Deck 25: The Nervous System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: The Nervous System
1
Initially, when a neuron receives a stimulus,
A) sodium diffuses out of the neuron.
B) neurotransmitters are released from axon terminals.
C) sodium channels close
D) sodium enters the neuron.
A) sodium diffuses out of the neuron.
B) neurotransmitters are released from axon terminals.
C) sodium channels close
D) sodium enters the neuron.
D
2
Which of the following is most likely to be myelinated?
A) an interneuron
B) the axon between your spinal cord and your big toe
C) an axon that only exists within the spinal cord
D) a neuron in the thalamus
A) an interneuron
B) the axon between your spinal cord and your big toe
C) an axon that only exists within the spinal cord
D) a neuron in the thalamus
B
3
Action potentials move faster in myelinated nerve fibers, because
A) sodium ions can leap from node to node.
B) dendrites do not need to connect directly to axons.
C) sodium ions can pass through myelin faster than they do across the plasma membrane of a neuron.
D) action potentials leap from node to node.
A) sodium ions can leap from node to node.
B) dendrites do not need to connect directly to axons.
C) sodium ions can pass through myelin faster than they do across the plasma membrane of a neuron.
D) action potentials leap from node to node.
D
4
Neurotransmitters carry a signal from a stimulated nerve cell to another nerve cell across a gap known as a
A) synaptic cleft.
B) target.
C) receptor.
D) cytokinin.
A) synaptic cleft.
B) target.
C) receptor.
D) cytokinin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The branched receiving ends of a nerve cell are called
A) dendrites.
B) axons.
C) neurons.
D) synapses.
A) dendrites.
B) axons.
C) neurons.
D) synapses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is the pathway an action potential would travel in a neuron?
A) cell body to axon to dendrite
B) axon to dendrite to cell body
C) dendrite to axon to cell body
D) dendrite to cell body to axon
A) cell body to axon to dendrite
B) axon to dendrite to cell body
C) dendrite to axon to cell body
D) dendrite to cell body to axon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
After a signal has been transmitted to a receiving cell, neurotransmitters are rapidly removed from the synaptic cleft because
A) if even one neurotransmitter escapes from the synaptic cleft, it will produce action potentials in other neurons.
B) if neurotransmitters are not removed, they will enter the receiving cell and stimulate action potentials in organelle membranes.
C) neurotransmitters that remain in the synaptic cleft continue to bind to receptors in the receiving cell, potentially initiating new action potentials.
D) making neurotransmitters from scratch is energetically expensive so the cell must recycle them.
A) if even one neurotransmitter escapes from the synaptic cleft, it will produce action potentials in other neurons.
B) if neurotransmitters are not removed, they will enter the receiving cell and stimulate action potentials in organelle membranes.
C) neurotransmitters that remain in the synaptic cleft continue to bind to receptors in the receiving cell, potentially initiating new action potentials.
D) making neurotransmitters from scratch is energetically expensive so the cell must recycle them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A myelin sheath
A) stores sodium ions.
B) acts as an electrical conductor.
C) acts as an insulator.
D) contains action potentials.
A) stores sodium ions.
B) acts as an electrical conductor.
C) acts as an insulator.
D) contains action potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Dendrites are highly branched so that they can
A) collect sensory information from a variety of locations in the body.
B) transmit instructions to many different cells.
C) transmit information faster than myelinated neurons.
D) create stronger action potentials by allowing more sodium to enter the cell at one time.
A) collect sensory information from a variety of locations in the body.
B) transmit instructions to many different cells.
C) transmit information faster than myelinated neurons.
D) create stronger action potentials by allowing more sodium to enter the cell at one time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements about axons is false?
A) They transmit self-sustaining signals.
B) They transmit signals in two directions.
C) They are a long extension of a neuron.
D) They have a terminus that transmits signals to other cells.
A) They transmit self-sustaining signals.
B) They transmit signals in two directions.
C) They are a long extension of a neuron.
D) They have a terminus that transmits signals to other cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A strong stimulus produces
A) stronger action potentials.
B) more action potentials.
C) both more and stronger action potentials.
D) more nodes of Ranvier.
A) stronger action potentials.
B) more action potentials.
C) both more and stronger action potentials.
D) more nodes of Ranvier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Where would you expect to see an absence of neurotransmitters?
A) in a synapse
B) in a myelin sheath
C) in a synaptic cleft
D) in the terminus of an axon
A) in a synapse
B) in a myelin sheath
C) in a synaptic cleft
D) in the terminus of an axon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a stimulus is strong enough to reach a threshold level,
A) an action potential is shut down.
B) an action potential occurs.
C) sodium channels in the myelin open.
D) the resting potential is restored.
A) an action potential is shut down.
B) an action potential occurs.
C) sodium channels in the myelin open.
D) the resting potential is restored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Axons transmit information in the form of
A) resting potentials.
B) sodium channels.
C) action potentials.
D) myelin sheaths.
A) resting potentials.
B) sodium channels.
C) action potentials.
D) myelin sheaths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Although many people worry about their sodium intake from salty foods, it would be unwise to eliminate sodium from one's diet completely. Which of the following problems would occur if there were no sodium in the body?
A) The myelin sheath of the neurons would begin to break down.
B) Axons would be unable to create the action potential necessary for rapid signal movement.
C) The synapses between neurons and their adjacent cells would collapse.
D) The speed of the neuron's action potential would increase to a dangerously high level.
A) The myelin sheath of the neurons would begin to break down.
B) Axons would be unable to create the action potential necessary for rapid signal movement.
C) The synapses between neurons and their adjacent cells would collapse.
D) The speed of the neuron's action potential would increase to a dangerously high level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An action potential travels in only one direction, because
A) the nodes of Ranvier are open only at the site of the action potential.
B) only the sodium channels "downstream" are open.
C) only the sodium channels at the site of the action potential remain open.
D) sodium ions can move only between nodes of Ranvier.
A) the nodes of Ranvier are open only at the site of the action potential.
B) only the sodium channels "downstream" are open.
C) only the sodium channels at the site of the action potential remain open.
D) sodium ions can move only between nodes of Ranvier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How does the central nervous system know how important a particular stimulus is?
A) by the frequency at which the action potentials are created by the stimulus
B) by the overall strength of the action potential produced by the stimulus
C) by the number of neurotransmitters that reach the brain through the circulatory system
D) by the amount of hormone that the stimulus releases from endocrine glands
A) by the frequency at which the action potentials are created by the stimulus
B) by the overall strength of the action potential produced by the stimulus
C) by the number of neurotransmitters that reach the brain through the circulatory system
D) by the amount of hormone that the stimulus releases from endocrine glands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
At resting potential, the overall charge of the plasma membrane is
A) positive because of the movement of myelin out of a neuron.
B) negative because of the sodium ions being pumped out of a neuron.
C) positive because sodium channels open in the axon but not in the cell body.
D) negative because of sodium channels close in the dendrite but not in the axon.
A) positive because of the movement of myelin out of a neuron.
B) negative because of the sodium ions being pumped out of a neuron.
C) positive because sodium channels open in the axon but not in the cell body.
D) negative because of sodium channels close in the dendrite but not in the axon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Botulism is a type of paralysis (inability to move muscles) caused by a specific type of bacteria. The bacteria release a toxin that prevents the release of acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter) from the neurons that form synapses with muscle cells. Why might botulism toxin cause paralysis?
A) Without acetylcholine, action potentials never get to muscles cells because they cannot move from one node of Ranvier to the next.
B) Since acetylcholine is responsible for establishing the concentration gradient of sodium ions, action potentials cannot form in the neurons of individuals with botulism.
C) If acetylcholine is not released, action potentials that stimulate muscle contraction cannot be transmitted across the synaptic cleft to muscle cells.
D) In the absence of acetylcholine, sensory neurons are unable to communicate with motor neurons so motor neurons never receive the signal to cause muscle contraction.
A) Without acetylcholine, action potentials never get to muscles cells because they cannot move from one node of Ranvier to the next.
B) Since acetylcholine is responsible for establishing the concentration gradient of sodium ions, action potentials cannot form in the neurons of individuals with botulism.
C) If acetylcholine is not released, action potentials that stimulate muscle contraction cannot be transmitted across the synaptic cleft to muscle cells.
D) In the absence of acetylcholine, sensory neurons are unable to communicate with motor neurons so motor neurons never receive the signal to cause muscle contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The figure below illustrates how a neuron with myelinated axon transmits signals. 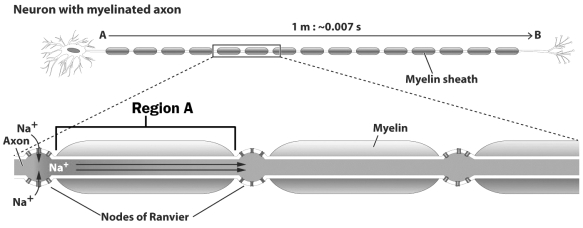
What is happening in Region A of this figure?
A) An action potential is moving between two nodes of Ranvier.
B) Neurotransmitters are rapidly diffusing between two nodes of Ranvier.
C) An electric charge is moving rapidly between two nodes of Ranvier.
D) Myelin is carrying sodium ions between two nodes of Ranvier.

What is happening in Region A of this figure?
A) An action potential is moving between two nodes of Ranvier.
B) Neurotransmitters are rapidly diffusing between two nodes of Ranvier.
C) An electric charge is moving rapidly between two nodes of Ranvier.
D) Myelin is carrying sodium ions between two nodes of Ranvier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The brain has important interactions with the endocrine system. Which part of the brain directly stimulates the release of hormones from the pituitary gland?
A) hypothalamus
B) cerebrum
C) cerebellum
D) central cortex
A) hypothalamus
B) cerebrum
C) cerebellum
D) central cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
After a long hard workout, you feel thirsty. What part of the brain stimulated your thirst?
A) pons
B) cerebellum
C) medulla oblongata
D) hypothalamus
A) pons
B) cerebellum
C) medulla oblongata
D) hypothalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which area of our brain acts as a "traffic manager"?
A) the thalamus
B) the cerebral cortex
C) the pons
D) the cerebellum
A) the thalamus
B) the cerebral cortex
C) the pons
D) the cerebellum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When you smell a flower, what part of the brain processes the odors you sense?
A) parietal
B) temporal
C) occipital
D) frontal
A) parietal
B) temporal
C) occipital
D) frontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
You bite into a juicy peach. What region of the cerebrum interprets the flavors in your mouth?
A) occipital
B) frontal
C) parietal
D) temporal
A) occipital
B) frontal
C) parietal
D) temporal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
High levels of thyroid hormones in the blood result in
A) production of thyrotropin-releasing hormone by the hypothalamus
B) decreased levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood.
C) release of thyroid-stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland.
D) activation of the adrenal glands by the nervous system.
A) production of thyrotropin-releasing hormone by the hypothalamus
B) decreased levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood.
C) release of thyroid-stimulating hormone from the pituitary gland.
D) activation of the adrenal glands by the nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements about a reflex arc is false?
A) It is an example of simple signal processing.
B) It does not require sending the signal to the brain.
C) It provides a means for immediate withdrawal from dangerous stimuli.
D) It uses signals that are mainly processed by the central nervous system.
A) It is an example of simple signal processing.
B) It does not require sending the signal to the brain.
C) It provides a means for immediate withdrawal from dangerous stimuli.
D) It uses signals that are mainly processed by the central nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The distance between an axon terminal and the receiving cell must be very small because
A) the plasma membranes of the two cells must be almost touching for action potentials to pass from one to the other.
B) neurons use the diffusion of neurotransmitters to transmit stimuli between cells and diffusion is only rapid over short distances.
C) the short distance creates a large surface area so that the receiving cell can receive a large number of neurotransmitters at once, ensuring rapid signal transmission.
D) the short distance allows sodium to be exchanged between the two cells, ensuring that the receiving cell has enough sodium to create an action potential.
A) the plasma membranes of the two cells must be almost touching for action potentials to pass from one to the other.
B) neurons use the diffusion of neurotransmitters to transmit stimuli between cells and diffusion is only rapid over short distances.
C) the short distance creates a large surface area so that the receiving cell can receive a large number of neurotransmitters at once, ensuring rapid signal transmission.
D) the short distance allows sodium to be exchanged between the two cells, ensuring that the receiving cell has enough sodium to create an action potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A reflex arc
A) has only sensory and interneurons.
B) is composed of three interneurons.
C) has a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron.
D) has an interneuron between two motor neurons.
A) has only sensory and interneurons.
B) is composed of three interneurons.
C) has a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron.
D) has an interneuron between two motor neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following best describes the flow of signals in our nervous system?
A) from motor neurons to sensory neurons to interneurons
B) from sensory neurons to interneurons to motor neurons
C) from interneurons to sensory neurons to motor neurons
D) from sensory neurons to motor neurons to interneurons
A) from motor neurons to sensory neurons to interneurons
B) from sensory neurons to interneurons to motor neurons
C) from interneurons to sensory neurons to motor neurons
D) from sensory neurons to motor neurons to interneurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A person with vitamin B deficiency often exhibits a "slow" nervous system. For example, their knee-jerk reflex is much slower than normal. Which of the following might explain why this is the case?
A) The neurons of people with vitamin B deficiency have more sodium channels in the plasma membranes of their neurons than normal.
B) People with a vitamin B deficiency produce less myelin than a normal person does.
C) Axons are slightly longer in a person with vitamin B deficiency, so the distance between transmitting and receiving cells is shorter.
D) People with vitamin B deficiencies produce weaker action potentials than normal people do.
A) The neurons of people with vitamin B deficiency have more sodium channels in the plasma membranes of their neurons than normal.
B) People with a vitamin B deficiency produce less myelin than a normal person does.
C) Axons are slightly longer in a person with vitamin B deficiency, so the distance between transmitting and receiving cells is shorter.
D) People with vitamin B deficiencies produce weaker action potentials than normal people do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is an example of a reflex arc?
A) After reading all the possible answers to this question, you choose answer A.
B) The pupils of your eyes increase in diameter when you walk into a dark room.
C) A cell in your body releases insulin in response to the intake of food.
D) On a hot day, your body releases sweat. As the sweat evaporates, your body cools.
A) After reading all the possible answers to this question, you choose answer A.
B) The pupils of your eyes increase in diameter when you walk into a dark room.
C) A cell in your body releases insulin in response to the intake of food.
D) On a hot day, your body releases sweat. As the sweat evaporates, your body cools.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The largest, most visible part of the human brain is the
A) hippocampus.
B) cerebrum.
C) hypothalamus.
D) thalamus.
A) hippocampus.
B) cerebrum.
C) hypothalamus.
D) thalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is not one of the three major regions of the human brain?
A) medulla
B) forebrain
C) midbrain
D) hindbrain
A) medulla
B) forebrain
C) midbrain
D) hindbrain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The area of the brain that filters and sorts signals from the spinal cord also determines which signals require an action without awareness, and which signals need to be sent to the conscious perception centers. This area of the brain is known as the
A) cerebrum.
B) pituitary gland.
C) thalamus.
D) cortex.
A) cerebrum.
B) pituitary gland.
C) thalamus.
D) cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The cerebrum has four major lobes. Which of the following is one of these?
A) parietal
B) cerebellum
C) thalamus
D) medulla oblongata
A) parietal
B) cerebellum
C) thalamus
D) medulla oblongata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is not part of the forebrain?
A) cerebrum
B) pons
C) thalamus
D) hypothalamus
A) cerebrum
B) pons
C) thalamus
D) hypothalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
As you complete this exam, which of part of the brain is helping your decide which answer is correct?
A) cerebellum
B) pons
C) thalamus
D) cerebral cortex
A) cerebellum
B) pons
C) thalamus
D) cerebral cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Our ability to invent tools and hunting tactics rests within the
A) pons.
B) hindbrain.
C) pituitary gland.
D) neocortex.
A) pons.
B) hindbrain.
C) pituitary gland.
D) neocortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The cerebral cortex of the human brain is much more highly and intricately folded than the same region in other animals. Why might this be the case?
A) The folds create more surface area for the production and release of the hormones that allow the human nervous system to interact with the endocrine system.
B) The folds are the remnants of the compression of the brain that occurs during childbirth.
C) The folds increase the surface area available for the complex thoughts and processing that occur in that region of the human brain.
D) Evolution has caused the brain to increase in size faster than the skull has increased in size. Folding allows our larger brain to more easily fit into our skulls
A) The folds create more surface area for the production and release of the hormones that allow the human nervous system to interact with the endocrine system.
B) The folds are the remnants of the compression of the brain that occurs during childbirth.
C) The folds increase the surface area available for the complex thoughts and processing that occur in that region of the human brain.
D) Evolution has caused the brain to increase in size faster than the skull has increased in size. Folding allows our larger brain to more easily fit into our skulls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Examine the figure below.
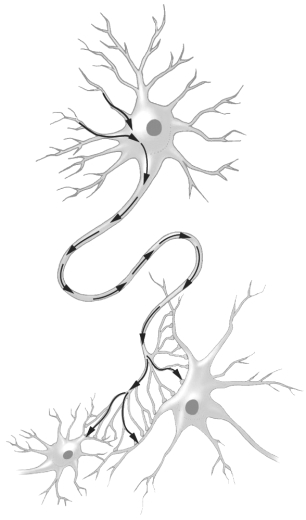
The path of the arrows in this figure indicates the movement of _______________ through a neuron.

The path of the arrows in this figure indicates the movement of _______________ through a neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The flow of ions across an axon's plasma membrane generates an electrical impulse known as the _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
_________ neurons receive information from the environment whereas ________ neurons carry out the orders of the central nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Action potentials and resting potentials are the same thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When a signal causes sodium ions to flow into a neuron it becomes ___________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The __________ nervous system ferries signals to and from the central nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Axons transmit self-_______ electrical signals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The thyroid gland releases hormones that increase the rate at which cells release energy in response to the ______-__________ hormone released from the pituitary gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In vertebrates, special cells produce an insulating sheath of _______ that wraps around the axon of a neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A signal-sending neuron releases a __________, a molecule that carries the signal across the synapse between nerve cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Neurotransmitters are released into a synaptic cleft by the process of __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The cerebral cortex is extensively folded to increase the amount of _______________ available for processing stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The brain and spinal cord make up the _______ nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A resting neuron is negatively charged inside relative to the outside.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
As a whole, the nervous system converts stimuli into _______ input-action potentials that convey information about stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Nodes of Ranvier are found only in ___________ neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The cerebrum has four major lobes, the parietal lobe, the frontal lobe, the temporal lobe, and the _________ lobe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The axons of many individual neurons may be bundled together to form communication pathways known as _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Neurotransmitters move from dendrites to cell bodies to axons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Action potentials can transmit information rapidly but weaken as they move along a neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The blood vessels indicated by the black arrow in the figure below transport hormones from the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus.
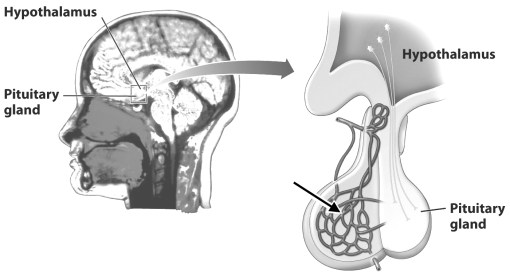


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The hypothalamus contains neurons that release hormones in response to action potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
One interneuron can send signals to the peripheral nervous system and the brain at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When the difference in charge across a neuron's cell membrane decreases the cell is depolarizing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why are the axon terminals of a neuron highly branched?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Everyone who abuses drugs from an early age will become an addict.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
One reason that the human race will probably not evolve larger brains is that it takes a lot of energy to run such a thinking machine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A neurotransmitter can inhibit the formation of an action potential in a receiving cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In order to respond to an incoming signal, such as your fingertip being burned by a candle's flame, the signal must be transmitted to the brain before your muscles can be told to respond and pull away.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



