Deck 7: Sampling Distribution of Means
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Sampling Distribution of Means
1
The sampling distribution of means is
A) an empirical distribution.
B) based on all possible populations.
C) a theoretical distribution.
D) based on the mean calculated for our current sample.
A) an empirical distribution.
B) based on all possible populations.
C) a theoretical distribution.
D) based on the mean calculated for our current sample.
C
2
The central limit theorem covers all of the following aspects of the sampling distribution of means, except the
A) standard deviation.
B) shape.
C) mean.
D) stability of the deviation scores.
A) standard deviation.
B) shape.
C) mean.
D) stability of the deviation scores.
D
3
The shape, mean, and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of means are all discussed in the
A) central limit theorem.
B) Pythagorean theorem.
C) trichotomy theorem.
D) Poisson limit theorem.
A) central limit theorem.
B) Pythagorean theorem.
C) trichotomy theorem.
D) Poisson limit theorem.
A
4
According to the central limit theorem, the mean of the sampling distribution of means will equal _______.
A) M
B) μ
C) 0
D) 1
A) M
B) μ
C) 0
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is true regarding the sampling distribution of means?
A) If the population from which a sample was drawn is not normal, then the sampling distribution cannot be normal.
B) If the sample drawn from the population is small enough, then the sampling distribution can be normal, even if the population itself is not.
C) If the sample drawn from the population is large enough, then the sampling distribution can be normal, even if the population itself is not.
D) None of the above statements is true.
A) If the population from which a sample was drawn is not normal, then the sampling distribution cannot be normal.
B) If the sample drawn from the population is small enough, then the sampling distribution can be normal, even if the population itself is not.
C) If the sample drawn from the population is large enough, then the sampling distribution can be normal, even if the population itself is not.
D) None of the above statements is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The mean of the sampling distribution of means is called the _________________.
A) expected value
B) standard error of the mean
C) grand mean
D) overall mean
A) expected value
B) standard error of the mean
C) grand mean
D) overall mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The symbol that represents the expected value of a sampling distribution of means is _____.
A) M
B) μ
C) μM
D) σM
A) M
B) μ
C) μM
D) σM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If we added up all of our means from a sampling distribution of means and divided by the number that represented all possible samples, the result would be the _______________.
A) standard error of the mean
B) grand mean
C) expected value
D) overall mean
A) standard error of the mean
B) grand mean
C) expected value
D) overall mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Given a population mean of 68 and a standard deviation of 6, the sampling distribution of means will have an expected value of __________.
A) M
B) 6
C) 68
D) More information is needed to make this determination.
A) M
B) 6
C) 68
D) More information is needed to make this determination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The amount that a sample mean is expected to vary from the population mean is given by the ________________.
A) average deviation
B) grand mean
C) expected value
D) standard error of the mean
A) average deviation
B) grand mean
C) expected value
D) standard error of the mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The symbol that represents the standard error of the mean is _______.
A) σM
B) Mσ
C) μσ
D) σμ
A) σM
B) Mσ
C) μσ
D) σμ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The standard error of the mean is based on the
A) standard deviation and the mean of a sample.
B) mean and the size of the sample.
C) standard deviation and the size of the sample.
D) shape of the distribution.
A) standard deviation and the mean of a sample.
B) mean and the size of the sample.
C) standard deviation and the size of the sample.
D) shape of the distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Given the same value for the standard deviation from two distributions but different sample sizes,
A) the smaller sample will more accurately predict the population mean.
B) the amount of standard error will be the same for both distributions.
C) the smaller sample will produce less standard error.
D) the larger sample will produce less standard error.
A) the smaller sample will more accurately predict the population mean.
B) the amount of standard error will be the same for both distributions.
C) the smaller sample will produce less standard error.
D) the larger sample will produce less standard error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Given the same standard deviation for two different distributions, as the size of the sample decreases
A) the expected value increases.
B) the expected value also decreases.
C) the size of the standard error also decreases.
D) the size of the standard error increases.
A) the expected value increases.
B) the expected value also decreases.
C) the size of the standard error also decreases.
D) the size of the standard error increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Given μ = 75 and a σ = 10, the expected value for a sampling distribution of means, based on sample sizes of 36, will be _______.
A) 75
B) 2.08
C) 10
D) 12.5
A) 75
B) 2.08
C) 10
D) 12.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A sample of n = 25 is selected at random from a population with a σ = 15. Approximately how much difference in the scores would you expect between the sample mean and the population mean?
A) 15 points
B) 1.67 points
C) 3 points
D) .6 point
A) 15 points
B) 1.67 points
C) 3 points
D) .6 point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In order to determine the standard error of the mean, we need to know
A) μ and σ.
B) σ and n.
C) M and σ.
D) μ and n.
A) μ and σ.
B) σ and n.
C) M and σ.
D) μ and n.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Given n = 9 and σM = 12, what is σ?
A) 3
B) 1.33
C) .75
D) 36
A) 3
B) 1.33
C) .75
D) 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The standard deviation for two different distributions is 12. The sample size for one of the distributions is 36. Which of the following sample sizes for the other distribution will produce the greatest amount of standard error?
A) 49
B) 64
C) 81
D) Not enough information is provided to make the determination.
A) 49
B) 64
C) 81
D) Not enough information is provided to make the determination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The mean for a set of scores is 52, the standard deviation is 14, and the sample size is 36. What is the standard error of the mean?
A) 1.14
B) 2.33
C) .39
D) 1.45
A) 1.14
B) 2.33
C) .39
D) 1.45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The standard deviation for a set of scores is 10 and the sample size is 42. What is the standard error of the mean?
A) 42 ÷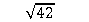
B) 42 ÷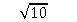
C) 10 ÷ 42
D) 10 ÷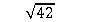
A) 42 ÷
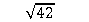
B) 42 ÷
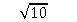
C) 10 ÷ 42
D) 10 ÷
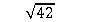

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of means is called the ______________.
A) sample deviation.
B) deviation of means
C) expected value
D) standard error of the mean
A) sample deviation.
B) deviation of means
C) expected value
D) standard error of the mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a sampling distribution of means, z-scores are in __________ units.
A) squared
B) metric
C) standard error
D) deviation score
A) squared
B) metric
C) standard error
D) deviation score

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In order to use the z-score formula for determining the probability of obtaining a sample mean, we need all of the following, except _____________.
A) N
B) σₘ
C) μ
D) M
A) N
B) σₘ
C) μ
D) M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The correct notation for determining the probability associated with sample means above 25 is _____________.
A) M = 25 + (z)(σₘ)
B) p(M > 25)
C) M = z + (25)(σₘ)
D) p(μ > 25)
A) M = 25 + (z)(σₘ)
B) p(M > 25)
C) M = z + (25)(σₘ)
D) p(μ > 25)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The formula used to convert a z-score to a sample mean includes all of the following elements, except __________.
A) μ
B) z
C) σ
D) σₘ
A) μ
B) z
C) σ
D) σₘ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Given a population mean of 78 and a standard error of the mean value of 2, what else do we need to use the formula to find the range of means that would be expected to occur 90% of the time?
A) The z-scores associated with the extreme high and low .1000 ends of the distribution.
B) The z-scores associated with the proportions between the mean and .1000.
C) The z-scores associated with extreme high and low .0500 ends of the distribution.
D) The z-scores associated with the proportion between the mean and .0500.
A) The z-scores associated with the extreme high and low .1000 ends of the distribution.
B) The z-scores associated with the proportions between the mean and .1000.
C) The z-scores associated with extreme high and low .0500 ends of the distribution.
D) The z-scores associated with the proportion between the mean and .0500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
M = μ + (z)(σM) is used to
A) locate the z-score associated with a certain mean.
B) convert a z-score to a sample mean.
C) convert a sample mean to a z-score.
D) find the probability associated with a certain mean.
A) locate the z-score associated with a certain mean.
B) convert a z-score to a sample mean.
C) convert a sample mean to a z-score.
D) find the probability associated with a certain mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In order to determine the proportion of sample means expected to lie above 95% of the distribution, look in column ______ of the normal distribution table.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Standard error
A) should be avoided.
B) is a standard deviation.
C) is due to mistakes made while collecting data.
D) has to be deducted from the standard deviation.
A) should be avoided.
B) is a standard deviation.
C) is due to mistakes made while collecting data.
D) has to be deducted from the standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Given a normally shaped distribution with a μ = 100 and a σ = 16, a sample of 36 individuals is randomly selected. The mean of the sample was 107. The z-score for the sample mean would be _______.
A) +2.62
B) -2.62
C) +.44
D) -.44
A) +2.62
B) -2.62
C) +.44
D) -.44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A normally shaped distribution has a μ = 36 and a σ = 12. A sample of 9 individuals is randomly selected and achieved a M = 32. What is the z-score for the obtained sample mean?
A) -.33
B) +.33
C) -1.00
D) +1.00
A) -.33
B) +.33
C) -1.00
D) +1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The scores from a population resulted in a normally shaped distribution with a μ = 52 and a σM = 3. The obtained sample mean of 47 converted to a z-score of _________.
A) +.56
B) -.56
C) +1.67
D) -1.67
A) +.56
B) -.56
C) +1.67
D) -1.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A sample of n = 49 is drawn at random from a population with a μ = 78 and a σ = 14. What is the probability that the sample mean will be 82 or higher?
A) .3859
B) .9772
C) .0228
D) .6141
A) .3859
B) .9772
C) .0228
D) .6141

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A sample of n = 9 is drawn at random from a population with a μ = 32 and a σ = 9. The probability that the sample mean will be 34 or below is _________.
A) .1429
B) .5871
C) .2514
D) .7486
A) .1429
B) .5871
C) .2514
D) .7486

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A normally shaped distribution has a μ = 36 and a σM = 2. The probability that a randomly drawn sample of n = 25 will have a mean of 38 or above is _________.
A) .0228
B) .9772
C) .1587
D) .8413
A) .0228
B) .9772
C) .1587
D) .8413

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A population of scores is normally distributed with a μ = 95 and a σM = 5. The probability that a randomly drawn sample of n = 12 will have a mean of 88 or above is _________.
A) .0808
B) .9192
C) .7190
D) .2810
A) .0808
B) .9192
C) .7190
D) .2810

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Given a normally shaped distribution with a μ = 62 and a σM = 5, what is p(M > 52)?
A) .9772
B) .0228
C) .0047
D) .9953
A) .9772
B) .0228
C) .0047
D) .9953

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a distribution is normally shaped with a μ = 40 and a σM = 4, what is p(M < 38)?
A) .6915
B) .3085
C) .8413
D) .1587
A) .6915
B) .3085
C) .8413
D) .1587

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A random sample of n = 25 individuals is drawn from a population with a μ = 63 and a σ = 9. The probability is .1000 that the mean of the sample will be above what value?
A) -1.28
B) +1.28
C) 65.3
D) 60.70
A) -1.28
B) +1.28
C) 65.3
D) 60.70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A sample of n = 36 individuals is drawn at random from a population that has a μ = 105 and a σ = 18. The probability is .0500 that the mean of the sample will be below what value?
A) 75.3
B) 134.7
C) 109.95
D) 100.05
A) 75.3
B) 134.7
C) 109.95
D) 100.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Explain what is meant by expected value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A standardized assessment inventory on the personality characteristic of "Perfectionism" has a μ = 70 and a σ = 12.
a. Compute σM for a sample of n = 100.
b. Compute σM for a sample of n = 25.
c. How is σM affected by sample size?
a. Compute σM for a sample of n = 100.
b. Compute σM for a sample of n = 25.
c. How is σM affected by sample size?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Given a normally shaped population distribution with a μ = 24 and a σ = 5, what is the probability that an obtained sample of size n = 8 will have a mean that is
a. above 21?
b. above 27?
c. below 27?
a. above 21?
b. above 27?
c. below 27?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A psychologist has developed an assessment instrument to measure the degree of people's desire for privacy. The test has been standardized with a μ = 60 and a σ = 12. If a sample of size n = 24 is drawn at random, determine
a. p(M < 55).
b. P(M > 58).
c. p(M < 58).
a. p(M < 55).
b. P(M > 58).
c. p(M < 58).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A population distribution is normally distributed with a μ = 57 and a σ = 7. What is the probability of obtaining a sample mean less than 55 if n = 18?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A random sample of size n = 48 is drawn from a normally shaped distribution with a μ = 110 and a σ = 17. What is the probability that the mean of the sample will be greater than 104?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A population distribution is normally distributed with a μ = 93 and a σ = 13. If n = 50, what proportion of sample means can be expected to be less than 97?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A random sample of size n = 40 is randomly drawn from a population that is normally distributed with a μ = 82 and a σ = 13. The probability is .02 that the sample mean will be above what value?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A normally shaped population distribution has μ = 55 and a σ = 5. If samples of size n = 20 are drawn at random, what range of sample means would be expected to occur 98% of the time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



