Deck 2: Cell Chemistry and Bioenergetics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Cell Chemistry and Bioenergetics
1
Which of the following chemicals do you NOT expect to be readily dissolved in water?
A) Uric acid
B) Hexane
C) Glycerol
D) Ethanol
E) Potassium chloride
A) Uric acid
B) Hexane
C) Glycerol
D) Ethanol
E) Potassium chloride
B
Explanation: Hexane is an alkane hydrocarbon incapable of hydrogen-bonding with water molecules, which results in an entropically unfavorable state when the two interact. All the other mentioned chemicals can be readily dissolved in water because they have polar bonds or can dissociate into ions.
Explanation: Hexane is an alkane hydrocarbon incapable of hydrogen-bonding with water molecules, which results in an entropically unfavorable state when the two interact. All the other mentioned chemicals can be readily dissolved in water because they have polar bonds or can dissociate into ions.
2
The cell can change the pH of its internal compartments using membrane transport proteins that pump protons into or out of a compartment. How many protons should be pumped into an endocytic vesicle that is 10-¹⁵ liters in volume and has a neutral pH in order to change the pH to 5? Avogadro's number is 6 × 10²³. Omit complications such as the membrane potential, buffers, and other cellular components.
A) 6000
B) 60,000
C) 120,000
D) 600,000
E) 6,000,000
A) 6000
B) 60,000
C) 120,000
D) 600,000
E) 6,000,000
A
Explanation: The initial number of hydronium ions would be: [H₃O⁺]₁ = 10-¹⁵ L × 10-⁷ mole/L = 10-²² mole. The final number at pH 5 would be: [H₃O⁺]₂ = 10-¹⁵ L × 10-⁵ mole/L = 10-²⁰ mole. The difference is: [H₃O⁺]₂ - [H₃O⁺]₁ = 9.9 × 10-²¹ mole. This is equivalent to approximately 6000 protons that need to be pumped in.
Explanation: The initial number of hydronium ions would be: [H₃O⁺]₁ = 10-¹⁵ L × 10-⁷ mole/L = 10-²² mole. The final number at pH 5 would be: [H₃O⁺]₂ = 10-¹⁵ L × 10-⁵ mole/L = 10-²⁰ mole. The difference is: [H₃O⁺]₂ - [H₃O⁺]₁ = 9.9 × 10-²¹ mole. This is equivalent to approximately 6000 protons that need to be pumped in.
3
The folding of proteins can be considered a simple conversion from the unfolded to the natively folded state. At about 27°C (or 300 K), the free-energy change of folding for a particular protein is measured to be -40 kJ/mole. If the enthalpy change (?H) of folding is -640 kJ/mole, what is the entropy change (?S) of folding for this protein? Write down your answer with the appropriate sign (+ or -) and in kJ/mole/K, e.g. -1000 kJ/mole/K.
-2 kJ/mole/K
4
Which of the following elements is not normally found in cells?
A) Copper
B) Iron
C) Silver
D) Cobalt
E) Zinc
A) Copper
B) Iron
C) Silver
D) Cobalt
E) Zinc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Weak noncovalent attractions in the cell can be very strong in a nonaqueous environment. Some of these attractions are as strong as covalent interactions in a vacuum (their bond energy is approximately 340 kJ/mole), but become more than twenty-five times weaker (their bond energy becomes approximately 13 kJ/mole) in water. What type of attraction shows this phenomenon?
A) Electrostatic attractions
B) Hydrogen bonds
C) van der Waals attractions
D) Hydrophobic force
E) All of the above
A) Electrostatic attractions
B) Hydrogen bonds
C) van der Waals attractions
D) Hydrophobic force
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the following diagram showing the distribution of thermal energy in a population of substrate molecules, the energy thresholds indicated by numbers represent ... 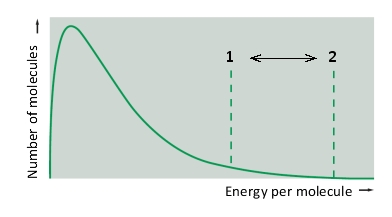
A) the activation energy at high and low temperature.
B) the reaction rate at high and low pH.
C) the activation energy with and without an enzyme.
D) the reaction rate at high and low substrate concentrations.
E) the activation energy at high and low substrate concentrations.

A) the activation energy at high and low temperature.
B) the reaction rate at high and low pH.
C) the activation energy with and without an enzyme.
D) the reaction rate at high and low substrate concentrations.
E) the activation energy at high and low substrate concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Sort the following from a low to a high contribution to the total mass of an E. coli bacterium. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters A to D only, e.g. DCBA.
(A) Water
(B) Sugars
(C) Proteins
(D) Nucleic acids
(A) Water
(B) Sugars
(C) Proteins
(D) Nucleic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the pH of a 10-⁸ M solution of hydrochloric acid? Round the pH value to the nearest integer, e.g. 10.
A) 8
B) 7
C) 6
D) 5
E) 4
A) 8
B) 7
C) 6
D) 5
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A hydrophobic molecule is typically …
A) able to form hydrogen bonds with itself but not with water.
B) able to form hydrogen bonds with water.
C) charged.
D) hard to dissolve in a solvent.
E) incapable of interacting favorably with water.
A) able to form hydrogen bonds with itself but not with water.
B) able to form hydrogen bonds with water.
C) charged.
D) hard to dissolve in a solvent.
E) incapable of interacting favorably with water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Enzymes are the cell's catalyst crew. They make the life of the cell possible by carrying out various reactions with astounding performance. Which of the following is NOT true regarding cellular enzymes?
A) Enzymes lower the activation energy of the reactions that they catalyze.
B) Enzymes can specifically drive substrate along certain reaction pathways.
C) Enzymes can push energetically unfavorable reactions forward by coupling them to energetically favorable reactions.
D) Enzymes are proteins, but RNA catalysts, called ribozymes, also exist.
E) Enzymes can change the equilibrium point for reactions that they catalyze.
A) Enzymes lower the activation energy of the reactions that they catalyze.
B) Enzymes can specifically drive substrate along certain reaction pathways.
C) Enzymes can push energetically unfavorable reactions forward by coupling them to energetically favorable reactions.
D) Enzymes are proteins, but RNA catalysts, called ribozymes, also exist.
E) Enzymes can change the equilibrium point for reactions that they catalyze.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The amino acid serine has an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a hydroxyl group. Which of the following better represents the structure of this amino acid at neutral pH? 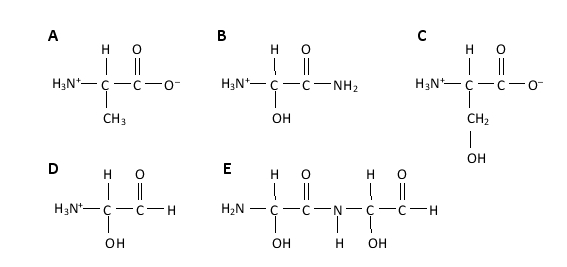


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A cellular enzyme catalyzes the catabolic reaction shown below. Its coenzyme is shown in the box. Which of the following is correct regarding this reaction? 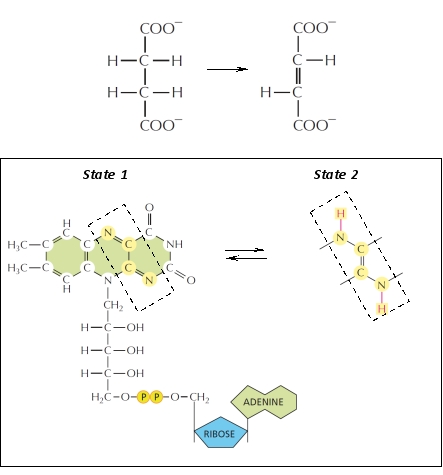
A) The substrate is reduced in this reaction and the coenzyme is converted from state 1 to state 2.
B) The substrate is oxidized in this reaction and the coenzyme is converted from state 1 to state 2.
C) The substrate is reduced in this reaction and the coenzyme is converted from state 2 to state 1.
D) The substrate is oxidized in this reaction and the coenzyme is converted from state 2 to state 1.

A) The substrate is reduced in this reaction and the coenzyme is converted from state 1 to state 2.
B) The substrate is oxidized in this reaction and the coenzyme is converted from state 1 to state 2.
C) The substrate is reduced in this reaction and the coenzyme is converted from state 2 to state 1.
D) The substrate is oxidized in this reaction and the coenzyme is converted from state 2 to state 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements is true regarding cellular metabolism?
A) A living organism decreases the entropy in its surroundings.
B) During catabolism, heat is generated, and the cell uses this heat to perform work during anabolism.
C) The heat released by an animal cell as part of its metabolic processes comes from the bond energies in the foodstuffs that are consumed by the animal.
D) Living organisms defy the second law of thermodynamics, but still obey the first law.
A) A living organism decreases the entropy in its surroundings.
B) During catabolism, heat is generated, and the cell uses this heat to perform work during anabolism.
C) The heat released by an animal cell as part of its metabolic processes comes from the bond energies in the foodstuffs that are consumed by the animal.
D) Living organisms defy the second law of thermodynamics, but still obey the first law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is true regarding reactions involving oxidation and reduction?
A) The carbon atom is more oxidized in formaldehyde (CH₂O) than in methanol (CH₃OH).
B) Oxidation of food in all organisms requires oxygen.
C) A molecule is oxidized if it gains an electron (plus a proton) in a reaction.
D) A dehydrogenation reaction is a reduction.
E) In an organic molecule, the number of C-H bonds increases as a result of oxidation.
A) The carbon atom is more oxidized in formaldehyde (CH₂O) than in methanol (CH₃OH).
B) Oxidation of food in all organisms requires oxygen.
C) A molecule is oxidized if it gains an electron (plus a proton) in a reaction.
D) A dehydrogenation reaction is a reduction.
E) In an organic molecule, the number of C-H bonds increases as a result of oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is true regarding a fatty acid molecule in water?
A) It is positively charged at physiological pH, but can become neutral when the pH is high enough.
B) It is positively charged at physiological pH, but can become neutral when the pH is low enough.
C) It is negatively charged at physiological pH, but can become neutral when the pH is high enough.
D) It is negatively charged at physiological pH, but can become neutral when the pH is low enough.
E) It is not charged at physiological pH.
A) It is positively charged at physiological pH, but can become neutral when the pH is high enough.
B) It is positively charged at physiological pH, but can become neutral when the pH is low enough.
C) It is negatively charged at physiological pH, but can become neutral when the pH is high enough.
D) It is negatively charged at physiological pH, but can become neutral when the pH is low enough.
E) It is not charged at physiological pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The bond energies associated with noncovalent attractions in the cell are too weak to resist disruption by thermal motion. However, cellular macromolecules can interact specifically AND strongly with each other (or fold by themselves) merely via such interactions. How is this possible?
A) The bond energies increase radically when two interacting molecules approach each other.
B) The interacting molecules also fortify their binding via covalent bonds to keep them from dissociation.
C) Many weak bonds together in a complementary geometry can afford a strong binding.
D) The cell lowers its internal temperature to reduce thermal motion of molecules and enhance the weak attractions.
A) The bond energies increase radically when two interacting molecules approach each other.
B) The interacting molecules also fortify their binding via covalent bonds to keep them from dissociation.
C) Many weak bonds together in a complementary geometry can afford a strong binding.
D) The cell lowers its internal temperature to reduce thermal motion of molecules and enhance the weak attractions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For each of the following pairs, indicate whether they interact via hydrogen bonds (H) or ionic bonds (I), or do not favorably interact (N). Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters H, I, and N only, e.g. HNNI.
( ) ATP and Mg²?
( ) Urea and water
( ) Glucose and the enzyme hexokinase (which uses glucose as a substrate)
( ) A phospholipid tail and inorganic phosphate
( ) ATP and Mg²?
( ) Urea and water
( ) Glucose and the enzyme hexokinase (which uses glucose as a substrate)
( ) A phospholipid tail and inorganic phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the following diagram showing the reaction pathway for a simple single-substrate enzymatic reaction, which of the quantities corresponds to the activation energy of the forward reaction? 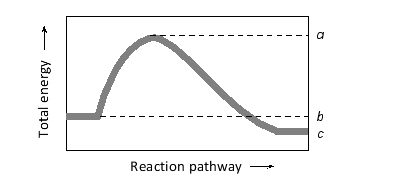
A) (a - b)
B) (a + b)
C) (a - c)
D) (a + c)
E) (b - c)

A) (a - b)
B) (a + b)
C) (a - c)
D) (a + c)
E) (b - c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following correctly summarizes the overall process of photosynthesis?
A) CO₂ + O₂ → H₂O + sugars
B) CH₂O + CO₂ + O₂ → H₂O + sugars
C) CO₂ + H₂O → H₂ + CO₂
D) CO₂ + H₂O → O₂ + sugars
A) CO₂ + O₂ → H₂O + sugars
B) CH₂O + CO₂ + O₂ → H₂O + sugars
C) CO₂ + H₂O → H₂ + CO₂
D) CO₂ + H₂O → O₂ + sugars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The three families of cellular macromolecules are polymerized and depolymerized by a general mechanism involving water. Each of them has a set of monomers whose polymerization changes the total free energy of the system. Which of the following statements is true regarding these macromolecules?
A) Each polymerization step requires free-energy input and proceeds by the consumption of one water molecule.
B) Each depolymerization step requires free-energy input and proceeds by the consumption of one water molecule.
C) Each polymerization step requires free-energy input and proceeds by the release of one water molecule.
D) Each depolymerization step requires free-energy input and proceeds by the release of one water molecule.
A) Each polymerization step requires free-energy input and proceeds by the consumption of one water molecule.
B) Each depolymerization step requires free-energy input and proceeds by the consumption of one water molecule.
C) Each polymerization step requires free-energy input and proceeds by the release of one water molecule.
D) Each depolymerization step requires free-energy input and proceeds by the release of one water molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Imagine the reaction A → B with a negative ΔG value under experimental conditions. Which of the following statements is true about this reaction?
A) The reaction is energetically unfavorable.
B) The reaction proceeds spontaneously and rapidly under these conditions.
C) Increasing the concentration of B molecules would increase the ΔG value (toward more positive values).
D) The reaction would result in a net decrease in the entropy (disorder) of the universe.
E) The reaction cannot proceed unless it is coupled to another reaction with a positive value of ΔG.
A) The reaction is energetically unfavorable.
B) The reaction proceeds spontaneously and rapidly under these conditions.
C) Increasing the concentration of B molecules would increase the ΔG value (toward more positive values).
D) The reaction would result in a net decrease in the entropy (disorder) of the universe.
E) The reaction cannot proceed unless it is coupled to another reaction with a positive value of ΔG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Steps 6 and 7 of glycolysis are catalyzed by the enzymes glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate kinase, respectively. Together, they ...
A) result in the oxidation of an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid.
B) produce both ATP and NADH.
C) couple the oxidation of a C-H bond to the activation of carrier molecules.
D) catalyze the only glycolytic reactions that create a high-energy phosphate linkage directly from inorganic phosphate.
E) All of the above.
A) result in the oxidation of an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid.
B) produce both ATP and NADH.
C) couple the oxidation of a C-H bond to the activation of carrier molecules.
D) catalyze the only glycolytic reactions that create a high-energy phosphate linkage directly from inorganic phosphate.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Arsenate is a toxic ion that can interfere with both glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. Arsenate resembles Pᵢ (inorganic phosphate) and can replace it in many enzymatic reactions. One such reaction is catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase in step 6 of glycolysis. Upon completion of the reaction, instead of the normal product, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, the mixed anhydride 1-arsenato-3-phosphoglycerate is formed; this undergoes rapid spontaneous hydrolysis into arsenate plus 3-phosphoglycerate, the latter being a normal product of step 7 in glycolysis. What would be the effect of arsenate poisoning in glycolysis?
A) It results in more ATP and NADH molecules generated for every glucose molecule.
B) It results in fewer ATP molecules generated per glucose molecule, but NADH generation is not directly affected.
C) It brings glycolysis to an abrupt stop.
D) It results in fewer ATP and NADH molecules generated per glucose molecule.
E) It does not affect the number of ATP or NADH molecules generated per glucose molecule.
A) It results in more ATP and NADH molecules generated for every glucose molecule.
B) It results in fewer ATP molecules generated per glucose molecule, but NADH generation is not directly affected.
C) It brings glycolysis to an abrupt stop.
D) It results in fewer ATP and NADH molecules generated per glucose molecule.
E) It does not affect the number of ATP or NADH molecules generated per glucose molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the reaction performed on the molecule labeled as substrate in the following diagram? What is the name of the activated carrier? 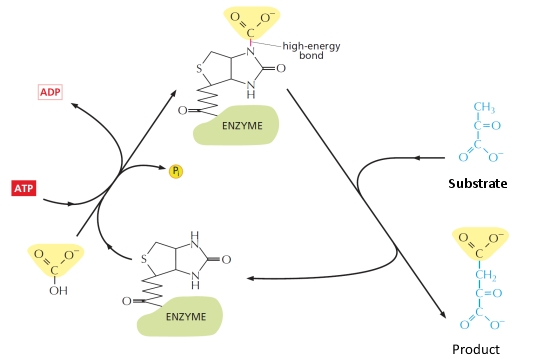
A) This is a methylation reaction and the activated carrier is ATP.
B) This is a methylation reaction and the activated carrier is S-adenosylmethionine.
C) This is a carboxylation reaction and the activated carrier is ATP.
D) This is a carboxylation reaction and the activated carrier is carboxylated biotin.
E) This is an acetylation reaction and the activated carrier is acetyl CoA.

A) This is a methylation reaction and the activated carrier is ATP.
B) This is a methylation reaction and the activated carrier is S-adenosylmethionine.
C) This is a carboxylation reaction and the activated carrier is ATP.
D) This is a carboxylation reaction and the activated carrier is carboxylated biotin.
E) This is an acetylation reaction and the activated carrier is acetyl CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Under anaerobic conditions, glycolysis provides most of the ATP that the cell needs. In animal cells, pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis, is converted to lactic acid by lactate dehydrogenase, as shown below:
CH3(CO)COO- + X ?CH3(CHOH)COO- + Y
What is the correct carrier pair (in place of X and Y) in this reaction?
A) X is (ADP + Pi), and Y is (ATP)
B) X is (NADP+), and Y is (NADPH + H+)
C) X is (NAD+), and Y is (NADH + H+)
D) X is (NADH + H+), and Y is (NAD+)
E) X is (NADP++ H+), and Y is (NADPH)
CH3(CO)COO- + X ?CH3(CHOH)COO- + Y
What is the correct carrier pair (in place of X and Y) in this reaction?
A) X is (ADP + Pi), and Y is (ATP)
B) X is (NADP+), and Y is (NADPH + H+)
C) X is (NAD+), and Y is (NADH + H+)
D) X is (NADH + H+), and Y is (NAD+)
E) X is (NADP++ H+), and Y is (NADPH)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Despite their overall similarity, NADH and NADPH are not used indiscriminately by the cell. What are the distinctive features of these two carrier molecules?
A) NADPH has an extra phosphate near its nicotinamide ring, giving it distinct electron-transfer properties.
B) In the cell, NADH is usually in excess over NAD⁺, but NADP⁺ is usually in excess over NADPH.
C) NADH is normally involved in anabolic reactions, whereas NADPH is normally involved in catabolism.
D) Both NADPH and NADH are recognized by the same enzymes with similar affinities, since the extra phosphate group in NADPH is not involved in such recognition.
E) In the cell, NADH is found mostly in the form that acts as an oxidizing agent, whereas NADPH is found mostly in the form that acts as a reducing agent.
A) NADPH has an extra phosphate near its nicotinamide ring, giving it distinct electron-transfer properties.
B) In the cell, NADH is usually in excess over NAD⁺, but NADP⁺ is usually in excess over NADPH.
C) NADH is normally involved in anabolic reactions, whereas NADPH is normally involved in catabolism.
D) Both NADPH and NADH are recognized by the same enzymes with similar affinities, since the extra phosphate group in NADPH is not involved in such recognition.
E) In the cell, NADH is found mostly in the form that acts as an oxidizing agent, whereas NADPH is found mostly in the form that acts as a reducing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What are the molecules that normally supply carbon and oxygen atoms, respectively, for the citric acid cycle?
A) Oxaloacetate, oxaloacetate
B) Acetyl CoA, O₂
C) Oxaloacetate, O₂
D) Acetyl CoA, H₂O
E) Pyruvate, pyruvate
A) Oxaloacetate, oxaloacetate
B) Acetyl CoA, O₂
C) Oxaloacetate, O₂
D) Acetyl CoA, H₂O
E) Pyruvate, pyruvate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Macromolecules in the cell can be made from their monomers using one of two polymerization schemes. One is called head polymerization, in which the reactive bond required for polymerization is carried on the end of the growing polymer. In contrast, in tail polymerization, the reactive bond is carried by each monomer for its own incorporation. In the figure, indicate the polymerization scheme and the type of macromolecule. 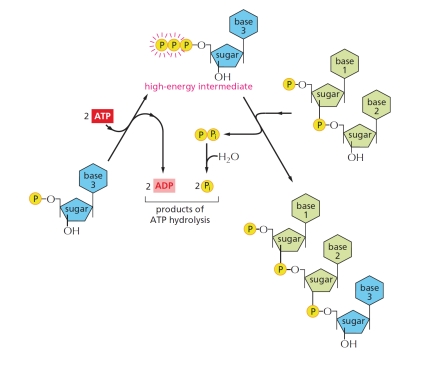
A) Head polymerization of a protein
B) Tail polymerization of a protein
C) Head polymerization of a polysaccharide
D) Head polymerization of a nucleic acid
E) Tail polymerization of a nucleic acid

A) Head polymerization of a protein
B) Tail polymerization of a protein
C) Head polymerization of a polysaccharide
D) Head polymerization of a nucleic acid
E) Tail polymerization of a nucleic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The free-energy change (?G) for a simple reaction, A ? B, is 0 kJ/mole at 37°C when the concentrations of A and B are 10 M and 0.1 M, respectively. What is the free-energy change for the reaction when the concentrations of A and B are instead 0.01 M and 1 M, respectively? Recall that ?G° = -5.9 × log(K?q). Write down your answer as a number with the appropriate sign (+ or -) and in kJ/mole, e.g. +11.8 kJ/mole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The enzyme phosphoglucose isomerase converts glucose 6-phosphate to its isomer fructose 6-phosphate in the second step of glycolysis. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is 0.36. Evaluating the ΔG° of the reaction (ΔG° = -5.9 × log Kₑq), decide which of the following conclusions is true.
A) The ΔG° is negative, therefore the reaction proceeds in the forward direction.
B) The ΔG° is negative, but whether or not the reaction proceeds would depend on ΔG, not ΔG°.
C) The ΔG° is positive, but in a cell that is active in glycolysis, the reaction can still proceed in the forward direction.
D) The ΔG° is positive, therefore the reaction proceeds in the reverse direction.
A) The ΔG° is negative, therefore the reaction proceeds in the forward direction.
B) The ΔG° is negative, but whether or not the reaction proceeds would depend on ΔG, not ΔG°.
C) The ΔG° is positive, but in a cell that is active in glycolysis, the reaction can still proceed in the forward direction.
D) The ΔG° is positive, therefore the reaction proceeds in the reverse direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The substrate for the glycolytic enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase is glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (with one phosphate group) while its product is 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (with two phosphate groups). Where does the extra phosphate group come from?
A) From combining two molecules of the substrate
B) ATP
C) Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
D) Pᵢ
E) NADH
A) From combining two molecules of the substrate
B) ATP
C) Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
D) Pᵢ
E) NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The equilibrium constant for the reaction that breaks down each molecule of substrate A to one molecule of B and one molecule of C is equal to 0.5. Starting with a mixture containing only molecules A at 1 M concentration, what will be the concentration of molecule A after reaching equilibrium under these conditions?
A) 0.5 M
B) 0.25 M
C) 0.125 M
D) 0.333 M
E) 0.667 M
A) 0.5 M
B) 0.25 M
C) 0.125 M
D) 0.333 M
E) 0.667 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
ATP is the main energy currency in cells, and it can especially be used to drive condensation reactions that produce macromolecular polymers. How does ATP normally catalyze the condensation reaction, which by itself is energetically unfavorable?
A) It transfers its terminal phosphate to an enzyme and is released as ADP.
B) It transfers its two terminal phosphates to an enzyme, and is released as AMP.
C) It covalently attaches to both of the substrates.
D) It transfers either one or two terminal phosphate(s) to one of the substrates and is released as either ADP or AMP.
E) It covalently attaches to the enzyme, forming an enzyme-AMP adduct.
A) It transfers its terminal phosphate to an enzyme and is released as ADP.
B) It transfers its two terminal phosphates to an enzyme, and is released as AMP.
C) It covalently attaches to both of the substrates.
D) It transfers either one or two terminal phosphate(s) to one of the substrates and is released as either ADP or AMP.
E) It covalently attaches to the enzyme, forming an enzyme-AMP adduct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is true regarding energy production and storage in plants and animals?
A) Plant and animal cells make starch for long-term energy storage.
B) Most of the ATP in a plant cell has been generated in the chloroplast and transported to other parts of the cell.
C) Oxidation of one gram of starch releases more energy than oxidation of fat, but since starch absorbs a lot of water, it is not as efficient as fat in energy storage.
D) Animals, but not plants, can store fats in the form of triacylglycerol (triglyceride).
E) Plant seeds often contain large amounts of fats and starch.
A) Plant and animal cells make starch for long-term energy storage.
B) Most of the ATP in a plant cell has been generated in the chloroplast and transported to other parts of the cell.
C) Oxidation of one gram of starch releases more energy than oxidation of fat, but since starch absorbs a lot of water, it is not as efficient as fat in energy storage.
D) Animals, but not plants, can store fats in the form of triacylglycerol (triglyceride).
E) Plant seeds often contain large amounts of fats and starch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Sort the following molecules from a low to high rate of diffusion inside the cytosol. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters A to D only, e.g. ADCB.
(A) Myoglobin (a protein)
(B) Glycine (an amino acid)
(C) Ribosome (a protein-RNA complex)
(D) CO?
(A) Myoglobin (a protein)
(B) Glycine (an amino acid)
(C) Ribosome (a protein-RNA complex)
(D) CO?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following represents an "activated" carrier molecule?
A) AMP
B) NADH
C) NAD⁺
D) NADP⁺
E) CoA
A) AMP
B) NADH
C) NAD⁺
D) NADP⁺
E) CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the end product of glycolysis in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells? How many carbon atoms does the molecule have?
A) Acetyl CoA; it has two carbon atoms attached to coenzyme A
B) Phosphoenolpyruvate; it has three carbon atoms
C) Glucose 6-phosphate; it has six carbon atoms
D) Pyruvate; it has three carbon atoms
E) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; it has three carbon atoms
A) Acetyl CoA; it has two carbon atoms attached to coenzyme A
B) Phosphoenolpyruvate; it has three carbon atoms
C) Glucose 6-phosphate; it has six carbon atoms
D) Pyruvate; it has three carbon atoms
E) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; it has three carbon atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The molecules inside the cell constantly collide with other molecules and diffuse through the cytoplasm in a random walk. The average net distance traveled by such a molecule after a certain time period t is proportional to the square root of t, i.e. (t)⁰.⁵, as well as to its diffusion coefficient. If, on average, it takes a molecule 100 milliseconds to travel a net distance of 0.5 µm from its starting point, how long would it normally take for the same molecule to travel a net distance of 5 µm from the same starting point?
A) 0.2 second
B) 0.3 second
C) 1 second
D) 10 seconds
E) 0.32 seconds
A) 0.2 second
B) 0.3 second
C) 1 second
D) 10 seconds
E) 0.32 seconds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the first reaction of the glycolytic pathway, the enzyme hexokinase uses ATP to catalyze the phosphorylation of glucose, yielding glucose 6-phosphate and ADP. The ΔG° value for this reaction is -17 kJ/mole. The enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase catalyzes a "reverse" reaction, in which glucose 6-phosphate is converted back to glucose, and a phosphate is released. The ΔG° value for this reaction is -14 kJ/mole. What is the ΔG° value for the following reaction? ATP + H₂O → ADP + Pᵢ
A) -3 kJ/mole
B) +3 kJ/mole
C) -31 kJ/mole
D) +31 kJ/mole
E) -15.5 kJ/mole
A) -3 kJ/mole
B) +3 kJ/mole
C) -31 kJ/mole
D) +31 kJ/mole
E) -15.5 kJ/mole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In an enzymatic reaction involving NADH or NADPH, reduction of a substrate accompanies the oxidation of these carrier molecules to NAD⁺ or NADP⁺, respectively. What else typically happens in such a reaction?
A) A molecule of water is released to the solution upon completion of the reaction.
B) A proton is released during the oxidation of the carriers.
C) A proton is taken up by the substrate that is being reduced.
D) A proton is taken up by the carrier molecule that is being oxidized.
E) A phosphate group is transferred to the substrate.
A) A molecule of water is released to the solution upon completion of the reaction.
B) A proton is released during the oxidation of the carriers.
C) A proton is taken up by the substrate that is being reduced.
D) A proton is taken up by the carrier molecule that is being oxidized.
E) A phosphate group is transferred to the substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The citric acid cycle is summarized in the following figure. Answer the following question(s) about this cycle.
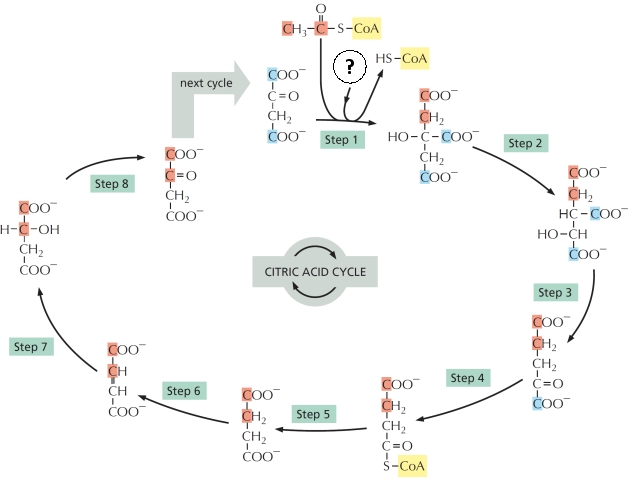
-In the citric acid cycle shown above, which steps produce either NADH or FADH?? List all such steps by their number, from the smallest number to the largest. Your answer would be a number composed of digits 1 to 8 only, e.g. 258.

-In the citric acid cycle shown above, which steps produce either NADH or FADH?? List all such steps by their number, from the smallest number to the largest. Your answer would be a number composed of digits 1 to 8 only, e.g. 258.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements below regarding glycolysis. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters T and F only, e.g. TTTT.
( ) Molecular oxygen is used in glycolysis to oxidize glucose.
( ) Along the glycolytic pathway, ATP is both consumed and generated.
( ) In the course of glycolysis, one molecule of NADH is formed per molecule of glucose.
( ) Following the production of one molecule of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, the rest of the glycolytic pathway generates four molecules of ATP.
( ) Molecular oxygen is used in glycolysis to oxidize glucose.
( ) Along the glycolytic pathway, ATP is both consumed and generated.
( ) In the course of glycolysis, one molecule of NADH is formed per molecule of glucose.
( ) Following the production of one molecule of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, the rest of the glycolytic pathway generates four molecules of ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements below regarding the cellular metabolism of nucleotides and amino acids. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters T and F only, e.g. TTTT.
( ) Nitrogen fixation occurs in the mitochondria in most animal cells to generate amino acids.
( ) All 20 natural amino acids must be provided in our diet and are therefore "essential."
( ) There are NO essential nucleotides that must be provided in the diet.
( ) Catabolism of amino acids in our body leads to the production of urea which is excreted.
Answers
( ) Nitrogen fixation occurs in the mitochondria in most animal cells to generate amino acids.
( ) All 20 natural amino acids must be provided in our diet and are therefore "essential."
( ) There are NO essential nucleotides that must be provided in the diet.
( ) Catabolism of amino acids in our body leads to the production of urea which is excreted.
Answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Indicate if each of the following descriptions matches lipids (1), nucleic acids (2), polysaccharides (3), or proteins (4). Your answer would be a four-digit number composed of digits 1 to 4 only, e.g. 1332.
( ) Their monomers contain phosphorus and nitrogen.
( ) They constitute almost half of the cell's dry mass.
( ) They are the main constituent of all cellular membranes.
( ) They are largely hydrophobic and can store energy.
( ) Their monomers contain phosphorus and nitrogen.
( ) They constitute almost half of the cell's dry mass.
( ) They are the main constituent of all cellular membranes.
( ) They are largely hydrophobic and can store energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The citric acid cycle is summarized in the following figure. Answer the following question(s) about this cycle.

-Aconitase catalyzes an isomerization reaction in the citric acid cycle shown above, in which H?O is first removed and then added back to the substrate. Which step is catalyzed by this enzyme? Write down the step number as your answer, e.g. 5.

-Aconitase catalyzes an isomerization reaction in the citric acid cycle shown above, in which H?O is first removed and then added back to the substrate. Which step is catalyzed by this enzyme? Write down the step number as your answer, e.g. 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Fill in the blank in the following paragraph.
"During intense 'anaerobic' physical exercise, the high energy demand in the muscle cells leads to an accumulation of lactic acid in these cells and their surrounding tissues. Similarly, the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae can produce ethanol when grown anaerobically. The lactate or ethanol production takes place in a process called ..."
"During intense 'anaerobic' physical exercise, the high energy demand in the muscle cells leads to an accumulation of lactic acid in these cells and their surrounding tissues. Similarly, the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae can produce ethanol when grown anaerobically. The lactate or ethanol production takes place in a process called ..."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Indicate whether each of the following molecules is an intermediate in glycolysis (G) or in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (T). Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters G and T only, e.g. GGTT.
( ) Fumarate
( ) Malate
( ) Phosphoenolpyruvate
( ) Succinate
( ) Fumarate
( ) Malate
( ) Phosphoenolpyruvate
( ) Succinate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements below regarding fatty acid metabolism. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters T and F only, e.g. TTTT.
( ) Most animals derive their energy from fatty acids between meals.
( ) Fatty acids are converted to acetyl CoA in the cytosol, which is then transported into mitochondria for further oxidation.
( ) Fatty acids are stored in fat droplets in the form of triacylglycerols.
( ) The breakdown of fatty acids into each acetyl CoA unit requires the hydrolysis of two ATP molecules.
( ) Most animals derive their energy from fatty acids between meals.
( ) Fatty acids are converted to acetyl CoA in the cytosol, which is then transported into mitochondria for further oxidation.
( ) Fatty acids are stored in fat droplets in the form of triacylglycerols.
( ) The breakdown of fatty acids into each acetyl CoA unit requires the hydrolysis of two ATP molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Indicate whether each of the following descriptions matches glycolysis (G) or the Krebs cycle (K). Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters G and K only, e.g. GGGK.
( ) It oxidizes acetyl CoA to CO?.
( ) In eukaryotic cells, it is carried out in the cytosol.
( ) It produces FADH?.
( ) ?-Ketoglutarate, one of its intermediates, is used to synthesize the amino acid glutamic acid.
( ) It oxidizes acetyl CoA to CO?.
( ) In eukaryotic cells, it is carried out in the cytosol.
( ) It produces FADH?.
( ) ?-Ketoglutarate, one of its intermediates, is used to synthesize the amino acid glutamic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Sort the following molecules (A to E) based on the oxidation of the carbon atom, from higher to lower oxidation states. Your answer would be a five-letter string composed of letters A to E only, e.g. ADCBE. Put the letter corresponding to the highest oxidation level on the left.
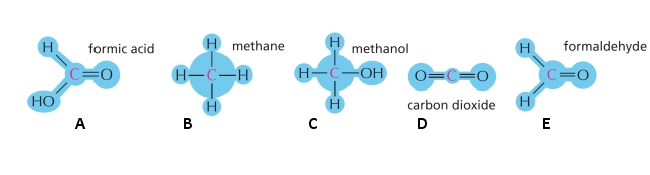


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Sort the following molecules based on the amount of energy that is released when their phosphate bond is hydrolyzed as indicated. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters A to D only, e.g. ADCB. Put the molecule with the highest amount of hydrolysis energy on the left.
(A) ATP when hydrolyzed to ADP
(B) Glucose 6-phosphate when hydrolyzed to glucose
(C) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate when hydrolyzed to 3-phosphoglycerate
(D) Phosphoenolpyruvate when hydrolyzed to pyruvate
(A) ATP when hydrolyzed to ADP
(B) Glucose 6-phosphate when hydrolyzed to glucose
(C) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate when hydrolyzed to 3-phosphoglycerate
(D) Phosphoenolpyruvate when hydrolyzed to pyruvate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The electron carriers NADH and FADH₂ donate their electrons to the electron-transport chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane, leading to ATP synthesis powered by an H⁺ gradient across the membrane. If, on average, the oxidation of each NADH or FADH₂ molecule in this pathway results in the production of 2.5 and 1.5 molecules of ATP, respectively, how many ATP (and GTP) molecules are produced on average as a result of the complete oxidation of one molecule of acetyl CoA in the mitochondrion? Consider only the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
A) 10
B) 12
C) 13.5
D) 14.5
E) 15
A) 10
B) 12
C) 13.5
D) 14.5
E) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The citric acid cycle is summarized in the following figure. Answer the following question(s) about this cycle.

-In the citric acid cycle shown above, which steps produce CO? as a by-product? List all such steps by their number, from the smallest number to the largest. Your answer would be a number composed of digits 1 to 8 only, e.g. 258.

-In the citric acid cycle shown above, which steps produce CO? as a by-product? List all such steps by their number, from the smallest number to the largest. Your answer would be a number composed of digits 1 to 8 only, e.g. 258.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The citric acid cycle is summarized in the following figure. Answer the following question(s) about this cycle.

In step 1 of the citric acid cycle drawn above, what is the molecule indicated with a question mark?
A) O₂
B) ATP
C) H₂O
D) H⁺
E) Pyruvate

In step 1 of the citric acid cycle drawn above, what is the molecule indicated with a question mark?
A) O₂
B) ATP
C) H₂O
D) H⁺
E) Pyruvate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



