Deck 13: From Gene to Protein
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: From Gene to Protein
1
Following transcription,
A) the strands of DNA bond back to each other.
B) the mRNA is digested.
C) the DNA molecule is broken down.
D) the ribosome is released from the tRNA molecule.
A) the strands of DNA bond back to each other.
B) the mRNA is digested.
C) the DNA molecule is broken down.
D) the ribosome is released from the tRNA molecule.
A
2
The order of the bases in DNA determines the order of the
A) amino acids in DNA.
B) bases in a protein.
C) amino acids in mRNA.
D) bases in mRNA.
A) amino acids in DNA.
B) bases in a protein.
C) amino acids in mRNA.
D) bases in mRNA.
D
3
The sugar molecule present in RNA is
A) uracil.
B) deoxyribose.
C) ribose.
D) sucrose.
A) uracil.
B) deoxyribose.
C) ribose.
D) sucrose.
C
4
Which of the following best describes the function of genes?
A) They control the production of enzymes.
B) They control the production of structural proteins.
C) They control the production of all proteins.
D) They control the production of amino acids.
A) They control the production of enzymes.
B) They control the production of structural proteins.
C) They control the production of all proteins.
D) They control the production of amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Bacteria and humans use the same DNA components, and both kinds of cells also perform transcription and translation. Which of the following choices is a potentially significant outcome of this shared mechanism?
A) Bacteria are able to transcribe and translate human DNA, and thus they potentially could produce human proteins.
B) Bacteria are able to transcribe and translate human DNA, thus they could evolve into humans.
C) Bacterial and human proteins are identical in amino acid sequence since the mechanism for producing them is the same.
D) Bacterial and human DNA are identical in sequence since the method for producing it is the same.
A) Bacteria are able to transcribe and translate human DNA, and thus they potentially could produce human proteins.
B) Bacteria are able to transcribe and translate human DNA, thus they could evolve into humans.
C) Bacterial and human proteins are identical in amino acid sequence since the mechanism for producing them is the same.
D) Bacterial and human DNA are identical in sequence since the method for producing it is the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is true of transcription?
A) It destroys the DNA template.
B) The DNA molecule must unwind.
C) Base pairing is unimportant.
D) The end result is a protein.
A) It destroys the DNA template.
B) The DNA molecule must unwind.
C) Base pairing is unimportant.
D) The end result is a protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A promoter would be located on
A) the template strand of a DNA molecule.
B) the anticodon of a tRNA molecule.
C) an mRNA molecule.
D) RNA polymerase.
A) the template strand of a DNA molecule.
B) the anticodon of a tRNA molecule.
C) an mRNA molecule.
D) RNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The key enzyme used during transcription is
A) RNA polymerase.
B) DNA polymerase.
C) rRNA
D) terminase.
A) RNA polymerase.
B) DNA polymerase.
C) rRNA
D) terminase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
During transcription,
A) the DNA strands replicate, producing four mRNA molecules.
B) each strand in the DNA molecule directs the production of an mRNA molecule.
C) a template strand of DNA directs the production of an mRNA molecule.
D) a template strand of DNA directs the production of all of the tRNA molecules needed for producing the gene's protein product.
A) the DNA strands replicate, producing four mRNA molecules.
B) each strand in the DNA molecule directs the production of an mRNA molecule.
C) a template strand of DNA directs the production of an mRNA molecule.
D) a template strand of DNA directs the production of all of the tRNA molecules needed for producing the gene's protein product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The majority of genes specify the production of _______ as their immediate product.
A) rRNA
B) tRNA
C) DNA
D) mRNA
A) rRNA
B) tRNA
C) DNA
D) mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The sequence of nucleotides on an mRNA molecule
A) is complementary to the DNA template strand.
B) matches the sequence of the ribosome that will translate the mRNA.
C) exactly matches the template strand (except where U is substituted for T).
D) is identical to that of the promoter.
A) is complementary to the DNA template strand.
B) matches the sequence of the ribosome that will translate the mRNA.
C) exactly matches the template strand (except where U is substituted for T).
D) is identical to that of the promoter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The bases present in an RNA molecule are
A) C, T, A, and G.
B) U, A, C, and G.
C) G, C ,U, and T.
D) U, C, T, and A.
A) C, T, A, and G.
B) U, A, C, and G.
C) G, C ,U, and T.
D) U, C, T, and A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles and thus do not have nuclei. Therefore,
A) prokaryotes are unable to undergo transcription and translation.
B) prokaryotic cells do not need to undergo translation.
C) prokaryotic transcription and translation both take place in the cytoplasm.
D) prokaryotes are unable to replicate their DNA.
A) prokaryotes are unable to undergo transcription and translation.
B) prokaryotic cells do not need to undergo translation.
C) prokaryotic transcription and translation both take place in the cytoplasm.
D) prokaryotes are unable to replicate their DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
As transcription begins, RNA polymerase binds to a segment of a gene called
A) a promoter.
B) an intron.
C) a start codon.
D) an anticodon.
A) a promoter.
B) an intron.
C) a start codon.
D) an anticodon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following does not take place in the nucleus?
A) transcription
B) intron removal
C) replication
D) translation
A) transcription
B) intron removal
C) replication
D) translation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When does a cell undergo transcription?
A) during S phase
B) all the time
C) only when the cell needs a specific protein
D) during interphase
A) during S phase
B) all the time
C) only when the cell needs a specific protein
D) during interphase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following would be found only in RNA?
A) deoxyribose and uracil
B) ribose and thymine
C) ribose and uracil
D) deoxyribose and uracil
A) deoxyribose and uracil
B) ribose and thymine
C) ribose and uracil
D) deoxyribose and uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
DNA molecules are double-stranded, while most RNA molecules are single-stranded. Which of the following choices is the most likely reason that RNA does not need to be double-stranded?
A) DNA reproduces itself directly, whereas RNA does not.
B) RNA reproduces itself directly, whereas DNA does not.
C) DNA undergoes translation that requires the use of both strands at the same time.
D) RNA undergoes transcription that can only read one strand at a time.
A) DNA reproduces itself directly, whereas RNA does not.
B) RNA reproduces itself directly, whereas DNA does not.
C) DNA undergoes translation that requires the use of both strands at the same time.
D) RNA undergoes transcription that can only read one strand at a time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The information in a gene is encoded by the
A) introns of eukaryotic cells.
B) amino acids that make up the genes.
C) base sequences of the gene's DNA.
D) rRNA that transfers amino acids to ribosomes.
A) introns of eukaryotic cells.
B) amino acids that make up the genes.
C) base sequences of the gene's DNA.
D) rRNA that transfers amino acids to ribosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a strand of DNA has the sequence CGTAA, the RNA made from this molecule will have the sequence
A) CGTAA.
B) GCUTT.
C) TAGCC.
D) GCAUU.
A) CGTAA.
B) GCUTT.
C) TAGCC.
D) GCAUU.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Each tRNA molecule has a site at one end that
A) acts as a promoter and a site at the other end that acts as a terminator.
B) binds to a codon and a site at the other end that binds to an anticodon.
C) binds to an amino acid and a site at the other end that binds to a promoter.
D) binds to an amino acid and a site at the other end that binds to a codon.
A) acts as a promoter and a site at the other end that acts as a terminator.
B) binds to a codon and a site at the other end that binds to an anticodon.
C) binds to an amino acid and a site at the other end that binds to a promoter.
D) binds to an amino acid and a site at the other end that binds to a codon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A chemical that causes the formation of a covalent bond between adenine and thymine is added to a cell. How does this drug affect protein production in the cell?
A) The chemical increases the efficiency of protein production by making it easier for tRNA to interact with the correct mRNA codons.
B) The chemical prevents transcription from occurring so proteins cannot be made.
C) The chemical prevents protein production because once made, the RNA cannot separate from its DNA template.
D) The chemical has no affect on protein production since mRNA contains uracil rather than thymine.
A) The chemical increases the efficiency of protein production by making it easier for tRNA to interact with the correct mRNA codons.
B) The chemical prevents transcription from occurring so proteins cannot be made.
C) The chemical prevents protein production because once made, the RNA cannot separate from its DNA template.
D) The chemical has no affect on protein production since mRNA contains uracil rather than thymine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a codon?
A) U
B) UU
C) UUG
D) UUGG
A) U
B) UU
C) UUG
D) UUGG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In bacteria, the antibiotic tetracycline blocks the site where tRNA molecules enter the ribosome. Bacteria die from treatment with tetracycline because the antibiotic
A) inhibits the cell from producing the mRNA.
B) causes the tRNA molecules randomly arrange into proteins that do not function.
C) causes tRNA rather than mRNA to be made into proteins.
D) prevents the bacteria from assembling essential proteins.
A) inhibits the cell from producing the mRNA.
B) causes the tRNA molecules randomly arrange into proteins that do not function.
C) causes tRNA rather than mRNA to be made into proteins.
D) prevents the bacteria from assembling essential proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the genetic code, an amino acid is specified by
A) a stop codon.
B) rRNA.
C) a series of four introns.
D) a sequence of three mRNA bases.
A) a stop codon.
B) rRNA.
C) a series of four introns.
D) a sequence of three mRNA bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The importance of tRNA is that it
A) carries a specific amino acid to the mRNA.
B) reads the DNA molecule.
C) contains codons that specify amino acids.
D) is important in the construction of ribosomes.
A) carries a specific amino acid to the mRNA.
B) reads the DNA molecule.
C) contains codons that specify amino acids.
D) is important in the construction of ribosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When one base is changed to another at a single position in the DNA sequence of a gene, a(n) _______ mutation has occurred.
A) insertion
B) deletion
C) frameshift
D) substitution
A) insertion
B) deletion
C) frameshift
D) substitution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the chart below to determine the chain of amino acids that would be produced by the entire sequence UGUACGAUAGGCUAG. 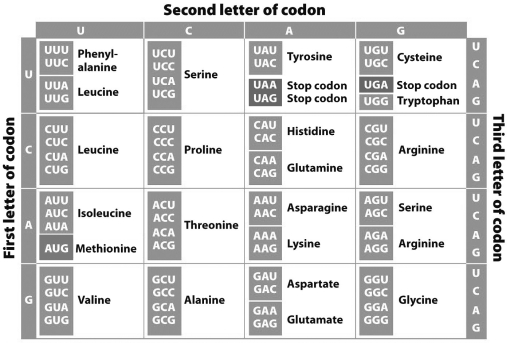
A) ACAUGCUAUAUCCCG
B) ACATGCTATATCCCG
C) cysteine-threonine-isoleucine-glycine
D) cysteine-threonine-isoleucine-glycine-stop

A) ACAUGCUAUAUCCCG
B) ACATGCTATATCCCG
C) cysteine-threonine-isoleucine-glycine
D) cysteine-threonine-isoleucine-glycine-stop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a particular stretch of DNA has the base sequence TAC, what will be the base sequence of the anticodon of the tRNA that carries the amino acid encoded by that stretch of DNA?
A) TAC
B) UAC
C) ATG
D) GUC
A) TAC
B) UAC
C) ATG
D) GUC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consider a build-at-home bookshelf that comes with instructions and various pieces of wood as an analogy for translation. In this analogy, what would best match the job of the ribosome?
A) the instructions
B) the person building the bookshelf
C) the pieces of wood
D) the bookshelf
A) the instructions
B) the person building the bookshelf
C) the pieces of wood
D) the bookshelf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A tRNA molecule produced in a laboratory has the anticodon for the amino acid serine, but carries the amino acid lysine. When it reaches the serine codon on a molecule of mRNA where translation is underway what is the most likely outcome?
A) It won't bind with the codon on the mRNA molecule.
B) A potentially dysfunctional protein will result.
C) A proofreading enzyme will change lysine to serine.
D) Translation will stop.
A) It won't bind with the codon on the mRNA molecule.
B) A potentially dysfunctional protein will result.
C) A proofreading enzyme will change lysine to serine.
D) Translation will stop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which molecules are involved in translation?
A) DNA and RNA
B) mDNA, tDNA, and rDNA
C) mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
D) proteins, amino acids, and DNA
A) DNA and RNA
B) mDNA, tDNA, and rDNA
C) mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
D) proteins, amino acids, and DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
It is possible for a mutation to occur and yet not alter the end product of translation if
A) the RNA polymerase skips over the mutated area.
B) the new codon encodes the same amino acid.
C) a deletion mutation removes the entire codon.
D) mutation affects the active site of the protein product.
A) the RNA polymerase skips over the mutated area.
B) the new codon encodes the same amino acid.
C) a deletion mutation removes the entire codon.
D) mutation affects the active site of the protein product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If introns were not removed from newly made mRNA, which of the following results would be the most likely to occur?
A) The introns could not be used to produce the proteins the cell needs from them.
B) The resulting protein would be longer than if the introns were removed.
C) The resulting DNA would not code for the correct gene.
D) The resulting rRNA would not code for the correct protein.
A) The introns could not be used to produce the proteins the cell needs from them.
B) The resulting protein would be longer than if the introns were removed.
C) The resulting DNA would not code for the correct gene.
D) The resulting rRNA would not code for the correct protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Each set of three bases in an mRNA molecule codes for one of 20 specific
A) rRNA molecules.
B) nucleotides.
C) amino acids.
D) proteins.
A) rRNA molecules.
B) nucleotides.
C) amino acids.
D) proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is not a feature of the genetic code?
A) Your unique genetic code is represented by your DNA sequence.
B) Each codon in the genetic code specifies only one amino acid.
C) The genetic code is redundant.
D) The same genetic code can be applied to virtually every organism on Earth.
A) Your unique genetic code is represented by your DNA sequence.
B) Each codon in the genetic code specifies only one amino acid.
C) The genetic code is redundant.
D) The same genetic code can be applied to virtually every organism on Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the chart below to determine the chain of amino acids that would be produced by the sequence of this very short, complete gene: UAUUAUGCCUGAGUGAAUUGCUA. 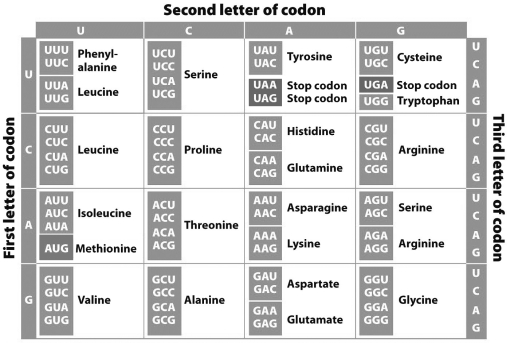
A) tyrosine-tyrosine-alanine
B) tyrosine-tyrosine-alanine-stop-valine-asparagine-cysteine
C) methionine-proline-glutamate
D) methionine-proline-glutamate-isoleucine-alanine

A) tyrosine-tyrosine-alanine
B) tyrosine-tyrosine-alanine-stop-valine-asparagine-cysteine
C) methionine-proline-glutamate
D) methionine-proline-glutamate-isoleucine-alanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
During translation,
A) many mRNA molecules work with one tRNA molecule and one rRNA molecule to produce a protein.
B) one tRNA molecule works with paired mRNA molecules and many rRNA molecules to produce a protein.
C) strings of bonded tRNA molecules work with one mRNA molecule and one rRNA molecule to produce a protein.
D) one mRNA molecule works with several rRNA molecules and many tRNA molecules to produce a protein.
A) many mRNA molecules work with one tRNA molecule and one rRNA molecule to produce a protein.
B) one tRNA molecule works with paired mRNA molecules and many rRNA molecules to produce a protein.
C) strings of bonded tRNA molecules work with one mRNA molecule and one rRNA molecule to produce a protein.
D) one mRNA molecule works with several rRNA molecules and many tRNA molecules to produce a protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is true of rRNA?
A) It is made up of base pairs.
B) It carries amino acids.
C) It is not translated.
D) It helps transcribe DNA.
A) It is made up of base pairs.
B) It carries amino acids.
C) It is not translated.
D) It helps transcribe DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A potential danger of a mutation to an organism is that
A) it can affect codons within the spacer DNA.
B) all mutations are fatal.
C) it can cause a change in the function of a gene's protein product.
D) it can increase the length of the introns of that organism's genome.
A) it can affect codons within the spacer DNA.
B) all mutations are fatal.
C) it can cause a change in the function of a gene's protein product.
D) it can increase the length of the introns of that organism's genome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following would you be most likely to find in an athlete who has won Olympic gold in the 100 meter sprint?
A) at least one copy of the R allele for ACTN3
B) at least one copy of the X allele for ACTN3
C) two copies of the X allele for ACTN3
D) two knocked-out copies of the R allele
A) at least one copy of the R allele for ACTN3
B) at least one copy of the X allele for ACTN3
C) two copies of the X allele for ACTN3
D) two knocked-out copies of the R allele

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The base sequence of mRNA specifies the sequence of amino acids in a _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Cells use three main types of RNA: mRNA, tRNA, and ____ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A _______ is the series of bases in mRNA that specifies a single amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
_______ is different than DNA replication in that it involves the copying of just a small portion of a chromosome rather than the entire chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The intermediary molecule that transmits information in a gene to a ribosome is ________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a eukaryotic protein is to function properly ________ must be removed from the initial mRNA molecule and the remaining _____ must be joined together before translation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A gene affects an organism's phenotype by controlling
A) protein production.
B) the mutation rate.
C) the organism's environment.
D) the organism's ribosomes.
A) protein production.
B) the mutation rate.
C) the organism's environment.
D) the organism's ribosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For translation to begin mRNA must first bind to a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If X is a base that is inserted into each of the following DNA sequences, on which of them is it most likely to have the greatest effect on the gene's protein product?
A) AATGATATCATCCGACGXA
B) AATGATATCATCCGXACGA
C) AATGATATXCATCCGACGA
D) AXATGATATCATCCGACGA
A) AATGATATCATCCGACGXA
B) AATGATATCATCCGXACGA
C) AATGATATXCATCCGACGA
D) AXATGATATCATCCGACGA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The third position in the _______ of some tRNAs is said to wobble because it can pair with one up to three different bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For a firefly to glow, the enzyme luciferase must assist a chemical reaction in the cells of the firefly. A scientist uses a chemical to induce a mutation in the luciferase gene in a strain of fireflies. Which of the following is true?
A) Even if the mutation changes the structure of the luciferase protein it will still be able to perform the chemical reactions needed to make the firefly glow.
B) The ability of the firefly to glow may or may not be affected by the mutation.
C) The mutation will affect the structure of the mRNA made from the gene, but not the structure of the protein made from the gene.
D) Any mutation in a gene causes that gene to stop making functional proteins.
A) Even if the mutation changes the structure of the luciferase protein it will still be able to perform the chemical reactions needed to make the firefly glow.
B) The ability of the firefly to glow may or may not be affected by the mutation.
C) The mutation will affect the structure of the mRNA made from the gene, but not the structure of the protein made from the gene.
D) Any mutation in a gene causes that gene to stop making functional proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The addition or deletion of bases in DNA can cause a _______ which causes a change in the reading of the mRNA codons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The _______ is a sequence of DNA where RNA polymerase binds to begin transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a molecule of mRNA is a sentence, its bases are the letters and the codons are the _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Most molecules of RNA are _______-stranded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Each tRNA molecule carries only one specific ________ ________ , but it can bind to up to three codons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Translation occurs in the _______ of the cell, where ribosomes are located.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The figure below depicts a gene and two different ways that gene could be mutated. 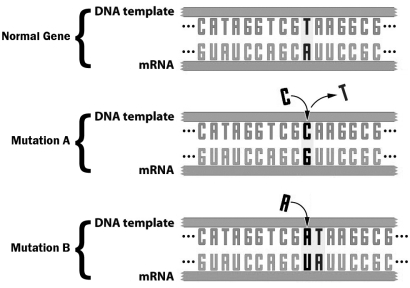
How does mutation A differ from mutation B?
A) Mutation A does not permanently change the sequence of the gene, but Mutation B does.
B) Mutation A involves the insertion of a base whereas Mutation B involves the deletion of a base.
C) Mutation A results in a possible change in one amino acid in the protein produced by the gene, but Mutation B affects several amino acids.
D) Mutation A can only occur in introns, but Mutation B can occur in both introns and exons.

How does mutation A differ from mutation B?
A) Mutation A does not permanently change the sequence of the gene, but Mutation B does.
B) Mutation A involves the insertion of a base whereas Mutation B involves the deletion of a base.
C) Mutation A results in a possible change in one amino acid in the protein produced by the gene, but Mutation B affects several amino acids.
D) Mutation A can only occur in introns, but Mutation B can occur in both introns and exons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
_______ is the specific type of nucleic acid found in ribosomes, which are important to protein syntheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Since they are so distantly related, the codons for serine in a black widow spider would probably be much different from the codons for serine in bluebirds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
rRNA plays a role in the formation of the covalent bonds between amino acids during translation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The three-dimensional structure of the protein made by a single mRNA molecule varies, but whatever the shape, the overall function of that protein does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Proteins are produced directly from DNA, with no intermediate steps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The stop codon is the sequence of bases at which transcription ends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Each time transcription occurs, all of the DNA in a cell is copied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A mutation occurs in the promoter of a gene. How might this mutation affect the production of the protein encoded by the gene?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The position of the start codon is important because every molecule of mRNA can be read by a ribosome in three different ways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Changing even a few bases in a molecule of DNA always affects the protein product adversely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In tRNA, an amino acid is covalently bonded to an anticodon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If both strands of the DNA of a gene underwent transcription and translation, they would produce the same mRNA and protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The first amino acid in most proteins is methionine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A codon can specify up to three different amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



