Deck 9: Transcriptional Regulation and Epigenetics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/115
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Transcriptional Regulation and Epigenetics
1
The lac operon in E. coli is regulated by allolactose, which _______ a(n) _______ of transcription.
A) activates; activator
B) inactivates; activator
C) activates; repressor
D) inactivates; repressor
A) activates; activator
B) inactivates; activator
C) activates; repressor
D) inactivates; repressor
D
2
The lac operator consists of approximately 20 base pairs of DNA located
A) 80-100 base pairs upstream of the transcription initiation site.
B) 20-40 base pairs upstream of the transcription initiation site.
C) in a position overlapping a few bases of the initiation site and extending downstream.
D) downstream of the entire operon.
A) 80-100 base pairs upstream of the transcription initiation site.
B) 20-40 base pairs upstream of the transcription initiation site.
C) in a position overlapping a few bases of the initiation site and extending downstream.
D) downstream of the entire operon.
C
3
If E. coli is in an environment that is rich in lactose, a metabolite of lactose binds to
A) a repressor, releasing it from the operator site and activating transcription of the genes involved in lactose breakdown.
B) RNA polymerase, activating it to transcribe the genes involved in lactose breakdown.
C) an activator protein, which binds to RNA polymerase and stimulates transcription of the genes involved in lactose breakdown.
D) the operator site of the lac operon, stimulating transcription of the genes involved in lactose breakdown.
A) a repressor, releasing it from the operator site and activating transcription of the genes involved in lactose breakdown.
B) RNA polymerase, activating it to transcribe the genes involved in lactose breakdown.
C) an activator protein, which binds to RNA polymerase and stimulates transcription of the genes involved in lactose breakdown.
D) the operator site of the lac operon, stimulating transcription of the genes involved in lactose breakdown.
A
4
A mutation in the i gene encoding the lac operon repressor protein causes this protein to lose its ability to bind to the operator site. Which would you expect to observe in an E. coli population having this mutation?
A) The cells would die if lactose were the only energy source available.
B) The cells would require lactose as their only energy source.
C) The cells would not be able to express lac genes when lactose is present.
D) The cells would express lac genes when lactose is absent.
A) The cells would die if lactose were the only energy source available.
B) The cells would require lactose as their only energy source.
C) The cells would not be able to express lac genes when lactose is present.
D) The cells would express lac genes when lactose is absent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
E. coli regulates the biosynthesis of the amino acid tryptophan through the tryptophan (trp) operon. When tryptophan levels are high inside the cell, tryptophan binds to a regulatory protein, which then binds to the operator site of the operon. This shuts down transcription of the genes encoding enzymes needed for tryptophan biosynthesis, and tryptophan biosynthesis is halted. The trp operon is an example of
A) positive control because binding of a repressor blocks transcription.
B) negative control because binding of a repressor blocks transcription.
C) positive control because binding of an activator stimulates transcription.
D) negative control because binding of an activator stimulates transcription.
A) positive control because binding of a repressor blocks transcription.
B) negative control because binding of a repressor blocks transcription.
C) positive control because binding of an activator stimulates transcription.
D) negative control because binding of an activator stimulates transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which information would be helpful in determining whether a particular bacterial gene is under positive or negative transcriptional control?
A) The gene is part of an operon.
B) The gene is regulated by the level of a metabolite inside the cell.
C) The gene codes for an enzyme that has an important metabolic purpose.
D) The gene is not transcribed when a repressor protein binds to DNA.
A) The gene is part of an operon.
B) The gene is regulated by the level of a metabolite inside the cell.
C) The gene codes for an enzyme that has an important metabolic purpose.
D) The gene is not transcribed when a repressor protein binds to DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A researcher hypothesizes that expression of a particular gene is under positive transcriptional control. What evidence would support his hypothesis?
A) A repressor protein is discovered that blocks transcription of this gene.
B) The gene is only expressed when catabolite activator protein binds to an upstream DNA site.
C) The gene is no longer regulated when an upstream DNA region undergoes mutation.
D) Mutation of the gene itself does not affect its regulation.
A) A repressor protein is discovered that blocks transcription of this gene.
B) The gene is only expressed when catabolite activator protein binds to an upstream DNA site.
C) The gene is no longer regulated when an upstream DNA region undergoes mutation.
D) Mutation of the gene itself does not affect its regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Regulation of the lac operon by lactose involves a(n) _______ that inhibits transcription, while regulation by glucose involves a(n) _______ that stimulates transcription.
A) activator; repressor
B) repressor; activator
C) promoter; promoter
D) operator; operator
A) activator; repressor
B) repressor; activator
C) promoter; promoter
D) operator; operator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How do repressors differ from activators of transcription in bacteria?
A) Repressors, but not activators, can act on one chromosome only.
B) Activators are proteins, repressors are not.
C) Repressors inhibit transcription, and activators stimulate transcription.
D) Activators bind to DNA, and repressors bind to RNA polymerase.
A) Repressors, but not activators, can act on one chromosome only.
B) Activators are proteins, repressors are not.
C) Repressors inhibit transcription, and activators stimulate transcription.
D) Activators bind to DNA, and repressors bind to RNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Two bacterial populations were prepared in a laboratory. Population A expresses the wild-type regulator protein that controls the transcription of gene X. Population B contains a mutation in the gene for this regulator protein and does not express any form of the protein. Which statement provides a possible hypothesis to explain the gene X expression data shown in the table below?
A) The regulator protein is an activator that is required for stimulating RNA polymerase to transcribe gene X.
B) The regulator protein binds to RNA polymerase to prevent it from binding to the promoter site and transcribing gene X.
C) The regulator protein is a repressor that binds to an operator site and blocks RNA polymerase from carrying out transcription.
D) The regulator protein is an inhibitor that binds to RNA polymerase and prevents it from binding to the promoter site.
A) The regulator protein is an activator that is required for stimulating RNA polymerase to transcribe gene X.
B) The regulator protein binds to RNA polymerase to prevent it from binding to the promoter site and transcribing gene X.
C) The regulator protein is a repressor that binds to an operator site and blocks RNA polymerase from carrying out transcription.
D) The regulator protein is an inhibitor that binds to RNA polymerase and prevents it from binding to the promoter site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
One way that a promoter differs from an enhancer is that it
A) is not a sequence of DNA.
B) does not bind a transcription factor.
C) is not located far away from the gene it regulates.
D) does not bind to an RNA polymerase.
A) is not a sequence of DNA.
B) does not bind a transcription factor.
C) is not located far away from the gene it regulates.
D) does not bind to an RNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
TATA boxes are found
A) in enhancers only.
B) in promoters only.
C) in both enhancers and promoters.
D) in neither enhancers nor promoters.
A) in enhancers only.
B) in promoters only.
C) in both enhancers and promoters.
D) in neither enhancers nor promoters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An investigation was carried out to identify different sections of mammalian DNA as either promoters or enhancers of gene Y transcription. Wild-type mammalian cells functioned normally, while mutant cells lacked the ability to produce functional cohesion protein. Based on the data in the table below, which conclusion is valid?
A) Both A and B are enhancers.
B) Both A and B are promoters.
C) A is an enhancer, and B is a promoter.
D) A is a promoter, and B is an enhancer.
A) Both A and B are enhancers.
B) Both A and B are promoters.
C) A is an enhancer, and B is a promoter.
D) A is a promoter, and B is an enhancer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Looping of DNA has been observed by investigators using electron microscopy techniques. The presence of which feature in DNA might be indicated by such observations?
A) Promoters
B) Enhancers
C) Base-pair repeats
D) DNA methylation
A) Promoters
B) Enhancers
C) Base-pair repeats
D) DNA methylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A reporter gene is one that
A) causes other genes to be expressed.
B) can produce an easily detectable product when expressed under the control of a regulatory sequence to which it has been ligated and cloned.
C) is always on.
D) is turned on by the products of other genes.
A) causes other genes to be expressed.
B) can produce an easily detectable product when expressed under the control of a regulatory sequence to which it has been ligated and cloned.
C) is always on.
D) is turned on by the products of other genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A researcher wants to isolate regulatory sequences of DNA bound to their transcription factors. She then wants to sequence the DNA fragments that form the binding sites that the transcription factors recognize and bind. Which technique should the researcher use for her first step?
A) Gene transfer assay
B) Electrophoretic-mobility shift assay
C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation
D) DNA affinity chromatography
A) Gene transfer assay
B) Electrophoretic-mobility shift assay
C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation
D) DNA affinity chromatography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An electrophoresis assay used to identify the sequences of DNA to which specific regulatory proteins bind is called
A) an electrophoretic-mobility shift assay.
B) DNA affinity chromatography.
C) Western blotting.
D) Southern blotting.
A) an electrophoretic-mobility shift assay.
B) DNA affinity chromatography.
C) Western blotting.
D) Southern blotting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Kadonaga and Tjian were able to isolate the transcription factor Sp1 by exploiting its ability to bind
A) the sequence TATA.
B) the sequence AAAUAAA.
C) the sequence GGGCGG.
D) RNA polymerase.
A) the sequence TATA.
B) the sequence AAAUAAA.
C) the sequence GGGCGG.
D) RNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Eukaryotic gene repressor proteins are thought to act by binding to
A) DNA sites in competition with activating proteins.
B) specific activating proteins, preventing their binding to DNA.
C) basal transcription factors, inhibiting transcription.
D) All of the above
A) DNA sites in competition with activating proteins.
B) specific activating proteins, preventing their binding to DNA.
C) basal transcription factors, inhibiting transcription.
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Many transcriptional activators are composed of two or more independent _______, each with its own separate function.
A) domains
B) genes
C) enhancers
D) proteins
A) domains
B) genes
C) enhancers
D) proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose a transcriptional activator binds to a specific DNA site near a promoter region. Which is a protein that is then stimulated to form a functional transcription complex at this site?
A) Transcriptional factors
B) Mediator proteins
C) RNA polymerase
D) All of the above
A) Transcriptional factors
B) Mediator proteins
C) RNA polymerase
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Investigators discovered two eukaryotic regulatory proteins that control expression of the same gene. Their findings are summarized in the table below. Which hypothesis is most consistent with these findings?
A) Both regulatory proteins block the binding of activators to DNA.
B) Both regulatory proteins affect transcription by binding to mediator proteins.
C) Regulatory protein I blocks the binding of activators to DNA, whereas regulatory protein II affects transcription by binding to mediator proteins.
D) Regulatory protein I affects transcription by binding to mediator proteins, whereas regulatory protein II blocks the binding of activators to DNA.
A) Both regulatory proteins block the binding of activators to DNA.
B) Both regulatory proteins affect transcription by binding to mediator proteins.
C) Regulatory protein I blocks the binding of activators to DNA, whereas regulatory protein II affects transcription by binding to mediator proteins.
D) Regulatory protein I affects transcription by binding to mediator proteins, whereas regulatory protein II blocks the binding of activators to DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What causes RNA polymerase to pause just after transcription is initiated?
A) Phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase
B) Phosphorylation of NELF and DSIF
C) Binding of NELF and DSIF to RNA polymerase
D) Production of P-TEFb
A) Phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase
B) Phosphorylation of NELF and DSIF
C) Binding of NELF and DSIF to RNA polymerase
D) Production of P-TEFb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose a mutation renders a cell incapable of producing functional P-TEFb. What effect would the mutation have on this cell?
A) RNA polymerases that are paused would not be able to resume elongation.
B) No transcription initiation complexes would be able to form.
C) No serine residues in the RNA polymerase CTD would be phosphorylated.
D) The cell would lose the ability to pause any of its transcription initiation complexes.
A) RNA polymerases that are paused would not be able to resume elongation.
B) No transcription initiation complexes would be able to form.
C) No serine residues in the RNA polymerase CTD would be phosphorylated.
D) The cell would lose the ability to pause any of its transcription initiation complexes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the role of the transcription factor c-Myc in human embryonic stem cells?
A) It acts to halt elongation of transcription.
B) It functions to speed up the formation of transcription initiation complexes.
C) It prevents NELF and DSIF from binding to transcription initiation complexes.
D) It recruits P-TEFb to release RNA polymerase from its paused state and continue transcript elongation.
A) It acts to halt elongation of transcription.
B) It functions to speed up the formation of transcription initiation complexes.
C) It prevents NELF and DSIF from binding to transcription initiation complexes.
D) It recruits P-TEFb to release RNA polymerase from its paused state and continue transcript elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Eukaryotic gene regulation is facilitated by
A) acetylation of histones.
B) phosphorylation of histones.
C) methylation of histones.
D) All of the above
A) acetylation of histones.
B) phosphorylation of histones.
C) methylation of histones.
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Methylation of histones results in
A) activation of transcription.
B) repression of transcription.
C) activation or repression of transcription, depending on the site.
D) neither activation nor repression of transcription, only condensation of chromatin.
A) activation of transcription.
B) repression of transcription.
C) activation or repression of transcription, depending on the site.
D) neither activation nor repression of transcription, only condensation of chromatin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Some types of cancer are able to progress because certain normally active genes are repressed. An anticancer drug was developed to counteract this by functioning as a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Such an agent will _______ and thus _______ the expression of genes.
A) halt acetylation of histones; repress
B) stimulate acetylation of histones; activate
C) halt removal of acetyl groups on histones; activate
D) stimulate removal of acetyl groups on histones; repress
A) halt acetylation of histones; repress
B) stimulate acetylation of histones; activate
C) halt removal of acetyl groups on histones; activate
D) stimulate removal of acetyl groups on histones; repress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which characteristic of chromatin would you expect to see increase when incubated with histone acetyltransferase enzymes?
A) Condensation to heterochromatin
B) Sensitivity to DNAse I
C) Decreased gene expression
D) Repression of transcription
A) Condensation to heterochromatin
B) Sensitivity to DNAse I
C) Decreased gene expression
D) Repression of transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which molecule provides a source of energy used by chromatin remodeling factors to alter DNA−histone interactions?
A) NADH
B) FADH2
C) ATP
D) Glucose
A) NADH
B) FADH2
C) ATP
D) Glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which is not a mechanism of histone change that is mediated by chromatin remodeling factors?
A) Sliding of histones along DNA
B) Proteolytic breakdown of histone proteins
C) Conformational change of histone tertiary structure
D) Dissociation of histones from DNA
A) Sliding of histones along DNA
B) Proteolytic breakdown of histone proteins
C) Conformational change of histone tertiary structure
D) Dissociation of histones from DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which enzyme would be most useful in an experimental investigation of the effects of chromatin remodeling factors on a particular section of chromatin?
A) DNAse I
B) Histone acetyltransferase
C) Histone deacetylase
D) Histone methyltransferase
A) DNAse I
B) Histone acetyltransferase
C) Histone deacetylase
D) Histone methyltransferase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
DNA methylation patterns in parental cells are established and maintained in progeny cells by which of the following mechanisms?
A) Enzymes put a methyl group on cytosine residues of newly replicated CpG sequences base-paired with G-methyl-C sequences.
B) Methyl-CTP is incorporated into DNA during replication across from G-methyl-C sequences only.
C) When its gene is activated, a methyl group is added to certain CpG sequences in the promoter region.
D) Methylation of genes on the X chromosome only.
A) Enzymes put a methyl group on cytosine residues of newly replicated CpG sequences base-paired with G-methyl-C sequences.
B) Methyl-CTP is incorporated into DNA during replication across from G-methyl-C sequences only.
C) When its gene is activated, a methyl group is added to certain CpG sequences in the promoter region.
D) Methylation of genes on the X chromosome only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A skin cell and a muscle cell taken from a single mouse differ in appearance and metabolism. If you were to examine the DNA in these two cells, how would they compare?
A) The DNA sequences are arranged in different orders in the two cells.
B) DNA sequences differ in various parts of the genomes of the two cells.
C) The cells contain the same DNA sequences but have different promoters and enhancers.
D) The same DNA sequences are present but different regions of chromatin are modified.
A) The DNA sequences are arranged in different orders in the two cells.
B) DNA sequences differ in various parts of the genomes of the two cells.
C) The cells contain the same DNA sequences but have different promoters and enhancers.
D) The same DNA sequences are present but different regions of chromatin are modified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Genomic imprinting is thought to result from
A) acetylation of histones.
B) methylation of cytosine residues in DNA.
C) binding of transcription factors to promoters.
D) binding of Xist RNA to genes.
A) acetylation of histones.
B) methylation of cytosine residues in DNA.
C) binding of transcription factors to promoters.
D) binding of Xist RNA to genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How are methylated sites in DNA maintained through multiple cycles of DNA replication during development?
A) DNA polymerase incorporates a 5-methyl cytosine next to a G bound to an existing 5-methyl cytosine.
B) DNA polymerase adds a methyl group to a cytosine next to a G bound to an existing 5-methyl cytosine.
C) A methylating enzyme adds a methyl group to a cytosine next to a G bound to an existing 5-methyl cytosine.
D) A methylating enzyme adds a methyl group to a guanosine next to a C bound to an existing 5-methyl guanosine.
A) DNA polymerase incorporates a 5-methyl cytosine next to a G bound to an existing 5-methyl cytosine.
B) DNA polymerase adds a methyl group to a cytosine next to a G bound to an existing 5-methyl cytosine.
C) A methylating enzyme adds a methyl group to a cytosine next to a G bound to an existing 5-methyl cytosine.
D) A methylating enzyme adds a methyl group to a guanosine next to a C bound to an existing 5-methyl guanosine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Xist lncRNA assists with X chromosome inactivation by binding which protein(s) to facilitate histone modification?
A) Histone acetylase
B) Polycomb proteins
C) DNA demethylase
D) All of the above
A) Histone acetylase
B) Polycomb proteins
C) DNA demethylase
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How do long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) function in regulating gene expression?
A) They bind to complementary DNA sites and interfere with RNA polymerase binding.
B) They form scaffolds to help stabilize protein complexes that modify chromatin.
C) They assist with DNA loop formation between enhancers to facilitate transcription initiation.
D) They catalyze the modification of histones to stimulate chromatin condensation.
A) They bind to complementary DNA sites and interfere with RNA polymerase binding.
B) They form scaffolds to help stabilize protein complexes that modify chromatin.
C) They assist with DNA loop formation between enhancers to facilitate transcription initiation.
D) They catalyze the modification of histones to stimulate chromatin condensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The table below provides information about RNA strands that were found to be involved in gene regulation in mammalian cells. Which strand(s) would be classified as lncRNAs?
A) I and IV
B) II and III
C) I only
D) I, II, III, and IV
A) I and IV
B) II and III
C) I only
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which statement concerning lncRNAs is true?
A) lncRNAs are extracellular signals that stimulate activation of specific genes.
B) lncRNAs catalyze the chemical modification of histones.
C) lncRNAs function in both activation and repression of gene expression.
D) lncRNAs are formed once RNA polymerase becomes active after having been paused.
A) lncRNAs are extracellular signals that stimulate activation of specific genes.
B) lncRNAs catalyze the chemical modification of histones.
C) lncRNAs function in both activation and repression of gene expression.
D) lncRNAs are formed once RNA polymerase becomes active after having been paused.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Low concentrations of lactose in a bacterial cell lead to a _______ binding to the operator site of the lac operon and blocking transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A bacterial operon is said to be under _______ control if it involves an activator protein that functions to stimulate RNA polymerase to initiate transcription of its genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The lac operon is under negative control by a repressor that is sensitive to lactose concentrations and is also under positive control by the activator protein _______, which is sensitive to glucose concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The diagram below illustrates how two _______-acting elements are positioned near the gene that they regulate.
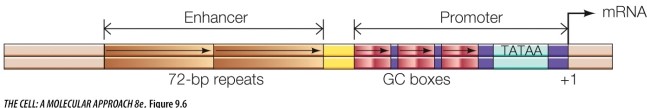


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
DNA is able to form _______, which enable transcription factors at enhancers to interact with the transcription initiation complexes at promoters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The results from several gene transfer assays carried out to locate regulatory DNA sequences are shown in the table below. Three different transcription factors were used in the assay as probes. Luciferase was used as the reporter protein, and production of light is noted with + signs. No production of light is noted with a 0. The results indicate that _______ of the five DNA sequences tested may be have some sort of gene regulatory role.
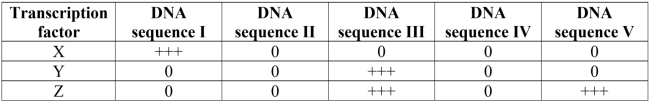


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A researcher has several transcription factors in purified form as well as a DNA fragment in purified form. He suspects the DNA fragment binds to one of the transcription factors. He can use the _______ technique to determine which transcription factor the DNA fragment binds to.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Chromosomes are organized into multiple loop structures that maintain specificity of enhancers for their cognate genes by the proteins _______ and _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Some transcriptional activators have two domains: a _______ domain and an activation domain, each of which carries out specific functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
P-TEFb contains a _______ that phosphorylates NELF, DSIF, and serine 2 in the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase, all of which lead to re-activation of RNA polymerase and transcriptional elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Acetylation of lysine residues on histones causes these proteins to lose _______ charges, which allows the chromatin structure to relax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An investigation identified whether histones nearest specific genes were acetylated or deacetylated. The results are summarized in the table below. Based on these results, it can be predicted that genes _______ would be actively expressed, while the others would not.
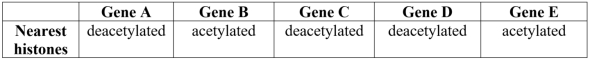


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
_______ use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to alter and restructure nucleosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Islet cells in the pancreas are the only cells in the human body that produce the hormone insulin. The table below compares the extent of methylation within the promoter region upstream of the gene encoding the insulin protein in three types of human cells. The results provide an example illustrating that methylation of DNA is correlated with transcriptional _______.
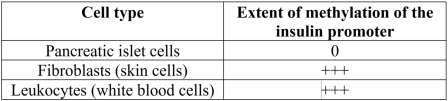


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Polycomb proteins are important in repressing gene transcription during development and differentiation. They act by _______ lysine residues in histones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The molecule providing the scaffolding in the figure below to allow multiple chromatin modifications is a(n) _______.
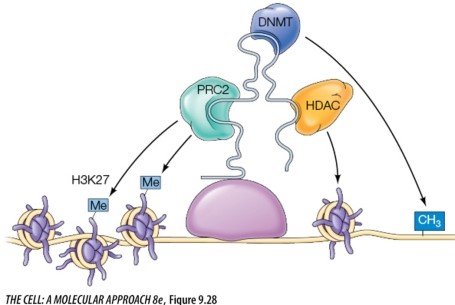


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The lac operon is regulated by the binding of an enhancer to sequences just upstream of the promoter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Some bacterial genes are regulated by transcriptional activators rather than by repressors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For each protein-coding gene, there is one promoter and one enhancer that act as regulatory elements for that gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
DNA-affinity chromatography is a useful method for purifying individual transcription factors from cell extracts, even though these proteins are present in extremely low quantities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Some corepressors bind to transcription factors at transcription initiation sites and recruit deacetylases that remove acetyl groups from histone lysine groups, leading to condensation of chromatin and repression of transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The light micrograph image below shows a section of a Drosophila chromosome. The arrows indicate regions containing histones that have been deacetylated.
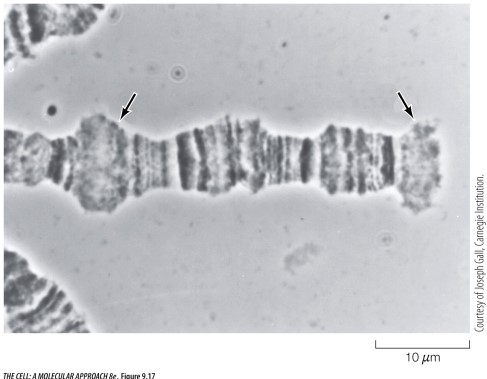


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Chromatin remodeling factors are responsible for shuffling and rearranging DNA sequences in chromatin to make them either more or less accessible for transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In eukaryotic cells, genes with methylated DNA tend to be more active than unmethylated genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Transmission of information that is not contained within the sequence of DNA to daughter cells at cell division is called epigenetic inheritance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
lncRNAs assist with changes in chromatin. In embryonic stem cells some of these molecules can act in a repressive role to suppress differentiation and maintain the stem cell state, while others can act in an activating role to allow differentiation to proceed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A mutation in the i gene of the lac operon produces a repressor that retains its DNA binding function but loses its ability to bind to lactose. Will bacteria with this mutant repressor be able to survive in a medium containing lactose as the only carbon source? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose a culture of E. coli is growing in media containing only glucose. The cells eventually deplete this glucose supply. Just as the last bit of glucose is used up, lactose and other sugars become available. How does both the loss of glucose and the addition of lactose affect expression of the lac operon in these cells?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The L-arabinose operon in an E. coli strain contains genes that code for enzymes used to break down the sugar L-arabinose. A regulatory gene located upstream from the operon encodes the regulatory protein AraC. AraC undergoes a conformational change when it binds to L-arabinose, and this form of AraC binds to the operator site of the operon, acting as an activator, to stimulate RNA polymerase to begin transcription. Explain whether this is an example of positive or negative control and how this compares to the control mechanism of the lac operon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms and do not undergo differentiation. Why is it important that these cells have gene regulatory mechanisms, some of which repress transcription and others that stimulate transcription?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What are three ways in which an enhancer's function differs from that of a promoter?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Describe an electrophoretic mobility shift assay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If you had genomic DNA and a purified transcription factor, how might you use that to determine the DNA sequence to which the transcription factor binds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What two different mechanisms do transcription factors use to regulate transcription of eukaryotic genes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A research lab working with mouse cells characterized three mutant cell lines summarized in the table below. Which of these is most likely to contain a mutated form of P-TEFb? Explain.
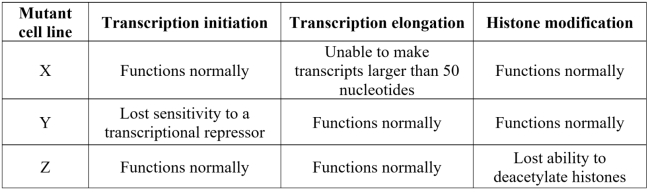


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Three amino acids, present in histone tails, that are chemically modified as part of gene regulatory processes are lysine, arginine, and _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Refer to the figure below.
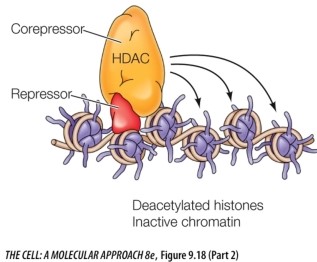 Explain how HDACs function to regulate gene expression.
Explain how HDACs function to regulate gene expression.
 Explain how HDACs function to regulate gene expression.
Explain how HDACs function to regulate gene expression.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Methylation of certain lysine residues in histones leads to gene silencing, whereas methylation of other lysine residues in the same histones leads to transcriptional activation. How can methylation lead to these two different outcomes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Some chromatin remodeling factors use energy from ATP hydrolysis to slide histones along a chromosome. Explain how this type of activity can regulate gene expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are often described as having a scaffolding role in the regulation of gene expression. Explain what that means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



