Deck 11: Analysis of Variance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/51
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Analysis of Variance
1
the problem with conducting multiple t-tests instead of using a post-hoc test is that you increase the risk of type-I errors.
True
2
Tukey HSD can only be used if each condition or level has equal number of participants (i.e., equal n's).
False
3
Whether or not a statistical procedure turns out to be significant has nothing to do with the size of the sample.
False
4
A significant effect is not always a meaningful effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
ANOVAs can be done for mean comparisons between two groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In an ANOVA with one factor that has three different conditions, there are a total of 4 levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Unlike a t-test, a one-way ANOVA is used when there is more than one dependent variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a 2 x 2 ANOVA, there are two factors, but a total of four conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Post-hoc tests such as the Tukey should be done regardless of statistical significance when conducting an one-way ANOVA with more than two levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a one-way ANOVA with 30 participants, and the factor has 4 levels, the between subjects degree of freedom is 25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In a 3 x 5 ANOVA with 60 participants, the total degrees of freedom is 59

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
ANOVA was designed to analyze mean differences when there are two or more groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
MSw is the quotient or ratio of SSw and dfw

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The F-statistic is calculated by taking the difference between MSb and MSw

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A factorial model ANOVA has more than 1 factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a two-way ANOVA, you can test two main effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
To obtain the degrees of freedom for the interaction in a two-way ANOVA, you multiply the number of levels in each factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Statistical significance is in part due to the size of the sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Tukey HSD allows you to determine which means differ in a one-way ANOVA with more than 2 levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An ANOVA assumes independence of observations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A 3 x 2 ANOVA is a ___-way ANOVA, with ___ conditions?
A) One; 6
B) Two; 5
C) Three; 6
D) Two; 6
A) One; 6
B) Two; 5
C) Three; 6
D) Two; 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A one-way ANOVA makes several assumptions. Which of the following is not an assumption?
A) Independent observations
B) Normal distribution in the data
C) The null hypothesis is the true state of the world
D) Each condition has the same number of observations
A) Independent observations
B) Normal distribution in the data
C) The null hypothesis is the true state of the world
D) Each condition has the same number of observations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In general, ANOVA tests for…
A) differences between means.
B) differences between dependent variables.
C) differences between means in only 3 or more groups.
D) Differences between medians between 2 or more groups.
A) differences between means.
B) differences between dependent variables.
C) differences between means in only 3 or more groups.
D) Differences between medians between 2 or more groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If there are two factors, one with 3 levels and the other with 2,, which is the most appropriate test to analyze data obtained from this design (assuming interval or ratio scale)?
A) 3 x 2 ANOVA
B) 2 x 2 ANOVA
C) One-way ANOVA
D) dependent samples t-tests
A) 3 x 2 ANOVA
B) 2 x 2 ANOVA
C) One-way ANOVA
D) dependent samples t-tests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is always true of a two-way ANOVA?
A) There are four levels in total.
B) There are two interaction effects.
C) There are two outcome variables
D) There are two factors.
A) There are four levels in total.
B) There are two interaction effects.
C) There are two outcome variables
D) There are two factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When conducting a one-way ANOVA with 30 participants and the factor has 4 levels, the degrees of freedom between is ____.
A) 3
B) 25
C) 26
D) 4
A) 3
B) 25
C) 26
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Based on this data, it can be assumed that this was a …
A) one-way ANOVA.
B) 2 x 2 ANOVA.
C) 1 x 2 ANOVA.
D) Independent samples t-test.
A) one-way ANOVA.
B) 2 x 2 ANOVA.
C) 1 x 2 ANOVA.
D) Independent samples t-test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How many levels are there for the independent variable?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How many participants were in this ANOVA?
A) 49
B) 55
C) 45
D) 50
A) 49
B) 55
C) 45
D) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the F-ratio?
A) .12
B) 1.22
C) 1.36
D) 49.78
A) .12
B) 1.22
C) 1.36
D) 49.78

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the critical value, assuming alpha = .05?
A) 2.61
B) 2.56
C) 2.45
D) There is insufficient information based on the source table.
A) 2.61
B) 2.56
C) 2.45
D) There is insufficient information based on the source table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is FALSE regarding post-hoc tests?
A) They should not be run if the omnibus ANOVA is not statistically significant
B) Tukey HSD test is a post-hoc test for multiple comparisons.
C) Post-hoc tests are generally done before ANOVAs are done.
D) None of the above are false.
A) They should not be run if the omnibus ANOVA is not statistically significant
B) Tukey HSD test is a post-hoc test for multiple comparisons.
C) Post-hoc tests are generally done before ANOVAs are done.
D) None of the above are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is the correct formula to obtain mean squares within?
A) Sums of squares between divided by degrees of freedom between.
B) Sums of squares within divided by degrees of freedom within.
C) Sums of squares within multiply degrees of freedom within.
D) Sums of squares within subtract degrees of freedom within.
A) Sums of squares between divided by degrees of freedom between.
B) Sums of squares within divided by degrees of freedom within.
C) Sums of squares within multiply degrees of freedom within.
D) Sums of squares within subtract degrees of freedom within.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How are ANOVA and t-tests similar? How are they different?
A) ANOVA allow for only comparisons between two means, whereas t-tests allow for comparisons for 2 or more means. They are similar in that both types of procedures tell us about differences between means.
B) t-tests allow for only comparisons between two means, whereas ANOVA allow for comparisons between two or more means. They are similar in that both types of procedures tell us about differences between means.
C) t-tests and ANOVAs both test for differences. However, t-tests test for differences between medians, but ANOVAs test for differences between Means
D) t-tests are ANOVAs are exactly the same. The only difference is that ANOVAs are used for samples and t-tests are used for populations.
A) ANOVA allow for only comparisons between two means, whereas t-tests allow for comparisons for 2 or more means. They are similar in that both types of procedures tell us about differences between means.
B) t-tests allow for only comparisons between two means, whereas ANOVA allow for comparisons between two or more means. They are similar in that both types of procedures tell us about differences between means.
C) t-tests and ANOVAs both test for differences. However, t-tests test for differences between medians, but ANOVAs test for differences between Means
D) t-tests are ANOVAs are exactly the same. The only difference is that ANOVAs are used for samples and t-tests are used for populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following best describes the F-ratio?
A) It is the ratio of MSb to MSw, and the smaller the F-value, the greater chance of it being statistically significant.
B) It is the ratio of SSb to SSw.
C) It is the ratio of MSb to MSw
D) The F-value is a ratio. Smaller F-values are associated with larger sample sizes.
A) It is the ratio of MSb to MSw, and the smaller the F-value, the greater chance of it being statistically significant.
B) It is the ratio of SSb to SSw.
C) It is the ratio of MSb to MSw
D) The F-value is a ratio. Smaller F-values are associated with larger sample sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In a two-way ANOVA, how many effects are there to test?
A) One main effect and two interactions.
B) Two interactions and two main effects.
C) Two main effects and one interaction.
D) One interaction and one main effect.
A) One main effect and two interactions.
B) Two interactions and two main effects.
C) Two main effects and one interaction.
D) One interaction and one main effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following pieces of information is necessary to determine critical value of the Tukey HSD in a one-way ANOVA?
A) dfb, the F-value, and the alpha level.
B) F-value, dfw, and the alpha level
C) Number of levels and dfb, and the alpha level
D) Number of levels, dfw, and the alpha level.
A) dfb, the F-value, and the alpha level.
B) F-value, dfw, and the alpha level
C) Number of levels and dfb, and the alpha level
D) Number of levels, dfw, and the alpha level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
There were ________ participants and the interaction has ____ degree(s) of freedom.
A) 30; 2
B) 30; 1
C) 30; 3
D) 40; 2
A) 30; 2
B) 30; 1
C) 30; 3
D) 40; 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
This ANOVA is best characterized as a…
A) 2 x 3 ANOVA
B) One-way ANOVA
C) 2 x 2 ANOVA
D) 2 x 1 ANOVA
A) 2 x 3 ANOVA
B) One-way ANOVA
C) 2 x 2 ANOVA
D) 2 x 1 ANOVA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
This ANOVA has how many possible main effect and interactions to test for?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) Insufficient information
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) Insufficient information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A Tukey HSD value tells you which of the following?
A) The size of a mean difference necessary to be significant
B) The probability of a mean difference to exist
C) The size of a mean difference necessary to be testable
D) The necessary sample size to detect an honestly significant difference (HSD)
A) The size of a mean difference necessary to be significant
B) The probability of a mean difference to exist
C) The size of a mean difference necessary to be testable
D) The necessary sample size to detect an honestly significant difference (HSD)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 2 x 3 ANOVA has ____ factors, ___ possible interaction(s), and ___ total conditions
A) 2; 2; 5
B) 2; 1; 6
C) 3; 1; 6
D) 2; 2; 6
A) 2; 2; 5
B) 2; 1; 6
C) 3; 1; 6
D) 2; 2; 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A researcher is interested whether vitamin supplements help with preventing the cold. The placebo group drank fruit juice that actually had no vitamins at all. The researcher then measured the number of days each participant spent sick in a month.
 Conduct a one-way ANOVA and determine if it is significant at the .05 level.
Conduct a one-way ANOVA and determine if it is significant at the .05 level.
 Conduct a one-way ANOVA and determine if it is significant at the .05 level.
Conduct a one-way ANOVA and determine if it is significant at the .05 level.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A researcher is interested whether vitamin supplements help with preventing the cold. The placebo group drank fruit juice that actually had no vitamins at all. The researcher then measured the number of days each participant spent sick in a month.
 Is a post-hoc test necessary? If so, conduct a Tukey HSD at the .05 level. The critical value is 3.514
Is a post-hoc test necessary? If so, conduct a Tukey HSD at the .05 level. The critical value is 3.514
 Is a post-hoc test necessary? If so, conduct a Tukey HSD at the .05 level. The critical value is 3.514
Is a post-hoc test necessary? If so, conduct a Tukey HSD at the .05 level. The critical value is 3.514
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Identify 2 assumptions of the one-way ANOVA and explain what it means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
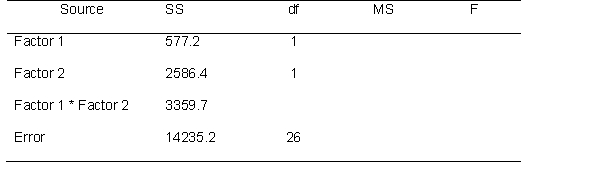
A researcher examining factors that influence sleep quality tested the effects of two variables. Her first factor has 2 levels and the second factor has 3 levels. She recruited 30 participants. Use the following source table to answer the next few questions.
 There are how many degrees of freedom for each source of variability?.
There are how many degrees of freedom for each source of variability?.
 There are how many degrees of freedom for each source of variability?.
There are how many degrees of freedom for each source of variability?.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
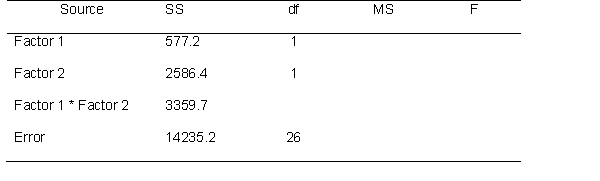
A researcher examining factors that influence sleep quality tested the effects of two variables. Her first factor has 2 levels and the second factor has 3 levels. She recruited 30 participants. Use the following source table to answer the next few questions.
 What is the critical value for each F ratio at the .05 significance level, and what is the observed F? Are any of the effect significant?
What is the critical value for each F ratio at the .05 significance level, and what is the observed F? Are any of the effect significant?
 What is the critical value for each F ratio at the .05 significance level, and what is the observed F? Are any of the effect significant?
What is the critical value for each F ratio at the .05 significance level, and what is the observed F? Are any of the effect significant?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
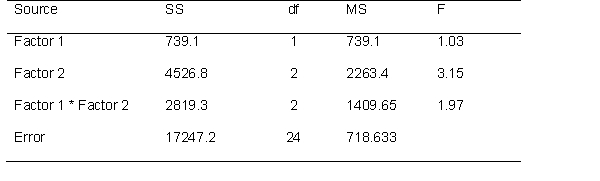
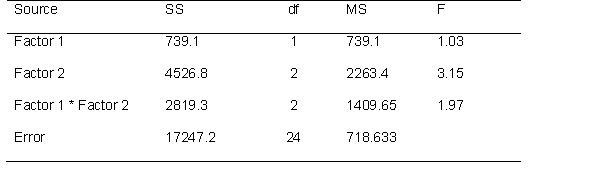
Use the following source table to answer the questions below.
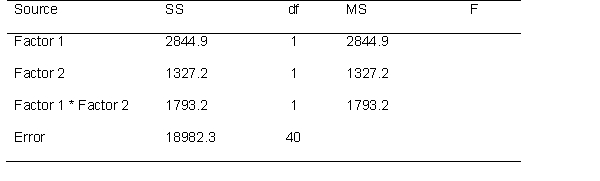 How many effects can one test?
How many effects can one test?
 How many effects can one test?
How many effects can one test?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the following source table to answer the questions below.
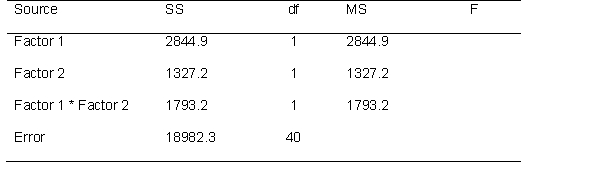 This is a ___ x ___ ANOVA. (fill in the blanks)
This is a ___ x ___ ANOVA. (fill in the blanks)
 This is a ___ x ___ ANOVA. (fill in the blanks)
This is a ___ x ___ ANOVA. (fill in the blanks)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the following source table to answer the questions below.
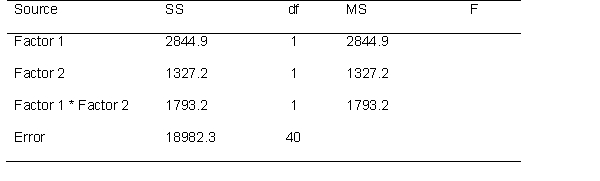 Determine if the effects are significant at the .05 level.
Determine if the effects are significant at the .05 level.
 Determine if the effects are significant at the .05 level.
Determine if the effects are significant at the .05 level.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why are post-hoc tests important with regards to making multiple comparisons?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



