Deck 7: Energy and Enzymes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Energy and Enzymes
1
A spherical rock rests at the top of a steep hill. The rock has
A) potential energy.
B) chemical energy.
C) kinetic energy.
D) no energy.
A) potential energy.
B) chemical energy.
C) kinetic energy.
D) no energy.
A
2
Living systems must work to remain ordered. They pass off their disorder in the form of
A) light.
B) sound.
C) heat.
D) water.
A) light.
B) sound.
C) heat.
D) water.
C
3
Which of the following is either consumed or synthesized in virtually every cellular reaction?
A) sugars
B) enzymes
C) ADP
D) ATP
A) sugars
B) enzymes
C) ADP
D) ATP
D
4
The metabolism of living organisms is made up of a series of reactions. These reactions are carefully controlled so that the organism
A) releases less carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
B) has time to react to its environment.
C) doesn't use up its food source too quickly.
D) can capture as much of the released energy as possible.
A) releases less carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
B) has time to react to its environment.
C) doesn't use up its food source too quickly.
D) can capture as much of the released energy as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Plants and animals use different energy storage molecules, yet they both use the same mechanism to "burn" their stored energy. How can plants and animals both be successful, even though they "burn" different energy storage molecules?
A) The internal components of plant and animal cells are identical.
B) The second law of thermodynamics says that all cells have the same energy transfer system.
C) The breaking of the chemical bonds of a storage molecule transfers energy, no matter what molecule is stored.
D) All organisms have the same enzymes to catalyze their energy-producing reactions.
A) The internal components of plant and animal cells are identical.
B) The second law of thermodynamics says that all cells have the same energy transfer system.
C) The breaking of the chemical bonds of a storage molecule transfers energy, no matter what molecule is stored.
D) All organisms have the same enzymes to catalyze their energy-producing reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The reuse of the same carbon molecules by plants, animals, and their environments through time is known as
A) activation energy.
B) a consumption tree.
C) carbon cycling.
D) the third law of thermodynamics.
A) activation energy.
B) a consumption tree.
C) carbon cycling.
D) the third law of thermodynamics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Photosynthetic organisms capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical bonds by forming
A) sugars.
B) enzymes.
C) work.
D) heat.
A) sugars.
B) enzymes.
C) work.
D) heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In photosynthesis, the carbon used to make sugars is
A) provided by enzymes.
B) provided by carbon dioxide.
C) extracted from DNA.
D) oxidized to make sugars.
A) provided by enzymes.
B) provided by carbon dioxide.
C) extracted from DNA.
D) oxidized to make sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
During photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy, a type of
A) potential energy.
B) kinetic energy.
C) heat.
D) metabolism.
A) potential energy.
B) kinetic energy.
C) heat.
D) metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following compounds is the least oxidized?
A) C6H11O6
B) CO2
C) CH4
D) HCOOH
A) C6H11O6
B) CO2
C) CH4
D) HCOOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The energy required for life processes must be extracted from an organism's
A) nucleus.
B) environment.
C) predators.
D) biosynthesis.
A) nucleus.
B) environment.
C) predators.
D) biosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Heat speeds up chemical reactions by
A) causing the cell to produce enzymes that lower the activation energy of the reactions.
B) decreasing the amount of oxygen available for redox reactions.
C) inhibiting catabolic reactions while promoting anabolic reactions.
D) causing substrate molecules to collide more often.
A) causing the cell to produce enzymes that lower the activation energy of the reactions.
B) decreasing the amount of oxygen available for redox reactions.
C) inhibiting catabolic reactions while promoting anabolic reactions.
D) causing substrate molecules to collide more often.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the reaction CH₂O + O₂ ® CO₂ + H₂O,
A) carbon is reduced and hydrogen is oxidized.
B) carbon is oxidized and oxygen is reduced.
C) carbon and hydrogen are reduced.
D) carbon and oxygen are oxidized.
A) carbon is reduced and hydrogen is oxidized.
B) carbon is oxidized and oxygen is reduced.
C) carbon and hydrogen are reduced.
D) carbon and oxygen are oxidized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When ATP breaks down into ADP and a phosphate group,
A) energy is absorbed by ADP and transferred to enzymes.
B) energy is released and can power cellular activities.
C) ADP becomes the active site in an enzyme.
D) the energy in the broken bond is transferred to the phosphate group.
A) energy is absorbed by ADP and transferred to enzymes.
B) energy is released and can power cellular activities.
C) ADP becomes the active site in an enzyme.
D) the energy in the broken bond is transferred to the phosphate group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
This graph depicts the amount of energy involved over the course of a chemical reaction. 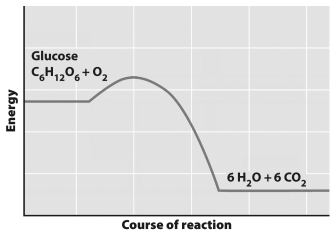
The graph indicates that
A) the products of this reaction have more energy that the substrates.
B) this reaction requires an input of energy to convert glucose and O2 to H2O and CO2.
C) this reaction can only run in one direction (from left to right on the graph).
D) this reaction only occurs in the presence of an enzyme.

The graph indicates that
A) the products of this reaction have more energy that the substrates.
B) this reaction requires an input of energy to convert glucose and O2 to H2O and CO2.
C) this reaction can only run in one direction (from left to right on the graph).
D) this reaction only occurs in the presence of an enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A molecule of sugar slowly "burns" in one of your cells. The products of these catabolic reactions are ___________ than the original sugar molecules.
A) less stable and have more energy
B) more stable and have more energy
C) more stable and have less energy
D) less stable and have less energy
A) less stable and have more energy
B) more stable and have more energy
C) more stable and have less energy
D) less stable and have less energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
_______ reactions use energy to build complex molecules.
A) Catabolic
B) Anabolic
C) Photosynthetic
D) Redox
A) Catabolic
B) Anabolic
C) Photosynthetic
D) Redox

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When humans cut down trees for lumber to build permanent structures, what aspect of metabolic cycling is disrupted?
A) The oxidation of wood products reduces the amount of photosynthesis that can occur.
B) The biosynthetic reactions that occur in the lumber cause too much catabolism to occur.
C) Carbon and other atoms tied up in wooden structures are not being recycled into other living organisms.
D) The DNA in the wood is unable to obey the first law of thermodynamics.
A) The oxidation of wood products reduces the amount of photosynthesis that can occur.
B) The biosynthetic reactions that occur in the lumber cause too much catabolism to occur.
C) Carbon and other atoms tied up in wooden structures are not being recycled into other living organisms.
D) The DNA in the wood is unable to obey the first law of thermodynamics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The second law of thermodynamics states that
A) metabolic reactions must be balanced.
B) the flow of energy connects living things to their environments.
C) energy can be created but not destroyed.
D) systems tend to become more disorderly.
A) metabolic reactions must be balanced.
B) the flow of energy connects living things to their environments.
C) energy can be created but not destroyed.
D) systems tend to become more disorderly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the reaction X + Y ® Z, Z is the
A) substrate.
B) product.
C) enzyme.
D) carbon molecule.
A) substrate.
B) product.
C) enzyme.
D) carbon molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
You observe that a solution turns from red to green very slowly. If you place a small piece of platinum in the solution, the change occurs much more rapidly, yet the platinum remains unchanged. Which of the following best explains this experimental result?
A) The platinum provided activation energy.
B) The platinum is an enzyme.
C) The platinum is a catalyst.
D) The platinum is an oxidizing agent.
A) The platinum provided activation energy.
B) The platinum is an enzyme.
C) The platinum is a catalyst.
D) The platinum is an oxidizing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
COX-2 inhibitors like Vioxx control inflammation without affecting COX-1, but patients taking these drugs are more susceptible to heart attack and stroke. Which of the following is a possible explanation of this side effect?
A) These newer COX-2 inhibitors must still interact with COX-1.
B) In creating these specific COX-2 inhibitors, scientists have changed the shape of aspirin so much that it no longer interacts with COX-2 at all.
C) In addition to controlling fever and inflammation, COX-2 plays a role in the maintaining the proper function of the circulatory system (heart and blood).
D) Inhibiting both COX-1 and COX-2 is necessary to prevent inflammation.
A) These newer COX-2 inhibitors must still interact with COX-1.
B) In creating these specific COX-2 inhibitors, scientists have changed the shape of aspirin so much that it no longer interacts with COX-2 at all.
C) In addition to controlling fever and inflammation, COX-2 plays a role in the maintaining the proper function of the circulatory system (heart and blood).
D) Inhibiting both COX-1 and COX-2 is necessary to prevent inflammation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A calorie represents
A) the number of grams of fat in a food product.
B) the number of times an enzyme can be reused before it must be replaced.
C) the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one liter of water by one degree Celsius.
D) the temperature at which a gram of food is completely converted into carbon dioxide.
A) the number of grams of fat in a food product.
B) the number of times an enzyme can be reused before it must be replaced.
C) the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one liter of water by one degree Celsius.
D) the temperature at which a gram of food is completely converted into carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Biosynthetic reactions require many things, including
A) carbon dioxide and water.
B) glucose and water.
C) enzymes and ATP.
D) sunlight and CTP.
A) carbon dioxide and water.
B) glucose and water.
C) enzymes and ATP.
D) sunlight and CTP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following strategies is not used by cells to help enzymes and substrates find each other?
A) locating enzymes used in the same biochemical pathway near each other in the cytoplasm
B) having certain reactions occur within a specific organelle
C) embedding more enzymes in the plasma membrane
D) producing heat to increase the frequency of molecular collisions
A) locating enzymes used in the same biochemical pathway near each other in the cytoplasm
B) having certain reactions occur within a specific organelle
C) embedding more enzymes in the plasma membrane
D) producing heat to increase the frequency of molecular collisions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What do catalysts and enzymes have in common?
A) They decrease the number of collisions between substrate molecules.
B) They increase the amount of activation energy required.
C) They increase the amount of substrate that is available.
D) They decrease the amount of activation energy required.
A) They decrease the number of collisions between substrate molecules.
B) They increase the amount of activation energy required.
C) They increase the amount of substrate that is available.
D) They decrease the amount of activation energy required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a human cell,
A) one enzyme usually catalyzes no more than five different chemical reactions.
B) nearly all chemical reactions are catalyzed by enzymes.
C) enzymes have to be constantly replaced as they are used up in the reactions that they catalyze.
D) some enzymes are specialized to store activation energy.
A) one enzyme usually catalyzes no more than five different chemical reactions.
B) nearly all chemical reactions are catalyzed by enzymes.
C) enzymes have to be constantly replaced as they are used up in the reactions that they catalyze.
D) some enzymes are specialized to store activation energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Enzymes can catalyze a reaction only
A) if they encounter a molecule of ATP.
B) if their active site is sufficiently oxidized.
C) if they have both products in their active site at the same time.
D) if they encounter a substrate that fits their active site.
A) if they encounter a molecule of ATP.
B) if their active site is sufficiently oxidized.
C) if they have both products in their active site at the same time.
D) if they encounter a substrate that fits their active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Some kinds of drain cleaners use enzymes rather than strong, more dangerous chemicals. These enzymes must be able to
A) catalyze a catabolic reaction.
B) raise the activation energy of the reaction that clears the clog.
C) create energy that can be used to break up the clog.
D) allow excess heat to be passed off into the environment.
A) catalyze a catabolic reaction.
B) raise the activation energy of the reaction that clears the clog.
C) create energy that can be used to break up the clog.
D) allow excess heat to be passed off into the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Organisms that maintain a constant body temperature rely on the heat produced by cells. Where does this heat come from?
A) Special metabolic pathways exist just for the production of heat.
B) Mitochondria produce heat in the form of ATP.
C) Plants store up heat as they perform photosynthesis. When an organism digests a plant, that heat is released.
D) Heat is a natural by-product of most chemical reactions.
A) Special metabolic pathways exist just for the production of heat.
B) Mitochondria produce heat in the form of ATP.
C) Plants store up heat as they perform photosynthesis. When an organism digests a plant, that heat is released.
D) Heat is a natural by-product of most chemical reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A given enzyme
A) can be used for many different kinds of chemical reactions.
B) is permanently changed during a chemical reaction.
C) has a special site where the products bind before the reaction begins.
D) lowers the activation energy of a particular reaction.
A) can be used for many different kinds of chemical reactions.
B) is permanently changed during a chemical reaction.
C) has a special site where the products bind before the reaction begins.
D) lowers the activation energy of a particular reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In many organelles, groups of different enzymes are located on membranes in close proximity to each other because
A) attaching enzymes to the membrane prevents the cell from losing them to the surrounding environment.
B) when enzymes are in close proximity, each one can catalyze more than one type of reaction.
C) these enzymes are involved in the same metabolic pathway and keeping them closer together increases the efficiency of the pathway.
D) all enzymes must act in groups to sufficiently reduce the amount of activation energy required for a reaction to occur.
A) attaching enzymes to the membrane prevents the cell from losing them to the surrounding environment.
B) when enzymes are in close proximity, each one can catalyze more than one type of reaction.
C) these enzymes are involved in the same metabolic pathway and keeping them closer together increases the efficiency of the pathway.
D) all enzymes must act in groups to sufficiently reduce the amount of activation energy required for a reaction to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the reaction H₂O + CO₂ + carbonic anhydrase® HCO₃- + H⁺+ carbonic anhydrase, carbonic anhydrase is a(n)
A) reactant.
B) product.
C) enzyme.
D) active site.
A) reactant.
B) product.
C) enzyme.
D) active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the figure below, E1, E2 and E3 represent three enzymes in the membrane of a mitochondrion. 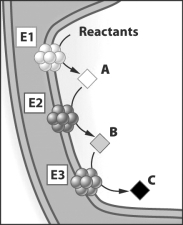
Which of the following is true?
A) B is the product of the activity of E2 and the substrate of E3.
B) If E2 doesn't function properly, A will not be produced.
C) E2 is the product of E1 and the substrate of E3.
D) C is the substrate for E1.

Which of the following is true?
A) B is the product of the activity of E2 and the substrate of E3.
B) If E2 doesn't function properly, A will not be produced.
C) E2 is the product of E1 and the substrate of E3.
D) C is the substrate for E1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An enzyme and its substrate find each other by
A) chance encounter.
B) magnetic attraction.
C) catalysis.
D) oxidative reactions.
A) chance encounter.
B) magnetic attraction.
C) catalysis.
D) oxidative reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Enzymes are a special class of
A) proteins.
B) nucleotides.
C) chemical bonds.
D) hormones.
A) proteins.
B) nucleotides.
C) chemical bonds.
D) hormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
This image diagrams the action of an enzyme. 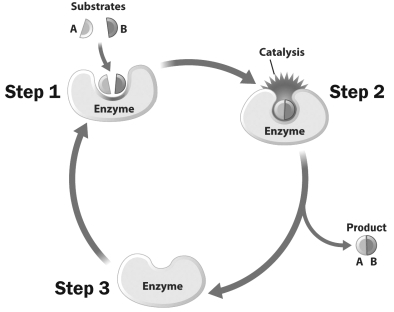
Notice that the enzyme is depicted as being more tightly wrapped around the substrates in step 2 than it is in step 1. Why is this?
A) When a substrate locks into the active site of an enzyme, the enzyme changes shape to mold itself around the substrates.
B) Generally, the size of a substrate is larger than the size of the active site it must fit into. When the substrate enters the active site, the active site must stretch to fit.
C) Before catalysis can occur, a substrate must change its shape so that it fits into the active site of the enzyme more precisely.
D) Most active sites are only designed to hold one substrate. In this image, two substrates enter the active site, creating a tighter fit.

Notice that the enzyme is depicted as being more tightly wrapped around the substrates in step 2 than it is in step 1. Why is this?
A) When a substrate locks into the active site of an enzyme, the enzyme changes shape to mold itself around the substrates.
B) Generally, the size of a substrate is larger than the size of the active site it must fit into. When the substrate enters the active site, the active site must stretch to fit.
C) Before catalysis can occur, a substrate must change its shape so that it fits into the active site of the enzyme more precisely.
D) Most active sites are only designed to hold one substrate. In this image, two substrates enter the active site, creating a tighter fit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In general, smaller animals have
A) longer life spans than larger animals.
B) slower metabolic rates than larger animals.
C) faster metabolic rates than larger animals.
D) the same life spans as larger animals.
A) longer life spans than larger animals.
B) slower metabolic rates than larger animals.
C) faster metabolic rates than larger animals.
D) the same life spans as larger animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Higher metabolic rates may shorten life spans, because
A) enzymes get used up more quickly than the cell can produce them.
B) toxic by-products build up quickly and are more likely to damage DNA.
C) cells and organs that run faster also wear out faster.
D) anabolism outpaces catabolism.
A) enzymes get used up more quickly than the cell can produce them.
B) toxic by-products build up quickly and are more likely to damage DNA.
C) cells and organs that run faster also wear out faster.
D) anabolism outpaces catabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The heat given off by living systems can increase the likelihood of a given chemical reaction's taking place. Why is this true?
A) The enzymes that catalyze reactions in living systems work increasingly better as the temperature decreases.
B) The heat given off lowers the internal cellular temperature, which allows reactions to proceed more quickly.
C) The heat allows photosynthesis to occur more rapidly.
D) The heat speeds molecular movement, increasing the likelihood of collisions between an enzyme and its substrate.
A) The enzymes that catalyze reactions in living systems work increasingly better as the temperature decreases.
B) The heat given off lowers the internal cellular temperature, which allows reactions to proceed more quickly.
C) The heat allows photosynthesis to occur more rapidly.
D) The heat speeds molecular movement, increasing the likelihood of collisions between an enzyme and its substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
_______ are the organelles where the breakdown products of food are oxidized, thereby generating most of a cell's ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Catabolic reactions are tightly coupled to _______ reactions that require energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
_______ blocks the activity of both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
All of the chemical energy in ATP is used during a chemical reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A molecule of methane burns, producing carbon dioxide, heat, light, and water. The direction of the event is dictated by the __________ law of thermodynamics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to the _____ ______ model, the active site of an enzyme adjusts its shape to mold around a substrate after binding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The capture and use of energy by living organisms involves numerous chemical reactions. Together all of these processes are known as _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy of a system and its surroundings remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Carbon dioxide is the product of the metabolic process called ____________ that occurs in both plants and animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A rotted log indicates that the ____________ law of thermodynamics has been operating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When chemical energy is converted into kinetic energy in a biological systems, _____ [more than all, less than all, or all] of the available energy is converted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An enzyme splits a disaccharide into two sugar monomers. The disaccharide is the _________ of this enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A catalyst affects the _______ at which a chemical reaction occurs, but it is not itself changed during the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The gain of electrons by one atom from another atom is referred to as _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The chemical reactions that occur in cells are catalyzed by _______ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Photosynthesis creates energy and cellular respiration destroys energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An insect devouring a leaf is an example of the second law of thermodynamics in action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is the _______ energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When ATP breaks into ADP and a phosphate group, energy is given off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The _______ of an enzyme is an area with a specialized shape and/or set of chemical properties that allows the enzyme to bind with a particular substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Sugar molecules are more oxidized than carbon dioxide molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Chemical reactions can occur without the input of any energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Exposing many proteins to high heat causes their three-dimensional shape to change. How might heat affect the function of an enzyme?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Enzymes catalyze only anabolic chemical reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The shape of an enzyme does not affect its activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Oxygen can be reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
As a molecule becomes more oxidized, it loses electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Enzymes can make otherwise impossible reactions happen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



