Deck 6: Political Participation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/79
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Political Participation
1
Citizenship refers to:
A) participation in or membership in a community.
B) state sponsored classification of people residing in a geographic area.
C) to political participation via Internet has resulted in new forms of participation.
D) all of the above.
A) participation in or membership in a community.
B) state sponsored classification of people residing in a geographic area.
C) to political participation via Internet has resulted in new forms of participation.
D) all of the above.
A
2
Who conducted one of the first major studies of citizenship in political sociology?
A) Talcott Parsons
B) T.H. Marshall
C) Bryan Turner
D) Seymour Martin Lipset
A) Talcott Parsons
B) T.H. Marshall
C) Bryan Turner
D) Seymour Martin Lipset
B
3
T.H. Marshall argued democracy and capitalism were incompatible for which reason?
A) capitalism requires competition and democracy emphasizes cooperation.
B) capitalism succeeds only in a context where those who command resources are deemed worthy and democracy assumes an equal distribution of power
C) capitalism is defined mainly by profit that leads to influence and democracy requires cooperation and free access
D) all of the above
A) capitalism requires competition and democracy emphasizes cooperation.
B) capitalism succeeds only in a context where those who command resources are deemed worthy and democracy assumes an equal distribution of power
C) capitalism is defined mainly by profit that leads to influence and democracy requires cooperation and free access
D) all of the above
D
4
Turner (1993) extended T.H. Marshall's theory of citizenship by suggesting citizenship as more than just political practices and to include _________ practices.
A) cultural
B) social
C) religious
D) economic
A) cultural
B) social
C) religious
D) economic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Pluralist view political participation as:
A) dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy.
B) as limited to small group of power elite.
C) new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation.
D) comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.
A) dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy.
B) as limited to small group of power elite.
C) new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation.
D) comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which perspective views political participation as comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power?
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The idea that political participation by participants of the Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s helped redistribute power in the U.S. based on race is a good example of what perspective?
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to pluralist who have studied the transformation citizenship and political participation in democratic societies such as the U.S., which of the following best summarizes the dangers of excessive interest-group liberalism for democratic societies?
A) tendency to turn control over to leaders.
B) decline in civic participation that challenges systems of privilege.
C) preservation of the status quo.
D) all of the above.
A) tendency to turn control over to leaders.
B) decline in civic participation that challenges systems of privilege.
C) preservation of the status quo.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Elite-managerial perspective views political participation as:
A) dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy.
B) as limited to small group of power elite.
C) new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation.
D) comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.
A) dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy.
B) as limited to small group of power elite.
C) new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation.
D) comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which perspective views political participation as limited to small group of power elite who have the ability to shape and enforce policy, who can allocate societal resources, and who have a seat at the table to make important decisions?
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Dahrendorf's argment that politics in comprised of organizations and groups competing and conflict for scarce resources best fits with which perspective?
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The class perspective views political participation as:
A) dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy.
B) as limited to small group of power elite.
C) new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation.
D) comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.
A) dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy.
B) as limited to small group of power elite.
C) new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation.
D) comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which perspective views political participation as dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy?
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class
A) elite-managerial
B) postmodern
C) pluralist
D) class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which perspective views political participation as individuals and groups actively gauging the costs and benefits of participating or not participating?
A) rational choice
B) postmaterialist
C) postmodern
D) institutionalist
A) rational choice
B) postmaterialist
C) postmodern
D) institutionalist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which perspective views political participation as new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation?
A) rational choice
B) postmaterialist
C) postmodern
D) institutionalist
A) rational choice
B) postmaterialist
C) postmodern
D) institutionalist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Postmodern approaches view participation as:
A) dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy.
B) as limited to small group of power elite.
C) new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation.
D) comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.
A) dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy.
B) as limited to small group of power elite.
C) new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation.
D) comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In his typology of postmodern personalities, Zygmant Bauman all of the following except:
A) the stroller
B) the vagabond
C) the rationalist
D) the player
A) the stroller
B) the vagabond
C) the rationalist
D) the player

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to Zygmant Bauman's typology of postmodern personalities, _________ is the nomad who finds no particular social identity upon which to land or settle.
A) the stroller
B) the vagabond
C) the tourist
D) the player
A) the stroller
B) the vagabond
C) the tourist
D) the player

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to Zygmant Bauman's typology of postmodern personalities, _________ seeks out social lives as a way to experience new or different things.
A) the stroller
B) the vagabond
C) the tourist
D) the player
A) the stroller
B) the vagabond
C) the tourist
D) the player

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to Zygmant Bauman's typology of postmodern personalities, _________ is about being strategic in how the social game itself is played.
A) the stroller
B) the vagabond
C) the tourist
D) the player
A) the stroller
B) the vagabond
C) the tourist
D) the player

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which theorist was interested in understanding how advanced capitalism distorts traditional notions of democracy?
A) Bauman
B) Milbrath
C) Habermas
D) Olsen
A) Bauman
B) Milbrath
C) Habermas
D) Olsen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The ________ typology of political participation suggests political participation relates to the resources, knowledge, and intention of the individual.
A) Bauman
B) Milbrath
C) Habermas
D) Olsen
A) Bauman
B) Milbrath
C) Habermas
D) Olsen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The ________ typology takes a more rational choice perspective arguing individuals are motivated to participate politically by individual goals and desire outcomes.
A) Bauman
B) Milbrath
C) Verba and Nie
D) Olsen
A) Bauman
B) Milbrath
C) Verba and Nie
D) Olsen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The ________ typology examines the position of certain individuals and groups in a hierarchy affords either more or less opportunity to influence the political domain.
A) Bauman
B) Milbrath
C) Verba and Nie
D) Olsen
A) Bauman
B) Milbrath
C) Verba and Nie
D) Olsen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
_________ and _________ are the two forms of political participation identified by political sociologists.
A) institutional; noninstitutional
B) material; postmaterial
C) traditional; radical
D) conventional; fundamental
A) institutional; noninstitutional
B) material; postmaterial
C) traditional; radical
D) conventional; fundamental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
People who engage in campaigning and canvassing most likely hold at least one of the following characteristics except:
A) older citizens
B) loyal party members
C) highly educated
D) young citizens
A) older citizens
B) loyal party members
C) highly educated
D) young citizens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the following are considered non-institutional forms of political participation except:
A) protest
B) terrorism
C) graffiti
D) lobbying
A) protest
B) terrorism
C) graffiti
D) lobbying

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Although often written off as vandalism and possible criminal, ________ can be a tool of protest or it can communicate with others and display political values and ideologies.
A) demonstrations
B) terrorism
C) graffiti
D) riots
A) demonstrations
B) terrorism
C) graffiti
D) riots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
________ capture the anger and disappointment that aggrieved populations have over policy or the state of current affairs.
A) demonstrations
B) terrorism
C) graffiti
D) riots
A) demonstrations
B) terrorism
C) graffiti
D) riots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
________ refers to the unconventional and often collective action-taken to show disapproval of, and the need for change in, some policy or condition.
A) protest
B) terrorism
C) graffiti
D) riots
A) protest
B) terrorism
C) graffiti
D) riots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Protest demonstrations include all of the following tactics except:
A) sit-ins
B) rallies
C) pickets
D) lobbying
A) sit-ins
B) rallies
C) pickets
D) lobbying

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Political sociologists have identified which of the following with explaining individual participation in protest?
A) social networks
B) connections to work
C) identity
D) all of the above
A) social networks
B) connections to work
C) identity
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
_________ refers to a broad spectrum of political actions related to things such as revolutions, strikes, wars, social movements, and coups d'etats.
A) demonstrations
B) political violence
C) social protest
D) contentious politics
A) demonstrations
B) political violence
C) social protest
D) contentious politics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
_________ refers to how connected individuals are in modern society and what implications this lack of connectedness would have on democratic processes.
A) social psychology
B) social capital
C) community
D) bowling alone
A) social psychology
B) social capital
C) community
D) bowling alone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
__________ refers to the social relationships that connect people to one another and that act as lines of communication, trust, and group identity.
A) social psychology
B) social capital
C) community
D) bowling alone
A) social psychology
B) social capital
C) community
D) bowling alone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
_________ conceptualizes social capital as the by-products of social interaction left by group memberships and ties between individuals that can then be transformed into social currency to be exchanged.
A) Bourdieu
B) Coleman
C) Putnam
D) Knoke
A) Bourdieu
B) Coleman
C) Putnam
D) Knoke

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
_________ conceptualizes social capital focuses on three processes relevant to civic engagement: transformation, fields, and stratification.
A) Bourdieu
B) Coleman
C) Putnam
D) Knoke
A) Bourdieu
B) Coleman
C) Putnam
D) Knoke

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to T.S. Marshall, citizenship of the late 20th century has transformed by the tension between capitalism and democracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Pluralist have grown concerned over a continued move toward liberalism that results in breakdown of social institutions, transfer of power to leaders, and weakening civic engagement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Pluralists view mass political participation as a form of tokenism and a way to appease disgruntled or aggrieved populations threatening or challenging the elite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Postmodernist view participation as comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Elite-managerial perspective views political participation as limited to small group of power elite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Rational choice theory views political participation as individuals and groups actively gauging the costs and benefits of participating or not participating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Rational choice views political participation as new cultural and political identities that have shaped new forms of political participation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The Milbrath typology of political participation suggests political participation relates to the resources, knowledge, and intention of the individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Research suggests that individuals likely to engage in political discourse are more likely to become politically active.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The use of violence or the threat of the use of violence can help achieve favorable political outcomes for protesting groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Zukin et al (2006) argue that political participation in the United State is in decline across all forms of participation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
According to political sociologists, citizenship has both ________ and _________ aspects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
_________ view political participation as comprised of mass participation and interest group vying for political power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
_________ perspective views political participation as limited to small group of power elite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
_________ perspective views political participation as dominated by capitalists through their ability to control decision-making, allocation of resources, and public policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
According to Zygmant Bauman's typology of postmodern personalities, _________ is someone who perhaps is oriented by superficial things, especially related to
fashion or looks.
fashion or looks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
_________ and _________ are the two forms of political participation identified by political sociologists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The ________ typology of political participation suggests political participation relates to the resources, knowledge, and intention of the individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The ________ typology takes a more rational choice perspective arguing individuals are motivated to participate politically by individual goals and desire outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The ________ typology examines the position of certain individuals and groups in a hierarchy affords either more or less opportunity to influence the political domain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
_________ is the most common institutional form of political participation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
_________ is an often overlooked institutional form of political participation in an everyday life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
________ capture the anger and disappointment that aggrieved populations have over policy or the state of current affairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
_________ refers to a broad spectrum of political actions related to things such as revolutions, strikes, wars, social movements, and coups d'etats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
__________ refers to the social relationships that connect people to one another and that act as lines of communication, trust, and group identity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
_________ refers to how connected individuals are in modern society and what implications this lack of connectedness would have on democratic processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In what ways has democratic participation declined in the US? How has it increased?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why do people participate in politics? When do people participate in politics? How does this shed light on the problems of "why" people participate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How do political leaders help mobilize and encourage participation in electoral politics? How do political leaders hinder the mobilization and discourage participation in electoral politics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How do the authors define citizenship?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What explains individual participation in protests and demonstrations?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is political participation, and how do we measure it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What's happening to political participation in the United States?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
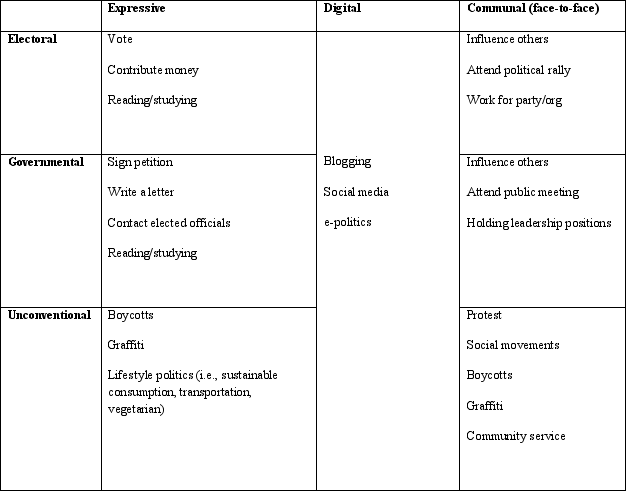
All forms of participation (expressive, communal, digital, and unconventional) constitutes grassroots democracy - in other words, we need people to be involved - the challenge is face-to-face, communal forms are what have constituted measures and signs of our democratic health. How many of you have done the following (go down list)? How many of you prefer expressive over communal forms of participation?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What do you think are the consequences of changes in political participation behavior in the United States?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Describe the various components of T.S. Marshall's idea of citizenship and how its changed over the last 200 hundred years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Compare and contrast two of the three typologies of political participation discussed in chapter six.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
what ways has the Internet and e-politics affected political participation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Describe Zygmant Bauman's typology of postmodern personalities: the stroller, the vagabond, the tourist, and the player. These personalities are useful for understanding contemporary forms of political participation that postmodern theorists argue emerged during the 1960s and today dominant how and why people participate in politics. Using this typology, try to think of the many ways this typology helps capture and explain why political participation (such as voting) in the United States have steadily declined over the last 40 years. How do the other theoretical perspectives (pluralist, elite, class, and rational choice) shed light on this same phenomenon of a decline in political participation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
How does social capital help explain why you hold the political opinions, attitudes, and values? How about for explaining your political participation record?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
How has political participation changed over the last forty years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How does social capital help explain why you hold the political opinions, attitudes, and values? How about for explaining your political participation record?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



