Deck 24: Animal Hormones
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Animal Hormones
1
You are walking in the woods and suddenly find yourself between a mother bear and her two cubs. All four nervous systems would send the same emergency message to the
A) thyroid glands.
B) adrenal glands.
C) islet cells.
D) pituitary glands.
A) thyroid glands.
B) adrenal glands.
C) islet cells.
D) pituitary glands.
B
2
Serotonin, one of the hormones thought to be involved in depression, is a water-soluble molecule. Where on the target cell would you expect to find receptors for this hormone?
A) in the cytoplasm
B) inside the nucleus
C) on the outside of the plasma membrane
D) in the interstitial fluid around the cell
A) in the cytoplasm
B) inside the nucleus
C) on the outside of the plasma membrane
D) in the interstitial fluid around the cell
C
3
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is produced by your pituitary gland when your brain detects lower than optimum levels of water in the body. In the kidneys, ADH promotes the uptake of water, creating more concentrated urine. ADH gets from the pituitary gland to the kidney through the
A) circulatory system.
B) nervous system.
C) endocrine system.
D) digestive system.
A) circulatory system.
B) nervous system.
C) endocrine system.
D) digestive system.
A
4
The conversion of glucose to glycogen is mediated by
A) insulin.
B) glucagon.
C) adrenalin.
D) estrogen.
A) insulin.
B) glucagon.
C) adrenalin.
D) estrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements correctly describes the activity of adrenaline?
A) It strings glucose molecules together to form glycogen.
B) In times of stress or danger, it causes glucose to be released for use as fuel.
C) It stimulates the movement of glucose out of the blood into storage tissues.
D) It promotes the storage of fatty acids.
A) It strings glucose molecules together to form glycogen.
B) In times of stress or danger, it causes glucose to be released for use as fuel.
C) It stimulates the movement of glucose out of the blood into storage tissues.
D) It promotes the storage of fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The target cells of epinephrine and norepinephrine are in the
A) pancreas.
B) thyroid.
C) hypothalamus.
D) liver.
A) pancreas.
B) thyroid.
C) hypothalamus.
D) liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
By what mechanism do most hormones travel through the organism that produces them?
A) circulatory system
B) diffusion
C) convection
D) the nervous system
A) circulatory system
B) diffusion
C) convection
D) the nervous system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The adrenal gland in humans is closest to the
A) liver.
B) kidneys.
C) stomach.
D) intestine.
A) liver.
B) kidneys.
C) stomach.
D) intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Calcitonin is secreted by the
A) adrenal glands.
B) kidneys.
C) pancreas.
D) thyroid gland.
A) adrenal glands.
B) kidneys.
C) pancreas.
D) thyroid gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Steroid hormones bind to receptors located in the cytoplasm of the cell because
A) their hydrophilic properties prevent them from interacting with proteins within the plasma membrane.
B) steroid hormones never leave the cell that produces them since they act only on the gene expression in the cell that makes them.
C) they are hydrophobic and can easily diffuse through a target cell's plasma membrane.
D) they do not fit through nuclear pores and, therefore, cannot cross the nuclear membrane.
A) their hydrophilic properties prevent them from interacting with proteins within the plasma membrane.
B) steroid hormones never leave the cell that produces them since they act only on the gene expression in the cell that makes them.
C) they are hydrophobic and can easily diffuse through a target cell's plasma membrane.
D) they do not fit through nuclear pores and, therefore, cannot cross the nuclear membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Adrenalin and norepinephrine
A) have an effect similar to glucagon.
B) are antagonists to glucagon.
C) have the same effect as calcitonin.
D) are antagonists to calcitonin.
A) have an effect similar to glucagon.
B) are antagonists to glucagon.
C) have the same effect as calcitonin.
D) are antagonists to calcitonin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Epinephrine is produced in the
A) pancreas.
B) kidneys.
C) adrenal glands.
D) hypothalamus.
A) pancreas.
B) kidneys.
C) adrenal glands.
D) hypothalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A diabetic would most likely inject insulin
A) after waking up in the morning.
B) preceding mealtime.
C) after a long walk.
D) when blood glucose levels are low.
A) after waking up in the morning.
B) preceding mealtime.
C) after a long walk.
D) when blood glucose levels are low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is not caused by insulin?
A) formation of glycogen
B) formation of glucagon
C) storage of fatty acids
D) storage of amino acids
A) formation of glycogen
B) formation of glucagon
C) storage of fatty acids
D) storage of amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following acts to lower blood glucose levels?
A) glucagon
B) norepinephrine
C) insulin
D) parathyroid hormone
A) glucagon
B) norepinephrine
C) insulin
D) parathyroid hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which hormone below is the antagonist of insulin?
A) parathyroid hormone
B) calcitonin
C) glucagon
D) gonadotropin
A) parathyroid hormone
B) calcitonin
C) glucagon
D) gonadotropin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Once a hormone enters the bloodstream,
A) it is usually broken down within minutes.
B) it remains active for months.
C) it is broken down after it has performed its function on target cells.
D) it produces enzymes that affect target cells.
A) it is usually broken down within minutes.
B) it remains active for months.
C) it is broken down after it has performed its function on target cells.
D) it produces enzymes that affect target cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following choices best explains how one hormone can regulate several different developmental events?
A) One hormone can affect different target tissues differently.
B) A hormone can migrate to a gland, where the endocrine system reshapes it for a different use.
C) Once a steroid hormone attaches to a receptor on the surface of a cell, it starts several different signal cascades that activate many genes at once.
D) Hormones are made up of molecules that separate once inside the cell to signal the development of different aspects of sexual maturity.
A) One hormone can affect different target tissues differently.
B) A hormone can migrate to a gland, where the endocrine system reshapes it for a different use.
C) Once a steroid hormone attaches to a receptor on the surface of a cell, it starts several different signal cascades that activate many genes at once.
D) Hormones are made up of molecules that separate once inside the cell to signal the development of different aspects of sexual maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Islet cells are found in the
A) pancreas and produce calcitonin.
B) thyroid gland and produce glucagon.
C) thyroid gland and produce parathyroid hormone.
D) pancreas and produce insulin.
A) pancreas and produce calcitonin.
B) thyroid gland and produce glucagon.
C) thyroid gland and produce parathyroid hormone.
D) pancreas and produce insulin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A single hormone molecule can have dramatic effects on a target cell, because it
A) causes the cell to produce thousands of copies of the hormone.
B) initiates a chain of events that amplifies its effect.
C) causes the nuclear membrane to break down and exposes DNA directly to the hormone.
D) becomes surrounded by enzymes that transport it to the nucleus.
A) causes the cell to produce thousands of copies of the hormone.
B) initiates a chain of events that amplifies its effect.
C) causes the nuclear membrane to break down and exposes DNA directly to the hormone.
D) becomes surrounded by enzymes that transport it to the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The parathyroid gland of a person with hyperparathyroidism produces very high levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH). You would expect a person with this condition to have
A) high levels of calcium in the blood.
B) low levels of glucose in the blood.
C) strong bones that resist fractures.
D) low levels of calcitonin in the blood.
A) high levels of calcium in the blood.
B) low levels of glucose in the blood.
C) strong bones that resist fractures.
D) low levels of calcitonin in the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements about the human reproductive system is true?
A) The level of hormones in mature females remains constant.
B) Females do not produce mature eggs continuously.
C) In females, progesterone stimulates the cyclical maturation and release of eggs from the ovaries.
D) Estrogen levels fall during the first two weeks of a woman's menstrual cycle.
A) The level of hormones in mature females remains constant.
B) Females do not produce mature eggs continuously.
C) In females, progesterone stimulates the cyclical maturation and release of eggs from the ovaries.
D) Estrogen levels fall during the first two weeks of a woman's menstrual cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In human females, eggs begin to develop at puberty due to the release of
A) gonadotropins.
B) calcitonin.
C) glucagon.
D) insulin.
A) gonadotropins.
B) calcitonin.
C) glucagon.
D) insulin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Acromegaly results from
A) too little gonadotropin.
B) a lack of progesterone.
C) insufficient amounts of growth hormone during puberty.
D) exposure to growth hormone after maturity.
A) too little gonadotropin.
B) a lack of progesterone.
C) insufficient amounts of growth hormone during puberty.
D) exposure to growth hormone after maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
After ovulation,
A) gonadotropin levels rise quickly.
B) estrogen levels rise quickly.
C) progesterone becomes the dominant hormone.
D) LH levels decrease slowly.
A) gonadotropin levels rise quickly.
B) estrogen levels rise quickly.
C) progesterone becomes the dominant hormone.
D) LH levels decrease slowly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A person who starts producing high levels of calcitonin probably has
A) a malfunction in their adrenal glands.
B) low levels of calcium in their blood.
C) normal levels of calcium in their blood.
D) high levels of calcium in their urine.
A) a malfunction in their adrenal glands.
B) low levels of calcium in their blood.
C) normal levels of calcium in their blood.
D) high levels of calcium in their urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Two causes of diabetes are defective insulin or too little insulin. Which of the following would also produce diabetes?
A) the production of too much insulin
B) a defective receptor on the insulin's target cells
C) signal amplification within the target cells after the insulin arrives
D) undirected movement of insulin through the bloodstream, rather than from cell to cell
A) the production of too much insulin
B) a defective receptor on the insulin's target cells
C) signal amplification within the target cells after the insulin arrives
D) undirected movement of insulin through the bloodstream, rather than from cell to cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The lining of the uterus is thickened and prepared to receive a fertilized egg by
A) follicle-stimulating hormone.
B) progesterone and estrogen.
C) luteinizing hormone.
D) androgens.
A) follicle-stimulating hormone.
B) progesterone and estrogen.
C) luteinizing hormone.
D) androgens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is true of birth control pills?
A) They prevent ovulation by maintaining consistently high levels of progesterone.
B) They prevent fertilization by changing the chemical makeup of the protective "shell" of the egg so that it cannot be penetrated by sperm.
C) They prevent sperm from entering the uterus.
D) They break down the synchronicity of ovulation and preparation of the uterus so that when the egg is released, the uterus is not at the right stage to receive it.
A) They prevent ovulation by maintaining consistently high levels of progesterone.
B) They prevent fertilization by changing the chemical makeup of the protective "shell" of the egg so that it cannot be penetrated by sperm.
C) They prevent sperm from entering the uterus.
D) They break down the synchronicity of ovulation and preparation of the uterus so that when the egg is released, the uterus is not at the right stage to receive it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In response to low levels of calcium in the blood,
A) calcitonin would be released by the thyroid gland.
B) parathyroid hormone would be released by the parathyroid gland.
C) epinephrine would be released by the adrenal glands.
D) glucagon would be released by the pancreas.
A) calcitonin would be released by the thyroid gland.
B) parathyroid hormone would be released by the parathyroid gland.
C) epinephrine would be released by the adrenal glands.
D) glucagon would be released by the pancreas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements about gonadotropins is false?
A) They maintain the function of reproductive organs and glands.
B) Their activity becomes important during puberty.
C) They are found only in females.
D) They are produced by the pituitary gland.
A) They maintain the function of reproductive organs and glands.
B) Their activity becomes important during puberty.
C) They are found only in females.
D) They are produced by the pituitary gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Four stages in the process of balancing glucose levels in the blood are highlighted by letters in the figure below. 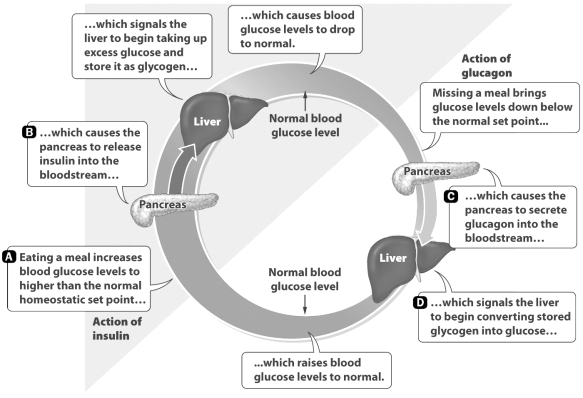
Which letter corresponds to the stage that is impacted by type 2 diabetes?
A) Stage A
B) Stage B
C) Stage C
D) Stage D

Which letter corresponds to the stage that is impacted by type 2 diabetes?
A) Stage A
B) Stage B
C) Stage C
D) Stage D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When blood glucose levels drop to a set point, the production of insulin drops off. This is an example of
A) positive feedback.
B) negative feedback.
C) homeostasis at work.
D) b and c above
A) positive feedback.
B) negative feedback.
C) homeostasis at work.
D) b and c above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In response to a dangerous situation, your body has produced epinephrine and norepinephrine. As the danger dissipates, how might the pancreas respond?
A) The pancreas probably releases glucagon to stimulate the synthesis of glycogen.
B) The pancreas probably releases hormones that signal the adrenal gland to stop producing epinephrine and norepinephrine.
C) The pancreas probably releases insulin to stimulate the liver to take up leftover glucose from the fight-or-flight response.
D) Adrenaline probably signals the pancreas to start releasing calcium.
A) The pancreas probably releases glucagon to stimulate the synthesis of glycogen.
B) The pancreas probably releases hormones that signal the adrenal gland to stop producing epinephrine and norepinephrine.
C) The pancreas probably releases insulin to stimulate the liver to take up leftover glucose from the fight-or-flight response.
D) Adrenaline probably signals the pancreas to start releasing calcium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following would be least affected by gonadotropins?
A) development of facial hair in human males
B) development of pubic hair
C) development of the thyroid gland
D) development of breasts in human females
A) development of facial hair in human males
B) development of pubic hair
C) development of the thyroid gland
D) development of breasts in human females

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following hormones are not produced by gonads?
A) gonadotropins
B) androgens
C) estrogens
D) progesterone
A) gonadotropins
B) androgens
C) estrogens
D) progesterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During the first two weeks of the menstrual cycle,
A) estrogen levels fall.
B) estrogen levels rise steadily.
C) the egg develops inside the corpus luteum.
D) the corpus luteum develops into a follicle.
A) estrogen levels fall.
B) estrogen levels rise steadily.
C) the egg develops inside the corpus luteum.
D) the corpus luteum develops into a follicle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
This graph shows the levels of estrogen and progesterone over the course of the menstrual cycle. 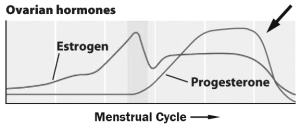
What event is caused by the rapid decrease in hormones in the region indicated by the arrow?
A) ovulation
B) menstruation
C) formation of the corpus luteum
D) follicle maturation

What event is caused by the rapid decrease in hormones in the region indicated by the arrow?
A) ovulation
B) menstruation
C) formation of the corpus luteum
D) follicle maturation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements about the functions follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) is false?
A) FSH and LH control the development of sperm.
B) A sudden and rapid increase in LH triggers ovulation.
C) FSH stimulates the maturation of follicles.
D) A decrease in LH stimulates menstruation.
A) FSH and LH control the development of sperm.
B) A sudden and rapid increase in LH triggers ovulation.
C) FSH stimulates the maturation of follicles.
D) A decrease in LH stimulates menstruation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The target cells of growth hormone are located
A) in bones.
B) in the pituitary gland.
C) in the gonads.
D) in the hypothalamus.
A) in bones.
B) in the pituitary gland.
C) in the gonads.
D) in the hypothalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Birth control pills prevent pregnancy by maintaining high levels of the hormone ___________, tricking the body into thinking it is pregnant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Parathyroid hormone is released into the blood when the amount of calcium in the blood is too ________ [high or low?].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Because steroid hormones are _____________, they are able to pass through a cell's plasma membrane without the assistance of membrane transport proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When liver cells are unable to respond to insulin, the level of glucose in the blood remains _________ than normal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The 28-day menstrual cycle is regulated by __________ and _____________, both of which are produced in the female gonad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The graph below shows the levels of gonadotropins throughout the menstrual cycle.
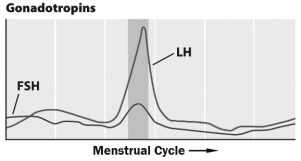
The darker gray region of the graph corresponds to the period when __________ occurs in the ovaries.

The darker gray region of the graph corresponds to the period when __________ occurs in the ovaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The beginning of ________ is marked by a sudden rise in sex hormone production by the gonads of adolescent humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In a human male, the _______ secrete hormones that coordinate the development of male reproductive structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A single hormone can have different effects on different tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Four to six weeks after conception, sex hormones trigger the production of the appropriate male or female ________, or sex organs, in an embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
During menopause, lower levels of estrogen cause a woman's bone to break down, releasing calcium to the body. How might this affect the levels of calcitonin and parathyroid hormone (PTH) in an otherwise healthy woman going through menopause?
A) Her levels of calcitonin should be high and her levels of PTH should be low.
B) Her levels of calcitonin should be low and her levels of PTH should be high.
C) Her levels of both calcitonin and PTH should be high.
D) Her levels of both calcitonin and PTH should be low.
A) Her levels of calcitonin should be high and her levels of PTH should be low.
B) Her levels of calcitonin should be low and her levels of PTH should be high.
C) Her levels of both calcitonin and PTH should be high.
D) Her levels of both calcitonin and PTH should be low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The hormone-producing tissues of animals make up the _______ system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A _______ is a specialized organ in which hormones are produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An adult male who feels that he is too short should
A) take growth hormone to stimulate bone growth.
B) accept his height because after puberty the growth centers of the bones are closed and hormone treatment will not affect his height.
C) take the growth hormone antagonist to stop growth hormone from prohibiting further bone growth.
D) take testosterone to restart puberty and growth hormone to stimulate bone growth.
A) take growth hormone to stimulate bone growth.
B) accept his height because after puberty the growth centers of the bones are closed and hormone treatment will not affect his height.
C) take the growth hormone antagonist to stop growth hormone from prohibiting further bone growth.
D) take testosterone to restart puberty and growth hormone to stimulate bone growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a human female, the hormone _______ controls the development of female reproductive structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The high levels of progesterone seen after ovulation in the human female are produced by a specific region of the ovary known as the __________ ___________, which disappears if pregnancy doesn't occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What happens to bovine somatotrophic hormone (BST) once it is consumed by a human?
A) BST is absorbed and transported by the blood to the brain, where it induces human growth.
B) BST is broken down by the digestive system to harmless nutrients that are absorbed and used to build other compounds needed by the body.
C) BST enters the blood stream and travels to the gonads, where it increases the production of sex hormones, causing early puberty in children.
D) BST is not affected or absorbed by the digestive system. It is removed from the body in fecal matter.
A) BST is absorbed and transported by the blood to the brain, where it induces human growth.
B) BST is broken down by the digestive system to harmless nutrients that are absorbed and used to build other compounds needed by the body.
C) BST enters the blood stream and travels to the gonads, where it increases the production of sex hormones, causing early puberty in children.
D) BST is not affected or absorbed by the digestive system. It is removed from the body in fecal matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The pancreas regulates _______ levels in the blood by producing a pair of antagonistic hormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In human females, the release of an egg from its follicle is called _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Hormones often alter _________ __________ by turning a certain gene or group of genes on or off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone both come from the pituitary gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Progesterone and luteinizing hormone have the same effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The development of all female reproductive structures is under the control of a single hormone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The female hormone estrogen prepares the uterine lining to receive a fertilized egg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Endocrine glands have ducts that open directly into blood vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Hormones are fed to chickens to increase egg production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In humans, sex hormones only begin to work after birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Some hormones do not need receptors and can directly interact with genes in a target cell's nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Gonadotropins continue playing a role in human development even after puberty is complete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



