Deck 12: Vestibular Sensation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/63
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Vestibular Sensation
1
The _______ system is the collective term for neurons in cranial nerve VIII and the set of organs located in the inner ear that sense head motion and head orientation with respect to gravity.
A) orientation
B) balance
C) vestibular
D) auditory
E) gravity sensation
A) orientation
B) balance
C) vestibular
D) auditory
E) gravity sensation
vestibular
2
Which five organs make up the vestibular system?
A) One semicircular canal and four otolith organs
B) Two semicircular canals and three otolith organs
C) Three semicircular canals and two otolith organs
D) Four semicircular canals and one otolith organ
E) Five semicircular canals
A) One semicircular canal and four otolith organs
B) Two semicircular canals and three otolith organs
C) Three semicircular canals and two otolith organs
D) Four semicircular canals and one otolith organ
E) Five semicircular canals
Three semicircular canals and two otolith organs
3
This term describes an illusory sense of spinning.
A) Kinesthesis
B) Graviception
C) Balance
D) Vertigo
E) Yaw
A) Kinesthesis
B) Graviception
C) Balance
D) Vertigo
E) Yaw
Vertigo
4
The _______ reflex helps us see visual stimuli clearly, even when the head is moving.
A) otolithic
B) semicircular
C) saccadic
D) tracking
E) vestibulo-ocular
A) otolithic
B) semicircular
C) saccadic
D) tracking
E) vestibulo-ocular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The reason that videos shot with handheld cameras seem so shaky and hard to follow is because when we see something with our own eyes, our _______ allows us to compensate for our own motion and maintain a steady image on the retina.
A) vection
B) vestibular-autonomic integration
C) vestibular-ocular reflex
D) sense of gravity
E) sense of linear acceleration
A) vection
B) vestibular-autonomic integration
C) vestibular-ocular reflex
D) sense of gravity
E) sense of linear acceleration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The _______ reflex is the term for eye movements that compensate for rotations of the head to maintain fixation on an object.
A) translational motion
B) angular motion
C) balance fixation
D) torsional motion
E) vestibulo-ocular
A) translational motion
B) angular motion
C) balance fixation
D) torsional motion
E) vestibulo-ocular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a person fixates on an object and then rotates her head to the right, the _______ reflex will cause her eyes to rotate to the left to maintain fixation.
A) vestibulo-ocular
B) torsional motion
C) translational motion
D) balance fixation
E) angular motion
A) vestibulo-ocular
B) torsional motion
C) translational motion
D) balance fixation
E) angular motion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The sense of _______ is comprised of three interacting sensory modalities: our sense of linear motion, angular motion, and tilt.
A) spatial awareness
B) spatial orientation
C) balance
D) movement
E) heading
A) spatial awareness
B) spatial orientation
C) balance
D) movement
E) heading

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
_______ flow inward to the central nervous system from sensors in the periphery, while _______ flow outward from the central nervous system to the periphery.
A) Afferent signals; efferent commands
B) Efferent commands; afferent signals
C) Kinesthetic signals; balance commands
D) Balance commands; kinesthetic signals
E) Amplitude signals; direction commands
A) Afferent signals; efferent commands
B) Efferent commands; afferent signals
C) Kinesthetic signals; balance commands
D) Balance commands; kinesthetic signals
E) Amplitude signals; direction commands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The neural processes of posture control by which weight is evenly distributed, enabling us to remain upright and stable, is called
A) the active sense.
B) the vestibulo-ocular reflex.
C) kinesthesis.
D) balance.
E) the passive sense.
A) the active sense.
B) the vestibulo-ocular reflex.
C) kinesthesis.
D) balance.
E) the passive sense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
_______ combines information from efferent commands (such as motor commands to turn the head) and afferent signals (such as the sense of angular motion) to improve our vestibular sense.
A) Vection
B) Graviception
C) Vertigo
D) Illusory self-motion
E) Active sensing
A) Vection
B) Graviception
C) Vertigo
D) Illusory self-motion
E) Active sensing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If you stand on the side of a hill you experience a tilt sensation which can also be described as
A) orientation.
B) balance.
C) graviception.
D) angular motion.
E) linear motion.
A) orientation.
B) balance.
C) graviception.
D) angular motion.
E) linear motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following, according to Gibson (1966), provides a "stable permanent framework of the environment" that provides an "underlying and ceaseless awareness of what is permanent in the world"?
A) Vection
B) Graviception
C) Vertigo
D) Illusory self-motion
E) Balance
A) Vection
B) Graviception
C) Vertigo
D) Illusory self-motion
E) Balance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
_______ are the toroidal tubes in the vestibular system that sense angular motion.
A) Otolith organs
B) Ossicles
C) Cochlea
D) Semicircular canals
E) Saccules
A) Otolith organs
B) Ossicles
C) Cochlea
D) Semicircular canals
E) Saccules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If you close your eyes and rotate your head from side to side, as if to say "no," you are experiencing _______, which is registered by your _______.
A) angular motion; otolith organs
B) angular motion; semicircular canals
C) linear motion; otolith organs
D) linear motion; semicircular canals
E) tilt; otolith organs
A) angular motion; otolith organs
B) angular motion; semicircular canals
C) linear motion; otolith organs
D) linear motion; semicircular canals
E) tilt; otolith organs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If you close your eyes and tilt your left ear towards your left shoulder, you are experiencing _______, which is registered by your _______.
A) angular motion; otolith organs
B) angular motion; semicircular canals
C) linear motion; otolith organs
D) tilt; semicircular canals
E) tilt; otolith organs
A) angular motion; otolith organs
B) angular motion; semicircular canals
C) linear motion; otolith organs
D) tilt; semicircular canals
E) tilt; otolith organs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The sense of _______ registers motion resulting from rotation.
A) orientation
B) tilt
C) balance
D) angular motion
E) linear motion
A) orientation
B) tilt
C) balance
D) angular motion
E) linear motion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose you are wearing virtual reality goggles and there is a delay between when you turn your head and when the computer updates the display in the goggles. This creates a(n) _______ that might result in motion sickness.
A) angular acceleration
B) sensory integration
C) sensory conflict
D) linear acceleration
E) tilt sensation
A) angular acceleration
B) sensory integration
C) sensory conflict
D) linear acceleration
E) tilt sensation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When you accelerate in a car and are pushed back into your seat, you are experiencing _______, which is registered by your _______.
A) angular motion; otolith organs
B) angular motion; semicircular canals
C) tilt; otolith organs
D) linear motion; semicircular canals
E) linear motion; otolith organs
A) angular motion; otolith organs
B) angular motion; semicircular canals
C) tilt; otolith organs
D) linear motion; semicircular canals
E) linear motion; otolith organs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The sense of _______ registers head inclination with respect to gravity.
A) orientation
B) tilt
C) balance
D) angular motion
E) linear motion
A) orientation
B) tilt
C) balance
D) angular motion
E) linear motion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The sense of _______ registers motion resulting from translation.
A) orientation
B) tilt
C) balance
D) angular motion
E) linear motion
A) orientation
B) tilt
C) balance
D) angular motion
E) linear motion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
_______ are the mechanical structures in the vestibular system that sense both linear acceleration and gravity.
A) Otolith organs
B) Ossicles
C) Semicircular canals
D) Cochlea
E) Saccules
A) Otolith organs
B) Ossicles
C) Semicircular canals
D) Cochlea
E) Saccules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which motion stimulus would yield the largest response from the vestibular system?
A) Constant rotation
B) Constant translation
C) Constant tilt
D) Linear acceleration
E) Angular motion
A) Constant rotation
B) Constant translation
C) Constant tilt
D) Linear acceleration
E) Angular motion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The term for rotation around the x-axis is _______, rotation around the y-axis is _______, and rotation around the z-axis is _______.
A) pitch; roll; yaw
B) pitch; yaw; roll
C) roll; yaw; pitch
D) roll; pitch; yaw
E) yaw; pitch; roll
A) pitch; roll; yaw
B) pitch; yaw; roll
C) roll; yaw; pitch
D) roll; pitch; yaw
E) yaw; pitch; roll

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When you take an elevator from the first floor to the fifth floor of a building, the motion you experience is called _______ translation.
A) positive x-axis
B) positive y-axis
C) positive z-axis
D) negative x-axis
E) negative z-axis
A) positive x-axis
B) positive y-axis
C) positive z-axis
D) negative x-axis
E) negative z-axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When you drive forward in a car, the motion you experience is called _______ translation.
A) positive x-axis
B) positive y-axis
C) positive z-axis
D) negative x-axis
E) negative z-axis
A) positive x-axis
B) positive y-axis
C) positive z-axis
D) negative x-axis
E) negative z-axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
_______ have stereocilia that transduce mechanical movement in the vestibular labyrinth into neural activity sent to the brain stem.
A) Semicircular canals
B) Otolith organs
C) Saccules
D) Utricles
E) Hair cells
A) Semicircular canals
B) Otolith organs
C) Saccules
D) Utricles
E) Hair cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A(n) _______ is the change in voltage of sensory receptor cells in response to stimulation.
A) voltage gradient
B) receptor potential
C) otolith response
D) utricle response
E) saccule response
A) voltage gradient
B) receptor potential
C) otolith response
D) utricle response
E) saccule response

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
_______ are specialized detectors of angular motion located in each semicircular canal in a swelling called the ampulla.
A) Cupulas
B) Cilia
C) Kinocilia
D) Ampullae
E) Cristae
A) Cupulas
B) Cilia
C) Kinocilia
D) Ampullae
E) Cristae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If, for some unfortunate reason, your cristae are destroyed, which sense would you then lack?
A) Angular motion
B) Linear motion
C) Linear acceleration
D) Tilt
E) Gravity
A) Angular motion
B) Linear motion
C) Linear acceleration
D) Tilt
E) Gravity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Semicircular-canal neurons respond to _______ and _______, but not _______.
A) acceleration; deceleration; constant velocity
B) acceleration; constant velocity; deceleration
C) deceleration; constant velocity; acceleration
D) roll; pitch; yaw
E) pitch; yaw; roll
A) acceleration; deceleration; constant velocity
B) acceleration; constant velocity; deceleration
C) deceleration; constant velocity; acceleration
D) roll; pitch; yaw
E) pitch; yaw; roll

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
_______ are specialized detectors of linear acceleration and gravity found in each otolith organ.
A) Saccules
B) Otoconia
C) Maculae
D) Utricles
E) Cristae
A) Saccules
B) Otoconia
C) Maculae
D) Utricles
E) Cristae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If, for some unfortunate reason, your maculae are destroyed, which senses would you then lack?
A) Linear motion and angular motion
B) Angular rotation and gravity
C) Angular rotation and tilt
D) Linear acceleration and gravity
E) Linear acceleration and angular acceleration
A) Linear motion and angular motion
B) Angular rotation and gravity
C) Angular rotation and tilt
D) Linear acceleration and gravity
E) Linear acceleration and angular acceleration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The two otolith organs are the _______ and the _______.
A) maculae; cristae
B) saccule; maculae
C) saccule; cristae
D) utricle; maculae
E) utricle; saccule
A) maculae; cristae
B) saccule; maculae
C) saccule; cristae
D) utricle; maculae
E) utricle; saccule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The _______ are tiny calcium carbonate stones in the ear that provide inertial mass for the otolith organs, enabling them to sense gravity and linear acceleration.
A) saccules
B) otoconia
C) maculae
D) utricles
E) cristae
A) saccules
B) otoconia
C) maculae
D) utricles
E) cristae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the graph.
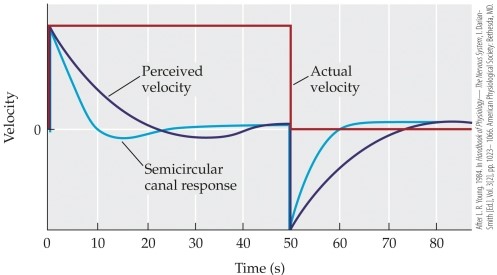 The data in this graph show that when subjects are rotated in the dark, they first feel a sense of motion consistent with their actual motion, but soon feel as if they are _______. After 30 seconds, they feel as if they have _______. If the motion abruptly stops, subjects feel as if they are rotating in the _______ direction.
The data in this graph show that when subjects are rotated in the dark, they first feel a sense of motion consistent with their actual motion, but soon feel as if they are _______. After 30 seconds, they feel as if they have _______. If the motion abruptly stops, subjects feel as if they are rotating in the _______ direction.
A) slowing down; sped up; opposite
B) slowing down; stopped; opposite
C) speeding up; slowed down; opposite
D) speeding up; stopped; same
E) slowing down; sped up; same
 The data in this graph show that when subjects are rotated in the dark, they first feel a sense of motion consistent with their actual motion, but soon feel as if they are _______. After 30 seconds, they feel as if they have _______. If the motion abruptly stops, subjects feel as if they are rotating in the _______ direction.
The data in this graph show that when subjects are rotated in the dark, they first feel a sense of motion consistent with their actual motion, but soon feel as if they are _______. After 30 seconds, they feel as if they have _______. If the motion abruptly stops, subjects feel as if they are rotating in the _______ direction.A) slowing down; sped up; opposite
B) slowing down; stopped; opposite
C) speeding up; slowed down; opposite
D) speeding up; stopped; same
E) slowing down; sped up; same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
_______ is an illusory sense of self motion produced when one is not, in fact, moving.
A) Vection
B) Yaw
C) Roll
D) Pitch
E) Tilt
A) Vection
B) Yaw
C) Roll
D) Pitch
E) Tilt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When participants are passively translated short distances while seated in a chair in the dark and then asked to use a joystick to actively move the chair to reproduce the distance that they just traveled, how do they do at this task?
A) They drastically underestimate the distance.
B) They slightly underestimate the distance.
C) They estimate the distance quite accurately.
D) They slightly overestimate the distance.
E) They drastically overestimate the distance.
A) They drastically underestimate the distance.
B) They slightly underestimate the distance.
C) They estimate the distance quite accurately.
D) They slightly overestimate the distance.
E) They drastically overestimate the distance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When participants stand on a tilted platform and then indicate which direction is "up" using a handheld haptic indicator, how do they do at this task?
A) They drastically underestimate the tilt.
B) They slightly underestimate the tilt.
C) They estimate the tilt quite accurately.
D) They slightly overestimate the tilt.
E) They drastically overestimate the tilt.
A) They drastically underestimate the tilt.
B) They slightly underestimate the tilt.
C) They estimate the tilt quite accurately.
D) They slightly overestimate the tilt.
E) They drastically overestimate the tilt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which situation might cause an illusory sense of self-motion due to multisensory integration?
A) Thinking about riding a rollercoaster
B) Sitting still in a rollercoaster car before it starts moving
C) Riding a rollercoaster
D) Watching a first-person IMAX movie of a rollercoaster ride
E) Watching an IMAX documentary about the history of rollercoasters
A) Thinking about riding a rollercoaster
B) Sitting still in a rollercoaster car before it starts moving
C) Riding a rollercoaster
D) Watching a first-person IMAX movie of a rollercoaster ride
E) Watching an IMAX documentary about the history of rollercoasters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose you are sitting still in a chair, wearing virtual reality glasses and experiencing the visual input of a roller coaster. You might feel like you are actually moving due to the sense of
A) linear acceleration.
B) vection.
C) tilt.
D) angular acceleration.
E) linear motion.
A) linear acceleration.
B) vection.
C) tilt.
D) angular acceleration.
E) linear motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When someone looks at visual display that rolls clockwise, they may start to feel as if they are
A) moving forward.
B) moving backward.
C) rotating counter-clockwise.
D) rotating clockwise.
E) falling.
A) moving forward.
B) moving backward.
C) rotating counter-clockwise.
D) rotating clockwise.
E) falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
_______ is a change in afference caused by self-generated activity.
A) Vection
B) Sensory reafference
C) Sensory exafference
D) Illusory self-motion
E) Active sensing
A) Vection
B) Sensory reafference
C) Sensory exafference
D) Illusory self-motion
E) Active sensing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
_______ is a change in afference caused by external stimuli.
A) Vection
B) Sensory reafference
C) Sensory exafference
D) Illusory self-motion
E) Active sensing
A) Vection
B) Sensory reafference
C) Sensory exafference
D) Illusory self-motion
E) Active sensing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The _______ innervate(s) glands, the heart, and the digestive system, and is responsible for regulation of many involuntary actions.
A) cranial nerves
B) autonomic nervous system
C) otolith organs
D) inferior rectus
E) vestibular nerve
A) cranial nerves
B) autonomic nervous system
C) otolith organs
D) inferior rectus
E) vestibular nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When you switch from lying down to standing up, which system or structure(s) is/are responsible for regulating the blood pressure in your head so that you don't faint?
A) Cranial nerves
B) Otolith organs
C) Inferior rectus
D) Autonomic nervous system
E) Vestibular nerve
A) Cranial nerves
B) Otolith organs
C) Inferior rectus
D) Autonomic nervous system
E) Vestibular nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
_______ typically result(s) from a disagreement between the motion and orientation signals provided by the semicircular canals, otolith organs, and vision.
A) Exhaustion
B) The tilt aftereffect
C) The vestibulo-ocular reflex
D) Motion sickness
E) Hallucinations
A) Exhaustion
B) The tilt aftereffect
C) The vestibulo-ocular reflex
D) Motion sickness
E) Hallucinations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If you read your phone while riding in the car, your visual input will not match your vestibular input and you might experience
A) the tilt aftereffect.
B) motion sickness.
C) the vestibulo-ocular reflex.
D) hallucinations.
E) exhaustion.
A) the tilt aftereffect.
B) motion sickness.
C) the vestibulo-ocular reflex.
D) hallucinations.
E) exhaustion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
People with damage to their vestibular systems experience _______ in their blood pressure after whole body tilt motion, compared to people with normal vestibular systems.
A) greater changes
B) the same changes
C) smaller changes
D) no change at all
E) gradually diminishing changes
A) greater changes
B) the same changes
C) smaller changes
D) no change at all
E) gradually diminishing changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Loss of _______ would result in severely degraded balance, possibly causing one to fall.
A) the autonomic nervous system
B) vestibulo-ocular reflexes
C) vestibulo-spinal responses
D) tilt aftereffects
E) vection
A) the autonomic nervous system
B) vestibulo-ocular reflexes
C) vestibulo-spinal responses
D) tilt aftereffects
E) vection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which brain area processes vestibular information?
A) Parietal lobe
B) Frontal lobe
C) Occipital lobe
D) Temporal lobe
E) All the above
A) Parietal lobe
B) Frontal lobe
C) Occipital lobe
D) Temporal lobe
E) All the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Vestibular information reaches the cortex via the _______ pathways.
A) thalamocortical
B) temperoparietal
C) occipitalparietal
D) superior frontal
E) inferior frontal
A) thalamocortical
B) temperoparietal
C) occipitalparietal
D) superior frontal
E) inferior frontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following describes a way that higher cognitive knowledge can influence motion perceptions?
A) If you are familiar with the curves in a road, the motion seems less intense.
B) If you are familiar with the curves in a road, the motion seems more intense.
C) The vestibular-ocular reflex can be affected by damage to the inner ear.
D) When listening to music, people sometimes sway back and forth.
E) When we get sleepy, we think about lying down.
A) If you are familiar with the curves in a road, the motion seems less intense.
B) If you are familiar with the curves in a road, the motion seems more intense.
C) The vestibular-ocular reflex can be affected by damage to the inner ear.
D) When listening to music, people sometimes sway back and forth.
E) When we get sleepy, we think about lying down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which symptom is quite common with vestibular dysfunctions?
A) Tactile agnosia
B) Hemifield neglect
C) Spatial disorientation
D) Anosmia
E) Object agnosia
A) Tactile agnosia
B) Hemifield neglect
C) Spatial disorientation
D) Anosmia
E) Object agnosia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The illusory sense of swaying, rocking, or tilting perceptions that occur after spending time on a boat and then returning to land is called
A) vection.
B) motion sickness.
C) Ménière's syndrome.
D) mal de debarquement syndrome.
E) vestibular flux.
A) vection.
B) motion sickness.
C) Ménière's syndrome.
D) mal de debarquement syndrome.
E) vestibular flux.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If you spend the day at the ocean playing in the waves, you might experience an illusory sense of rocking motion while you are falling asleep at night. This is known as
A) Ménière's syndrome.
B) mal de debarquement syndrome.
C) vection.
D) motion sickness.
E) vestibular flux.
A) Ménière's syndrome.
B) mal de debarquement syndrome.
C) vection.
D) motion sickness.
E) vestibular flux.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The sudden and unexpected onset of dizziness, imbalance, and spatial disorientation causing a patient to fall down or experience motion sickness so severe that they repeatedly vomit is called
A) vection.
B) illusory tilt.
C) Ménière's syndrome.
D) mal de debarquement syndrome.
E) vestibular flux.
A) vection.
B) illusory tilt.
C) Ménière's syndrome.
D) mal de debarquement syndrome.
E) vestibular flux.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What are the three modalities of spatial orientation perception?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the vestibulo-ocular reflex?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What are the otolith organs and what do they sense?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is vection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Describe where and how motion signals are registered in the semicircular canals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Describe two syndromes that result from failures of the vestibular system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 63 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



