Deck 8: Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Supply
1
An increase in the price of soybeans results in a:
A) decrease in the quantity supplied of wheat and increase in the supply of soybeans
B) increase in the quantity supplied of wheat and decrease in the supply of soybeans
C) decrease in the supply of wheat and increase in the quantity supplied of soybeans
D) increase in the supply of wheat and decrease in the quantity supplied of soybeans
A) decrease in the quantity supplied of wheat and increase in the supply of soybeans
B) increase in the quantity supplied of wheat and decrease in the supply of soybeans
C) decrease in the supply of wheat and increase in the quantity supplied of soybeans
D) increase in the supply of wheat and decrease in the quantity supplied of soybeans
C
2
A decrease in the price of oil results in:
A) a decrease in the quantity supplied of natural gas
B) an increase in the supply of wheat
C) an increase in the quantity supplied of oil
D) all of the above
A) a decrease in the quantity supplied of natural gas
B) an increase in the supply of wheat
C) an increase in the quantity supplied of oil
D) all of the above
B
3
All of the following are determinants of supply except:
A) input prices
B) income
C) technology
D) output prices
A) input prices
B) income
C) technology
D) output prices
B
4
An increase in the number of greenhouses in New York City results in:
A) an increase in the quantity supplied of flowers
B) an increase in the supply of flowers
C) diminishing returns to flower production
D) economies to scale in flower production
A) an increase in the quantity supplied of flowers
B) an increase in the supply of flowers
C) diminishing returns to flower production
D) economies to scale in flower production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Ethanol has resulted in:
A) higher corn prices
B) higher corn and soybean prices
C) higher corn prices, but lower soybean prices
D) lower corn and soybean prices
A) higher corn prices
B) higher corn and soybean prices
C) higher corn prices, but lower soybean prices
D) lower corn and soybean prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An increase in the supply of cut flowers will:
A) shift the demand curve for flowers
B) cause a movement along the demand curve for flowers
C) leave consumption of flowers the same
D) not enough information to answer
A) shift the demand curve for flowers
B) cause a movement along the demand curve for flowers
C) leave consumption of flowers the same
D) not enough information to answer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If wheat farmers have a good year, with higher than expected yields, ceteris paribus, then:
A) the price of wheat will increase
B) the price of wheat will decrease
C) it just depends on the price of corn
D) not enough information to answer
A) the price of wheat will increase
B) the price of wheat will decrease
C) it just depends on the price of corn
D) not enough information to answer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A drought will:
A) decrease the supply of grains
B) decrease the quantity of grains supplied
C) shift the supply curve down
D) result in a movement along the supply of grains
A) decrease the supply of grains
B) decrease the quantity of grains supplied
C) shift the supply curve down
D) result in a movement along the supply of grains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Agricultural research results in:
A) an upward movement along the supply curve of wheat
B) a downward movement along the supply curve of wheat
C) an outward shift in the supply curve of wheat
D) a inward shift in the supply curve of wheat
A) an upward movement along the supply curve of wheat
B) a downward movement along the supply curve of wheat
C) an outward shift in the supply curve of wheat
D) a inward shift in the supply curve of wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An increase in the price of fertilizer will cause:
A) the supply of fertilizer to increase
B) the quantity supplied of fertilizer to increase
C) a shift in the supply of fertilizer
D) a movement along the supply curve of wheat
A) the supply of fertilizer to increase
B) the quantity supplied of fertilizer to increase
C) a shift in the supply of fertilizer
D) a movement along the supply curve of wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Elasticities are:
A) in units of quantity
B) in units of price
C) unitless
D) in units of quantity/price
A) in units of quantity
B) in units of price
C) unitless
D) in units of quantity/price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The point elasticity of the supply of hamburger is equal to:
A) the slope of the supply curve of hamburger
B) the percentage change in hamburger supplied divided by the percentage change in the price of hamburger
C) the percentage change in the price of hamburger divided by the percentage change in the quantity supplied of hamburger
D) the arc elasticity of the supply of hamburger
A) the slope of the supply curve of hamburger
B) the percentage change in hamburger supplied divided by the percentage change in the price of hamburger
C) the percentage change in the price of hamburger divided by the percentage change in the quantity supplied of hamburger
D) the arc elasticity of the supply of hamburger

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An elasticity measures:
A) how prices affect inflation
B) the Law of Supply
C) how economic variables influence the stock market
D) how responsive one variable is to another
A) how prices affect inflation
B) the Law of Supply
C) how economic variables influence the stock market
D) how responsive one variable is to another

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Agricultural biotechnology results in the following changes in the food market:
A) an increase in equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity
B) a decrease in equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity
C) a decrease in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity
D) an increase in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity
A) an increase in equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity
B) a decrease in equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity
C) a decrease in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity
D) an increase in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Supply is:
A) The relationship between the price of a good and amount available
B) How much food is in the food chain
C) How much food customers purchase
D) Equal to income in low-income nations
A) The relationship between the price of a good and amount available
B) How much food is in the food chain
C) How much food customers purchase
D) Equal to income in low-income nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the price of a good increases:
A) The quantity supplied of the good will increase
B) The supply of the good will increase
C) The quantity supplied of the good will decrease
D) The supply of the good will decrease
A) The quantity supplied of the good will increase
B) The supply of the good will increase
C) The quantity supplied of the good will decrease
D) The supply of the good will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
an individual firm will supply goods until:
A) The quantity supplied equals quantity demanded
B) MR > MC
C) MR < MC
D) MR = MC
A) The quantity supplied equals quantity demanded
B) MR > MC
C) MR < MC
D) MR = MC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An individual firm supply curve equals:
A) AVC above MC
B) MC below AVC
C) MC above AVC
D) AVC below MC
A) AVC above MC
B) MC below AVC
C) MC above AVC
D) AVC below MC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An individual firm's supply curve equals:
A) MR above the break-even point
B) MC above the shut-down point
C) MC above the break-even point
D) MC above the shut-down point
A) MR above the break-even point
B) MC above the shut-down point
C) MC above the break-even point
D) MC above the shut-down point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the price is below minimum AVC, the firm's supply equals:
A) Zero
B) MR
C) MC
D) AVC
A) Zero
B) MR
C) MC
D) AVC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The market supply curve is:
A) The horizontal sum of all individual firms' supply curves
B) The vertical sum of all individual firms' supply curves
C) The horizontal sum of individual firms' demand curves
D) The vertical sum of all individual firms' demand curves
A) The horizontal sum of all individual firms' supply curves
B) The vertical sum of all individual firms' supply curves
C) The horizontal sum of individual firms' demand curves
D) The vertical sum of all individual firms' demand curves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The market supply curve:
A) Slopes up due to diminishing marginal returns
B) Slopes up due to the Law of Supply
C) Slopes up due to economies of scale
D) Slopes up due to scarcity
A) Slopes up due to diminishing marginal returns
B) Slopes up due to the Law of Supply
C) Slopes up due to economies of scale
D) Slopes up due to scarcity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
a supply schedule shows:
A) How quantity supplied changes over time
B) How quantity supplied changes with different prices
C) How quantity supplied changes with different incomes
D) How prices change at a fixed quantity supplied
A) How quantity supplied changes over time
B) How quantity supplied changes with different prices
C) How quantity supplied changes with different incomes
D) How prices change at a fixed quantity supplied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Law of Supply is due to:
A) Diminishing marginal returns
B) Rationality
C) Scarcity
D) The profit-maximizing behavior of firms
A) Diminishing marginal returns
B) Rationality
C) Scarcity
D) The profit-maximizing behavior of firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the supply equation:
A) The price is the independent variable and quantity supplied is the dependent variable
B) The price is the dependent variable and quantity supplied is the independent variable
C) Both price and quantity supplied are independent variables
D) Both price and quantity supplied are dependent variables
A) The price is the independent variable and quantity supplied is the dependent variable
B) The price is the dependent variable and quantity supplied is the independent variable
C) Both price and quantity supplied are independent variables
D) Both price and quantity supplied are dependent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Economists draw supply curves "backward" due to:
A) Adam Smith
B) John Maynard Keynes
C) Alfred Marshall
D) John Phillip Sousa
A) Adam Smith
B) John Maynard Keynes
C) Alfred Marshall
D) John Phillip Sousa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The elasticity of supply:
A) Decreases over time
B) Tells how impossible it is to increase food supply
C) Tells how responsive supply is to changes in weather
D) Tells how responsive supply is to changes in price
A) Decreases over time
B) Tells how impossible it is to increase food supply
C) Tells how responsive supply is to changes in weather
D) Tells how responsive supply is to changes in price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An inelastic supply curve:
A) Has a steep slope
B) Has a shallow slope
C) Has a horizontal slope
D) Depends on the units used in the graph
A) Has a steep slope
B) Has a shallow slope
C) Has a horizontal slope
D) Depends on the units used in the graph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An elastic supply curve is:
A) Less steep than an inelastic supply curve
B) More steep than an inelastic supply curve
C) The same steepness of an inelastic supply curve
D) Vertical
A) Less steep than an inelastic supply curve
B) More steep than an inelastic supply curve
C) The same steepness of an inelastic supply curve
D) Vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A unitary elastic supply curve:
A) =1
B) >1
C) <1
D) Not enough information to know
A) =1
B) >1
C) <1
D) Not enough information to know

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the price of oranges increases by one percent and wheat supply increases by six percent then the elasticity of supply of wheat is equal to:
A) 1
B) 8
C) 1/6
D) Not enough information to know
A) 1
B) 8
C) 1/6
D) Not enough information to know

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the price of shirts increases 10 percent and the quantity supplied of shirts increases 5 percent, then the elasticity of supply of shirts is:
A) Unitary elastic
B) Elastic
C) Inelastic
D) Not enough information to know
A) Unitary elastic
B) Elastic
C) Inelastic
D) Not enough information to know

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The price elasticity of supply will:
A) Increase over time
B) Decrease over time
C) Not change over time
D) Not enough information to know
A) Increase over time
B) Decrease over time
C) Not change over time
D) Not enough information to know

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If bread supply increases from 10 to 12 million loaves,then the percentage change in bread supply is equal to:
A) 1.2
B) 0.2
C) 2
D) 1
A) 1.2
B) 0.2
C) 2
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An arc elasticity of supply is:
A) The same as the point elasticity of supply
B) Differs from the point elasticity of supply due to the starting and ending values
C) Is less accurate than the point elasticity of supply
D) Is in the shape of an arc
A) The same as the point elasticity of supply
B) Differs from the point elasticity of supply due to the starting and ending values
C) Is less accurate than the point elasticity of supply
D) Is in the shape of an arc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
if the price of corn increases, then the supply of wheat:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Stays the same
D) Not enough information to know
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Stays the same
D) Not enough information to know

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The cross price elasticity of supply of corn and wheat is:
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Unitary
D) Zero
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Unitary
D) Zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The price elasticity of supply refers to:
A) How responsive consumers are to changes in price
B) The cross price elasticity of supply
C) The own price elasticity of supply
D) How responsive supply is to production decisions
A) How responsive consumers are to changes in price
B) The cross price elasticity of supply
C) The own price elasticity of supply
D) How responsive supply is to production decisions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The arc elasticity of supply equals:
A) The point elasticity of supply at the starting values
B) The point elasticity of supply at the ending values
C) The average of the point elasticity of supply at the starting and ending values
D) Something in between the point elasticity of supply at the starting and ending values
A) The point elasticity of supply at the starting values
B) The point elasticity of supply at the ending values
C) The average of the point elasticity of supply at the starting and ending values
D) Something in between the point elasticity of supply at the starting and ending values

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The cross price elasticity of supply of Coke and Pepsi is:
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Unitary
D) Zero
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Unitary
D) Zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
41. The cross price elasticity of supply of steak and leather is:
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Unitary
D) Zero
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Unitary
D) Zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the price of oil increases:
A) The supply of oil will increase
B) The supply of oil will decrease
C) The quantity supplied of oil will increase
D) The quantity supplied of oil will decrease
A) The supply of oil will increase
B) The supply of oil will decrease
C) The quantity supplied of oil will increase
D) The quantity supplied of oil will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the price of oil increases:
A) The supply of wheat will increase
B) The supply of wheat will decrease
C) The quantity supplied of wheat will increase
D) The quantity supplied of wheat will decrease
A) The supply of wheat will increase
B) The supply of wheat will decrease
C) The quantity supplied of wheat will increase
D) The quantity supplied of wheat will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the price of oil increases:
A) The supply of natural gas will increase
B) The supply of natural gas will decrease
C) The quantity supplied of natural gas will increase
D) The quantity supplied of natural gas will decrease
A) The supply of natural gas will increase
B) The supply of natural gas will decrease
C) The quantity supplied of natural gas will increase
D) The quantity supplied of natural gas will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the price of oil increases:
A) There is a movement along up the supply curve of oil
B) There is a movement along down the supply curve of oil
C) There is an upward shift in the supply curve of oil
D) There is a downward shift in the supply curve of oil
A) There is a movement along up the supply curve of oil
B) There is a movement along down the supply curve of oil
C) There is an upward shift in the supply curve of oil
D) There is a downward shift in the supply curve of oil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the price of wheat decreases:
A) There is a movement along up the supply curve of wheat
B) There is a movement along down the supply curve of wheat
C) There is an upward shift in the supply curve of wheat
D) There is a downward shift in the supply curve of wheat
A) There is a movement along up the supply curve of wheat
B) There is a movement along down the supply curve of wheat
C) There is an upward shift in the supply curve of wheat
D) There is a downward shift in the supply curve of wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Technological change:
A) Shifts the demand curve to the right
B) Shifts the demand curve to the left
C) Shifts the supply curve to the right
D) Shifts the supply curve to the left
A) Shifts the demand curve to the right
B) Shifts the demand curve to the left
C) Shifts the supply curve to the right
D) Shifts the supply curve to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
GMOs are controversial because:
A) They could have unanticipated consequences on human health
B) They could have unanticipated consequences on the environment
C) Glyphosate could be a carcinogen
D) All of the above
A) They could have unanticipated consequences on human health
B) They could have unanticipated consequences on the environment
C) Glyphosate could be a carcinogen
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Complements in production are:
A) Goods produced either/or
B) Goods produced together
C) Unrelated goods
D) Saying something nice to a producer
A) Goods produced either/or
B) Goods produced together
C) Unrelated goods
D) Saying something nice to a producer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Substitutes in production are:
A) Goods produced either/or
B) Goods produced together
C) Unrelated goods
D) Saying something nice to a producer
A) Goods produced either/or
B) Goods produced together
C) Unrelated goods
D) Saying something nice to a producer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why do we study supply and demand? Explain thoroughly and carefully.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Supply Curve.
A. Define the term, "supply curve."
B. What does the supply curve represent, intuitively?
C. How is the market supply curve derived?
D. List the determinants of supply.
E. Carefully describe and explain the difference between the movement along and a shift in supply.
A. Define the term, "supply curve."
B. What does the supply curve represent, intuitively?
C. How is the market supply curve derived?
D. List the determinants of supply.
E. Carefully describe and explain the difference between the movement along and a shift in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A. What is the equation of the cross-price elasticity of supply of beef and pork?
B. What is the sign of the cross-price elasticity of supply of beef and pork? Explain.
C. What is the equation of the cross-price elasticity of demand of beef and pork?
D. What is the sign of the cross-price elasticity of demand of beef and pork? Explain.
B. What is the sign of the cross-price elasticity of supply of beef and pork? Explain.
C. What is the equation of the cross-price elasticity of demand of beef and pork?
D. What is the sign of the cross-price elasticity of demand of beef and pork? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Own-Price Elasticity of Supply (Es).
Suppose that the price of pizza increases from P0=USD 6/pizza to P1=USD 10/pizza, resulting in an increase in pizzas produced from Q0= 10 pizzas to Q1= 12 pizzas.
A. Calculate ε at the initial values of P and Q.
B. Is pizza supply elastic or inelastic? Demonstrate and explain.
C. Is the pizza firm in the immediate run, short run, or long run? Explain.
Suppose that the price of pizza increases from P0=USD 6/pizza to P1=USD 10/pizza, resulting in an increase in pizzas produced from Q0= 10 pizzas to Q1= 12 pizzas.
A. Calculate ε at the initial values of P and Q.
B. Is pizza supply elastic or inelastic? Demonstrate and explain.
C. Is the pizza firm in the immediate run, short run, or long run? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Cross-Price Elasticity of Supply (Esxy)..
A. What is the formula and sign of the cross-price elasticity of supply of pizza and bread sticks? Note: assume that the bread sticks are made from left-over pizza dough.
B. What is the formula and sign of the cross-price elasticity of supply of pepperoni pizza and cheese pizza?
A. What is the formula and sign of the cross-price elasticity of supply of pizza and bread sticks? Note: assume that the bread sticks are made from left-over pizza dough.
B. What is the formula and sign of the cross-price elasticity of supply of pepperoni pizza and cheese pizza?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider a competitive market for pork with the quantity supplied (per year) at various prices are given as follows:
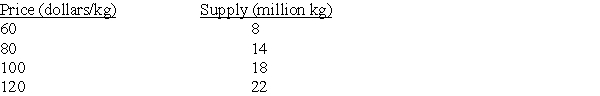
A. Calculate the price elasticity of supply when the price is USD 80/kg.
B. Calculate the price elasticity of supply when the price is USD 100/kg.
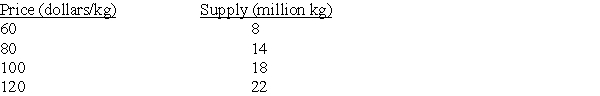
A. Calculate the price elasticity of supply when the price is USD 80/kg.
B. Calculate the price elasticity of supply when the price is USD 100/kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Organic vegetables are traded in a competitive world market, and the world price is USD 9/lb. unlimited quantities are available for import into the United States at this price. The U.S. domestic supply for various price levels are shown as follows:

A. What is the equation for supply?
B. At a price of USD 9/lb, what is the price elasticity of supply?
C. At a price of USD 12/lb, what is the price elasticity of supply?

A. What is the equation for supply?
B. At a price of USD 9/lb, what is the price elasticity of supply?
C. At a price of USD 12/lb, what is the price elasticity of supply?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Write an essay on how economic thinking could help improve your life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



