Deck 18: Adaptation and Speciation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Adaptation and Speciation
1
Some species of orchids attract insects to assist them in reproduction by producing flowers that look like female bees. The flowers fool male bees into attempting to mate with them. This example shows adaptive evolution by
A) the orchids.
B) the bees.
C) all flowering plants.
D) ancestral bees.
A) the orchids.
B) the bees.
C) all flowering plants.
D) ancestral bees.
A
2
Which of the following most likely is not an adaptation by plants to attract animals for assistance with mating?
A) production of nectar
B) brightly colored flower petals
C) absence of petals
D) sweet-smelling fragrance
A) production of nectar
B) brightly colored flower petals
C) absence of petals
D) sweet-smelling fragrance
C
3
Adaptive evolution allows species to
A) reduce mutation rate.
B) decrease genetic variation.
C) adjust to environmental changes.
D) hybridize.
A) reduce mutation rate.
B) decrease genetic variation.
C) adjust to environmental changes.
D) hybridize.
C
4
Populations of weaver ants work together to "sew" leaves into a living nest. The nest building behavior of weaver ants
A) illustrates that the ants can consciously plan their nests.
B) represents a complex behavioral adaptation.
C) shows that these ants can get along without interacting with other species.
D) illustrates that adaptive evolution is goal-oriented.
A) illustrates that the ants can consciously plan their nests.
B) represents a complex behavioral adaptation.
C) shows that these ants can get along without interacting with other species.
D) illustrates that adaptive evolution is goal-oriented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Every year, environmental signals in Africa cause flycatchers to return to the Netherlands to breed. When they arrive, they depend on freshly hatched caterpillars for food. Global climate change has caused the caterpillars to hatch earlier in the Netherlands, but the environmental cues in Africa remain the same. Now, when the flycatchers return to the Netherlands the caterpillars are no longer available as a food source. Which of the following is likely to happen to this species of flycatcher?
A) Flycatchers will adapt to environmental change because mutations that cause flycatchers to recognize earlier environmental signals in Africa will increase in frequency in flycatcher populations
B) Flycatchers will adapt to environmental change because mutations that aid flycatchers in utilizing other food sources (besides caterpillars) will increase in frequency in flycatcher populations.
C) Flycatchers will not adapt to environmental change because their population does not have alleles that aid in survival under these conditions.
D) All of the above are possible scenarios.
A) Flycatchers will adapt to environmental change because mutations that cause flycatchers to recognize earlier environmental signals in Africa will increase in frequency in flycatcher populations
B) Flycatchers will adapt to environmental change because mutations that aid flycatchers in utilizing other food sources (besides caterpillars) will increase in frequency in flycatcher populations.
C) Flycatchers will not adapt to environmental change because their population does not have alleles that aid in survival under these conditions.
D) All of the above are possible scenarios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Adaptive evolution
A) is large-scale movement of a single species over a new geographic area.
B) occurs when a more adapted species causes the extinction of a less adapted one.
C) is the process by which natural selection improves the match between an organism and its environment over time.
D) is an increase in the adaptiveness of many species that have already evolved.
A) is large-scale movement of a single species over a new geographic area.
B) occurs when a more adapted species causes the extinction of a less adapted one.
C) is the process by which natural selection improves the match between an organism and its environment over time.
D) is an increase in the adaptiveness of many species that have already evolved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When a brightly colored guppy population is placed in an area containing many predators, the population changes in only a few generations to one containing only guppies with drab, dull colors that blend into their environment. This is an example of how natural selection can
A) force new color mutations to occur.
B) convert a dominant allele into a recessive allele.
C) improve the match between guppies and their environment.
D) change the color preferences of female guppies.
A) force new color mutations to occur.
B) convert a dominant allele into a recessive allele.
C) improve the match between guppies and their environment.
D) change the color preferences of female guppies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The soapberry bugs shown in the figure below adapted to a change in food source in as fast as 30 years. 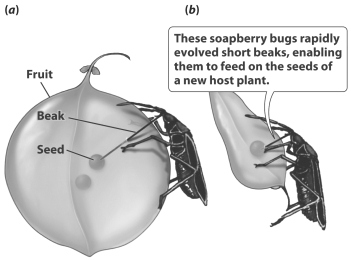
For evolution to occur this quickly,
A) the mutation creating alleles for shorter beaks must have been present in the soapberry bug population before its food source changed.
B) the soapberry bugs must have mutated their beak length genes when they ran out of food.
C) the life cycle of the soapberry bug (time from egg hatching to reproductive age) must be very long.
D) soapberry bugs must have had several other food sources besides the fruit they normally ate.

For evolution to occur this quickly,
A) the mutation creating alleles for shorter beaks must have been present in the soapberry bug population before its food source changed.
B) the soapberry bugs must have mutated their beak length genes when they ran out of food.
C) the life cycle of the soapberry bug (time from egg hatching to reproductive age) must be very long.
D) soapberry bugs must have had several other food sources besides the fruit they normally ate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Using reproductive isolation as a method of defining a species is not useful for
A) species whose ranges overlap.
B) species that cannot produce hybrids.
C) organisms known only from fossils.
D) organisms that reproduce sexually.
A) species whose ranges overlap.
B) species that cannot produce hybrids.
C) organisms known only from fossils.
D) organisms that reproduce sexually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Individuals of the same species generally
A) experience prezygotic barriers to reproduction.
B) do not interbreed extensively.
C) share many common physical and behavioral characteristics.
D) vary only very slightly in appearance.
A) experience prezygotic barriers to reproduction.
B) do not interbreed extensively.
C) share many common physical and behavioral characteristics.
D) vary only very slightly in appearance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Eastern skunk cabbage, which blooms in very early spring, produces chemicals that smell like decaying meat. This plant has probably become adapted to mate with the assistance of
A) butterflies.
B) honeybees.
C) flies.
D) wind.
A) butterflies.
B) honeybees.
C) flies.
D) wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The faster a cheetah can run, the more likely it is to capture its prey. Cheetahs with longer legs are able to run faster than those with shorter legs. Although the existing cheetah population shows a variety of leg lengths, cheetah legs are not increasing in length from one generation to the next. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
A) Cheetah populations no longer contain the alleles needed to grow longer legs.
B) Cheetahs with long legs are reproductively isolated from cheetahs with short legs.
C) Natural selection does not act on the genes involved in determining leg length.
D) The longer the length of a cheetah leg, the more likely the leg bone is to break.
A) Cheetah populations no longer contain the alleles needed to grow longer legs.
B) Cheetahs with long legs are reproductively isolated from cheetahs with short legs.
C) Natural selection does not act on the genes involved in determining leg length.
D) The longer the length of a cheetah leg, the more likely the leg bone is to break.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a postzygotic isolating mechanism?
A) Gametes cannot join.
B) Zygote fails to develop.
C) Breeding seasons are different.
D) Courtship behaviors are different.
A) Gametes cannot join.
B) Zygote fails to develop.
C) Breeding seasons are different.
D) Courtship behaviors are different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is not true of adaptations?
A) They are often complex.
B) They help organisms better match their environments.
C) They can occur quickly or slowly.
D) They lead to an organism becoming perfectly adapted.
A) They are often complex.
B) They help organisms better match their environments.
C) They can occur quickly or slowly.
D) They lead to an organism becoming perfectly adapted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is responsible for the nearly perfect match in color pattern between a species of praying mantis (an insect) and the leaves on which it rests?
A) genetic drift
B) adaptive evolution
C) the Hardy-Weinberg equation
D) speciation
A) genetic drift
B) adaptive evolution
C) the Hardy-Weinberg equation
D) speciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Two species live in the same area but breed in different parts of their habitat. These species are
A) geographically isolated.
B) ecologically isolated.
C) artificially isolated.
D) likely to produce hybrids.
A) geographically isolated.
B) ecologically isolated.
C) artificially isolated.
D) likely to produce hybrids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For the quality of an adaptation to improve over time, _______ must already exist within the population.
A) genetic limitations
B) genetic variation
C) speciation
D) ecological trade-offs
A) genetic limitations
B) genetic variation
C) speciation
D) ecological trade-offs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The classification of bacterial species does not fit the usual definition of species. This is because bacteria
A) cannot exchange genetic material.
B) are eukaryotic.
C) have a high rate of gene flow.
D) reproduce asexually.
A) cannot exchange genetic material.
B) are eukaryotic.
C) have a high rate of gene flow.
D) reproduce asexually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is not true?
A) Adaptations are complex and always predesigned.
B) Some adaptations are so complex that they may appear to be predesigned.
C) Adaptations often involve more than a single characteristic of organisms.
D) Some adaptations help organisms defend against predators.
A) Adaptations are complex and always predesigned.
B) Some adaptations are so complex that they may appear to be predesigned.
C) Adaptations often involve more than a single characteristic of organisms.
D) Some adaptations help organisms defend against predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A flower is red, has a long tube formed by fusion of petals, has nectar at the base of the tube, has no landing platform, and opens during the day. It has probably become adapted to mate with the assistance of
A) mice.
B) bees.
C) hummingbirds.
D) bats.
A) mice.
B) bees.
C) hummingbirds.
D) bats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Polyploidy in plants can lead to
A) prezygotic isolation.
B) reduced chromosome numbers.
C) reversed meiosis.
D) postzygotic isolation.
A) prezygotic isolation.
B) reduced chromosome numbers.
C) reversed meiosis.
D) postzygotic isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The formation of a new species
A) can occur slowly or rapidly.
B) takes at least 1 million years.
C) is evolutionarily insignificant.
D) never happens.
A) can occur slowly or rapidly.
B) takes at least 1 million years.
C) is evolutionarily insignificant.
D) never happens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Great controversy exists regarding the "hobbits" of Flores Island. Which of the following arguments would not support the hypothesis that hobbits are the same species as modern humans?
A) The different structure of the wrist bones found on Flores Island is an example of the level of nature variation exhibited by Homo sapiens.
B) Reconstructions of the hobbit brain show that it has unique structural features not seen in the brains of modern humans.
C) Modern populations of human pygmies of approximately the same size as the Flores hobbits exist on islands in the Philippines.
D) The island of Flores has never been isolated from other human populations by enough distance to prevent gene flow.
A) The different structure of the wrist bones found on Flores Island is an example of the level of nature variation exhibited by Homo sapiens.
B) Reconstructions of the hobbit brain show that it has unique structural features not seen in the brains of modern humans.
C) Modern populations of human pygmies of approximately the same size as the Flores hobbits exist on islands in the Philippines.
D) The island of Flores has never been isolated from other human populations by enough distance to prevent gene flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Polyploidy can lead to
A) a high rate of gene flow between populations.
B) geographic isolation.
C) fewer chromosomes.
D) reproductive isolation.
A) a high rate of gene flow between populations.
B) geographic isolation.
C) fewer chromosomes.
D) reproductive isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Populations within a species are connected by
A) gene flow.
B) speciation.
C) continental drift.
D) genetic drift.
A) gene flow.
B) speciation.
C) continental drift.
D) genetic drift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In general, geographic isolation occurs when
A) populations migrate to new environments.
B) gene flow is reduced by over 75 percent due to climate change.
C) mutations overcome genetic drift across physical barriers.
D) populations are separated by a distance that is great enough to limit gene flow.
A) populations migrate to new environments.
B) gene flow is reduced by over 75 percent due to climate change.
C) mutations overcome genetic drift across physical barriers.
D) populations are separated by a distance that is great enough to limit gene flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The current diversity of dog breeds is due to
A) artificial selection by humans.
B) geographic isolation.
C) polyploidy.
D) a lack of biodiversity among dogs.
A) artificial selection by humans.
B) geographic isolation.
C) polyploidy.
D) a lack of biodiversity among dogs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the figure below (left), two populations of one species of fruit flies are raised for several generations on different nutrients (starch and maltose). On the right, the members of the two populations were reintroduced and the mating frequencies of flies from the two different populations were recorded. 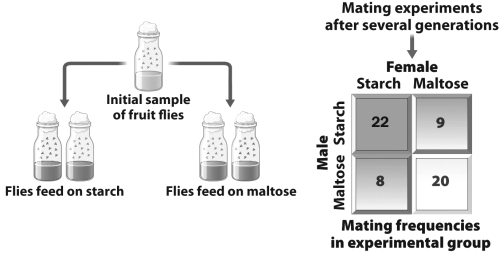
Which of the following is true?
A) After only a few generations, these two populations have undergone speciation since they no longer mate with each other at high levels.
B) The two populations are in the early stages of reproductive isolation since male flies are more likely to mate with female flies that were raised on the same medium.
C) Fruit flies grown on starch for several generations are no longer capable of consuming maltose.
D) The original population of fruit flies actually consisted of two different species of fruit flies. When hybridization occurred between the two populations, only sterile offspring were produced.

Which of the following is true?
A) After only a few generations, these two populations have undergone speciation since they no longer mate with each other at high levels.
B) The two populations are in the early stages of reproductive isolation since male flies are more likely to mate with female flies that were raised on the same medium.
C) Fruit flies grown on starch for several generations are no longer capable of consuming maltose.
D) The original population of fruit flies actually consisted of two different species of fruit flies. When hybridization occurred between the two populations, only sterile offspring were produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
For two populations to accumulate enough genetic differences to cause speciation, the factors that promote these differences
A) must operate in populations that are not physically separated.
B) must have a greater effect than does the amount of ongoing gene flow.
C) need to be combined with the forces of genetic drift.
D) should include polyploidy.
A) must operate in populations that are not physically separated.
B) must have a greater effect than does the amount of ongoing gene flow.
C) need to be combined with the forces of genetic drift.
D) should include polyploidy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Speciation
A) can result from geographic isolation.
B) is directed.
C) occurs only in ring species.
D) reduces variation.
A) can result from geographic isolation.
B) is directed.
C) occurs only in ring species.
D) reduces variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Geographic isolation limits the _______ between populations of a species.
A) genetic differences
B) adaptation
C) directional selection
D) gene flow
A) genetic differences
B) adaptation
C) directional selection
D) gene flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Examine the figure below. 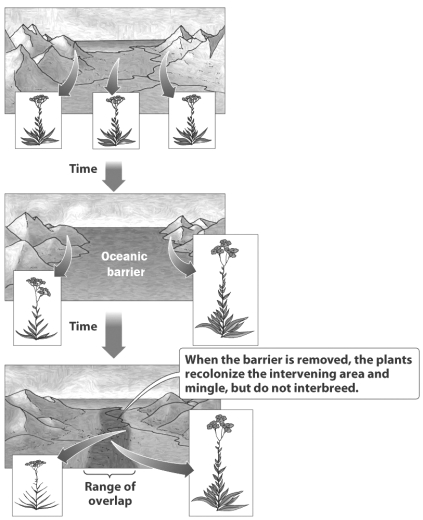
Why have the two plant populations depicted become so different in the time they were separated by the ocean?
A) Founder's effect. a small group of individuals carrying only the tall allele established a new population on the right side of the ocean.
B) The amount of gene flow between the two populations increased when the ocean separated the plants so mutations moved from one population to another.
C) When sea level rose, it killed all of the plants on the right side of the figure. A new species evolved from another plant species already existing in the mountains of the right.
D) The separated populations adapted to the different environments on each side of the ocean and became reproductively isolated.

Why have the two plant populations depicted become so different in the time they were separated by the ocean?
A) Founder's effect. a small group of individuals carrying only the tall allele established a new population on the right side of the ocean.
B) The amount of gene flow between the two populations increased when the ocean separated the plants so mutations moved from one population to another.
C) When sea level rose, it killed all of the plants on the right side of the figure. A new species evolved from another plant species already existing in the mountains of the right.
D) The separated populations adapted to the different environments on each side of the ocean and became reproductively isolated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The improvement of the match between organisms and their environments over time is called ________ evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following does not provide an example of geographic isolation?
A) Two populations live in two valleys on opposite sides of a mountain range.
B) Two populations live on different mountains with a valley between them.
C) Two populations live on opposite sides of a river.
D) Two populations live in different parts of a small lake.
A) Two populations live in two valleys on opposite sides of a mountain range.
B) Two populations live on different mountains with a valley between them.
C) Two populations live on opposite sides of a river.
D) Two populations live in different parts of a small lake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Sympatric speciation
A) occurs only in plants.
B) is impossible, because the populations of a species must be isolated from one another for speciation to occur.
C) is always a result of polyploidy.
D) occurs when a new species emerges from a population in the absence of a geographical barrier.
A) occurs only in plants.
B) is impossible, because the populations of a species must be isolated from one another for speciation to occur.
C) is always a result of polyploidy.
D) occurs when a new species emerges from a population in the absence of a geographical barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A rainforest is a highly complex habitat, with organisms living at various levels in the trees, on the ground, and underground. Is it possible to consider two populations living in the same tree to be geographically isolated?
A) No, because if they are in the same tree, they are in the same geographic area.
B) No, because if they are in the same square acre, they cannot be considered to be geographically isolated.
C) Yes, because they can still undergo sympatric speciation.
D) Yes, because there are so many habitats in one tree that the populations may never interact.
A) No, because if they are in the same tree, they are in the same geographic area.
B) No, because if they are in the same square acre, they cannot be considered to be geographically isolated.
C) Yes, because they can still undergo sympatric speciation.
D) Yes, because there are so many habitats in one tree that the populations may never interact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Polyploidy can lead to very rapid speciation in plants because
A) polyploidy increases the amount of gene flow between polyploid plants and nonpolyploid plants.
B) the DNA sequences of essential genes are altered to such a degree that the polyploid plant can no longer mate with the original species.
C) the gametes of polyploid plants have too many chromosomes and cannot fuse to the gametes of the original species.
D) when a plant becomes polyploid, it often loses the ability to make gametes of any type.
A) polyploidy increases the amount of gene flow between polyploid plants and nonpolyploid plants.
B) the DNA sequences of essential genes are altered to such a degree that the polyploid plant can no longer mate with the original species.
C) the gametes of polyploid plants have too many chromosomes and cannot fuse to the gametes of the original species.
D) when a plant becomes polyploid, it often loses the ability to make gametes of any type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is an example of a prezygotic barrier that can isolate two species living in the same geographic area?
A) The members of two populations of birds living in neighboring forests freely interbreed.
B) One species of cichlid has the same mating behavior as another cichlid species in the same lake.
C) The gametes of one species of orchid in a rainforest are unable to fuse with the gametes of another species of orchid in the same rainforest.
D) Two species of wildflowers mate and produce a hybrid that is capable of successfully breeding with either species.
A) The members of two populations of birds living in neighboring forests freely interbreed.
B) One species of cichlid has the same mating behavior as another cichlid species in the same lake.
C) The gametes of one species of orchid in a rainforest are unable to fuse with the gametes of another species of orchid in the same rainforest.
D) Two species of wildflowers mate and produce a hybrid that is capable of successfully breeding with either species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A large population of animals is split in two by a physical barrier. Over time, the genetic make up of the two resulting populations becomes more and more different, until each population becomes a separate species. This is an example of
A) sympatric speciation.
B) allopatric speciation.
C) genetic drift.
D) reproductive isolation.
A) sympatric speciation.
B) allopatric speciation.
C) genetic drift.
D) reproductive isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is an example of reproductive isolation?
A) Male deer with large branching antlers are more likely to mate.
B) A blue lizard washes away from a population of mostly green lizards during a hurricane and ends up on an island containing no other lizards to mate with.
C) One population of frogs mates in the deep water of a pond and another population of frogs mates on the shore of the same pond.
D) One individual from a population of fruit flies from an apple orchard is blown by heavy winds into another orchard where it mates with a different population of fruit flies.
A) Male deer with large branching antlers are more likely to mate.
B) A blue lizard washes away from a population of mostly green lizards during a hurricane and ends up on an island containing no other lizards to mate with.
C) One population of frogs mates in the deep water of a pond and another population of frogs mates on the shore of the same pond.
D) One individual from a population of fruit flies from an apple orchard is blown by heavy winds into another orchard where it mates with a different population of fruit flies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Speciation cannot occur without geographic isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The offspring of two individuals of different species that interbreed are known as _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Pre- and postzygotic barriers can keep species ________ isolated from each other, even if they live in the same area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
__________ barriers cause speciation to occur by preventing fertilization from occurring when two individuals of different populations attempt to mate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An ecological ________ can limit a population's ability to adapt to its environment, as the organisms must compromise between what is possible developmentally and what is possible genetically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The population of salamanders, a _______ species found along the Pacific coast of the United States, forms a circle around a desert-like valley. Neighboring salamander species mate, but those on opposite sides of the valley do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Speciation generally occurs at a ________ rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Adaptations result from natural selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A biological species is a group of interbreeding populations that is ________ isolated from other species of organisms living in the same region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The great diversity of life on Earth is caused by ________-the formation of new species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Sympatric speciation can occur in the absence of geographic isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Two species live near each other but do not respond to each other's courtship displays. This is an example of ________ isolation, a type of prezygotic barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
_________ speciation occurs when a new species arises in the absence of geographic isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When speciation is caused by a rapid change in chromosomal number such as ________, new species form in a single generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An organism is polyploid if it has more than two complete sets of ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Gene flow prevents two populations from becoming genetically different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Geographic isolation can result in speciation but usually only over long periods of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The death of zygotes produced by the mating of individuals of two different populations is an example of how ___________ barriers can lead to reproductive isolation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Speciation can occur when populations of a species are separated by a barrier becoming ________ isolated and subsequently become reproductively isolated from one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Humans have directed the evolution of other organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Sympatric speciation requires geographic isolation of populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Sympatric speciation always follows allopatric speciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Before the cultivation of the apple tree, apple maggot fly laid their eggs exclusively on the fruit of Hawthorne trees. As apple orchards became more prominent, apple maggot flies began to lay their eggs on both the fruit of the Hawthorne tree and the fruit of cultivated apple trees. Now, apple maggot flies that live on apple trees mate and lay their eggs at different times of the year than apple maggot flies that live on Hawthorne trees. Is this an example of reproductive isolation? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Even though humans are causing the extinction of large numbers of species, the process of speciation should replace them within a few decades.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
It takes at least 25 generations of reproduction before a new species can be formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Groups of organisms that live in regions with high mountains usually contain more species than those that live in nonmountainous regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



