Deck 11: The Flowering of the Middle Ages, 1150-1215
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: The Flowering of the Middle Ages, 1150-1215
1
What was Abelard's Sic et Non (1122-1123)? Why is it considered innovative?
Answer would ideally include the following. Sic et Non (Yes and No) was a textbook for Abelard's students that aimed to arrive at truth by presenting questions on 156 subjects. Each question was followed by answers in the form of quotations taken from various authorities' opinions on that subject. Scholars had earlier recognized that these authorities sometimes contradicted one another, but Abelard's text was the first to pointedly call attention to these conflicts. He was trying to encourage his students to ask questions of authorities and to use logic to reconcile opposing positions.
2
How were universities run, and how did students learn?
Answer would ideally include the following. Universities often began as schools connected to monasteries and cathedrals. Each university's curriculum differed from that of other universities in content and duration, but for the most part, students learned by memorizing masters' lectures because books were expensive. Technically, masters and students were considered clerics; thus they were exempt from secular courts and enjoyed other special privileges. Students paid for their education and often sought out especially popular teachers.
3
Describe the common elements in twelfth-century churches built in the Romanesque style.
Answer would ideally include the following. Romanesque churches typically boasted massive stone and masonry walls, with interiors lightened by paintings in bright colors and ornamented by jeweled reliquaries and altars. Sculpture was used on both the exterior and the interior, softening the geometric forms of the various parts of the church. The interior was further enlivened by services conducted by priests wearing elaborate vestments.
4
What are the most important facts of Eleanor of Aquitaine's life?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Describe Henry II of England's new judicial visitation (eyres) system. What were its advantages, and for whom?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which 1194 event changed the administrative system of the French kings? What was changed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why was ruling always a risk for emperors such as Frederick I (Barbarossa)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What were the basic beliefs of the Cathars, or Albigensians?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Describe the main events of the Fourth Crusade (1202-1204).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Describe the Northern Crusades. Include who led them, against whom they were directed, and what they accomplished.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Discuss the most visible reminder of thirteenth-century beliefs: the Gothic cathedrals. How did Gothic architecture differ from Romanesque architecture? What religious purposes were Gothic cathedrals intended to serve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Describe the universities, schools, and students of the eleventh and twelfth centuries. Be sure to consider the curricula, the lives of students, and areas of specialization of study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How did Frederick I come to power, and what was the significance of his coming to power? What benefits did his rule bring to Germany? How was his rule detrimental to the territories he controlled and, eventually, to his own success as a ruler?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Describe and explain the emergence of troubadours, the various types of literature they wrote in the vernacular, and the values and themes they expressed in elite secular culture. Why did troubadours emerge in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Discuss the crusading impulses of the late twelfth and thirteenth centuries. What impact did these crusades have on the societies of the Middle East, Spain, the Baltic States, and the regions of southern France that were home to the Albigensian heresy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following factors contributed to the success and advancement of the Middle Ages?
A) Industrialization of the economy
B) The introduction of fiat currency
C) A return to Christianity
D) An emphasis on learning
A) Industrialization of the economy
B) The introduction of fiat currency
C) A return to Christianity
D) An emphasis on learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Schools and universities were set up in Europe in the Middle Ages to do which of the following?
A) Prepare students to run the civil administration of local states and principalities
B) Give students the same education that students would have received at Plato's Academy in ancient Athens
C) Train future priests and monks
D) Teach future scientists about the scientific method
A) Prepare students to run the civil administration of local states and principalities
B) Give students the same education that students would have received at Plato's Academy in ancient Athens
C) Train future priests and monks
D) Teach future scientists about the scientific method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Students studying the quadrivium focused on
A) grammar, rhetoric, logic, and astrology.
B) physical education, music, literature, and logic.
C) arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy.
D) the Old Testament, the New Testament, patristic writings, and the creeds.
A) grammar, rhetoric, logic, and astrology.
B) physical education, music, literature, and logic.
C) arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy.
D) the Old Testament, the New Testament, patristic writings, and the creeds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What did Peter Abelard find even more difficult to bear than his castration?
A) His separation from Heloise
B) The disapproval of Heloise's uncle
C) His inability to continue teaching
D) The condemnation of his book by the Council of Soissons
A) His separation from Heloise
B) The disapproval of Heloise's uncle
C) His inability to continue teaching
D) The condemnation of his book by the Council of Soissons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Like Peter Abelard, Peter the Chanter gained renown for his
A) illicit love affairs.
B) lectures and disputations.
C) efforts at religious reform.
D) attempts to convert non-Christians to the faith.
A) illicit love affairs.
B) lectures and disputations.
C) efforts at religious reform.
D) attempts to convert non-Christians to the faith.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why did universities refuse to enroll women during the Middle Ages?
A) There were simply no women capable of enrolling, since nearly all women at the time were illiterate.
B) Masters and students were considered clerics, and as a result women had no chance of enrolling.
C) They lacked housing that could accommodate women, and coed housing was regarded as immoral.
D) They regarded all women as corrupting temptresses who would divert men from their chosen path of study.
A) There were simply no women capable of enrolling, since nearly all women at the time were illiterate.
B) Masters and students were considered clerics, and as a result women had no chance of enrolling.
C) They lacked housing that could accommodate women, and coed housing was regarded as immoral.
D) They regarded all women as corrupting temptresses who would divert men from their chosen path of study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Gothic style was first associated with which of the following?
A) The Capetian kings of France
B) The papacy
C) The Norman kings of England
D) The Italian cities
A) The Capetian kings of France
B) The papacy
C) The Norman kings of England
D) The Italian cities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is Gregorian chant most closely associated with?
A) Troubadour poetry
B) Romanesque churches
C) Pope Gregory
D) The Franciscan order
A) Troubadour poetry
B) Romanesque churches
C) Pope Gregory
D) The Franciscan order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is most characteristic of Gothic architecture?
A) Low ceilings and broad interior spaces
B) Pointed arches and stained glass
C) Stone construction
D) Dark interiors
A) Low ceilings and broad interior spaces
B) Pointed arches and stained glass
C) Stone construction
D) Dark interiors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
At the close of the twelfth century, western Europeans saw their monarchs not as rulers of a people but rather as
A) heads of powerful dynasties and royal houses.
B) potential rulers over all Christian nations.
C) judges and military leaders within institutionalized governments.
D) rulers of a clearly defined territory.
A) heads of powerful dynasties and royal houses.
B) potential rulers over all Christian nations.
C) judges and military leaders within institutionalized governments.
D) rulers of a clearly defined territory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The war over the English throne (1139-1153) granted new privileges and powers to which of the following groups?
A) Peasants and merchants
B) Barons and high churchmen
C) Anglo-Saxon citizens
D) Knights
A) Peasants and merchants
B) Barons and high churchmen
C) Anglo-Saxon citizens
D) Knights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the twelfth century, royal justices toured England making visits called eyres, at which they
A) presided over trials for murder, rape, arson, and certain other crimes.
B) delivered writs containing the king's verdicts.
C) collected petitions from litigants to be tried by the king himself.
D) gave the sheriff the names of those suspected of crimes in the vicinity.
A) presided over trials for murder, rape, arson, and certain other crimes.
B) delivered writs containing the king's verdicts.
C) collected petitions from litigants to be tried by the king himself.
D) gave the sheriff the names of those suspected of crimes in the vicinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How did Henry II's six-year conflict with his archbishop, Thomas Becket, over whether churchmen were to submit to royal courts end?
A) Henry was forced to back down and allow religious courts to adjudicate in disputes involving the clergy.
B) Henry forced Becket into exile in France.
C) Henry's henchmen murdered Becket in his cathedral.
D) Henry forced Becket to back down and relinquish control of ecclesiastical courts.
A) Henry was forced to back down and allow religious courts to adjudicate in disputes involving the clergy.
B) Henry forced Becket into exile in France.
C) Henry's henchmen murdered Becket in his cathedral.
D) Henry forced Becket to back down and relinquish control of ecclesiastical courts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What significance did Henry II's marriage to Eleanor have for future European dynastic holdings?
A) It attached significant portions of Flanders to Henry's English and French holdings.
B) It gave Henry possession of the Capetian lands of northern-central France.
C) It brought Scotland and Ireland under English rule.
D) It gave the English crown possession of Aquitaine in southwestern France.
A) It attached significant portions of Flanders to Henry's English and French holdings.
B) It gave Henry possession of the Capetian lands of northern-central France.
C) It brought Scotland and Ireland under English rule.
D) It gave the English crown possession of Aquitaine in southwestern France.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following territories was directly controlled by Henry II?
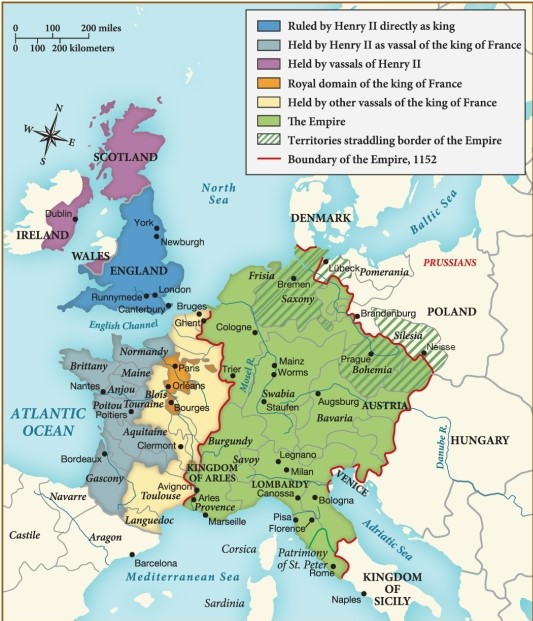
A) Scotland
B) England
C) Austria
D) Denmark

A) Scotland
B) England
C) Austria
D) Denmark

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How did the kings of England benefit from Henry II's judicial reforms?
A) The fees and fines collected by the courts went into the king's treasury.
B) The certitude of judgment and punishment made the English more law-abiding.
C) The work of the justices allowed the kings to devote themselves to the profitable administration of their French holdings.
D) The use of members of the nobility as justices made rebellion less likely.
A) The fees and fines collected by the courts went into the king's treasury.
B) The certitude of judgment and punishment made the English more law-abiding.
C) The work of the justices allowed the kings to devote themselves to the profitable administration of their French holdings.
D) The use of members of the nobility as justices made rebellion less likely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How was scutage a sign of the expansion of the commercial economy?
A) It came from taxes on the extremely profitable English wool trade.
B) It transformed personal service into a cash payment.
C) It challenged the tax-free status of church revenues.
D) It was a special tax on the building of new marketplaces.
A) It came from taxes on the extremely profitable English wool trade.
B) It transformed personal service into a cash payment.
C) It challenged the tax-free status of church revenues.
D) It was a special tax on the building of new marketplaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
King John angered his barons by
A) cementing an alliance with the king of France, whom they despised.
B) attempting to force his vassals to join him on the Fourth Crusade.
C) imposing higher scutages and feudal dues on his vassals.
D) having Thomas Becket murdered in his own cathedral.
A) cementing an alliance with the king of France, whom they despised.
B) attempting to force his vassals to join him on the Fourth Crusade.
C) imposing higher scutages and feudal dues on his vassals.
D) having Thomas Becket murdered in his own cathedral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Although the Magna Carta (1215) came to be viewed as the first document to guarantee the legal rights of all Englishmen, it was originally intended to serve as a(n)
A) enhancement of the rights of the English church against the English king.
B) guarantee of the customary rights of the English barons.
C) expansion of the customary powers of the English monarch in exchange for a guarantee of financial support from the barons and lesser nobility.
D) reduction of the rights of English serfs.
A) enhancement of the rights of the English church against the English king.
B) guarantee of the customary rights of the English barons.
C) expansion of the customary powers of the English monarch in exchange for a guarantee of financial support from the barons and lesser nobility.
D) reduction of the rights of English serfs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How did Philip II of France dramatically increase the size of his kingdom in 1204?
A) He confiscated the northern French territories held by King John of England.
B) He seized all church lands in the territories.
C) He used money he confiscated from the Jews to buy additional land.
D) He married Isabel of Burgundy and seized her father's dukedom when he died in 1204.
A) He confiscated the northern French territories held by King John of England.
B) He seized all church lands in the territories.
C) He used money he confiscated from the Jews to buy additional land.
D) He married Isabel of Burgundy and seized her father's dukedom when he died in 1204.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following was a lasting accomplishment of the French king Philip II?
A) A revision of his kingdom's tax code to make it more progressive despite vehement opposition from the French aristocracy
B) Philip's imposition of a royal administration based on extensive record keeping
C) The Edict of Toleration, which guaranteed to all of Philip's subjects-including Jews-protection from religious persecution
D) The establishment of schools for boys and girls that provided basic instruction in reading and writing
A) A revision of his kingdom's tax code to make it more progressive despite vehement opposition from the French aristocracy
B) Philip's imposition of a royal administration based on extensive record keeping
C) The Edict of Toleration, which guaranteed to all of Philip's subjects-including Jews-protection from religious persecution
D) The establishment of schools for boys and girls that provided basic instruction in reading and writing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
King Frederick I (Barbarossa) was elected by the German princes in order to do which of the following?
A) Consolidate their forces in preparation for war against the Lombards in northern Italy
B) Consolidate their defenses against invasion by the forces of Pope Alexander III (r. 1159-1181)
C) End the protracted warfare between the Staufers (or Hohenstaufens) and the Welfs
D) End the fighting over the leadership of the crusades against the Muslims in the east
A) Consolidate their forces in preparation for war against the Lombards in northern Italy
B) Consolidate their defenses against invasion by the forces of Pope Alexander III (r. 1159-1181)
C) End the protracted warfare between the Staufers (or Hohenstaufens) and the Welfs
D) End the fighting over the leadership of the crusades against the Muslims in the east

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Although Frederick I subdued the northern Italian communes, he began the reversal of his own fortune when he
A) set German magistrates over the cities; their arrogance and despotism infuriated commoners and aristocrats alike.
B) granted the Italian cities self-governing powers, thus allowing a reassertion of northern Italian political independence.
C) permitted Italian bishops governance of the communes on the condition that they agree to serve under his name.
D) asserted that all German emperors were also emperors of Rome; this assertion hardened papal resistance to Frederick and alienated the aristocrats of northern Italy as well.
A) set German magistrates over the cities; their arrogance and despotism infuriated commoners and aristocrats alike.
B) granted the Italian cities self-governing powers, thus allowing a reassertion of northern Italian political independence.
C) permitted Italian bishops governance of the communes on the condition that they agree to serve under his name.
D) asserted that all German emperors were also emperors of Rome; this assertion hardened papal resistance to Frederick and alienated the aristocrats of northern Italy as well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The defeat of Frederick Barbarossa at the battle of Legnano in 1176 marked the
A) end of the German Empire.
B) acquisition of all of Italy by the popes.
C) independence of northern Italian cities from the emperor.
D) rise of Venice to commercial supremacy.
A) end of the German Empire.
B) acquisition of all of Italy by the popes.
C) independence of northern Italian cities from the emperor.
D) rise of Venice to commercial supremacy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How was Frederick I able to acquire the lands of Burgundy and Provence?
A) By conquering the land
B) Through his marriage to Beatrice
C) Through diplomatic agreement
D) By receiving them as gifts
A) By conquering the land
B) Through his marriage to Beatrice
C) Through diplomatic agreement
D) By receiving them as gifts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the late twelfth century, states that had been formed in Hungary and Russia by powerful individual rulers began to fragment because, compared to England and France, they lacked
A) the blessing and support of the pope.
B) light infantry troops that could patrol the countryside and enforce the king's law.
C) clear mechanisms for royal succession.
D) a free merchant class whose profits enabled monarchs to pay for military campaigns.
A) the blessing and support of the pope.
B) light infantry troops that could patrol the countryside and enforce the king's law.
C) clear mechanisms for royal succession.
D) a free merchant class whose profits enabled monarchs to pay for military campaigns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What disastrous event in 1204 drastically and permanently undercut the power of the Byzantine Empire?
A) The battle of Manzikert
B) The siege of Constantinople by the Ottoman Turks
C) The capture of Constantinople by crusaders
D) The reconquest of Jerusalem by Saladin
A) The battle of Manzikert
B) The siege of Constantinople by the Ottoman Turks
C) The capture of Constantinople by crusaders
D) The reconquest of Jerusalem by Saladin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Literature and music changed on the European continent in the twelfth century once poets and songwriters began to
A) write their work in the vernacular.
B) address religious themes.
C) champion the achievements of hitherto exploited peasants.
D) discover the literature and music of ancient Greece.
A) write their work in the vernacular.
B) address religious themes.
C) champion the achievements of hitherto exploited peasants.
D) discover the literature and music of ancient Greece.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What language was troubadour poetry originally written in?
A) Languedoc, the vernacular of Aquitaine
B) Occitan, the vernacular of southern France
C) Greek
D) Latin
A) Languedoc, the vernacular of Aquitaine
B) Occitan, the vernacular of southern France
C) Greek
D) Latin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Although historians often rely on the term courtly love in describing the theme of the troubadours' poetry, the underlying theme of this literature is actually the
A) power of women.
B) courage of great heroes.
C) luxuries and amusements of court life.
D) waning of religious enthusiasm.
A) power of women.
B) courage of great heroes.
C) luxuries and amusements of court life.
D) waning of religious enthusiasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Modern scholars now believe that many aristocratic women in southern France in the twelfth century were
A) powerful lords in their own right.
B) valued mostly as aristocratic brides.
C) rarely interested in troubadour verse.
D) mostly interested in religious poetry.
A) powerful lords in their own right.
B) valued mostly as aristocratic brides.
C) rarely interested in troubadour verse.
D) mostly interested in religious poetry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the medieval courts, jongleurs were
A) musicians.
B) jugglers.
C) poets.
D) painters.
A) musicians.
B) jugglers.
C) poets.
D) painters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The primary function of epic poetry and chivalrous literature was to provide which of the following?
A) Diversion and entertainment for monks in otherwise rigorous monastic orders
B) A way for church leaders to tame the violent behavior of knights, which posed a danger to the well-being of others
C) Entertainment and dignity for the peasantry, who otherwise might have revolted
D) A common identity and code of behavior for knights and nobles in the midst of larger societal and military changes
A) Diversion and entertainment for monks in otherwise rigorous monastic orders
B) A way for church leaders to tame the violent behavior of knights, which posed a danger to the well-being of others
C) Entertainment and dignity for the peasantry, who otherwise might have revolted
D) A common identity and code of behavior for knights and nobles in the midst of larger societal and military changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The religious movements of the twelfth century
A) were critical of the emphasis placed on the Eucharist.
B) were initiated by clergymen and did not involve the laity.
C) did not retreat from society but actively involved urban populations.
D) tended not to appeal to women or the wealthy.
A) were critical of the emphasis placed on the Eucharist.
B) were initiated by clergymen and did not involve the laity.
C) did not retreat from society but actively involved urban populations.
D) tended not to appeal to women or the wealthy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Friar was a name used to describe the monks of which of the following monastic orders?
A) The Carthusians
B) The Franciscans
C) The Jesuits
D) The Benedictines
A) The Carthusians
B) The Franciscans
C) The Jesuits
D) The Benedictines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The followers of St. Francis of Assisi were known as mendicants, meaning that they
A) gave away all that they had to the poor.
B) begged.
C) performed manual labor.
D) repaired torn clothing.
A) gave away all that they had to the poor.
B) begged.
C) performed manual labor.
D) repaired torn clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The Beguines, who established informal pious communities,
A) worked to support themselves.
B) elected to live according to the Benedictine rule.
C) rejected emotional spirituality.
D) broke away from the Dominican order because of its growing opulence.
A) worked to support themselves.
B) elected to live according to the Benedictine rule.
C) rejected emotional spirituality.
D) broke away from the Dominican order because of its growing opulence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What did the twelfth-century heretics known as dualists believe?
A) That there were two churches-one public and false, the other secret and true
B) That the Bible permitted a man to have two wives
C) That there was no Holy Ghost, only the Father and the Son
D) That the universe was torn between good and evil forces
A) That there were two churches-one public and false, the other secret and true
B) That the Bible permitted a man to have two wives
C) That there was no Holy Ghost, only the Father and the Son
D) That the universe was torn between good and evil forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Why were the Cathars declared heretical, while the Franciscans, who were also concerned about the excess of wealth, were not?
A) The Cathars had invaded neighboring regions of France and destroyed symbols of church wealth like golden altars and silver chalices.
B) The Cathar elite engaged in scandalous sexual behavior, while the Franciscans did not.
C) The Cathars challenged the legitimacy and spiritual authority of the church hierarchy, while the Franciscans did not.
D) The Cathars had spread into more regions of Europe than had the Franciscans.
A) The Cathars had invaded neighboring regions of France and destroyed symbols of church wealth like golden altars and silver chalices.
B) The Cathar elite engaged in scandalous sexual behavior, while the Franciscans did not.
C) The Cathars challenged the legitimacy and spiritual authority of the church hierarchy, while the Franciscans did not.
D) The Cathars had spread into more regions of Europe than had the Franciscans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Although the Third Crusade (1189-1192) was intended to recapture Jerusalem after it fell to the armies of Saladin in 1187, what was the actual result of the crusade?
A) It put a final stop to European efforts to retake the Holy Land.
B) Islamic hegemony over the Holy Land would continue for hundreds of years.
C) The Holy Land wouldn't be retaken until the Fourth Crusade in 1225.
D) The Muslim forces were in turn defeated, and Jerusalem again became part of the Byzantine Empire.
A) It put a final stop to European efforts to retake the Holy Land.
B) Islamic hegemony over the Holy Land would continue for hundreds of years.
C) The Holy Land wouldn't be retaken until the Fourth Crusade in 1225.
D) The Muslim forces were in turn defeated, and Jerusalem again became part of the Byzantine Empire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The Fourth Crusade proved to be
A) an unmitigated disaster for Constantinople and the Byzantine Empire.
B) the most humiliating of the crusader campaigns because of the loss of the crusader states.
C) the very last of the European crusades to the Holy Land.
D) one of the most prestigious crusades because it was led by the most powerful monarchs in Europe.
A) an unmitigated disaster for Constantinople and the Byzantine Empire.
B) the most humiliating of the crusader campaigns because of the loss of the crusader states.
C) the very last of the European crusades to the Holy Land.
D) one of the most prestigious crusades because it was led by the most powerful monarchs in Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements regarding the Third Crusade is supported by this map?
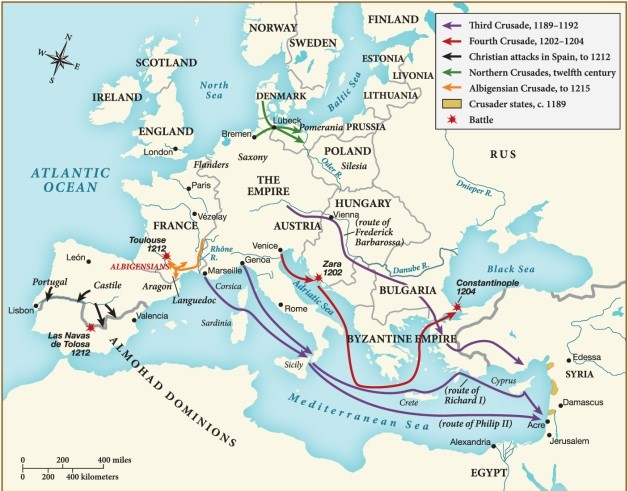
A) It was primarily contained to France.
B) It was carried out by crusader states against the Empire.
C) It sought to conquer Constantinople in the Byzantine Empire.
D) It traversed the Mediterranean Sea to target the Middle Eastern region.

A) It was primarily contained to France.
B) It was carried out by crusader states against the Empire.
C) It sought to conquer Constantinople in the Byzantine Empire.
D) It traversed the Mediterranean Sea to target the Middle Eastern region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
On receiving the news of the crusaders' sack of Constantinople (1204), the pope ordered them to
A) proceed immediately to Jerusalem.
B) give back the booty and submit to trial by the city fathers.
C) return the plunder and perform public penance for their sins under threat of excommunication.
D) remain there for a year to consolidate their gains.
A) proceed immediately to Jerusalem.
B) give back the booty and submit to trial by the city fathers.
C) return the plunder and perform public penance for their sins under threat of excommunication.
D) remain there for a year to consolidate their gains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The Dominican order began as an order that sought to
A) reduce corruption in the papal court.
B) convert pagans in the Baltic and Slavic East.
C) minister to heretics in Europe.
D) accompany crusaders to the Holy Land.
A) reduce corruption in the papal court.
B) convert pagans in the Baltic and Slavic East.
C) minister to heretics in Europe.
D) accompany crusaders to the Holy Land.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When were Christians able to complete their reconquista of the Iberian peninsula?
A) In 1212, as a result of the battle of Las Navas de Tolosa
B) In the 1100s through the assistance of the southern French kings
C) Not until 1492
D) In the 1300s, after a plague had severely weakened the remaining Muslim kingdoms in the south of Spain
A) In 1212, as a result of the battle of Las Navas de Tolosa
B) In the 1100s through the assistance of the southern French kings
C) Not until 1492
D) In the 1300s, after a plague had severely weakened the remaining Muslim kingdoms in the south of Spain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following regions of Spain was under the control of Islam during the reconquest?
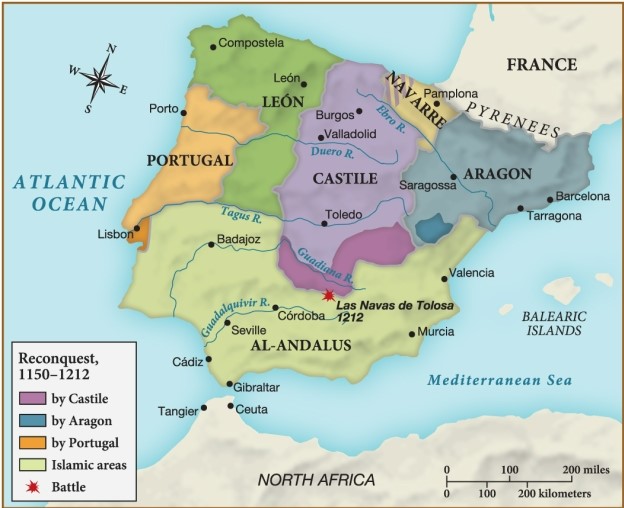
A) León
B) Aragon
C) Al-Andalus
D) Castile

A) León
B) Aragon
C) Al-Andalus
D) Castile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Based on this map, which region of Spain had the greatest success during the reconquest in reclaiming territory from the Al-Andalus?
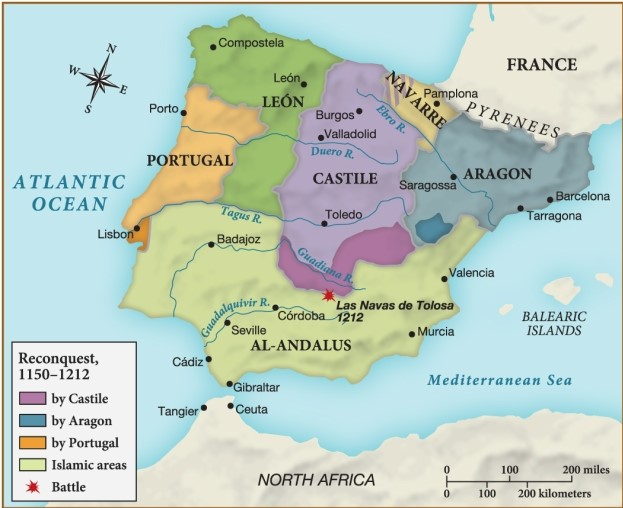
A) Castile
B) Navarre
C) Aragon
D) León

A) Castile
B) Navarre
C) Aragon
D) León

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The Northern Crusades, although less well known than the crusades to the Holy Land, produced longer lasting results, such as the
A) Germanization of the northern lands along the Baltic Sea.
B) Christianization of the land that would become Denmark.
C) rolling back of the Greek Orthodox church as a strong regional power.
D) withdrawal of northern European powers from further crusades to the Holy Land.
A) Germanization of the northern lands along the Baltic Sea.
B) Christianization of the land that would become Denmark.
C) rolling back of the Greek Orthodox church as a strong regional power.
D) withdrawal of northern European powers from further crusades to the Holy Land.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How did the Slavic ruling classes benefit from the Northern Crusades?
A) By converting to Christianity and profiting from other crusades further to the east
B) By joining in the crusades in the Middle East
C) By launching crusades against orthodox Christians to the east
D) By acquiring precious metals from the papacy as a reward for their conversion
A) By converting to Christianity and profiting from other crusades further to the east
B) By joining in the crusades in the Middle East
C) By launching crusades against orthodox Christians to the east
D) By acquiring precious metals from the papacy as a reward for their conversion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following statements is justified by this map?
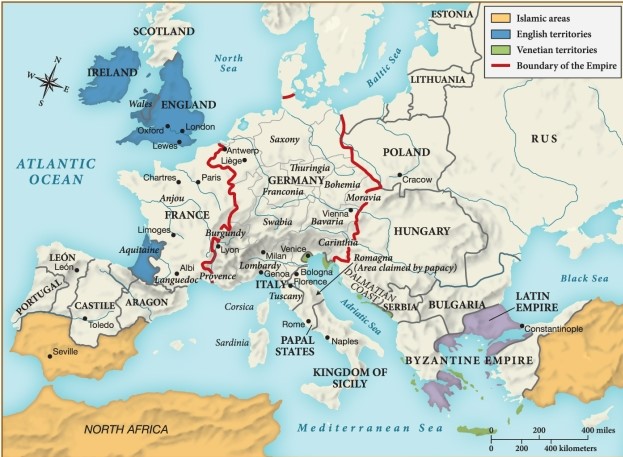
A) By about 1215, the Empire had lost significant ground to the Venetians.
B) By about 1215, most of France had come under control of the English by way of strategic marriages.
C) By about 1215, areas under Islamic influence were primarily isolated to North Africa and the Middle East.
D) By about 1215, the Byzantine Empire was slowly encroaching on eastern European territory sought by Germany.

A) By about 1215, the Empire had lost significant ground to the Venetians.
B) By about 1215, most of France had come under control of the English by way of strategic marriages.
C) By about 1215, areas under Islamic influence were primarily isolated to North Africa and the Middle East.
D) By about 1215, the Byzantine Empire was slowly encroaching on eastern European territory sought by Germany.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



