Deck 15: Vaccination, Immunoassays, and Immune Disorders
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/74
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Vaccination, Immunoassays, and Immune Disorders
1
A vaccination _________________. (Select all that apply)
A) is a simple method of altering an immune response
B) protects against pathogens for which there aren't effective treatments
C) is the administration of a virulent antigen to stimulate an adaptive response
D) allows a prompts protective secondary response to subsequent pathogen exposures
A) is a simple method of altering an immune response
B) protects against pathogens for which there aren't effective treatments
C) is the administration of a virulent antigen to stimulate an adaptive response
D) allows a prompts protective secondary response to subsequent pathogen exposures
A,B,D
2
The first forms of artificially acquired active immunity _____________. (Select all that apply)
A) were practiced by the Chinese over 3000 years ago
B) were introduced by Egyptian physicians 5000 years ago
C) provided protection against smallpox through variolation
D) provided protection against measles through inhalation of powdered scabs
A) were practiced by the Chinese over 3000 years ago
B) were introduced by Egyptian physicians 5000 years ago
C) provided protection against smallpox through variolation
D) provided protection against measles through inhalation of powdered scabs
A,C
3
What problems could be encountered when practicing variolation to protect against smallpox? (Select all that apply)
A) approximately 1% of patients developed active smallpox disease and died
B) some patients suffered an allergic reaction to the variolation process
C) variolation is only effective in younger people
D) while variolated patients were developing their immunity, they were highly contagious and represented an epidemic threat
A) approximately 1% of patients developed active smallpox disease and died
B) some patients suffered an allergic reaction to the variolation process
C) variolation is only effective in younger people
D) while variolated patients were developing their immunity, they were highly contagious and represented an epidemic threat
A,D
4
How did Edward Jenner provide artificially acquired active immunity against smallpox?
A) He had patients inhale powder made by grinding smallpox scabs.
B) He inoculated patients by scratching them with a needle covered in the fluid from smallpox blisters.
C) He inoculated patients by scratching them with a needle covered in the fluid from cowpox blisters.
D) He insisted on inoculating all family members to establish herd immunity.
A) He had patients inhale powder made by grinding smallpox scabs.
B) He inoculated patients by scratching them with a needle covered in the fluid from smallpox blisters.
C) He inoculated patients by scratching them with a needle covered in the fluid from cowpox blisters.
D) He insisted on inoculating all family members to establish herd immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Jenner's new procedure for establishing artificially acquired active immunity against smallpox, __________. (Select all that apply)
A) is known as vaccination
B) was safer than variolation because it did not use material from the smallpox virus
C) was effective because the cowpox and smallpox viruses share common epitopes
D) used cowpox virus to activate the immune system and generate memory cells to attack subsequently invading smallpox viruses
A) is known as vaccination
B) was safer than variolation because it did not use material from the smallpox virus
C) was effective because the cowpox and smallpox viruses share common epitopes
D) used cowpox virus to activate the immune system and generate memory cells to attack subsequently invading smallpox viruses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is NOT a quality of a successful modern vaccine?
A) Activation of both humoral and cell-mediated responses
B) Provide short-term memory response for initial immunity
C) Designed to cause minimal side effects or discomfort
D) Full and lifelong immunity without the need for boosters
A) Activation of both humoral and cell-mediated responses
B) Provide short-term memory response for initial immunity
C) Designed to cause minimal side effects or discomfort
D) Full and lifelong immunity without the need for boosters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why does the injection of a viral pathogen weakened to prevent causing the infection, still provide long-term immunity in a patient? (Select all that apply)
A) the epitopes of a weakened viral pathogen are still able to bind lymphocyte receptors
B) the weakened viral pathogen is able to generate TC cells
C) the weakened viral pathogen will generate the specific memory cells needed for lifelong immunity
D) weakened viral pathogens trigger TR cell activity
A) the epitopes of a weakened viral pathogen are still able to bind lymphocyte receptors
B) the weakened viral pathogen is able to generate TC cells
C) the weakened viral pathogen will generate the specific memory cells needed for lifelong immunity
D) weakened viral pathogens trigger TR cell activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a disadvantage of using live vaccines?
A) Live vaccines provide lifelong pathogen protection
B) Live vaccines are stored under special conditions to maintain the living cells
C) Live vaccines produce extremely strong cell-mediated responses
D) Live vaccines have a low risk of mutating from an attenuated form back to the virulence form of the pathogen
A) Live vaccines provide lifelong pathogen protection
B) Live vaccines are stored under special conditions to maintain the living cells
C) Live vaccines produce extremely strong cell-mediated responses
D) Live vaccines have a low risk of mutating from an attenuated form back to the virulence form of the pathogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
______________vaccines contain attenuated toxins and require regular boosters.
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Toxoid
D) Conjugated
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Toxoid
D) Conjugated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
______________vaccines contain live whole pathogens in a weakened form.
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Toxoid
D) Conjugated
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Toxoid
D) Conjugated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
______________vaccines contain pathogen fragments with high immunogenicity.
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Subunit
D) Conjugated
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Subunit
D) Conjugated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
______________vaccines contain attenuated pathogens incapable of reproducing so multiple doses are required and they are safe for immunocompromised patients.
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Subunit
D) Conjugated
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Subunit
D) Conjugated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
DNA or nucleic acid vaccines represent the vaccines of the future because ____________. (Select all that apply)
A) they are highly effective against pathogens with low mutation rates
B) the complementary DNA created enters the nuclei of host cells and leads to both antibody and cell-mediated protection
C) they are administered with a gene gun into muscle tissues, eliminating the use of needles
D) they do not require refrigeration
A) they are highly effective against pathogens with low mutation rates
B) the complementary DNA created enters the nuclei of host cells and leads to both antibody and cell-mediated protection
C) they are administered with a gene gun into muscle tissues, eliminating the use of needles
D) they do not require refrigeration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
______________vaccines are among the safest of all vaccine types.
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Subunit
D) Conjugated
A) Live attenuated
B) Inactivated
C) Subunit
D) Conjugated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The flu vaccine is often administered as an inhaled mist. This is a highly effective practice as the vaccine antigen immediately encounters the lymphocytes in the _______________.
A) BALT
B) spleen
C) tonsils
D) GALT
A) BALT
B) spleen
C) tonsils
D) GALT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Type I diabetic patients are often prioritized for flu immunizations. They are considered immune compromised because hyperglycemia above 150 mg/dl can ______________. (Select all that apply)
A) increase lymphocyte apoptosis
B) suppress antibody production
C) reduce the phagocytic ability of neutrophils
D) promote neutrophil chemotaxis
A) increase lymphocyte apoptosis
B) suppress antibody production
C) reduce the phagocytic ability of neutrophils
D) promote neutrophil chemotaxis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
One of the greatest achievements of modern medicine in the U.S. has been the elimination of childhood diseases. Unfortunately, a recent decline in vaccination rates has led to the rebound of some infections, the most prominent in 2018 being _________________.
A) measles
B) mumps
C) diphtheria
D) pertussis
A) measles
B) mumps
C) diphtheria
D) pertussis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
__________ is the inadvertent protection of unimmunized individuals because most of the population is immunized so the pathogen lacks a reservoir.
A) Adaptive immunity
B) Innate immunity
C) Passive immunity
D) Herd immunity
A) Adaptive immunity
B) Innate immunity
C) Passive immunity
D) Herd immunity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A free rider ___________________.
A) is a patient who has adaptive immunity to a pathogen because they have survived an initial infection
B) receives vaccinations at no cost as part of the Affordable Care Act
C) is unvaccinated but receives the benefit of infection protection because of herd immunity
D) is a patient who is unable to reach the herd immunity threshold
A) is a patient who has adaptive immunity to a pathogen because they have survived an initial infection
B) receives vaccinations at no cost as part of the Affordable Care Act
C) is unvaccinated but receives the benefit of infection protection because of herd immunity
D) is a patient who is unable to reach the herd immunity threshold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Pain-free, needle-free modern immunization options include ___________________. (Select all that apply)
A) using a patch of short microneedles
B) using a gene gun to inject cDNA particles into host tissues with a quick puff of helium gas
C) nasal spray mists to protect against measles by activating lymphocytes in the host nodes
D) consumption of genetically modified foods designed to deliver antigens to activate lymphocytes in the GALT
A) using a patch of short microneedles
B) using a gene gun to inject cDNA particles into host tissues with a quick puff of helium gas
C) nasal spray mists to protect against measles by activating lymphocytes in the host nodes
D) consumption of genetically modified foods designed to deliver antigens to activate lymphocytes in the GALT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Reported side effects of vaccines are relatively rare because of modern safety standards. Patient complaints about vaccines are usually limited to _________________. (Select all that apply)
A) minor discomfort at the injection site for up to 48 hours
B) allergic reaction to the vaccine
C) the inconvenience of booster injections
D) perceived ineffectiveness of the vaccine
A) minor discomfort at the injection site for up to 48 hours
B) allergic reaction to the vaccine
C) the inconvenience of booster injections
D) perceived ineffectiveness of the vaccine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Dr. Andrew Wakefield fraudulently published a manuscript claiming a connection between children receiving the MMR vaccine and the onset of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). As a result, ______________. (Select all that apply)
A) there has been a steady increase in the number of ASD diagnoses due to MMR vaccination
B) some parents have refused to vaccinate their children, fearing they will put them at risk of developing ASD
C) the prevalence of measles and other preventable childhood diseases is on the rise
D) Wakefield has completed addition research to validate his findings
A) there has been a steady increase in the number of ASD diagnoses due to MMR vaccination
B) some parents have refused to vaccinate their children, fearing they will put them at risk of developing ASD
C) the prevalence of measles and other preventable childhood diseases is on the rise
D) Wakefield has completed addition research to validate his findings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Patients age 65+ should receive the following immunizations:______________________ (Select all that apply)
A) Human papillomavirus vaccine
B) Influenza vaccine
C) Zoster vaccine
D) Rotavirus vaccine
A) Human papillomavirus vaccine
B) Influenza vaccine
C) Zoster vaccine
D) Rotavirus vaccine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Vaccine testing on different age groups and cohorts with underlying medical conditions, like asthma, occurs during the ________ stage of development.
A) exploratory
B) regulatory
C) phase I clinical trial
D) phase III clinical trial
A) exploratory
B) regulatory
C) phase I clinical trial
D) phase III clinical trial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
During a major medical crisis like the COVID-19 pandemic, the Food and Drug Administration can compress the timeline of vaccine development by issuing a(n) ______________.
A) Vaccine Acceleration Protocol
B) Emergency Use Authorization
C) CDC Override Authorization
D) Pandemic Preparedness Plan
A) Vaccine Acceleration Protocol
B) Emergency Use Authorization
C) CDC Override Authorization
D) Pandemic Preparedness Plan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Potential immunization strategies for the safe, rapid development of a COVID-19 vaccine include___________. (Select all that apply)
A) using just the spikes from SARS-CoV-2 plus an adjuvant
B) delivering SARS-CoV-2 proteins in previously approved viral vectors like adenovirus type 26
C) introducing SARS-C0V-2 spikes by lipid nanoparticles
D) repurposing approved vaccines like MMR to boost the host's general immune response to fight SARS-CoV-2
A) using just the spikes from SARS-CoV-2 plus an adjuvant
B) delivering SARS-CoV-2 proteins in previously approved viral vectors like adenovirus type 26
C) introducing SARS-C0V-2 spikes by lipid nanoparticles
D) repurposing approved vaccines like MMR to boost the host's general immune response to fight SARS-CoV-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Immunoassays ______________. (Select all that apply)
A) can be used to confirm the presence of specific macromolecules like antigens and antibodies
B) are antigen-based tests
C) can accurately quantify very small amounts of macromolecules
D) are part of the field of serology
A) can be used to confirm the presence of specific macromolecules like antigens and antibodies
B) are antigen-based tests
C) can accurately quantify very small amounts of macromolecules
D) are part of the field of serology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Monoclonal antibodies are ______________. (Select all that apply)
A) identical antibodies all secreted by the same B cell or its clones
B) excellent diagnostic tools in the clinical setting
C) routinely used by research scientists to identify and quantify specific macromolecules in the laboratory
D) are predominantly IgM
A) identical antibodies all secreted by the same B cell or its clones
B) excellent diagnostic tools in the clinical setting
C) routinely used by research scientists to identify and quantify specific macromolecules in the laboratory
D) are predominantly IgM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Indicate the correct order of steps for the production of monoclonal antibodies.
1) Hybridomas transferred to small wells and tested for antigen reactivity
2) B cells are harvested from the spleen of a mouse injected with antigen
3) Mixture of B cells, myeloma cells, and hybridomas are transferred to media that promotes only hybridoma survival
4) Long-lived hybridomas are grown in culture and their monoclonal antibodies collected for use
5) B cells mixed with multiple myeloma cells in special growth media to encourage hybridoma formation
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 2, 5, 3, 1, 4
C) 2, 3, 5, 1, 4
D) 3, 5, 2, 4, 1
1) Hybridomas transferred to small wells and tested for antigen reactivity
2) B cells are harvested from the spleen of a mouse injected with antigen
3) Mixture of B cells, myeloma cells, and hybridomas are transferred to media that promotes only hybridoma survival
4) Long-lived hybridomas are grown in culture and their monoclonal antibodies collected for use
5) B cells mixed with multiple myeloma cells in special growth media to encourage hybridoma formation
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 2, 5, 3, 1, 4
C) 2, 3, 5, 1, 4
D) 3, 5, 2, 4, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How can anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies be used to fight the malignant cells of Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma if both healthy and cancerous B cells possess CD20 on their surfaces?
A) The monoclonal antibodies have a higher affinity for binding the malignant B cells, allowing them to be selectively eliminated.
B) Both groups of B cells are destroyed by the monoclonal antibodies, but host damage is minimal as stem cells are unaffected and quickly generate more healthy B cells.
C) The monoclonal antibodies preferentially bind and destroy the stem cells responsible for producing the malignant B cells.
D) The monoclonal antibodies effectively eliminate malignant and healthy B cells, but the host is not negatively affected because their level of T cells increases to compensate for the lost B cells.
A) The monoclonal antibodies have a higher affinity for binding the malignant B cells, allowing them to be selectively eliminated.
B) Both groups of B cells are destroyed by the monoclonal antibodies, but host damage is minimal as stem cells are unaffected and quickly generate more healthy B cells.
C) The monoclonal antibodies preferentially bind and destroy the stem cells responsible for producing the malignant B cells.
D) The monoclonal antibodies effectively eliminate malignant and healthy B cells, but the host is not negatively affected because their level of T cells increases to compensate for the lost B cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Precipitation reactions _________________________. (Select all that apply)
A) are the newest form of immunoassays
B) form dense, lattice-like complexes of antigens/antibodies that settle out of solution providing a clear visual positive result
C) use large amounts of reactants
D) are the most popular type of immunoassay in clinical laboratories
A) are the newest form of immunoassays
B) form dense, lattice-like complexes of antigens/antibodies that settle out of solution providing a clear visual positive result
C) use large amounts of reactants
D) are the most popular type of immunoassay in clinical laboratories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Determine the titer for the results of the agglutination assay shown below.
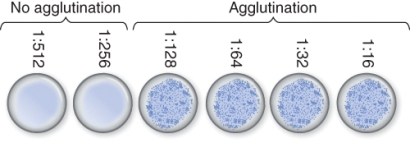
A) 1:512
B) 1:128v
C) 521
D) 128

A) 1:512
B) 1:128v
C) 521
D) 128

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What type of agglutination reaction is demonstrated below?
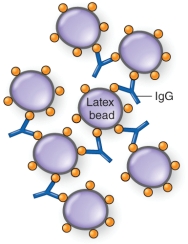
A) direct agglutination
B) indirect agglutination
C) passive agglutination
D) modified passive agglutination

A) direct agglutination
B) indirect agglutination
C) passive agglutination
D) modified passive agglutination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
ABO blood typing is determined by performing a ___________ test.
A) precipitation
B) direct agglutination
C) passive agglutination
D) ELISA
A) precipitation
B) direct agglutination
C) passive agglutination
D) ELISA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Neutralization _______________________. (Select all that apply)
A) is a cell-mediated immunoassay
B) was used more than 100 years ago to protect patients from the tetanospasmin toxin secreted by Clostridium tetani
C) is currently being used to help COVID-19 patients by administering convalescent plasma
D) is the process of antibody binding to a harmful antigen to prevent damaging effects on the host
A) is a cell-mediated immunoassay
B) was used more than 100 years ago to protect patients from the tetanospasmin toxin secreted by Clostridium tetani
C) is currently being used to help COVID-19 patients by administering convalescent plasma
D) is the process of antibody binding to a harmful antigen to prevent damaging effects on the host

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Antibody probes, made by conjugating an enzyme that generates a colored product to the FC portion of a specific antibody, provide positive visual endpoints in immunoassays such as _________________. (Select all that apply)
A) immunodot assays
B) ELISAs
C) Western blots
D) fluorescent antibody assays
A) immunodot assays
B) ELISAs
C) Western blots
D) fluorescent antibody assays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Performing an ELISA for diagnostic purposes in the clinical laboratory is beneficial because ________. (Select all that apply)
A) it is a quantitative assay
B) it lends itself to high-volume testing
C) although it lacks sensitivity, the test is quick and easy to perform
D) it can be modified to diagnose autoimmune disorders and to screen for HIV
A) it is a quantitative assay
B) it lends itself to high-volume testing
C) although it lacks sensitivity, the test is quick and easy to perform
D) it can be modified to diagnose autoimmune disorders and to screen for HIV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Fluorescent antibody assays ________________. (Select all that apply)
A) use an enzyme-conjugated antibody probe
B) are considered to be direct tests when the antibody probe binds the suspected pathogen
C) are considered to be indirect tests when the antibody probe binds another antibody
D) are routinely used to diagnose HIV infection
A) use an enzyme-conjugated antibody probe
B) are considered to be direct tests when the antibody probe binds the suspected pathogen
C) are considered to be indirect tests when the antibody probe binds another antibody
D) are routinely used to diagnose HIV infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The confirmatory assay used to provide a definitive HIV diagnosis is the ___________.
A) immunodot assay
B) ELISA
C) Western blot
D) indirect fluorescence assay
A) immunodot assay
B) ELISA
C) Western blot
D) indirect fluorescence assay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Asthma, hay fever, and hive are all examples of a Type _____ hypersensitivity.
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A type I hypersensitivity response is mediated by ____________.
A) IgM
B) IgG
C) IgA
D) IgE
A) IgM
B) IgG
C) IgA
D) IgE

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Urticaria is characterized by ______________.
A) an inflammatory response of the nasal epithelium leading to congestion, runny nose and sneezing
B) an inflammatory response causing a narrowing of the bronchioles resulting in shortness of breath
C) hives that itch intensely
D) a systemic allergic response leading to shock
A) an inflammatory response of the nasal epithelium leading to congestion, runny nose and sneezing
B) an inflammatory response causing a narrowing of the bronchioles resulting in shortness of breath
C) hives that itch intensely
D) a systemic allergic response leading to shock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Atopy is best described as ____________________. (Select all that apply)
A) a genetic predisposition to allergic responses
B) a medical condition that requires desensitization treatments
C) a type II hypersensitive response
D) responsible for causing frequent inflammation, coughing, and gastrointestinal problems that are sometimes mistaken for infection
A) a genetic predisposition to allergic responses
B) a medical condition that requires desensitization treatments
C) a type II hypersensitive response
D) responsible for causing frequent inflammation, coughing, and gastrointestinal problems that are sometimes mistaken for infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Anaphylaxis ________________ (Select all that apply)
A) is a type IV hypersensitivity
B) is a severe immunodeficiency
C) is a medical emergency because patients experience bronchiole constriction and shock
D) is an example of immunologic tolerance
A) is a type IV hypersensitivity
B) is a severe immunodeficiency
C) is a medical emergency because patients experience bronchiole constriction and shock
D) is an example of immunologic tolerance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Although allergies cannot be cured, treatment options to minimize symptoms include ____________. (Select all that apply)
A) allergen removal from the patient's environment
B) administering graded allergen doses to shift host antibody production from IgG to IgM
C) administration of corticosteroids to inhibit lymphocyte activity and reduce IgE levels
D) the use of antihistamines or histamine blockers to prevent the intracellular signaling that causes allergy symptoms
A) allergen removal from the patient's environment
B) administering graded allergen doses to shift host antibody production from IgG to IgM
C) administration of corticosteroids to inhibit lymphocyte activity and reduce IgE levels
D) the use of antihistamines or histamine blockers to prevent the intracellular signaling that causes allergy symptoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What immunoglobulins participate in Type II cytotoxic hypersensitivities?
A) IgA
B) IgA and IgM
C) IgM and IgG
D) IgG
A) IgA
B) IgA and IgM
C) IgM and IgG
D) IgG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A patient with Type O blood ___________________. (Select all that apply)
A) has no A or B surface antigens present on their RBCs
B) has both A and B surface antigens present on their RBCs
C) is known as the universal recipient because they can receive any blood type
D) possesses both anti-A and anti-B antibodies in their serum
A) has no A or B surface antigens present on their RBCs
B) has both A and B surface antigens present on their RBCs
C) is known as the universal recipient because they can receive any blood type
D) possesses both anti-A and anti-B antibodies in their serum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following blood types has no antibodies present in the serum?
A) Type A
B) Type B
C) Type AB
D) Type O
A) Type A
B) Type B
C) Type AB
D) Type O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following diseases is NOT associated with Type II cytotoxic hypersensitivity?
A) thrombocytopenic purpura
B) Goodpasture's syndrome
C) Type II diabetes
D) Myasthenia gravis
A) thrombocytopenic purpura
B) Goodpasture's syndrome
C) Type II diabetes
D) Myasthenia gravis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following pairings can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)?
A) Rh- mother carrying a Rh- fetus
B) Rh+ mother carrying a Rh- fetus
C) Rh- mother carrying a Rh+ fetus
D) Rh+ mother carrying a Rh+ fetus
A) Rh- mother carrying a Rh- fetus
B) Rh+ mother carrying a Rh- fetus
C) Rh- mother carrying a Rh+ fetus
D) Rh+ mother carrying a Rh+ fetus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Rh-negative mothers who are in their second or subsequent pregnancy will often receive this treatment to prevent hemolytic disease of the newborn?
A) An Rh immune globulin, or antiserum directed against Rh-positive antibodies, is administered during pregnancy and within 72 hours of delivery.
B) An Rh immune globulin, or antiserum directed against Rh-negative antibodies, is administered during pregnancy and within 72 hours of delivery.
C) A series of graded injections of Rh-positive antigen is administered during pregnancy to switch anti-Rh IgG (which crosses the placenta) to anti-Rh IgM (which cannot cross the placenta).
D) A series of graded injections of Rh-negative antigen is administered during pregnancy to switch anti-Rh IgG (which crosses the placenta) to anti-Rh IgM (which cannot cross the placenta).
A) An Rh immune globulin, or antiserum directed against Rh-positive antibodies, is administered during pregnancy and within 72 hours of delivery.
B) An Rh immune globulin, or antiserum directed against Rh-negative antibodies, is administered during pregnancy and within 72 hours of delivery.
C) A series of graded injections of Rh-positive antigen is administered during pregnancy to switch anti-Rh IgG (which crosses the placenta) to anti-Rh IgM (which cannot cross the placenta).
D) A series of graded injections of Rh-negative antigen is administered during pregnancy to switch anti-Rh IgG (which crosses the placenta) to anti-Rh IgM (which cannot cross the placenta).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A newborn suffering from erythroblastosis fetalis may be treated _________________. (Select all that apply)
A) with a complete transfusion
B) by administering anti-Rh positive antisera
C) by phototherapy to degrade the excess bilirubin causing jaundice
D) by infusing plasma
A) with a complete transfusion
B) by administering anti-Rh positive antisera
C) by phototherapy to degrade the excess bilirubin causing jaundice
D) by infusing plasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Myasthenia gravis, a Type II hypersensitivity, is characterized by ___________________.
A) purple patches due to excessive internal bleeding
B) glomerulonephritis and impaired ultrafiltration
C) muscle weakness and fatigue
D) a dramatically escalated metabolic rate
A) purple patches due to excessive internal bleeding
B) glomerulonephritis and impaired ultrafiltration
C) muscle weakness and fatigue
D) a dramatically escalated metabolic rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Graves' disease, a Type II hypersensitivity, is characterized by ___________________.
A) purple patches due to excessive internal bleeding
B) glomerulonephritis and impaired ultrafiltration
C) muscle weakness and fatigue
D) a dramatically escalated metabolic rate
A) purple patches due to excessive internal bleeding
B) glomerulonephritis and impaired ultrafiltration
C) muscle weakness and fatigue
D) a dramatically escalated metabolic rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Goodpasture's syndrome, a Type II hypersensitivity, is characterized by ___________________.
A) purple patches due to excessive internal bleeding
B) glomerulonephritis and impaired ultrafiltration
C) muscle weakness and fatigue
D) a dramatically escalated metabolic rate
A) purple patches due to excessive internal bleeding
B) glomerulonephritis and impaired ultrafiltration
C) muscle weakness and fatigue
D) a dramatically escalated metabolic rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What immunoglobulins participate in Type III cytotoxic hypersensitivities?
A) IgA
B) IgA and IgM
C) IgM and IgG
D) IgG
A) IgA
B) IgA and IgM
C) IgM and IgG
D) IgG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Indicate the correct order of events leading to an Arthus reaction.
1) formation of immune complexes consisting of excess soluble antigen
2) lysosomal granules trigger an intense, localized response
3) damage to skin and accompanying blood vessels occurs
4) immune complexes settle out on the basement membrane of tissues
5) degranulation of neutrophils attempting to clear deposited immune complexes
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 1, 4, 5, 2, 3
C) 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
D) 5, 3, 1, 4, 2
1) formation of immune complexes consisting of excess soluble antigen
2) lysosomal granules trigger an intense, localized response
3) damage to skin and accompanying blood vessels occurs
4) immune complexes settle out on the basement membrane of tissues
5) degranulation of neutrophils attempting to clear deposited immune complexes
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 1, 4, 5, 2, 3
C) 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
D) 5, 3, 1, 4, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following features does NOT characterize serum sickness?
A) results from treating a patient with antisera
B) represents a Type III hypersensitivity
C) results in chronic joint pain, rash, renal failure, and edema
D) symptoms tend to be localized
A) results from treating a patient with antisera
B) represents a Type III hypersensitivity
C) results in chronic joint pain, rash, renal failure, and edema
D) symptoms tend to be localized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
_____________ is an example of a Type III hypersensitivity and an autoimmune disease.
A) contact dermatitis
B) anaphylaxis
C) rheumatoid arthritis
D) erythroblastosis fetalis
A) contact dermatitis
B) anaphylaxis
C) rheumatoid arthritis
D) erythroblastosis fetalis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Type IV delayed cell-mediated hypersensitivities result in host damage due to the action of _______________. (Select all that apply)
A) activated B cells
B) activated T cells
C) NK cells
D) phagocytes
A) activated B cells
B) activated T cells
C) NK cells
D) phagocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The photo below shows a patient suffering from _________ which is a type _____ hypersensitivity.
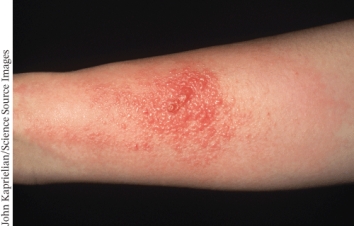
A) the Arthus reaction; III
B) Lupus; II
C) contact dermatitis; IV
D) urticaria; I

A) the Arthus reaction; III
B) Lupus; II
C) contact dermatitis; IV
D) urticaria; I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Contact dermatitis ________________. (Select all that apply)
A) is an immediate hypersensitive response with symptoms appearing within minutes of exposure to the sensitizing antigen
B) is an antibody-mediated hypersensitive response
C) is the result of a hapten binding to a host skin protein triggering a damaging inflammatory response
D) may result from exposure to common materials like latex, metals, and cosmetic components
A) is an immediate hypersensitive response with symptoms appearing within minutes of exposure to the sensitizing antigen
B) is an antibody-mediated hypersensitive response
C) is the result of a hapten binding to a host skin protein triggering a damaging inflammatory response
D) may result from exposure to common materials like latex, metals, and cosmetic components

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Transplant rejection occurs when donor tissue displays a foreign Class _____ MHC molecule leading to their destruction by ____________________.
A) I; TC cells
B) II; TC cells
C) I; TH cells
D) II; TH cells
A) I; TC cells
B) II; TC cells
C) I; TH cells
D) II; TH cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
____________ is an example of an organ-specific autoimmune disease.
A) Serum sickness
B) Type I diabetes
C) Lupus
D) Pernicious anemia
A) Serum sickness
B) Type I diabetes
C) Lupus
D) Pernicious anemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Immunologists believe autoimmune diseases may originate because __________. (Select all that apply)
A) of a genetic predisposition
B) of an error in the clonal selection process
C) a bacterial infection leads to an alteration of self-antigens on host cell plasma membranes
D) of abnormally high levels of vitamin D
A) of a genetic predisposition
B) of an error in the clonal selection process
C) a bacterial infection leads to an alteration of self-antigens on host cell plasma membranes
D) of abnormally high levels of vitamin D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
___________ is an autoimmune disease that manifests with weakness, hyperpigmentation, loss of hair and depression as the adrenal cortex is attacked.
A) Addison's disease
B) Multiple sclerosis
C) Graves' disease
D) Goodpasture's syndrome
A) Addison's disease
B) Multiple sclerosis
C) Graves' disease
D) Goodpasture's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
___________ is an autoimmune disease characterized by cold sensitivity, weight gain, fatigue, and joint pain.
A) Type I diabetes
B) Multiple sclerosis
C) Hashimoto's thyroiditis
D) Goodpasture's syndrome
A) Type I diabetes
B) Multiple sclerosis
C) Hashimoto's thyroiditis
D) Goodpasture's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells result in hyperglycemia, frequent urination, weight loss, and blurred vision in _____________.
A) Type I diabetes
B) Multiple sclerosis
C) Hashimoto's thyroiditis
D) Goodpasture's syndrome
A) Type I diabetes
B) Multiple sclerosis
C) Hashimoto's thyroiditis
D) Goodpasture's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Numbness/weakness in limbs, visual impairment, tremors, and slurred speech result as the myelin sheath is damaged by autoimmune attack in ______________.
A) Type I diabetes
B) Multiple sclerosis
C) Hashimoto's thyroiditis
D) Goodpasture's syndrome
A) Type I diabetes
B) Multiple sclerosis
C) Hashimoto's thyroiditis
D) Goodpasture's syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
___________ is a primary immunodeficiency in which T cells are defective, resulting in abnormal thymus development, wasting of the body, and unusual facial features.
A) Bruton's agammaglobulinemia
B) DiGeorge syndrome
C) Chronic granulomatouos disease
D) Severe combined immunodeficiency
A) Bruton's agammaglobulinemia
B) DiGeorge syndrome
C) Chronic granulomatouos disease
D) Severe combined immunodeficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
___________ is a primary immunodeficiency in which both B and T cells are defective.
A) Bruton's agammaglobulinemia
B) DiGeorge syndrome
C) Chronic granulomatouos disease
D) Severe combined immunodeficiency
A) Bruton's agammaglobulinemia
B) DiGeorge syndrome
C) Chronic granulomatouos disease
D) Severe combined immunodeficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
_______ is an example of a secondary immunodeficiency disorder.
A) Adenosine deaminase deficiency
B) DiGeorge syndrome
C) Chronic granulomatouos disease
D) Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
A) Adenosine deaminase deficiency
B) DiGeorge syndrome
C) Chronic granulomatouos disease
D) Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Patients with a humoral immunodeficiency suffer from _______ opportunistic infections.
A) viral
B) intracellular
C) bacterial
D) fungal
A) viral
B) intracellular
C) bacterial
D) fungal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Patients with SCID may be successfully treated with __________.
A) adenosine deaminase
B) gene therapy
C) a bone marrow transplant
D) convalescent plasma
A) adenosine deaminase
B) gene therapy
C) a bone marrow transplant
D) convalescent plasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



