Deck 11: Neuroscience Methods
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Neuroscience Methods
1
Discuss two ethical concerns of neuroscience research by explaining why researchers need to be aware of them for the wellbeing of participants.
Safety concerns: While modern technologies such as MRI and fMRI pose a much smaller safety concern than older technologies such as CAT and PET scans, it is still vital that researchers carefully follow safe protocols. For example, it is critical that participants get screened for metals that would be attracted by the MRI machine or participants might face serious injuries.
Atypical brain anomalies: Researchers should be prepared to handle situations in which a brain scan shows abnormal or atypical brain growth. One suggestion is for researchers to have appropriate experts to recommend participants speak with for further diagnoses since many researchers are not medically trained to do so.
Atypical brain anomalies: Researchers should be prepared to handle situations in which a brain scan shows abnormal or atypical brain growth. One suggestion is for researchers to have appropriate experts to recommend participants speak with for further diagnoses since many researchers are not medically trained to do so.
2
Compare and contrast two different neuroimaging techniques that require different machines and/or apparatus by highlighting a strength and a weakness of each technique.
EEG and fMRI are both techniques that can look at participants' reaction to stimuli over time. EEG is relatively simple, and cheaper than fMRI and another strength is that it can be used with younger children since head movement does not influence the data the same way it would for fMRI. However, a major limitation of EEG is that it has very poor spatial resolution.
fMRI on the other hand has great spatial resolution. However, it has low spatial resolution compared to EEG and can be expensive to conduct research with.
fMRI on the other hand has great spatial resolution. However, it has low spatial resolution compared to EEG and can be expensive to conduct research with.
3
Briefly describe how an MRI machine works by discussing what the machine does to particles in the human body. Your answer should include how radiofrequency pulses are generated and what relaxation means.
Radiofrequency coils emit radiofrequency pulse that disrupts the random rotation of hydrogen protons. Protons align in a particular direction when this happens. When the pulse stops, the protons return to their original state and this process is called relaxation. Because different parts of the brain have different densities, the machine is able to register this and develop an image of the brain.
4
Describe what motion artifact is by explaining what techniques can produce them, and how this influences the design of neuroscience research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Discuss the EEG technique and the type of data that researcher obtains. Then discuss how measuring ERP is uses this technique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When compared to an fMRI, an EEG has…
A) higher spatial resolution.
B) a harder time with a wide age range due to potential motion artifacts.
C) data that is harder to process because participants must keep their heads still.
D) higher temporal resolution.
A) higher spatial resolution.
B) a harder time with a wide age range due to potential motion artifacts.
C) data that is harder to process because participants must keep their heads still.
D) higher temporal resolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The general way in which hemodynamic response work to produce a measurable BOLD response in the context of fMRI research is that brain regions that are more activated require more…
A) water.
B) fat.
C) glucose.
D) oxygen.
A) water.
B) fat.
C) glucose.
D) oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In using EEG, the wavelengths of an excited and stimulated young child is generally _____________ than when that same child is sleeping.
A) shorter in length
B) thicker
C) noisier
D) longer in length
A) shorter in length
B) thicker
C) noisier
D) longer in length

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
based on the following abstract taken from the journal Trends in Neuroscience and Education (citation below). The authors of the paper examined two different methods of mathematics instruction and used brain-imaging techniques to demonstrate how the methods might influence learning. Instructors are advised to use the reference below to retrieve the original abstract for their use.
Wirebring, L. K., Lithner, J., Jonsson, B. , Liljekvist, Y., Norqvist, M., & Nyberg, L. (2015). Learning mathematics without a suggested solution method: Durable effects on performance and brain activity. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 4(1), 6-14.
-From the abstract, what can we know about brain activity in the angular gyrus of participants?
A) There were larger spikes in the brain waves recorded from the angular gyrus of participants who had created this solution method themselves as compared to participants who were presented with a solution method.
B) There were greater blood-oxygen-level changes in the angular gyrus of participants who had created the solution method themselves as compared to participants who were presented with a solution method.
C) There were smaller blood-oxygen-level changes in the angular gyrus of participants who had created the solution method themselves as compared to participants who were presented with a solution method.
D) There were smaller spikes in the brain waves recorded from the angular gyrus of participants who had created the solution method themselves as compared to participants who were presented with a solution method.
Wirebring, L. K., Lithner, J., Jonsson, B. , Liljekvist, Y., Norqvist, M., & Nyberg, L. (2015). Learning mathematics without a suggested solution method: Durable effects on performance and brain activity. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 4(1), 6-14.
-From the abstract, what can we know about brain activity in the angular gyrus of participants?
A) There were larger spikes in the brain waves recorded from the angular gyrus of participants who had created this solution method themselves as compared to participants who were presented with a solution method.
B) There were greater blood-oxygen-level changes in the angular gyrus of participants who had created the solution method themselves as compared to participants who were presented with a solution method.
C) There were smaller blood-oxygen-level changes in the angular gyrus of participants who had created the solution method themselves as compared to participants who were presented with a solution method.
D) There were smaller spikes in the brain waves recorded from the angular gyrus of participants who had created the solution method themselves as compared to participants who were presented with a solution method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
based on the following abstract taken from the journal Trends in Neuroscience and Education (citation below). The authors of the paper examined two different methods of mathematics instruction and used brain-imaging techniques to demonstrate how the methods might influence learning. Instructors are advised to use the reference below to retrieve the original abstract for their use.
Wirebring, L. K., Lithner, J., Jonsson, B. , Liljekvist, Y., Norqvist, M., & Nyberg, L. (2015). Learning mathematics without a suggested solution method: Durable effects on performance and brain activity. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 4(1), 6-14.
-What information cannot be obtained by the methods of the study?
A) How quickly the angular gyrus increases its activation while the participant is solving a test question.
B) How strongly the fronto-parietal network is activated during the test phase across conditions.
C) How other brain regions differ from each other in terms of activation.
D) How strongly other brain regions are activated during test phase.
Wirebring, L. K., Lithner, J., Jonsson, B. , Liljekvist, Y., Norqvist, M., & Nyberg, L. (2015). Learning mathematics without a suggested solution method: Durable effects on performance and brain activity. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 4(1), 6-14.
-What information cannot be obtained by the methods of the study?
A) How quickly the angular gyrus increases its activation while the participant is solving a test question.
B) How strongly the fronto-parietal network is activated during the test phase across conditions.
C) How other brain regions differ from each other in terms of activation.
D) How strongly other brain regions are activated during test phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
based on the following abstract taken from the journal Trends in Neuroscience and Education (citation below). The authors of the paper examined two different methods of mathematics instruction and used brain-imaging techniques to demonstrate how the methods might influence learning. Instructors are advised to use the reference below to retrieve the original abstract for their use.
Wirebring, L. K., Lithner, J., Jonsson, B. , Liljekvist, Y., Norqvist, M., & Nyberg, L. (2015). Learning mathematics without a suggested solution method: Durable effects on performance and brain activity. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 4(1), 6-14.
-The researchers would like to test that the fronto-parietal region in the brain plays an essential role for solving mathematics problems by randomly assigning participants to receive a procedure that causes a small group of neurons to fire in a particular region in the brain. Which procedure are they using?
A) CT
B) PET
C) EEG
D) TMS
Wirebring, L. K., Lithner, J., Jonsson, B. , Liljekvist, Y., Norqvist, M., & Nyberg, L. (2015). Learning mathematics without a suggested solution method: Durable effects on performance and brain activity. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 4(1), 6-14.
-The researchers would like to test that the fronto-parietal region in the brain plays an essential role for solving mathematics problems by randomly assigning participants to receive a procedure that causes a small group of neurons to fire in a particular region in the brain. Which procedure are they using?
A) CT
B) PET
C) EEG
D) TMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
based on the following abstract taken from the journal Trends in Neuroscience and Education (citation below). The authors of the paper examined two different methods of mathematics instruction and used brain-imaging techniques to demonstrate how the methods might influence learning. Instructors are advised to use the reference below to retrieve the original abstract for their use.
Wirebring, L. K., Lithner, J., Jonsson, B. , Liljekvist, Y., Norqvist, M., & Nyberg, L. (2015). Learning mathematics without a suggested solution method: Durable effects on performance and brain activity. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 4(1), 6-14.
-In this study, which of the following would most likely disqualify the participant from participating (i.e., which of the following would make a participant ineligible to participate)?
A) Having corrected-vision
B) Being right-handed
C) Having claustrophobia
D) Having a record of taking math through high school
Wirebring, L. K., Lithner, J., Jonsson, B. , Liljekvist, Y., Norqvist, M., & Nyberg, L. (2015). Learning mathematics without a suggested solution method: Durable effects on performance and brain activity. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 4(1), 6-14.
-In this study, which of the following would most likely disqualify the participant from participating (i.e., which of the following would make a participant ineligible to participate)?
A) Having corrected-vision
B) Being right-handed
C) Having claustrophobia
D) Having a record of taking math through high school

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
based on the description below:
A researcher is interested in testing how brain tumors influence in Wernicke's area (i.e., a region of the brain). Past research indicates that damage to Wernicke's area often leads to an inability to produce and understand basic nouns and verbs. The researcher's study includes three phases. In phase 1, she recruits fifteen individuals who have brain tumors around Wernicke's area to serve as her sample of individuals with brain tumors and fifteen individuals without brain tumors to serve as controls. In phase 2, she will administer a task to examine how participants in both groups' brain activation might differ in a naming task of common objects that participants will be viewing during the study, and participants will also be asked to produce the nouns and verbs that are associated with the picture. In phase 3, the researcher examines how participants in both groups might differ in a comprehension task in which participants will be listening to audio stimuli and selecting images that correspond to a description. Participants will be paid for their participation.
-Which of the following might be a strong concern of the IRB and a corresponding request that they might make?
A) Researchers should not only recruit right-handed individuals for a study like this. They must include an equal sized sample of left-handed individuals.
B) The research team is using a procedure that is too invasive and dangerous. They should use a different apparatus.
C) The research team should compensate the group with tumors more than the group without since they are receiving the experimental manipulation.
D) The research team should provide a source of diagnosis and treatment (if necessary) for the group who is found to have brain tumors near Wernicke's area.
A researcher is interested in testing how brain tumors influence in Wernicke's area (i.e., a region of the brain). Past research indicates that damage to Wernicke's area often leads to an inability to produce and understand basic nouns and verbs. The researcher's study includes three phases. In phase 1, she recruits fifteen individuals who have brain tumors around Wernicke's area to serve as her sample of individuals with brain tumors and fifteen individuals without brain tumors to serve as controls. In phase 2, she will administer a task to examine how participants in both groups' brain activation might differ in a naming task of common objects that participants will be viewing during the study, and participants will also be asked to produce the nouns and verbs that are associated with the picture. In phase 3, the researcher examines how participants in both groups might differ in a comprehension task in which participants will be listening to audio stimuli and selecting images that correspond to a description. Participants will be paid for their participation.
-Which of the following might be a strong concern of the IRB and a corresponding request that they might make?
A) Researchers should not only recruit right-handed individuals for a study like this. They must include an equal sized sample of left-handed individuals.
B) The research team is using a procedure that is too invasive and dangerous. They should use a different apparatus.
C) The research team should compensate the group with tumors more than the group without since they are receiving the experimental manipulation.
D) The research team should provide a source of diagnosis and treatment (if necessary) for the group who is found to have brain tumors near Wernicke's area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
based on the description below:
A researcher is interested in testing how brain tumors influence in Wernicke's area (i.e., a region of the brain). Past research indicates that damage to Wernicke's area often leads to an inability to produce and understand basic nouns and verbs. The researcher's study includes three phases. In phase 1, she recruits fifteen individuals who have brain tumors around Wernicke's area to serve as her sample of individuals with brain tumors and fifteen individuals without brain tumors to serve as controls. In phase 2, she will administer a task to examine how participants in both groups' brain activation might differ in a naming task of common objects that participants will be viewing during the study, and participants will also be asked to produce the nouns and verbs that are associated with the picture. In phase 3, the researcher examines how participants in both groups might differ in a comprehension task in which participants will be listening to audio stimuli and selecting images that correspond to a description. Participants will be paid for their participation.
-In the first phase of the research, the researcher is likely using a(n)…
A) fMRI.
B) MRI
C) NIRS.
D) EEG.
A researcher is interested in testing how brain tumors influence in Wernicke's area (i.e., a region of the brain). Past research indicates that damage to Wernicke's area often leads to an inability to produce and understand basic nouns and verbs. The researcher's study includes three phases. In phase 1, she recruits fifteen individuals who have brain tumors around Wernicke's area to serve as her sample of individuals with brain tumors and fifteen individuals without brain tumors to serve as controls. In phase 2, she will administer a task to examine how participants in both groups' brain activation might differ in a naming task of common objects that participants will be viewing during the study, and participants will also be asked to produce the nouns and verbs that are associated with the picture. In phase 3, the researcher examines how participants in both groups might differ in a comprehension task in which participants will be listening to audio stimuli and selecting images that correspond to a description. Participants will be paid for their participation.
-In the first phase of the research, the researcher is likely using a(n)…
A) fMRI.
B) MRI
C) NIRS.
D) EEG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
based on the description below:
A researcher is interested in testing how brain tumors influence in Wernicke's area (i.e., a region of the brain). Past research indicates that damage to Wernicke's area often leads to an inability to produce and understand basic nouns and verbs. The researcher's study includes three phases. In phase 1, she recruits fifteen individuals who have brain tumors around Wernicke's area to serve as her sample of individuals with brain tumors and fifteen individuals without brain tumors to serve as controls. In phase 2, she will administer a task to examine how participants in both groups' brain activation might differ in a naming task of common objects that participants will be viewing during the study, and participants will also be asked to produce the nouns and verbs that are associated with the picture. In phase 3, the researcher examines how participants in both groups might differ in a comprehension task in which participants will be listening to audio stimuli and selecting images that correspond to a description. Participants will be paid for their participation.
-In phase 2 and 3 of the research, the researcher is more interested in _______________ than ________________.
A) brain waves; BOLD response
B) brain region; response timing
C) response timing; brain region
D) discrete brain response; brain region
A researcher is interested in testing how brain tumors influence in Wernicke's area (i.e., a region of the brain). Past research indicates that damage to Wernicke's area often leads to an inability to produce and understand basic nouns and verbs. The researcher's study includes three phases. In phase 1, she recruits fifteen individuals who have brain tumors around Wernicke's area to serve as her sample of individuals with brain tumors and fifteen individuals without brain tumors to serve as controls. In phase 2, she will administer a task to examine how participants in both groups' brain activation might differ in a naming task of common objects that participants will be viewing during the study, and participants will also be asked to produce the nouns and verbs that are associated with the picture. In phase 3, the researcher examines how participants in both groups might differ in a comprehension task in which participants will be listening to audio stimuli and selecting images that correspond to a description. Participants will be paid for their participation.
-In phase 2 and 3 of the research, the researcher is more interested in _______________ than ________________.
A) brain waves; BOLD response
B) brain region; response timing
C) response timing; brain region
D) discrete brain response; brain region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
based on the description below:
A researcher is interested in testing how brain tumors influence in Wernicke's area (i.e., a region of the brain). Past research indicates that damage to Wernicke's area often leads to an inability to produce and understand basic nouns and verbs. The researcher's study includes three phases. In phase 1, she recruits fifteen individuals who have brain tumors around Wernicke's area to serve as her sample of individuals with brain tumors and fifteen individuals without brain tumors to serve as controls. In phase 2, she will administer a task to examine how participants in both groups' brain activation might differ in a naming task of common objects that participants will be viewing during the study, and participants will also be asked to produce the nouns and verbs that are associated with the picture. In phase 3, the researcher examines how participants in both groups might differ in a comprehension task in which participants will be listening to audio stimuli and selecting images that correspond to a description. Participants will be paid for their participation.
-For this study, it is most likely that…
A) the second and third phase of the research should use different groups of participants because visual and audio stimuli should not be shown to the same group.
B) the second and third phase of the research should use different brain scan techniques because one is showing visual stimuli while the other is showing audio stimuli.
C) all the phases of the research uses the same type of machine to do brain scans.
D) the first phase and third phase uses the same type of machine to do brain scans but the second phase uses a different type of machine.
A researcher is interested in testing how brain tumors influence in Wernicke's area (i.e., a region of the brain). Past research indicates that damage to Wernicke's area often leads to an inability to produce and understand basic nouns and verbs. The researcher's study includes three phases. In phase 1, she recruits fifteen individuals who have brain tumors around Wernicke's area to serve as her sample of individuals with brain tumors and fifteen individuals without brain tumors to serve as controls. In phase 2, she will administer a task to examine how participants in both groups' brain activation might differ in a naming task of common objects that participants will be viewing during the study, and participants will also be asked to produce the nouns and verbs that are associated with the picture. In phase 3, the researcher examines how participants in both groups might differ in a comprehension task in which participants will be listening to audio stimuli and selecting images that correspond to a description. Participants will be paid for their participation.
-For this study, it is most likely that…
A) the second and third phase of the research should use different groups of participants because visual and audio stimuli should not be shown to the same group.
B) the second and third phase of the research should use different brain scan techniques because one is showing visual stimuli while the other is showing audio stimuli.
C) all the phases of the research uses the same type of machine to do brain scans.
D) the first phase and third phase uses the same type of machine to do brain scans but the second phase uses a different type of machine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The purpose of dMRI is to examine ______________ between brain areas.
A) activation
B) usage
C) connections
D) motion artifacts
A) activation
B) usage
C) connections
D) motion artifacts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What technique most likely generated the brain image below? 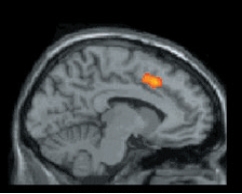
A) EEG
B) ERP
C) dMRI
D) fMRI

A) EEG
B) ERP
C) dMRI
D) fMRI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
MRI machines generate what kind of pulse?
A) Radiofrequency
B) Magneticfrequency
C) Radioactive
D) Nuclearmagnetic
A) Radiofrequency
B) Magneticfrequency
C) Radioactive
D) Nuclearmagnetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
MRI machines _______________ the _______________ of hydrogen atoms
A) disrupt; nuclei
B) disrupt; protons
C) align; protons
D) vibrate; bonds
A) disrupt; nuclei
B) disrupt; protons
C) align; protons
D) vibrate; bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following reasons is a primary disadvantage that CT scans have over MRI, fMRI, and dMRI?
A) CT scans only show structure whereas MRI, fMRI, and dMRI are all methods that allow researchers to examine brain activation.
B) CT scans uses X-rays and expose participants to radiation.
C) CT scans are better for examining research questions about timing whereas MRI, fMRI, and dMRI look at brain regions.
D) CT scans are only usable on adults, whereas MRI, fMRI, and dMRI can be used effectively as early as infancy.
A) CT scans only show structure whereas MRI, fMRI, and dMRI are all methods that allow researchers to examine brain activation.
B) CT scans uses X-rays and expose participants to radiation.
C) CT scans are better for examining research questions about timing whereas MRI, fMRI, and dMRI look at brain regions.
D) CT scans are only usable on adults, whereas MRI, fMRI, and dMRI can be used effectively as early as infancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
NIRS is a technique that uses _____________________ and measures the extent to which it ____________________________.
A) radiation; gets absorbed into the brain
B) light; reflects
C) sound; reflects
D) magnetic; pulses
A) radiation; gets absorbed into the brain
B) light; reflects
C) sound; reflects
D) magnetic; pulses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
ERP allows researchers to examine changes in...
A) which specific regions of the brain activated.
B) how specific brain regions interact.
C) blood oxygen levels in the brain.
D) brainwave patterns.
A) which specific regions of the brain activated.
B) how specific brain regions interact.
C) blood oxygen levels in the brain.
D) brainwave patterns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following likely contributed to the increase in neuroscience research?
A) Technological advancements
B) Increased stringency in ethical conduct
C) Increased awareness of how radiation influences the brain
D) None of the above are legitimate reasons.
A) Technological advancements
B) Increased stringency in ethical conduct
C) Increased awareness of how radiation influences the brain
D) None of the above are legitimate reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When using EEG to obtain data, one of the weaknesses is that it…
A) can only measure one type of brainwave at a time.
B) can only tell you about regions of interest and nothing about other parts of the brain.
C) can often lead to very noisy or messy data with lots of variability and thus requires many trials.
D) can only be used with adults.
A) can only measure one type of brainwave at a time.
B) can only tell you about regions of interest and nothing about other parts of the brain.
C) can often lead to very noisy or messy data with lots of variability and thus requires many trials.
D) can only be used with adults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A researcher is interested in assessing how visual stimuli that portrays prejudice is processed by the brain compared with stimuli that portrays neutral stimuli. To verify his team's hypothesis that this specific region of the brain is, indeed, involved with the processing of prejudice information, the team should use…
A) an fMRI scan.
B) an MRI scan.
C) an EEG.
D) a CT scan.
A) an fMRI scan.
B) an MRI scan.
C) an EEG.
D) a CT scan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is a safety concern when using an MRI machine?
A) The participant needs to be awake and cannot fall asleep.
B) The participant should not be wearing or have any ferromagnetic materials in their body.
C) The participant must be tested for allergies to radioactive substances.
D) The participant should be claustrophobic.
A) The participant needs to be awake and cannot fall asleep.
B) The participant should not be wearing or have any ferromagnetic materials in their body.
C) The participant must be tested for allergies to radioactive substances.
D) The participant should be claustrophobic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the context of psychological science, which of the following provide a way for researchers to interpret and validate data obtained from neuroimaging techniques?
A) Researcher self-report
B) Use of multiple neuroimaging techniques
C) Behavioral measures completed by the research participant
D) All of the above are equally useful methods.
A) Researcher self-report
B) Use of multiple neuroimaging techniques
C) Behavioral measures completed by the research participant
D) All of the above are equally useful methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements is false regarding the use of neuroscience?
A) There is still room for neuroscience techniques to evolve and improve.
B) Individuals, especially those with less expertise, are more skeptical about neuroscience evidence than evidence without a neuroscience explanation.
C) Neuroscience techniques usually still lead to outcomes with measurement error.
D) Neuroscience techniques often generate large amounts of data that require specialized expertise to analyze.
A) There is still room for neuroscience techniques to evolve and improve.
B) Individuals, especially those with less expertise, are more skeptical about neuroscience evidence than evidence without a neuroscience explanation.
C) Neuroscience techniques usually still lead to outcomes with measurement error.
D) Neuroscience techniques often generate large amounts of data that require specialized expertise to analyze.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Tractography serves what purpose in which neuroimaging technique?
A) It draws the wave patterns in when using EEG or measuring ERP.
B) It measures the number of voxels that are activated in fMRI.
C) It measures neural pathways in dMRI.
D) It measures relative size in MRI.
A) It draws the wave patterns in when using EEG or measuring ERP.
B) It measures the number of voxels that are activated in fMRI.
C) It measures neural pathways in dMRI.
D) It measures relative size in MRI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
dMRI scans help researchers understand regions that have high concentrations of oxygenated blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If a researcher is interested in the timing of brain activity, he or she should use EEG or measure ERP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In EEG research, brainwaves with longer wavelengths generally mean deeper and more abstract cognitive processing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
fMRI provides greater spatial resolution than EEG does

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
fMRI scans generally use a gray scale with darker colors (i.e, black) representing greater activation and light (i.e., white) colors representing relatively lower activation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
MRI technology uses a radiofrequency pulse to push protons of hydrogen atoms out of alignment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
fMRI enables researchers to obtain images of the brain while the brain is processing information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When using fMRI, researchers are measuring hemodynamic responses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
As long as you have protected the safety of the participant who is undergoing a neuroimaging procedure, there are generally no other ethical concerns in neuroscience research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
T2-weighted images differ from T1-weighted images in that they are generated from stronger radiofrequency pulses and are therefore higher in spatial resolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
ERPs can measure changes in a person's EEG procedure when faced with a specific target stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In an MRI scan of any sorts, the participant generally needs to keep their head still to prevent motion artifacts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
MRI, fMRI, and dMRI use the same scanning technology and machine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
EEG is a technique that can be used with children and adults, and is generally easy to administer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Neuroscience research has been so popular lately that the fad has caused individuals to be skeptical of their findings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



