for Italy's assistance in maintaining Europe's power balance.
C) He liberated Sicily and southern Italy with the assistance of his red-shirted volunteers and then threw his support behind King Victor Emmanuel.
D) He rallied his network of exiled Italians and French sympathizers to foment revolution in France and distract Napoleon from Italian politics.
A) He convinced the Austrian government that Napoleon was acting in bad faith in his deal to grant them Venetia, and they backed out of the agreement and exited Italy.
B) He signed a secret agreement with Otto von Bismarck, in which Prussia would assist in unifying Italy in exchange for Italy's assistance in maintaining Europe's power balance.
C) He liberated Sicily and southern Italy with the assistance of his red-shirted volunteers and then threw his support behind King Victor Emmanuel.
D) He rallied his network of exiled Italians and French sympathizers to foment revolution in France and distract Napoleon from Italian politics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
William I appointed Otto von Bismarck chancellor in 1862 in the hope that Bismarck would do which of the following?
A) Provoke France into a war so that Prussia could seize Alsace and Lorraine
B) Put down the growing power of the liberals in the Prussian parliament
C) Negotiate with Polish nationalists so they would accept their role in the Prussian state
D) Turn the public against Karl Marx and other leading German socialists
A) Provoke France into a war so that Prussia could seize Alsace and Lorraine
B) Put down the growing power of the liberals in the Prussian parliament
C) Negotiate with Polish nationalists so they would accept their role in the Prussian state
D) Turn the public against Karl Marx and other leading German socialists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
By urging Austria to join Prussia in a war to save the provinces of Schleswig and Holstein from Danish territorial ambitions, Bismarck shrewdly
A) engineered Prussia's establishment of the first German colonies in southwest Africa.
B) lulled Austria into believing that Prussia had no individual territorial ambitions within the greater German Confederation.
C) precipitated France's alliance with Russia, which provoked Francis Joseph into sending troops to the Franco-Austrian border, thus dividing his army in half.
D) affected Austria's political and military overextension and set the stage for an Austro-Prussian confrontation.
A) engineered Prussia's establishment of the first German colonies in southwest Africa.
B) lulled Austria into believing that Prussia had no individual territorial ambitions within the greater German Confederation.
C) precipitated France's alliance with Russia, which provoked Francis Joseph into sending troops to the Franco-Austrian border, thus dividing his army in half.
D) affected Austria's political and military overextension and set the stage for an Austro-Prussian confrontation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements regarding the unification of Germany is supported by this map?
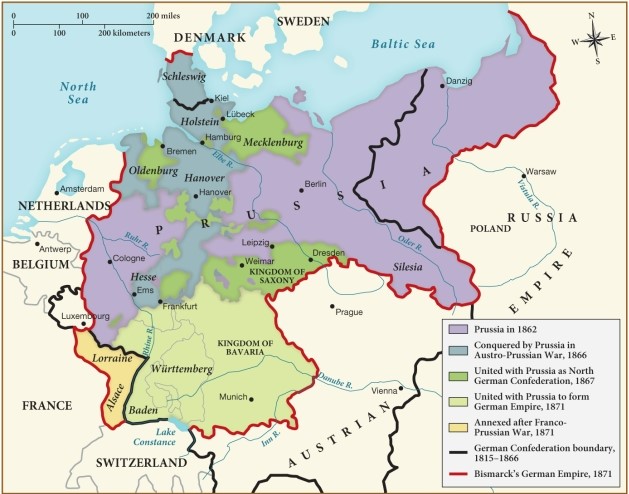
A) The territories of Alsace and Lorraine were ceded to France from the German Confederation following the Franco-Prussian War.
B) By 1871, the Austrian Empire had fully become part of the German Empire as a result of the Austro-Prussian War.
C) The German Empire gained most of its territory in 1871 following the unification of Prussia and the Kingdom of Bavaria.
D) The German Empire gained most of Poland and Switzerland by the end of the Franco-Prussian War.

A) The territories of Alsace and Lorraine were ceded to France from the German Confederation following the Franco-Prussian War.
B) By 1871, the Austrian Empire had fully become part of the German Empire as a result of the Austro-Prussian War.
C) The German Empire gained most of its territory in 1871 following the unification of Prussia and the Kingdom of Bavaria.
D) The German Empire gained most of Poland and Switzerland by the end of the Franco-Prussian War.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Why did Otto von Bismarck grant Germans universal male suffrage despite his conservative principles?
A) He believed the Bundesrat, the upper house made up largely of German princes, could effectively block any of the more populist measures the Reichstag might propose.
B) He thought that only by appealing to a wide segment of the German people could he hope to secure enough support for a radical reform of Germany's fledgling social welfare system.
C) He understood that the future lay with democratic government and especially with the working classes, who he believed would always vote in favor of war.
D) He trusted that "ordinary" Germans would be more conservative and loyal to the monarchy than the liberals in the Prussian parliament.
A) He believed the Bundesrat, the upper house made up largely of German princes, could effectively block any of the more populist measures the Reichstag might propose.
B) He thought that only by appealing to a wide segment of the German people could he hope to secure enough support for a radical reform of Germany's fledgling social welfare system.
C) He understood that the future lay with democratic government and especially with the working classes, who he believed would always vote in favor of war.
D) He trusted that "ordinary" Germans would be more conservative and loyal to the monarchy than the liberals in the Prussian parliament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Following Austria's defeat in the Austro-Prussian War, Francis Joseph reluctantly agreed to the establishment of a "dual monarchy," which granted Magyars
A) the right to marry into the Habsburg royal family.
B) a separate Hungarian legislature whose approval would be required for all future declarations of war.
C) the right to compete on an equal basis with Austrians for posts in the imperial civil service.
D) a restored Hungarian parliament with control over domestic matters in Hungary.
A) the right to marry into the Habsburg royal family.
B) a separate Hungarian legislature whose approval would be required for all future declarations of war.
C) the right to compete on an equal basis with Austrians for posts in the imperial civil service.
D) a restored Hungarian parliament with control over domestic matters in Hungary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In Victorian Britain, Parliament passed a law that enabled women to do what for the first time?
A) Enter medical schools
B) Own property or keep the wages they earned
C) Vote
D) Appear in public at night without a male companion
A) Enter medical schools
B) Own property or keep the wages they earned
C) Vote
D) Appear in public at night without a male companion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What made the nineteenth-century Victorian culture such a unique social phenomenon?
A) It encouraged British imperialists to fully assimilate native peoples into British culture.
B) It gave rise to a widespread aping of royal dress and manners among British aristocrats made rich by colonial commerce.
C) Never before had a British monarch influenced popular mores and manners to such a degree.
D) Queen Victoria began the modern cult of celebrity through carefully managed propaganda.
A) It encouraged British imperialists to fully assimilate native peoples into British culture.
B) It gave rise to a widespread aping of royal dress and manners among British aristocrats made rich by colonial commerce.
C) Never before had a British monarch influenced popular mores and manners to such a degree.
D) Queen Victoria began the modern cult of celebrity through carefully managed propaganda.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In 1848, the United States added which of the following to its territory?
A) North and South Dakota
B) Oklahoma
C) Kansas
D) California
A) North and South Dakota
B) Oklahoma
C) Kansas
D) California

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
By 1870, Indians still held a majority of land in which U.S. territory?
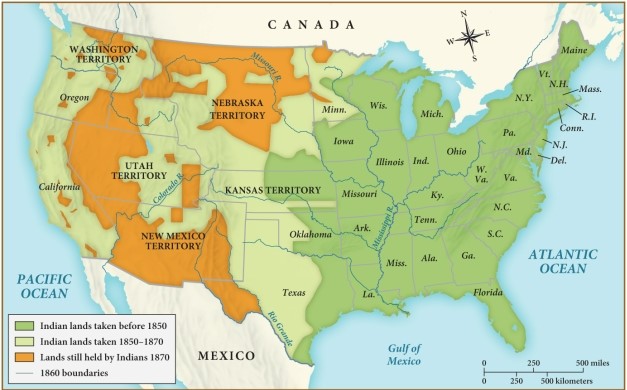
A) Minnesota
B) California
C) Kansas
D) New Mexico

A) Minnesota
B) California
C) Kansas
D) New Mexico

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The U.S. Civil War was fought over which major issues?
A) The question of manifest destiny and divisions over a law banning further western expansion
B) The demands of southern states to reopen the Atlantic slave trade and conflicts over industrial expansion
C) The preservation of the union and the abolition of slavery
D) The annexation of Texas and other territories from Mexico and the unwillingness of southern states to recognize the right of slaves to vote
A) The question of manifest destiny and divisions over a law banning further western expansion
B) The demands of southern states to reopen the Atlantic slave trade and conflicts over industrial expansion
C) The preservation of the union and the abolition of slavery
D) The annexation of Texas and other territories from Mexico and the unwillingness of southern states to recognize the right of slaves to vote

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The British made Canada a united, self-governing dominion in 1867, in part to
A) reduce colonial administration expenses and free up funds that were more urgently needed in India.
B) undercut a demand by the United States that it be allowed to annex Canada.
C) encourage the Irish to emigrate there.
D) encourage other colonies to assimilate British mores, tastes, and opinions more quickly.
A) reduce colonial administration expenses and free up funds that were more urgently needed in India.
B) undercut a demand by the United States that it be allowed to annex Canada.
C) encourage the Irish to emigrate there.
D) encourage other colonies to assimilate British mores, tastes, and opinions more quickly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How did the process of Haussmannization, named for Georges-Eugène Haussmann, reshape the urban landscape of Paris?
A) Crowded mixed neighborhoods of winding medieval streets gave way to wide boulevards lined with spacious, showy dwellings, resulting in the segregation of rich and poor.
B) It rezoned the city so that rich and poor lived together, with equal access to new amenities like parks and the opera.
C) New public housing projects were created to house the working classes in the center of the city, while the wealthy moved out to the suburbs.
D) The poor and working classes were forced out of the city to make way for monumental palaces built to honor Napoleon III.
A) Crowded mixed neighborhoods of winding medieval streets gave way to wide boulevards lined with spacious, showy dwellings, resulting in the segregation of rich and poor.
B) It rezoned the city so that rich and poor lived together, with equal access to new amenities like parks and the opera.
C) New public housing projects were created to house the working classes in the center of the city, while the wealthy moved out to the suburbs.
D) The poor and working classes were forced out of the city to make way for monumental palaces built to honor Napoleon III.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What European scientist made huge advances in public health by advancing the germ theory of disease?
A) Joseph Lister
B) Louis Pasteur
C) Charles Darwin
D) Florence Nightingale
A) Joseph Lister
B) Louis Pasteur
C) Charles Darwin
D) Florence Nightingale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Midcentury demands for educational reform developed primarily out of the concerns of which of the following?
A) The clergy
B) Factory owners
C) Book publishers
D) Governments
A) The clergy
B) Factory owners
C) Book publishers
D) Governments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Why were laws requiring the education of children difficult to enforce?
A) Most governments feared that educated citizens would be converted to socialism.
B) Families of farm laborers and unskilled urban workers were too mobile.
C) Many poorer parents needed their children's help with farmwork or domestic tasks.
D) Churches pressured families to send their children to church-run schools instead of state schools.
A) Most governments feared that educated citizens would be converted to socialism.
B) Families of farm laborers and unskilled urban workers were too mobile.
C) Many poorer parents needed their children's help with farmwork or domestic tasks.
D) Churches pressured families to send their children to church-run schools instead of state schools.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
East Indian troops of the British army launched the Indian Rebellion of 1857 because they were angered by tightening British control and by
A) the decision of British commanders to separate Muslim soldiers from Hindu soldiers and train the former as special highly paid guard units.
B) Britain's imposition of direct political rule on India, rather than ruling indirectly through the East India Company, which had been relatively lax in its oversight.
C) the decision by the British army to require soldiers to swear an oath of loyalty to a woman, Queen Victoria.
D) the rumor that Britain would force soldiers to use cartridges greased with cow and pig fat, which violated Hindu and Muslim religious rules, respectively.
A) the decision of British commanders to separate Muslim soldiers from Hindu soldiers and train the former as special highly paid guard units.
B) Britain's imposition of direct political rule on India, rather than ruling indirectly through the East India Company, which had been relatively lax in its oversight.
C) the decision by the British army to require soldiers to swear an oath of loyalty to a woman, Queen Victoria.
D) the rumor that Britain would force soldiers to use cartridges greased with cow and pig fat, which violated Hindu and Muslim religious rules, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
French overseas expansion included a push to establish dominion over which of the following territories in the 1860s?
A) Quebec, Canada
B) Cochin China
C) Senegal and the Gambia
D) Syria and Lebanon
A) Quebec, Canada
B) Cochin China
C) Senegal and the Gambia
D) Syria and Lebanon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Suez Canal, which opened in 1869, connected the
A) Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea.
B) Black Sea with the Mediterranean Sea.
C) Red Sea with the Indian Ocean.
D) Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
A) Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea.
B) Black Sea with the Mediterranean Sea.
C) Red Sea with the Indian Ocean.
D) Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The bloody war that raged in China until 1864 pitted the French and British-supported Qing dynasty against which group?
A) The xenophobic and nationalist Manchus
B) The Russian-supported Yuan
C) Members of the rival Han and their supporters
D) Supporters of the Taiping
A) The xenophobic and nationalist Manchus
B) The Russian-supported Yuan
C) Members of the rival Han and their supporters
D) Supporters of the Taiping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What was the goal of the Japanese reformers who enacted the Meiji Restoration in 1868?
A) To restore Japan to its state before it encountered Western values and culture
B) To find a way to benefit from European trade without allowing the influence of Western culture to invade Japanese society
C) To combine the innovations of Western science with a restoration of Eastern values as a way of "making new"
D) To fully westernize Japanese society and wipe away the old-fashioned Eastern values that had held Japan back from global society
A) To restore Japan to its state before it encountered Western values and culture
B) To find a way to benefit from European trade without allowing the influence of Western culture to invade Japanese society
C) To combine the innovations of Western science with a restoration of Eastern values as a way of "making new"
D) To fully westernize Japanese society and wipe away the old-fashioned Eastern values that had held Japan back from global society

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What ideology proposed by Mikhail Bakunin argued that the centralized political state was the root of social injustice and therefore must be destroyed?
A) Positivism
B) Anarchism
C) Nihilism
D) Socialism
A) Positivism
B) Anarchism
C) Nihilism
D) Socialism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What differentiated Karl Marx's views about the possibilities for social change from those of utopian socialists?
A) Unlike utopian socialists, who believed in cooperation, Marx was a realist whose views were based on scientific analysis and who saw class struggle as the basis for social change.
B) Marx believed that change could only occur through the destruction of all state power, while utopian socialists continued to encourage collaboration with government reformers.
C) Utopian socialists believed that social reform would come gradually but steadily, while Karl Marx argued that social change was not possible at all.
D) Marx believed that social reform would come through workers' cooperatives and government reform, while utopian socialists believed it could only come through class struggle.
A) Unlike utopian socialists, who believed in cooperation, Marx was a realist whose views were based on scientific analysis and who saw class struggle as the basis for social change.
B) Marx believed that change could only occur through the destruction of all state power, while utopian socialists continued to encourage collaboration with government reformers.
C) Utopian socialists believed that social reform would come gradually but steadily, while Karl Marx argued that social change was not possible at all.
D) Marx believed that social reform would come through workers' cooperatives and government reform, while utopian socialists believed it could only come through class struggle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The 1871 Paris Commune was promoted as a social revolution offering which of the following enticements?
A) Free love and the abolition of marriage
B) The liberation of all workers, including women workers
C) The burning of Paris as an act of cleansing
D) The restoration of the authority of the Catholic church
A) Free love and the abolition of marriage
B) The liberation of all workers, including women workers
C) The burning of Paris as an act of cleansing
D) The restoration of the authority of the Catholic church

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Realism in the arts rejected which of the following?
A) Socialism and utopian thinking
B) Gender equality as a reasonable goal
C) Romanticism and fervent religious sentiment
D) Democracy and science
A) Socialism and utopian thinking
B) Gender equality as a reasonable goal
C) Romanticism and fervent religious sentiment
D) Democracy and science

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Gustave Flaubert's novel Madame Bovary (1857) and Édouard Manet's painting Olympia (1865) explored what social theme?
A) Middle-class materialism
B) Women's sexuality
C) Religious hypocrisy
D) The lives of prostitutes
A) Middle-class materialism
B) Women's sexuality
C) Religious hypocrisy
D) The lives of prostitutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What was the target of Otto von Bismarck's Kulturkampf in the 1870s?
A) Liberal political institutions
B) Nationalist movements
C) Artists
D) Organized religion
A) Liberal political institutions
B) Nationalist movements
C) Artists
D) Organized religion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Pope Pius IX and his Syllabus of Errors (1864) put the Catholic church at odds with
A) progress, liberalism, and modern civilization.
B) Karl Marx, mutualism, and anarchists.
C) Charles Darwin, feminism, and secular education.
D) materialists, imperialists, and nationalists.
A) progress, liberalism, and modern civilization.
B) Karl Marx, mutualism, and anarchists.
C) Charles Darwin, feminism, and secular education.
D) materialists, imperialists, and nationalists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The pilgrimage of millions to Lourdes, France, following Bernadette Soubirous's visions of the Virgin Mary is representative of what new development within the Catholic church?
A) The modernization of the church, as it used tourism, railroads, and shopping centers to make the religious experience more up-to-date
B) The church's return to using practices like pilgrimages and selling indulgences to fill its coffers in the wake of governmental attacks
C) The shift in regional power of the Catholic church from Rome to France as a result of the Vatican losing credibility in the wake of the Kulturkampf
D) The loss of authority of the pope, as he was replaced with local visionaries and mystics who gained the support of the masses throughout Europe
A) The modernization of the church, as it used tourism, railroads, and shopping centers to make the religious experience more up-to-date
B) The church's return to using practices like pilgrimages and selling indulgences to fill its coffers in the wake of governmental attacks
C) The shift in regional power of the Catholic church from Rome to France as a result of the Vatican losing credibility in the wake of the Kulturkampf
D) The loss of authority of the pope, as he was replaced with local visionaries and mystics who gained the support of the masses throughout Europe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Why was the English naturalist Charles Darwin's book On the Origin of Species (1859) so controversial?
A) Darwin claimed that women were inherently inferior to men and that they therefore should not be accorded rights of citizenship or property.
B) Darwin challenged Judeo-Christian dogma, arguing that life had taken shape over millions of years through a process called evolution, not through God's miraculous creation of the universe in six days.
C) Darwin believed that nonwhite peoples were inherently superior to and more highly evolved than whites.
D) Darwin argued that the principles of the scientific method, which had been in use since the scientific revolution, were fundamentally flawed.
A) Darwin claimed that women were inherently inferior to men and that they therefore should not be accorded rights of citizenship or property.
B) Darwin challenged Judeo-Christian dogma, arguing that life had taken shape over millions of years through a process called evolution, not through God's miraculous creation of the universe in six days.
C) Darwin believed that nonwhite peoples were inherently superior to and more highly evolved than whites.
D) Darwin argued that the principles of the scientific method, which had been in use since the scientific revolution, were fundamentally flawed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What theory led many Europeans to believe that they could solve all social problems through the scientific analysis of facts?
A) Marxism
B) Liberalism
C) Positivism
D) Social Darwinism
A) Marxism
B) Liberalism
C) Positivism
D) Social Darwinism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The English social theorist Herbert Spencer (1820-1903) argued that
A) only a strong, centralized state could contain the forces of the struggle for survival.
B) Darwin's research shed little light on contemporary cultural or racial differences.
C) unregulated industrial competition would lead to a war between capitalists and workers.
D) the unfit should be allowed to perish so as not to block the path of progress.
A) only a strong, centralized state could contain the forces of the struggle for survival.
B) Darwin's research shed little light on contemporary cultural or racial differences.
C) unregulated industrial competition would lead to a war between capitalists and workers.
D) the unfit should be allowed to perish so as not to block the path of progress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In his 1869 work The Subjection of Women, John Stuart Mill
A) argued that women did not have the mental capacity to take part in politics.
B) showed the family as a despotic institution, lacking modern values such as rights and freedom.
C) offered scientific proof that women were passive and lacked sexual feeling.
D) claimed that women were naturally weak and needed men to tell them what to do.
A) argued that women did not have the mental capacity to take part in politics.
B) showed the family as a despotic institution, lacking modern values such as rights and freedom.
C) offered scientific proof that women were passive and lacked sexual feeling.
D) claimed that women were naturally weak and needed men to tell them what to do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Based on this map, which of the following European nations posed the greatest threat to the declining Ottoman Empire by 1871?
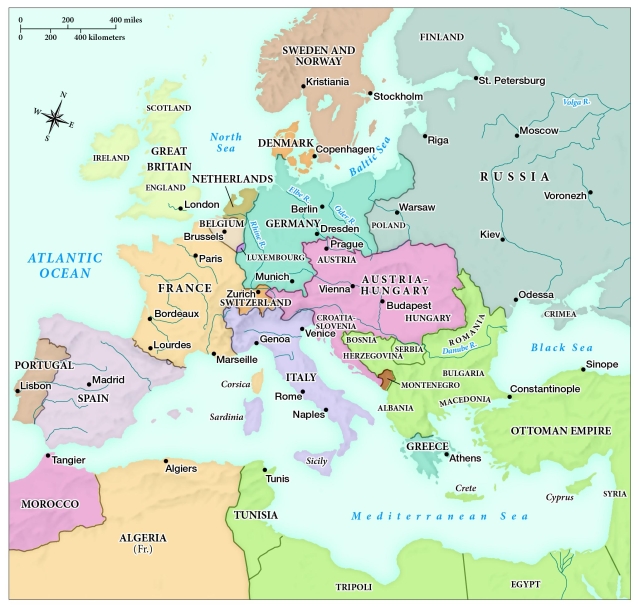
A) Denmark
B) Sweden and Norway
C) Great Britain
D) Austria-Hungary

A) Denmark
B) Sweden and Norway
C) Great Britain
D) Austria-Hungary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



