Deck 13: Explaining Dichotomous Outcomes: Logistic Regression
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Explaining Dichotomous Outcomes: Logistic Regression
1
For which one of these dependent variables would you use logistic regression?
A) income in dollars
B) number of children
C) hours worked per week
D) whether or not one owns a gun
A) income in dollars
B) number of children
C) hours worked per week
D) whether or not one owns a gun
D
2
Logistic regression uses "e", otherwise known as:
A) the exponential logarithm
B) the logistic logarithm
C) the natural logarithm
D) the regression logarithm
A) the exponential logarithm
B) the logistic logarithm
C) the natural logarithm
D) the regression logarithm
C
3
If we wanted to explain work behavior, for which of the following variables would we use logistic regression?
A) hours worked
B) occupational prestige score
C) currently employed or not
D) type of industry
A) hours worked
B) occupational prestige score
C) currently employed or not
D) type of industry
C
4
According to GSS2006 data, a white woman living in a big city has a 50% of saying she is afraid to walk alone at night in her neighborhood. This percentage translated into odds is:
A) 1 to 2
B) 1 to 1
C) 2 to 1
D) 4 to 1
A) 1 to 2
B) 1 to 1
C) 2 to 1
D) 4 to 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the predicted probability is 50%, what is the z-value in a logistic regression?
A) 0
B) .5
C) 1
D) 2
A) 0
B) .5
C) 1
D) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the GSS2008, respondents were asked if the aged should live with their children. 59% said this was a good idea, while 41% said it was a bad idea. Here is a logistic regression equation:
Dependent Variable: Should Aged Live with Their Children?
(1=good idea, 0 = bad idea)
Which of the following statements is closest to the truth?
A) A ninety-year-old is three times as likely to think this is a good idea than a 20-year-old.
B) A ninety-year-old is twice as likely to think this is a good idea than a 20-year-old.
C) A ninety-year-old is half as likely to think this is a good idea than a 20-year-old.
D) A ninety-year-old is equally likely to think this is a good idea as a 20-year-old.
Dependent Variable: Should Aged Live with Their Children?
(1=good idea, 0 = bad idea)
Which of the following statements is closest to the truth?
A) A ninety-year-old is three times as likely to think this is a good idea than a 20-year-old.
B) A ninety-year-old is twice as likely to think this is a good idea than a 20-year-old.
C) A ninety-year-old is half as likely to think this is a good idea than a 20-year-old.
D) A ninety-year-old is equally likely to think this is a good idea as a 20-year-old.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Does having various types of children affect the probability of going to the zoo? Here is a logistic regression equation:
Dependent Variable: Visited Zoo in Past Year? (Yes=1, No=0)
Who is most likely to go to the zoo?
A) Someone with four-year-old triplets
B) Someone with nine-year-old triplets
C) Someone with fifteen-year-old triplets
D) Someone with a four-year-old, a nine-year-old, and a fifteen-year-old
Dependent Variable: Visited Zoo in Past Year? (Yes=1, No=0)
Who is most likely to go to the zoo?
A) Someone with four-year-old triplets
B) Someone with nine-year-old triplets
C) Someone with fifteen-year-old triplets
D) Someone with a four-year-old, a nine-year-old, and a fifteen-year-old

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A question asked every year in the GSS is called FEAR: "Is there any area right around here - that is, within a mile - where you would be afraid to walk alone at night?" Here is a logistic regression equation using this as the dependent variable with GSS2006 data:
Dependent Variable: Afraid to Walk Alone? (No=0, Yes=1)
In terms of a percentage difference, how do a white, non-city-dwelling male and a black, city-dwelling female differ?
A) They differ by 40%
B) They differ by 45%
C) They differ by 50%
D) They differ by 55%
Dependent Variable: Afraid to Walk Alone? (No=0, Yes=1)
In terms of a percentage difference, how do a white, non-city-dwelling male and a black, city-dwelling female differ?
A) They differ by 40%
B) They differ by 45%
C) They differ by 50%
D) They differ by 55%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to GSS2006 data, a white man living in a big city has a 25% chance of saying he is afraid to walk alone at night in her neighborhood, while a white woman living in a big city has a 50% chance of saying she is afraid of saying she is afraid to walk alone at night in her neighborhood. Which of the following is the odds ratio (men's to women's)?
A) .33
B) .5
C) 2
D) 3
A) .33
B) .5
C) 2
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the GSS2008, respondents were asked if the aged should live with their children. Here is a simple logistic regression equation. Race is coded as follows: White and Blacks = 0, Others (i.e. not whites or blacks) =1.
Dependent Variable: Should Aged Live with Their Children? (1=good idea, 0 = bad idea)
What is this slope translated into an odds ratio?
A) .18
B) 1.22
C) 1.70
D) 5.00
Dependent Variable: Should Aged Live with Their Children? (1=good idea, 0 = bad idea)
What is this slope translated into an odds ratio?
A) .18
B) 1.22
C) 1.70
D) 5.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the odds ratio for a gender variable (where women are coded as 1) is .33, what would the odds ratio be for the same gender variable if men had been coded as 1?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 6
D) 10
A) 2
B) 3
C) 6
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The logistic slope for a dichotomous variable is +1.10. What is the odds ratio?
A) 1.10
B) .33
C) 0
D) 3
A) 1.10
B) .33
C) 0
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the relationship between odds ratios and predicted probabilities?
A) They really the same thing.
B) They are usually very similar.
C) You can use only one at a time.
D) They can be quite different.
A) They really the same thing.
B) They are usually very similar.
C) You can use only one at a time.
D) They can be quite different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Beyerlein, Soule, and Martin, in their research on protest, study the connections among:
A) prayers, protest, and police
B) marches, masculinity, and the military
C) sit-ins, sanctuary cities, and sentencing
D) activism, attitudes, and art
A) prayers, protest, and police
B) marches, masculinity, and the military
C) sit-ins, sanctuary cities, and sentencing
D) activism, attitudes, and art

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Beyerlein, Soule, and Martin use which method in their research on protest?
A) survey research
B) secondary analysis
C) experimentation
D) content analysis
A) survey research
B) secondary analysis
C) experimentation
D) content analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Beyerlein, Soule, and Martin, in their research on protest, use which regression techniques?
A) logistic regression and interaction effects
B) logistic regression and nested modeling
C) interaction effects and nested modeling
D) logistic regression, interaction effects, and nested modeling
A) logistic regression and interaction effects
B) logistic regression and nested modeling
C) interaction effects and nested modeling
D) logistic regression, interaction effects, and nested modeling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Beyerlein, Soule, and Martin, in their research on protest, explore evidence for the concept of:
A) protest legitimacy
B) political legitimacy
C) privileged legitimacy
D) police legitimacy
A) protest legitimacy
B) political legitimacy
C) privileged legitimacy
D) police legitimacy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In their research on attitudes toward global warming, McCright and Dunlap use data from:
A) the General Social Survey
B) the American National Election Studies
C) the World Values Survey
D) Gallup polls
A) the General Social Survey
B) the American National Election Studies
C) the World Values Survey
D) Gallup polls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which combination of regression techniques to McCright and Dunlap use in their research on attitudes toward global warming?
A) logistic regression and nested modeling
B) logistic regression and interaction effects
C) nested modeling and interaction effects
D) nested modeling and standardized effects
A) logistic regression and nested modeling
B) logistic regression and interaction effects
C) nested modeling and interaction effects
D) nested modeling and standardized effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What aspect of global warming do McCright and Dunlap use as their dependent variable?
A) whether or not the respondent thinks the effects of global warming have begun
B) whether or not the respondent thinks humans are responsible for global warming
C) whether or not the respondent cares about global warming
D) whether or not the respondent has given money to an organization fighting global warming
A) whether or not the respondent thinks the effects of global warming have begun
B) whether or not the respondent thinks humans are responsible for global warming
C) whether or not the respondent cares about global warming
D) whether or not the respondent has given money to an organization fighting global warming

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
According to McCright and Dunlap, which of the following types of people is LEAST likely to have said that global warming has already begun?
A) a non-educated liberal Democrat who claims to understand global warming not at all
B) a highly-educated liberal Democrat who claims to understand global warming very well
C) a non-educated conservative Republican who claims to understand global warming not at all
D) a highly-educated conservative Republican who claims to understand global warming very well
A) a non-educated liberal Democrat who claims to understand global warming not at all
B) a highly-educated liberal Democrat who claims to understand global warming very well
C) a non-educated conservative Republican who claims to understand global warming not at all
D) a highly-educated conservative Republican who claims to understand global warming very well

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In SPSS, which of the following versions of R-Square does logistic regression output give you?
A) Cox and Snell
B) Nagelkerke
C) Both of these
D) Neither of these
A) Cox and Snell
B) Nagelkerke
C) Both of these
D) Neither of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What does not appear in SPSS logistic regression output?
A) unstandardized slopes
B) standardized slopes
C) statistical significance
D) a measure of R-square
A) unstandardized slopes
B) standardized slopes
C) statistical significance
D) a measure of R-square

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In SPSS, the logistic regression output gives you a column headed "Exp(B)." What does this mean?
A) e to the power of the slope
B) e multiplied by the slope
C) the slope to the power of e
D) the expected value of the slope
A) e to the power of the slope
B) e multiplied by the slope
C) the slope to the power of e
D) the expected value of the slope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If you try to run a regular regression using a dichotomy in SPSS, SPSS will:
A) do it
B) do it, but give you a warning message
C) give you an error message
D) cease to work
A) do it
B) do it, but give you a warning message
C) give you an error message
D) cease to work

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Explain why, if your dependent variable is a dichotomy, logistic regression is preferred to regular regression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A friend of yours uses logistic regression to try to explain variation in the number of guns people own, but SPSS keeps giving him an error when he tries to run his model. Explain why this is happening, and offer your friend a suggestion for fixing the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
GSS2008 respondents were asked: "Should divorce in this country be easier or more difficult to obtain than it is now?" 48% of the respondents say it should be harder. A logistic regression equation:
Dependent Variable: Divorce Should be Harder to Obtain (Yes=1, No=0)
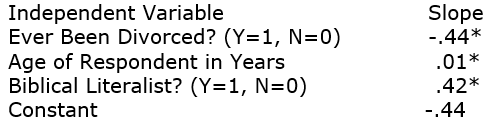 Based on the results, describe the two extreme possibilities (i.e. the two types of people whose probabilities would differ the most) and then calculate probabilities for both of them.
Based on the results, describe the two extreme possibilities (i.e. the two types of people whose probabilities would differ the most) and then calculate probabilities for both of them.
Dependent Variable: Divorce Should be Harder to Obtain (Yes=1, No=0)
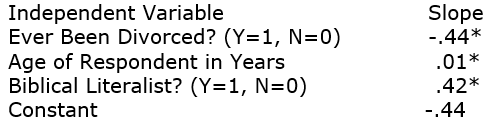 Based on the results, describe the two extreme possibilities (i.e. the two types of people whose probabilities would differ the most) and then calculate probabilities for both of them.
Based on the results, describe the two extreme possibilities (i.e. the two types of people whose probabilities would differ the most) and then calculate probabilities for both of them.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
We want to learn more about variation in attitudes towards anti-American Muslims. We notice that the 2008GSS had a new variable called LIBMSLM: "If some people in your community suggested that a book an anti-American Muslim clergyman wrote which preaches hatred of the United State should be taken out of your public library, would you favor removing this book or not?" 50% of Americans said remove it, 50% said do not remove it. Here is a logistic regression equation:
Dependent Variable: Remove Book? (Yes=0, No=1)
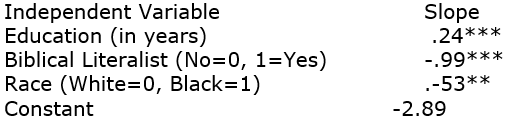 Based on the results, describe the two extreme possibilities (i.e. the two types of people whose probabilities would differ the most) and then calculate probabilities for both of them.
Based on the results, describe the two extreme possibilities (i.e. the two types of people whose probabilities would differ the most) and then calculate probabilities for both of them.
Dependent Variable: Remove Book? (Yes=0, No=1)
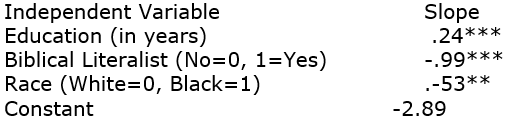 Based on the results, describe the two extreme possibilities (i.e. the two types of people whose probabilities would differ the most) and then calculate probabilities for both of them.
Based on the results, describe the two extreme possibilities (i.e. the two types of people whose probabilities would differ the most) and then calculate probabilities for both of them.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Here is a logistic regression equation that includes an interaction effect. EDUC is measured in years, RACE is coded White=0, Blacks=1. The dependent variable is SPANKING: where 0=disagrees with spanking children, 1=in favor of spanking children (all slopes statistically significant):
SPANKING = 2.44 - 1.27(RACE) - .11(EDUC) + .16(RACE)(EDUC)
By calculating four examples (two white people: one with 10 years of education, one with 20 years of education; two black people: one with 10 years of education, one with 20 years of education), tell the story behind this model.
SPANKING = 2.44 - 1.27(RACE) - .11(EDUC) + .16(RACE)(EDUC)
By calculating four examples (two white people: one with 10 years of education, one with 20 years of education; two black people: one with 10 years of education, one with 20 years of education), tell the story behind this model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The 2008GSS asked respondents if they can speak a language other than English. Using only those born in the U.S., here are logistic regression results with an interaction effect:
Dependent Variable: Can Speak Language Other than English? (No=0, 1=Yes)
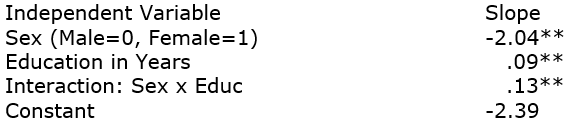 Run the following examples and tell the resulting story:
Run the following examples and tell the resulting story:
a man with 10 years of education
a man with 20 years of education
a woman with 10 years of education
a woman with 20 years of education
Dependent Variable: Can Speak Language Other than English? (No=0, 1=Yes)
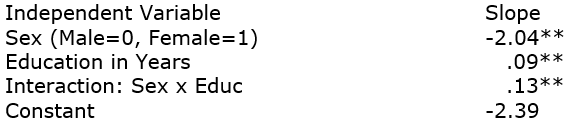 Run the following examples and tell the resulting story:
Run the following examples and tell the resulting story:a man with 10 years of education
a man with 20 years of education
a woman with 10 years of education
a woman with 20 years of education

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The GSS2008 asks people if they have seen an x-rated movie in the past year. Below is a logistic regression equation. The "Happy Marriage" variable is measured as follows: 0=Not Happy, 1=Pretty Happy, and 2=Very Happy.
Dependent Variable: Seen X-Rated Movie in Past Year? (No=0, 1=Yes)
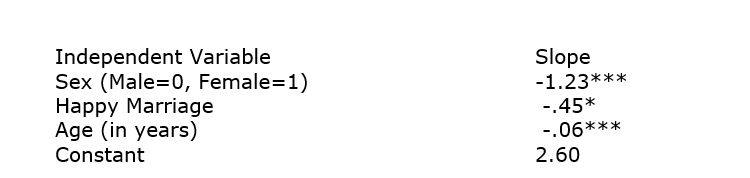 Calculate probabilities for a 40-year-old man in a pretty happy marriage and a 40-year-old woman in a pretty happy marriage. Then, use these examples to show that e-1.23 is the odds ratio of female odds to male odds.
Calculate probabilities for a 40-year-old man in a pretty happy marriage and a 40-year-old woman in a pretty happy marriage. Then, use these examples to show that e-1.23 is the odds ratio of female odds to male odds.
Dependent Variable: Seen X-Rated Movie in Past Year? (No=0, 1=Yes)
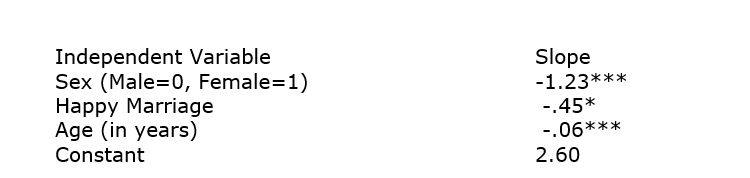 Calculate probabilities for a 40-year-old man in a pretty happy marriage and a 40-year-old woman in a pretty happy marriage. Then, use these examples to show that e-1.23 is the odds ratio of female odds to male odds.
Calculate probabilities for a 40-year-old man in a pretty happy marriage and a 40-year-old woman in a pretty happy marriage. Then, use these examples to show that e-1.23 is the odds ratio of female odds to male odds.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Group A has a 60% chance of owning a home, while Group B has a 20% chance of owning a home. Use these examples to show that the odds ratio of owning a home is NOT the same as the ratio of the likelihoods of owning a home.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the wake of 9/11, the GSS asked a new set of questions in 2006 regarding civil rights. One of them was: "Suppose the government suspected that a terrorist act was about to happen. Do you think the authorities should have the right to detain people for as long as they want without putting them on trial?" 53.5% of the respondents said yes, 46.5% said no. Here is a logistic regression model that uses two independent variables: Political Views (Extremely Liberal=0, up to Extremely Conservative=6) and Party Identification (Strong Democrat=0, up to Strong Republican=6).
Dependent Variable: OK with Indefinite Detention? No=0, Yes=1
 Calculate predicted probabilities for an extremely liberal Democrat and an extremely conservative Republican.
Calculate predicted probabilities for an extremely liberal Democrat and an extremely conservative Republican.
Dependent Variable: OK with Indefinite Detention? No=0, Yes=1
 Calculate predicted probabilities for an extremely liberal Democrat and an extremely conservative Republican.
Calculate predicted probabilities for an extremely liberal Democrat and an extremely conservative Republican.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
By describing their dependent variable, explain why Beyerlein, Soule, and Martin use logistic regression in their article on protest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



