Deck 10: Controlling Microbial Growth in the Body: Antimicrobial Drugs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Controlling Microbial Growth in the Body: Antimicrobial Drugs
1
Which of the following is a primary advantage of semisynthetic drugs?
A) They are less stable and consequently have fewer side effects.
B) They work faster.
C) They have a broader spectrum of action.
D) They must be administered intravenously.
E) They are not readily absorbed, so they persist longer.
A) They are less stable and consequently have fewer side effects.
B) They work faster.
C) They have a broader spectrum of action.
D) They must be administered intravenously.
E) They are not readily absorbed, so they persist longer.
C
2
β-lactamase production is an example of which of the following types of resistance?
A) alteration of the target of the drug
B) inactivation of the drug
C) change in the permeability of the drug
D) overproduction of an enzyme in a key metabolic pathway
E) removal of the drug via a pump
A) alteration of the target of the drug
B) inactivation of the drug
C) change in the permeability of the drug
D) overproduction of an enzyme in a key metabolic pathway
E) removal of the drug via a pump
B
3
A drug is structurally similar to PABA and inhibits folic acid synthesis.It is most likely a(n)
A) nucleic acid analog.
B) penicillin.
C) tetracycline.
D) azole.
E) sulfonamide.
A) nucleic acid analog.
B) penicillin.
C) tetracycline.
D) azole.
E) sulfonamide.
E
4
Which of the following antibiotics disrupts cytoplasmic membrane function in fungi?
A) streptomycin
B) erythromycin
C) tetracycline
D) penicillin
E) amphotericin B
A) streptomycin
B) erythromycin
C) tetracycline
D) penicillin
E) amphotericin B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following groups of drugs can become incorporated into the bones and teeth of a fetus?
A) beta-lactams
B) aminoglycosides
C) quinolones
D) tetracyclines
E) sulfonamides
A) beta-lactams
B) aminoglycosides
C) quinolones
D) tetracyclines
E) sulfonamides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Who proposed the concept of chemotherapy,that compounds might selectively kill pathogens without harming people?
A) Gerhard Domagk
B) Alexander Fleming
C) Paul Ehrlich
D) Selman Waksman
E) Joseph Lister
A) Gerhard Domagk
B) Alexander Fleming
C) Paul Ehrlich
D) Selman Waksman
E) Joseph Lister

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following can result when antibiotic therapy disrupts the normal microbiota?
A) anaphylactic shock
B) black hairy tongue
C) pseudomembranous colitis
D) thrush
E) both pseudomembranous colitis and thrush
A) anaphylactic shock
B) black hairy tongue
C) pseudomembranous colitis
D) thrush
E) both pseudomembranous colitis and thrush

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Most broad-spectrum antibiotics act by
A) inhibiting the synthesis of the cell wall.
B) inhibiting protein synthesis.
C) inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis.
D) inhibiting metabolic pathways.
E) disrupting the cytoplasmic membrane.
A) inhibiting the synthesis of the cell wall.
B) inhibiting protein synthesis.
C) inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis.
D) inhibiting metabolic pathways.
E) disrupting the cytoplasmic membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following antifungals works by binding to ergosterol in membranes?
A) fluconazole
B) turbinafine
C) amphotericin B
D) nystatin
E) both amphotericin B and nystatin
A) fluconazole
B) turbinafine
C) amphotericin B
D) nystatin
E) both amphotericin B and nystatin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following drugs specifically targets cell walls that contain mycolic acid?
A) vancomycin
B) penicillin
C) methicillin
D) isoniazid
E) bacitracin
A) vancomycin
B) penicillin
C) methicillin
D) isoniazid
E) bacitracin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Most drugs that inhibit the synthesis of the cell wall act by
A) preventing the cross-linkage of NAM subunits.
B) blocking the secretion of cell wall molecules from the cytoplasm.
C) preventing the formation of alanine-alanine bridges.
D) disrupting the formation of the mycolic acid layer of the cell wall.
E) preventing the formation of β-lactamases.
A) preventing the cross-linkage of NAM subunits.
B) blocking the secretion of cell wall molecules from the cytoplasm.
C) preventing the formation of alanine-alanine bridges.
D) disrupting the formation of the mycolic acid layer of the cell wall.
E) preventing the formation of β-lactamases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Bacillus licheniformis secretes a compound that inhibits the growth of other Gram-positive bacteria.This is an example of a(n)
A) analog.
B) antibiotic.
C) chemotherapeutic.
D) porin.
E) toxin.
A) analog.
B) antibiotic.
C) chemotherapeutic.
D) porin.
E) toxin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is NOT a target of drugs that inhibit protein synthesis?
A) the shape of the 30S ribosomal subunit
B) interference with alanine-alanine bridges
C) the enzymatic site of the 50S ribosomal subunit
D) movement of the ribosome from one codon to the next
E) the tRNA docking site
A) the shape of the 30S ribosomal subunit
B) interference with alanine-alanine bridges
C) the enzymatic site of the 50S ribosomal subunit
D) movement of the ribosome from one codon to the next
E) the tRNA docking site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An antimicrobial that inhibits cell wall synthesis will result in which of the following?
A) Cells become more susceptible to osmotic pressure.
B) Cells cannot attach to their hosts.
C) Ribosomes lose their function.
D) The sterols in the cell wall become nonfunctional.
E) The replication of cells, including cancer cells, slows down.
A) Cells become more susceptible to osmotic pressure.
B) Cells cannot attach to their hosts.
C) Ribosomes lose their function.
D) The sterols in the cell wall become nonfunctional.
E) The replication of cells, including cancer cells, slows down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A compound is extracted from a microbial culture and is modified in the laboratory for use as an oral medication.This product would be a(n)
A) antibiotic.
B) analog.
C) semisynthetic antimicrobial.
D) synthetic antimicrobial.
E) probiotic.
A) antibiotic.
B) analog.
C) semisynthetic antimicrobial.
D) synthetic antimicrobial.
E) probiotic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
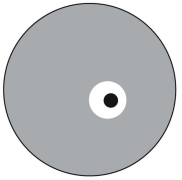
Figure represents a Petri plate.The gray area is where bacteria A is growing,the black area is where bacteria B is growing.The white area is a zone where neither organism is growing.What is the best interpretation of what is observed on the plate?
A) Bacteria B is producing an antibiotic that inhibits the growth of bacteria A.
B) Bacteria A produces a compound that inhibits the growth of bacteria B.
C) Bacteria A grows faster than bacteria B.
D) Bacterial colony B has depleted the nutrients in the area around the colony.
E) No conclusion can be made from this information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Amoxicillin is very effective for treating infections with Gram-positive bacteria but rarely causes side effects in humans.This is an example of
A) selective toxicity.
B) narrow spectrum of action.
C) a broad-spectrum antimicrobial.
D) antibiotic resistance.
E) altruism.
A) selective toxicity.
B) narrow spectrum of action.
C) a broad-spectrum antimicrobial.
D) antibiotic resistance.
E) altruism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Beta-lactam antibiotics have an effect on which of the following types of cells?
A) animal cells
B) bacterial cells
C) fungal cells
D) virus-infected cells
E) both animal and fungal cells
A) animal cells
B) bacterial cells
C) fungal cells
D) virus-infected cells
E) both animal and fungal cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What does "narrow spectrum antimicrobial" mean?
A) The antimicrobial is effective for a very short time.
B) The antimicrobial is effective against a few microbes.
C) The antimicrobial can only be administered to a small segment of the population.
D) The antimicrobial is activated by a specific wavelength in the visible spectrum.
E) The antimicrobial is effective on all bacteria but not eukaryotes.
A) The antimicrobial is effective for a very short time.
B) The antimicrobial is effective against a few microbes.
C) The antimicrobial can only be administered to a small segment of the population.
D) The antimicrobial is activated by a specific wavelength in the visible spectrum.
E) The antimicrobial is effective on all bacteria but not eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The first antimicrobial widely available for treatment of bacterial infections was a synthetic compound which
A) was an antimetabolic analog.
B) was a nucleotide analog.
C) was an attachment antagonist.
D) disrupted cytoplasmic membranes.
E) interfered with bacterial cell wall synthesis.
A) was an antimetabolic analog.
B) was a nucleotide analog.
C) was an attachment antagonist.
D) disrupted cytoplasmic membranes.
E) interfered with bacterial cell wall synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The cooperative activity of drugs such as beta-lactam antibiotics and clavulanic acid,a β-lactamase inhibitor,is known as
A) cross resistance.
B) antimetabolism.
C) synergism.
D) selective toxicity.
E) chemotherapy.
A) cross resistance.
B) antimetabolism.
C) synergism.
D) selective toxicity.
E) chemotherapy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
It is inappropriate to prescribe antibacterial agents to treat colds or flu because
A) the microbes involved can develop resistance rapidly.
B) these diseases are transmitted by endospores, which are difficult to kill.
C) these diseases exhibit cross resistance.
D) these diseases are caused by viruses.
E) these diseases can act synergistically with each other.
A) the microbes involved can develop resistance rapidly.
B) these diseases are transmitted by endospores, which are difficult to kill.
C) these diseases exhibit cross resistance.
D) these diseases are caused by viruses.
E) these diseases can act synergistically with each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The mechanism of action of the antibiotic vancomycin is
A) inhibition of protein synthesis.
B) inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
C) inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis.
D) inhibition of a metabolic pathway.
E) disruption of cytoplasmic membranes.
A) inhibition of protein synthesis.
B) inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
C) inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis.
D) inhibition of a metabolic pathway.
E) disruption of cytoplasmic membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The antimicrobials called quinolones act by
A) disrupting cytoplasmic membranes.
B) inhibiting cell wall synthesis.
C) inhibiting DNA replication.
D) inhibiting a metabolic pathway.
E) inhibiting protein synthesis.
A) disrupting cytoplasmic membranes.
B) inhibiting cell wall synthesis.
C) inhibiting DNA replication.
D) inhibiting a metabolic pathway.
E) inhibiting protein synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How does resistance to drugs spread in bacterial populations?
A) Exposure to drugs causes mutations in bacterial genes.
B) Horizontal gene transfer between bacteria spreads R (resistance) plasmids.
C) Genetic recombination during sexual reproduction.
D) Exposure to drugs induces immunity.
E) Exposure to drugs alters gene expression in bacteria.
A) Exposure to drugs causes mutations in bacterial genes.
B) Horizontal gene transfer between bacteria spreads R (resistance) plasmids.
C) Genetic recombination during sexual reproduction.
D) Exposure to drugs induces immunity.
E) Exposure to drugs alters gene expression in bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Infection of the ________ would be the hardest to treat with antimicrobial drugs.
A) heart
B) kidneys
C) liver
D) brain
E) colon
A) heart
B) kidneys
C) liver
D) brain
E) colon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Antimicrobials known as "attachment antagonists" are particularly useful for preventing
A) bacterial protein synthesis.
B) cell membrane synthesis.
C) virus infection.
D) nucleic acid synthesis.
E) biofilm formation.
A) bacterial protein synthesis.
B) cell membrane synthesis.
C) virus infection.
D) nucleic acid synthesis.
E) biofilm formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The broth dilution test can provide information for determining
A) the molecular target of an antibiotic.
B) the MIC (minimum inhibitor concentration).
C) the rate of diffusion of an antibiotic.
D) the MBC (minimum bactericidal concentration), with an additional step.
E) both the MIC and the MBC (with an additional step).
A) the molecular target of an antibiotic.
B) the MIC (minimum inhibitor concentration).
C) the rate of diffusion of an antibiotic.
D) the MBC (minimum bactericidal concentration), with an additional step.
E) both the MIC and the MBC (with an additional step).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following interferes with cell wall synthesis by blocking alanine bridge formation?
A) beta-lactams
B) cycloserine
C) bacitracin
D) vancomycin
E) both cycloserine and vancomycin
A) beta-lactams
B) cycloserine
C) bacitracin
D) vancomycin
E) both cycloserine and vancomycin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A "zone of inhibition" is associated with which of the following tests used to determine the efficacy of antibiotics?
A) Etest
B) diffusion susceptibility test
C) broth dilution test
D) both the Etest and diffusion susceptibility test
E) both the broth dilution and the MBC tests
A) Etest
B) diffusion susceptibility test
C) broth dilution test
D) both the Etest and diffusion susceptibility test
E) both the broth dilution and the MBC tests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Disruption of the normal microbiota can result in infections caused by which of the following microbes?
A) Mycobacterium
B) Candida albicans
C) Clostridium difficile
D) both Mycobacterium and Clostridium difficile
E) Candida albicans, Mycobacterium, and Clostridium difficile
A) Mycobacterium
B) Candida albicans
C) Clostridium difficile
D) both Mycobacterium and Clostridium difficile
E) Candida albicans, Mycobacterium, and Clostridium difficile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Antimicrobials that block protein synthesis by binding to the mRNA are
A) aminoglycosides.
B) antisense nucleic acids.
C) macrolides.
D) beta-lactams.
E) nucleic acid analogs.
A) aminoglycosides.
B) antisense nucleic acids.
C) macrolides.
D) beta-lactams.
E) nucleic acid analogs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following drugs inhibits nucleic acid synthesis specifically in most bacteria?
A) fluoroquinolones
B) actinomycin
C) rifampin
D) tetracycline
E) 5-fluorocytosine
A) fluoroquinolones
B) actinomycin
C) rifampin
D) tetracycline
E) 5-fluorocytosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The tetracyclines interfere with
A) protein synthesis.
B) cell wall synthesis.
C) cell membrane component synthesis.
D) nucleic acid synthesis.
E) folic acid synthesis.
A) protein synthesis.
B) cell wall synthesis.
C) cell membrane component synthesis.
D) nucleic acid synthesis.
E) folic acid synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Pentamidine is an example of an antimicrobial
A) used to treat bacterial infections.
B) effective against helminths.
C) used to treat viral infections.
D) effective against eukaryotes, especially protozoa.
E) used to treat both bacterial and fungal infections.
A) used to treat bacterial infections.
B) effective against helminths.
C) used to treat viral infections.
D) effective against eukaryotes, especially protozoa.
E) used to treat both bacterial and fungal infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following steps in the folic acid synthesis pathway is specifically inhibited by sulfonamides?
A) the conversion of tetrahydrofolic acid to PABA
B) the conversion of PABA to dihydrofolic acid
C) the conversion of dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid
D) the conversion of PABA to tetrahydrofolic acid
E) the conversion of dihydrofolic acid to PABA
A) the conversion of tetrahydrofolic acid to PABA
B) the conversion of PABA to dihydrofolic acid
C) the conversion of dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid
D) the conversion of PABA to tetrahydrofolic acid
E) the conversion of dihydrofolic acid to PABA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Some bacteria are resistant to antimicrobials due to the activity of ________,which removes many of them.
A) plasmids
B) porins
C) efflux pumps
D) lipopolysaccharides
E) ribosomes
A) plasmids
B) porins
C) efflux pumps
D) lipopolysaccharides
E) ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Who discovered the first antimicrobial widely available to the general public?
A) Domagk
B) Ehrlich
C) Fleming
D) Waksman
E) Ehrlich and Waksman
A) Domagk
B) Ehrlich
C) Fleming
D) Waksman
E) Ehrlich and Waksman

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The therapeutic range of an antimicrobial is the
A) ratio of the dose a patient can tolerate to the effective dose.
B) range of microorganisms the antimicrobial effects.
C) range of concentrations at which the antimicrobial is both effective and non-toxic.
D) ratio of the concentration of antimicrobial in the blood to the oral dose.
E) length of time the medication persists in the body after a single dose.
A) ratio of the dose a patient can tolerate to the effective dose.
B) range of microorganisms the antimicrobial effects.
C) range of concentrations at which the antimicrobial is both effective and non-toxic.
D) ratio of the concentration of antimicrobial in the blood to the oral dose.
E) length of time the medication persists in the body after a single dose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements is true of selective toxicity?
A) Selective toxicity takes advantage of structural differences between host and pathogen.
B) To be effective, an antimicrobial agent must be more toxic to the patient than the pathogen.
C) Selective toxicity takes advantage of metabolic differences between host and pathogen.
D) Antimicrobial agents must target structural differences between host and pathogen and be more toxic to the patient than the pathogen.
E) Selective toxicity takes advantage of structural and/or metabolic differences between host and pathogen.
A) Selective toxicity takes advantage of structural differences between host and pathogen.
B) To be effective, an antimicrobial agent must be more toxic to the patient than the pathogen.
C) Selective toxicity takes advantage of metabolic differences between host and pathogen.
D) Antimicrobial agents must target structural differences between host and pathogen and be more toxic to the patient than the pathogen.
E) Selective toxicity takes advantage of structural and/or metabolic differences between host and pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Nucleotide or nucleoside (acids/analogs/antisense)are antimicrobial agents that mimic the chemical structure of DNA building blocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Biofilms contribute to the spread of resistance to antimicrobials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a subculture of an MIC test grows in an MBC test,the concentration of the drug was bactericidal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Methicillin is an example of the beta-lactam class of drugs that
A) disrupts cytoplasmic membranes.
B) inhibits cell wall synthesis.
C) inhibits nucleic acid synthesis.
D) inhibits metabolic pathways.
E) inhibits protein synthesis.
A) disrupts cytoplasmic membranes.
B) inhibits cell wall synthesis.
C) inhibits nucleic acid synthesis.
D) inhibits metabolic pathways.
E) inhibits protein synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The mechanism of action of erythromycin is
A) inhibition of protein synthesis.
B) inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
C) inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis.
D) inhibition of a metabolic pathway.
E) disruption of cytoplasmic membranes.
A) inhibition of protein synthesis.
B) inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
C) inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis.
D) inhibition of a metabolic pathway.
E) disruption of cytoplasmic membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Medications administered intravenously can provide much higher effective concentrations than other delivery methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Any drug that acts against a disease is called a(n)(analog/antibiotic/chemotherapeutic)agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Selective (action/toxicity/treatment)means that a given antimicrobial agent is more toxic to a pathogen than to the host being treated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Antisense nucleic acids interfere with protein synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Nucleic acid analog drugs have no effect on human cell replication function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The antimicrobial polymyxin
A) inhibits protein synthesis.
B) inhibits nucleic acid synthesis.
C) blocks a metabolic pathway.
D) disrupts cytoplasmic membranes.
E) inhibits cell wall synthesis.
A) inhibits protein synthesis.
B) inhibits nucleic acid synthesis.
C) blocks a metabolic pathway.
D) disrupts cytoplasmic membranes.
E) inhibits cell wall synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria enables many antimicrobial drugs to enter the cell more easily.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Secondary infections that result from the killing of some of the normal microbiota are called (antagonism/superinfections/resistance).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Organs that are commonly affected by drug toxicity include the kidneys and the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Some bacterial cells are resistant to a variety of antimicrobials because they actively pump the drugs out of the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Drug-resistant populations of microbes arise when
A) exposure to drugs selectively kills sensitive cells, allowing overgrowth of resistant cells.
B) exposure to drugs causes mutations that produce resistance.
C) resistant cells become numerous in a population due to their greater vigor.
D) the patient becomes immune to the drug.
E) synergy between medications occurs.
A) exposure to drugs selectively kills sensitive cells, allowing overgrowth of resistant cells.
B) exposure to drugs causes mutations that produce resistance.
C) resistant cells become numerous in a population due to their greater vigor.
D) the patient becomes immune to the drug.
E) synergy between medications occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A microbe resistant to a variety of different antimicrobials is said to have (cross/drug/multiple)resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Because all cells engage in protein synthesis,there are few antimicrobial drugs that selectively inhibit this process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Paul Erhlich coined the term antibiotics for the "magic bullet" antimicrobials he pursued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
AZT and Valaciclovir are antiviral nucleoside analogs that interfere with
A) protein synthesis.
B) cell wall synthesis.
C) cell membrane component synthesis.
D) nucleic acid synthesis.
E) viral attachment.
A) protein synthesis.
B) cell wall synthesis.
C) cell membrane component synthesis.
D) nucleic acid synthesis.
E) viral attachment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Discuss the cellular factors that might make a drug's spectrum of action narrow rather than broad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The abbreviation (MBC/MIC/MID)stands for the smallest amount of a drug that will inhibit the growth and reproduction of a pathogen.(Be sure to use all capital letters.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A (bacteriocidial/bacteriostatic/minimum)concentration of a drug is one at which microbes survive but are not able to grow and reproduce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Some bacteria develop resistance to groups of drugs because the drugs are all structurally similar to each other; this is a phenomenon known as (cross/multiple/synergistic)resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
External infections can be treated by (intramuscular/surface/topical)administration,in which a drug is applied directly to the site of infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Why can microbial resistance to antibiotics and other drugs be considered a primarily genetic phenomenon?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Semisynthetic drugs developed to combat resistance are often called (analog/second generation/synergist)drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Antiviral medications frequently block unique (proteins/enzymes/molecules)to prevent production of a new virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
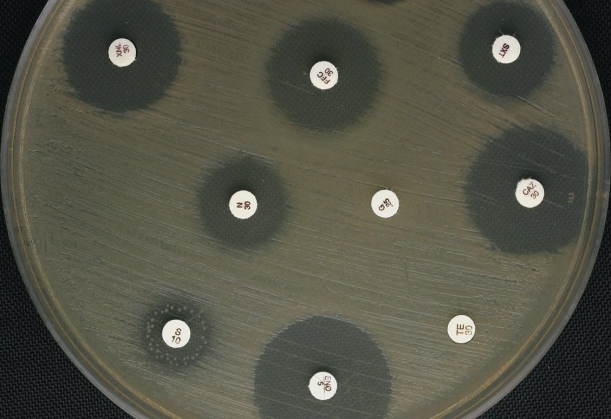

Examine the diffusion susceptibility plate results shown in Figure 10.2.Propose an explanation for the appearance of the zone around the S/10 disk,and discuss the implications for therapeutic use of this antibiotic for the pathogen tested.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The ratio of a medication's dose that can be tolerated to its effective dose is the therapeutic (MIC/index/range)of the medication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Competition between beneficial microbes and potential pathogens is called microbial (antagonisms/synergy/toxicity).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Drugs known as beta-lactams interfere with bacterial (DNA/folic acid/cell wall)synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A newly discovered prokaryote produces a compound with promising antimicrobial effects.Devise a set of tests to determine whether the antimicrobial is broad or narrow spectrum and bactericidal or bacteriostatic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Explain the concept of selective toxicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Medications which block viral entry into cells include (adhesin/analog/attachment)antagonists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



