Deck 28: Defenses against Disease
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Defenses against Disease
1
Prostaglandins
A) shut down capillaries near a wound.
B) produce histamines.
C) act as antigens to attract lymphocytes.
D) stimulate fever in response to wounding.
A) shut down capillaries near a wound.
B) produce histamines.
C) act as antigens to attract lymphocytes.
D) stimulate fever in response to wounding.
D
2
_______ on the surface of disease organisms help the vertebrate immune system recognize the specific invader.
A) Platelets
B) Antigens
C) Lymphocytes
D) Antibodies
A) Platelets
B) Antigens
C) Lymphocytes
D) Antibodies
B
3
The human immune system contains trillions of specialized cells of several kinds, all of which help destroy invaders. What are these cells called?
A) red blood cells
B) white blood cells
C) lymphatic cells
D) blood plasma
A) red blood cells
B) white blood cells
C) lymphatic cells
D) blood plasma
B
4
Complement proteins
A) kill invaders.
B) are precursors to antibodies.
C) repel macrophages.
D) break down antigens.
A) kill invaders.
B) are precursors to antibodies.
C) repel macrophages.
D) break down antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Different genetic versions of a particular pathogen are known as different
A) species.
B) strains.
C) antibodies.
D) disease hosts.
A) species.
B) strains.
C) antibodies.
D) disease hosts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following do not directly cause diseases?
A) bacteria
B) cockroaches
C) protists
D) viruses
A) bacteria
B) cockroaches
C) protists
D) viruses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why is it important that white blood cells are able to travel outside the human circulatory system?
A) In order to form a complement, white blood cells must leave the circulatory vessels.
B) White blood cells are the antibodies that target parasites.
C) Pathogens may be found in areas of the body other than within circulatory vessels.
D) White blood cells must leave the circulatory system in order to return red blood cells to the circulatory vessels.
A) In order to form a complement, white blood cells must leave the circulatory vessels.
B) White blood cells are the antibodies that target parasites.
C) Pathogens may be found in areas of the body other than within circulatory vessels.
D) White blood cells must leave the circulatory system in order to return red blood cells to the circulatory vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What prevents pathogens from entering our bodies through the delicate tissues of the lungs?
A) the lining of the lungs has a low pH that creates an inhospitable environment for most pathogens.
B) the tubes entering the lungs are lined with mucus that traps pathogens and is then removed from the respiratory system.
C) the cells of the lungs are covered by several layers of dead cells that prevent pathogens from getting to living lung tissue.
D) certain cells in the lungs produce toxins that paralyze pathogens before they can infect the body.
A) the lining of the lungs has a low pH that creates an inhospitable environment for most pathogens.
B) the tubes entering the lungs are lined with mucus that traps pathogens and is then removed from the respiratory system.
C) the cells of the lungs are covered by several layers of dead cells that prevent pathogens from getting to living lung tissue.
D) certain cells in the lungs produce toxins that paralyze pathogens before they can infect the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following both prevents blood loss and the invasion of pathogens in vertebrates?
A) the formation of blood clots
B) phagocytosis
C) humoral immunity
D) cell-mediated immunity
A) the formation of blood clots
B) phagocytosis
C) humoral immunity
D) cell-mediated immunity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Histamine
A) makes capillaries near a wound more porous.
B) is converted to prostaglandin near a wound.
C) closes down arterioles near a wound.
D) is an antibody.
A) makes capillaries near a wound more porous.
B) is converted to prostaglandin near a wound.
C) closes down arterioles near a wound.
D) is an antibody.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
During a major infection, you get a high fever because
A) the bacteria in your body produce chemicals that cause the brain to raise your temperature to make the environment more appropriate to bacterial growth.
B) your immune system signals the brain to raise body temperature to limit bacterial growth and speed up phagocytosis.
C) pathogens damage tissues throughout your body, causing an extreme inflammatory response.
D) your low energy levels prevent the brain from maintaining the negative feedback loop that controls body temperature.
A) the bacteria in your body produce chemicals that cause the brain to raise your temperature to make the environment more appropriate to bacterial growth.
B) your immune system signals the brain to raise body temperature to limit bacterial growth and speed up phagocytosis.
C) pathogens damage tissues throughout your body, causing an extreme inflammatory response.
D) your low energy levels prevent the brain from maintaining the negative feedback loop that controls body temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The body responds to tissue damage by mounting an immediate and coordinated sequence of events called the
A) specific immune response.
B) prostaglandin response.
C) inflammatory response.
D) histamine response.
A) specific immune response.
B) prostaglandin response.
C) inflammatory response.
D) histamine response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements correctly describes the immune response when the invading organism is a virus?
A) The antigen molecules on the viral DNA allow the immune system to prevent the infection.
B) Lymphocytes are not involved in the immune response.
C) The lack of nucleic acid in a virus complicates the immune response.
D) Lymphocytes respond to infected human cells rather than to the virus itself.
A) The antigen molecules on the viral DNA allow the immune system to prevent the infection.
B) Lymphocytes are not involved in the immune response.
C) The lack of nucleic acid in a virus complicates the immune response.
D) Lymphocytes respond to infected human cells rather than to the virus itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
At the site of a wound or cut, platelets combine with proteins in our blood to form
A) macrophages.
B) antibodies.
C) prostaglandins.
D) clots.
A) macrophages.
B) antibodies.
C) prostaglandins.
D) clots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following areas of the human body is not the location of a major concentration of white blood cells?
A) tonsils
B) appendix
C) kidneys
D) spleen
A) tonsils
B) appendix
C) kidneys
D) spleen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Any pathogens that macrophages find indigestible can be isolated from other cells by
A) phagocytosis.
B) producing antigens.
C) producing antibodies.
D) encapsulation.
A) phagocytosis.
B) producing antigens.
C) producing antibodies.
D) encapsulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Fevers are a defense mechanism that helps our bodies fight off invading parasites. Based on this information, should you "starve a fever"?
A) Yes, because the reduced food intake will allow the body to generate more energy to fight off the parasite.
B) Yes, because eating feeds the infecting parasite more than it feeds the host.
C) No, because foods that are good for humans are toxic to our parasites.
D) No, because the body needs food in order to generate enough metabolic heat to maintain the fever.
A) Yes, because the reduced food intake will allow the body to generate more energy to fight off the parasite.
B) Yes, because eating feeds the infecting parasite more than it feeds the host.
C) No, because foods that are good for humans are toxic to our parasites.
D) No, because the body needs food in order to generate enough metabolic heat to maintain the fever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Interferons are thought to "interfere" with viral infection because they
A) prevent virus particles from entering neighboring, uninfected cells.
B) create holes in the plasma membranes of infected cells.
C) attach to the DNA of viruses, preventing their replication.
D) prevent the function of natural killer cells, making it more difficult for the immune system to fight off an infection.
A) prevent virus particles from entering neighboring, uninfected cells.
B) create holes in the plasma membranes of infected cells.
C) attach to the DNA of viruses, preventing their replication.
D) prevent the function of natural killer cells, making it more difficult for the immune system to fight off an infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is likely to be first on the scene of a bacterial infection?
A) macrophages
B) neutrophils
C) T helper cells
D) killer T cells
A) macrophages
B) neutrophils
C) T helper cells
D) killer T cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
While pruning your roses, you get scratched by a thorn. A few days later, you notice that the scratch is filled with yellowish pus. What is this pus?
A) Neutrophils and macrophages that die after consuming their fill of the bacteria that entered your wound.
B) Living bacteria that have been successful in avoiding your immune system.
C) Dead self cells and bacterial waste products.
D) Concentrated prostaglandins produced by injured tissue cells.
A) Neutrophils and macrophages that die after consuming their fill of the bacteria that entered your wound.
B) Living bacteria that have been successful in avoiding your immune system.
C) Dead self cells and bacterial waste products.
D) Concentrated prostaglandins produced by injured tissue cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Each T cell and each B cell binds only to one specific type of
A) antibody.
B) neutrophil.
C) antigen.
D) prostaglandin.
A) antibody.
B) neutrophil.
C) antigen.
D) prostaglandin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Lymphocytes develop from
A) macrophages.
B) antigen-antibody interactions.
C) neutrophils.
D) stem cells in bone marrow.
A) macrophages.
B) antigen-antibody interactions.
C) neutrophils.
D) stem cells in bone marrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Memory cells
A) include B and T cells that remain in the body for long periods of time after the first exposure to a pathogen.
B) are macrophages that store copies of antibodies for decades.
C) make copies of T cells that remain active long after the primary response has ended.
D) become T cells during a secondary response to a pathogen.
A) include B and T cells that remain in the body for long periods of time after the first exposure to a pathogen.
B) are macrophages that store copies of antibodies for decades.
C) make copies of T cells that remain active long after the primary response has ended.
D) become T cells during a secondary response to a pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following would explain why doctors are very careful to match certain DNA sequences in an organ donor to those of an organ recipient in the case of a necessary organ transplant?
A) The DNA of a person determines what specific antibody a person makes. In the case of an organ transplant, you want to make sure that the antibody made in the new organ did not react with the antibody made by the recipient.
B) The structures on the surface of cells are determined by DNA, and if the surfaces of the cells of the donor and the recipient are different, the recipient's immune system may attack the new organ.
C) Different DNA sequences may cause the donor and the recipient to produce different strains of interferon, which would result in an autoimmune disease.
D) Antibodies can travel through cells to the nucleus and will attack DNA that does not have the self sequence. This can cause organ rejection.
A) The DNA of a person determines what specific antibody a person makes. In the case of an organ transplant, you want to make sure that the antibody made in the new organ did not react with the antibody made by the recipient.
B) The structures on the surface of cells are determined by DNA, and if the surfaces of the cells of the donor and the recipient are different, the recipient's immune system may attack the new organ.
C) Different DNA sequences may cause the donor and the recipient to produce different strains of interferon, which would result in an autoimmune disease.
D) Antibodies can travel through cells to the nucleus and will attack DNA that does not have the self sequence. This can cause organ rejection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements about fighting invasions of disease-causing agents in humans is false?
A) The organism must be able to distinguish between itself and foreign invaders.
B) Antibodies are produced.
C) Antibodies result in the production of antigens.
D) Cells engulf some of the invaders.
A) The organism must be able to distinguish between itself and foreign invaders.
B) Antibodies are produced.
C) Antibodies result in the production of antigens.
D) Cells engulf some of the invaders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An autoimmune disease would occur if
A) B cells fail to recognize B cells.
B) helper T cells fail to bind to infected cells.
C) B cells and T cells fail to recognize "home team" cells.
D) antibodies from a virus are reactivated in "home team" cells.
A) B cells fail to recognize B cells.
B) helper T cells fail to bind to infected cells.
C) B cells and T cells fail to recognize "home team" cells.
D) antibodies from a virus are reactivated in "home team" cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Examine the figure below. 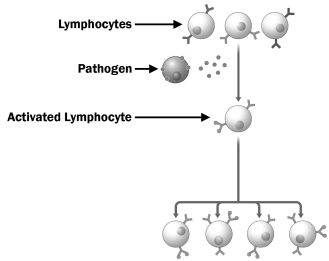
Why is only one of the lymphocytes in this diagram activated by the pathogen?
A) Antigens move through the immune system by diffusion, so the lymphocyte closest to the site of infection binds the antigen first. Once a lymphocyte is activated, it produces chemicals that prevent the activation of other lymphocytes.
B) Lymphocytes are only activated if all of their receptors are bound by antigens. In this case, there were only enough antigens to fully activate one cell.
C) Your immune system contains many different lymphocytes, each displaying a different antigen-binding protein. In this case, the antigen only matched the binding protein on the cell that was activated.
D) Lymphocytes can only be activated by chemicals produced by the innate immune system. Only one of the cells in this diagram has been exposed to these chemicals.

Why is only one of the lymphocytes in this diagram activated by the pathogen?
A) Antigens move through the immune system by diffusion, so the lymphocyte closest to the site of infection binds the antigen first. Once a lymphocyte is activated, it produces chemicals that prevent the activation of other lymphocytes.
B) Lymphocytes are only activated if all of their receptors are bound by antigens. In this case, there were only enough antigens to fully activate one cell.
C) Your immune system contains many different lymphocytes, each displaying a different antigen-binding protein. In this case, the antigen only matched the binding protein on the cell that was activated.
D) Lymphocytes can only be activated by chemicals produced by the innate immune system. Only one of the cells in this diagram has been exposed to these chemicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The term clonal in clonal selection refers to the fact that
A) a lymphocyte can be easily converted into a stem cell line for laboratory research.
B) a single activated B cell produces many identical copies of the antibody, which react to the antigen that activated the B cell.
C) an activated B cell can convert itself quickly into helper and killer T cells that are specific for the same antigen.
D) once activated, a specific lymphocyte makes many identical copies of itself.
A) a lymphocyte can be easily converted into a stem cell line for laboratory research.
B) a single activated B cell produces many identical copies of the antibody, which react to the antigen that activated the B cell.
C) an activated B cell can convert itself quickly into helper and killer T cells that are specific for the same antigen.
D) once activated, a specific lymphocyte makes many identical copies of itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A vaccine contains
A) antibodies.
B) active B cells.
C) antigens.
D) active killer T cells.
A) antibodies.
B) active B cells.
C) antigens.
D) active killer T cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The fetus of a lion receives antibodies that were produced by its mother while it was still in the womb. This is an example of
A) active immunity.
B) a secondary immune response.
C) a primary immune response.
D) passive immunity.
A) active immunity.
B) a secondary immune response.
C) a primary immune response.
D) passive immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Once B cells become effector cells, they
A) produce the antigens that attach to antibodies.
B) release free-standing antibodies.
C) release free-standing antigens.
D) bind to infected T cells.
A) produce the antigens that attach to antibodies.
B) release free-standing antibodies.
C) release free-standing antigens.
D) bind to infected T cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The antibodies released by activated B cells specifically target
A) killer T cells.
B) antigens.
C) macrophages.
D) platelets.
A) killer T cells.
B) antigens.
C) macrophages.
D) platelets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements about vaccinations given to humans is true?
A) The vaccination acts as the first exposure to a virus, allowing the much more effective second exposure response to occur when the virus actually infects the body.
B) A vaccination primes the body so that it will no longer respond to an invasion by a virus.
C) There is a chance of a person's getting the disease from a vaccination, since vaccination involves the injection of the entire living disease organism.
D) Vaccinations prime the virus so that the virus will not kill as many body cells as it would in an unvaccinated person.
A) The vaccination acts as the first exposure to a virus, allowing the much more effective second exposure response to occur when the virus actually infects the body.
B) A vaccination primes the body so that it will no longer respond to an invasion by a virus.
C) There is a chance of a person's getting the disease from a vaccination, since vaccination involves the injection of the entire living disease organism.
D) Vaccinations prime the virus so that the virus will not kill as many body cells as it would in an unvaccinated person.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Active immunity results from injecting
A) a harmless form of a pathogen.
B) live pathogens.
C) live B cells from another person.
D) antibodies.
A) a harmless form of a pathogen.
B) live pathogens.
C) live B cells from another person.
D) antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a bacterial strain commonly spread in hospitals. If MRSA entered the surgical site of a patient, what is the first level of the immune system it would have to defeat to cause an infection?
A) innate immune system
B) humoral immunity
C) cell-mediated immunity
D) autoimmune system
A) innate immune system
B) humoral immunity
C) cell-mediated immunity
D) autoimmune system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Examine the figure below. 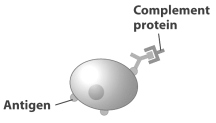
Which of the following could happen to the pathogen depicted in this figure?
A) The pathogen could use the complement protein to infect a self cell.
B) The complement protein could attract a killer B cell that would phagocytize the pathogen
C) The complement proteins could attract other complement proteins that would form a hole in the pathogen's plasma membrane.
D) The complement protein could attract a killer T cell that would inject toxins into the pathogen.

Which of the following could happen to the pathogen depicted in this figure?
A) The pathogen could use the complement protein to infect a self cell.
B) The complement protein could attract a killer B cell that would phagocytize the pathogen
C) The complement proteins could attract other complement proteins that would form a hole in the pathogen's plasma membrane.
D) The complement protein could attract a killer T cell that would inject toxins into the pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements about infection by HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, is false?
A) Most AIDS victims go through a period of up to 15 years between infection and the onset of AIDS symptoms.
B) In the early part of the infection, killer T lymphocytes destroy helper T lymphocytes infected by the virus.
C) The antigens on the protein coat of the HIV remain the same through time.
D) The victim's immune system eventually collapses, and normally harmless infections cause death.
A) Most AIDS victims go through a period of up to 15 years between infection and the onset of AIDS symptoms.
B) In the early part of the infection, killer T lymphocytes destroy helper T lymphocytes infected by the virus.
C) The antigens on the protein coat of the HIV remain the same through time.
D) The victim's immune system eventually collapses, and normally harmless infections cause death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements about the human immune response is true?
A) Host cells are never destroyed by macrophages, even if they are damaged.
B) Neutrophils mount a specific response to particular species of invading organisms.
C) The immune response is more effective during the second exposure to an invader.
D) Lymphocytes are one of the components of blood clots.
A) Host cells are never destroyed by macrophages, even if they are damaged.
B) Neutrophils mount a specific response to particular species of invading organisms.
C) The immune response is more effective during the second exposure to an invader.
D) Lymphocytes are one of the components of blood clots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Helper T cells
A) stimulate the proliferation of killer T cells when bound to their specific antigen.
B) stimulate the proliferation of B cells when bound to their specific antigen.
C) proliferate rapidly when bound to their specific antigen.
D) all of the above
A) stimulate the proliferation of killer T cells when bound to their specific antigen.
B) stimulate the proliferation of B cells when bound to their specific antigen.
C) proliferate rapidly when bound to their specific antigen.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Killer T cells
A) directly kill viruses.
B) kill cells that are infected by viruses.
C) cause B cells to proliferate when they are bound to their antigen.
D) bind to B cells and then to infected cells.
A) directly kill viruses.
B) kill cells that are infected by viruses.
C) cause B cells to proliferate when they are bound to their antigen.
D) bind to B cells and then to infected cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A disease-causing agent is called a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
_______ nodes are pockets that contain specialized cells and trap bacteria and viruses roaming the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The diagnosis of cancer represents a failure of the body's cancer ______________ system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Macrophages and neutrophils make up a _______ response to invaders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
This graph depicts the immune response following a vaccine and a booster shot.
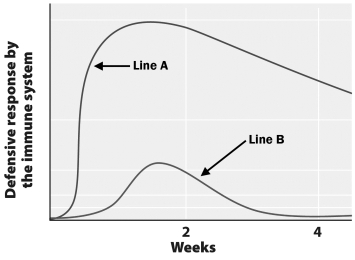
The line labeled with the letter _____ represents the response after the initial vaccine.

The line labeled with the letter _____ represents the response after the initial vaccine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The ______ ______ is a coordinated combination of specialized cells and molecules that give us the ability to resist specific pathogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
__________ proteins attach to antibodies bound to antigens on the surfaces of invading cells. This helps macrophages bind to these cells in preparation for phagocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Interferons summon _____________ cells that destroy any self cells that display viral proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Neutrophils usually get to a wound site __________ [before or after?] macrophages begin phagocytizing bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
White blood cells called macrophages destroy invading pathogens by phagocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
At various points along the lymphatic ducts lie _____ _____, pockets of tissue containing huge numbers of white blood cells that trap bacteria, viruses, and foreign proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
During the inflammatory response, swelling occurs as a result of the leaking of ___________ out of the blood vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
_____ blood cells are a kind of defensive cells found in the interstitial fluid between the cells in the most vulnerable parts of the body and circulating in the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The _______ immune system is a specific defense against parasites and internal diseases that exists only in vertebrate animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The immune system can detect cancerous cells because they display different cell surface proteins and carbohydrates than normal self cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A vaccine stimulates the formation of _________ cells by introducing the immune system to a killed or weakened form of a virus before they are exposed to the actual pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A lymphocyte is activated when unique _______-binding proteins on its surface recognize specific molecules found on the surface of a specific pathogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The immune system can distinguish a self cell from a non-self cell based on the mixture of ________ and ________ on the plasma membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Our first exposure to a particular antigen brings on a _______ immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
_______cells remain in our body after the initial exposure to a disease organism and help the immune system recognize that particular organism during a second exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The human immune system has a more effective response to an invader during a second exposure than during the first exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Adaptive immune responses are faster at responding to the invasion of a pathogen than innate immune responses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Why does an area with tissue damage become warm and red during the inflammatory response?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Lymphocytes surround and digest the damaged host cells and the marked cells of the invading organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the case of AIDS, death is more likely to result from other infections that the immune system cannot control than from HIV itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Macrophages are smaller than neutrophils but have a similar function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A fever is the product of an out-of-control immune response to a parasite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



