Deck 32: Plant Growth and Reproduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 32: Plant Growth and Reproduction
1
At the tip of a filament within a flower you would find
A) a petal.
B) an anther.
C) a carpel.
D) an ovary.
A) a petal.
B) an anther.
C) a carpel.
D) an ovary.
B
2
Pollen is produced in the
A) ovules.
B) anthers.
C) style.
D) stigma.
A) ovules.
B) anthers.
C) style.
D) stigma.
B
3
Plants exhibit indeterminate growth. This means that
A) they are perennials.
B) they may complete their life cycles in one, two, or three years.
C) the length of time it takes to grow to reach maturity is variable.
D) the final form of the plant is not entirely predictable.
A) they are perennials.
B) they may complete their life cycles in one, two, or three years.
C) the length of time it takes to grow to reach maturity is variable.
D) the final form of the plant is not entirely predictable.
D
4
Groups of perpetually young undifferentiated cells from which new cells arise are termed
A) seeds.
B) meristems.
C) root caps.
D) phloem.
A) seeds.
B) meristems.
C) root caps.
D) phloem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In which of the following structures would an egg be found?
A) stamen
B) petal
C) sepal
D) carpel
A) stamen
B) petal
C) sepal
D) carpel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Plant and animal growth is indeterminate and determinant, respectively; why is indeterminate growth more beneficial to plants than to animals?
A) Plants are stationary in their habitat while animals can move; indeterminate growth allows a plant to respond to environmental conditions.
B) Plants are commonly eaten by animals while animals are rarely eaten by plants.
C) Indeterminate growth allows plants to become larger than animals.
D) Indeterminate growth allows plants to avoid reproducing when environmental conditions are unfavorable.
A) Plants are stationary in their habitat while animals can move; indeterminate growth allows a plant to respond to environmental conditions.
B) Plants are commonly eaten by animals while animals are rarely eaten by plants.
C) Indeterminate growth allows plants to become larger than animals.
D) Indeterminate growth allows plants to avoid reproducing when environmental conditions are unfavorable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In plants double fertilization means that
A) the zygote has twice the diploid number of chromosomes.
B) two pollen grains are needed to fertilize an egg.
C) one sperm fertilizes two eggs.
D) one sperm fertilizes an egg, the other fertilizes another cell in the embryo sac.
A) the zygote has twice the diploid number of chromosomes.
B) two pollen grains are needed to fertilize an egg.
C) one sperm fertilizes two eggs.
D) one sperm fertilizes an egg, the other fertilizes another cell in the embryo sac.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When a plant germinates from a seed it has
A) two root apical meristems and two shoot apical meristems.
B) one root apical meristem and one shoot apical meristem.
C) two root apical meristems and four shoot apical meristems.
D) four root apical meristems and two shoot apical meristems.
A) two root apical meristems and two shoot apical meristems.
B) one root apical meristem and one shoot apical meristem.
C) two root apical meristems and four shoot apical meristems.
D) four root apical meristems and two shoot apical meristems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Growth of the cells of the lateral meristem is responsible for increasing the
A) number of lateral roots.
B) number of formant buds.
C) thickness of the stem.
D) length of the stem.
A) number of lateral roots.
B) number of formant buds.
C) thickness of the stem.
D) length of the stem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The outer bark on trees often appears cracked and uneven because
A) different regions of the bark grow at different rates.
B) the cork cambium reabsorbs some of the bark.
C) increases in stem length stretch the bark.
D) increases in stem thickness stretch the bark.
A) different regions of the bark grow at different rates.
B) the cork cambium reabsorbs some of the bark.
C) increases in stem length stretch the bark.
D) increases in stem thickness stretch the bark.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The aspen grove shown in the photo below may be formed from clones. 
If this grove is indeed comprised of clones, it would not be surprising to observe that
A) individual trees are of equal height.
B) individual trees have equal girth.
C) individual trees flower at the same time.
D) all of the above

If this grove is indeed comprised of clones, it would not be surprising to observe that
A) individual trees are of equal height.
B) individual trees have equal girth.
C) individual trees flower at the same time.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Embryo sacs are formed in the
A) stamen.
B) carpel.
C) anther.
D) sepal.
A) stamen.
B) carpel.
C) anther.
D) sepal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following components is correctly matched with its location?
A) A carpel is part of a style.
B) A sepal is part of a stamen.
C) A stigma is part of a carpel.
D) An anther is part of a stigma.
A) A carpel is part of a style.
B) A sepal is part of a stamen.
C) A stigma is part of a carpel.
D) An anther is part of a stigma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In which of the following structures is sperm produced?
A) stamen
B) carpel
C) sepal
D) petal
A) stamen
B) carpel
C) sepal
D) petal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The growth of cells within the cark cambium results in the production of
A) heartwood.
B) bark
C) secondary phloem.
D) sapwood.
A) heartwood.
B) bark
C) secondary phloem.
D) sapwood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Imagine driving a nail into a tree trunk. Which of the following tissues would the nail point first contact?
A) heartwood
B) cork cambium
C) vascular cambium
D) sapwood
A) heartwood
B) cork cambium
C) vascular cambium
D) sapwood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Plants growth above ground can be accomplished by adding new
A) leaf units.
B) bud units.
C) stem units.
D) bud-stem-leaf units
A) leaf units.
B) bud units.
C) stem units.
D) bud-stem-leaf units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
During pollination pollen is moved from
A) stigmas to sepals.
B) anthers to stigmas.
C) ovules to anthers.
D) carpels to stamens.
A) stigmas to sepals.
B) anthers to stigmas.
C) ovules to anthers.
D) carpels to stamens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following would not be derived from vascular cambium?
A) bark
B) xylem
C) more undifferentiated cells
D) phloem
A) bark
B) xylem
C) more undifferentiated cells
D) phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following would be haploid?
A) pollen
B) guard cells
C) root hairs
D) all of the above
A) pollen
B) guard cells
C) root hairs
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The tube cell in a pollen grain grows through the style and provides a pathway for the _____ to enter the _____.
A) egg; sperm
B) sperm; anther
C) sperm; embryo sac
D) anther; filament
A) egg; sperm
B) sperm; anther
C) sperm; embryo sac
D) anther; filament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Sexual reproduction in mosses and angiosperms result in a zygote and seed, respectively. In what way(s) is the seed superior to the zygote?
A) The zygote must grow immediately, but the seed can lie dormant until growth conditions are favorable.
B) The seed carries its own food to start life while the zygote is nourished by the female gametophyte.
C) The seed has a coat, which protects it from the environment, while the zygote lacks a coat.
D) all of the above
A) The zygote must grow immediately, but the seed can lie dormant until growth conditions are favorable.
B) The seed carries its own food to start life while the zygote is nourished by the female gametophyte.
C) The seed has a coat, which protects it from the environment, while the zygote lacks a coat.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Pollen grains develop from
A) haploid male spores.
B) the ovum.
C) haploid sperm.
D) embryo sacs.
A) haploid male spores.
B) the ovum.
C) haploid sperm.
D) embryo sacs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At what point in the plant life cycle does cell division result in haploid cells?
A) when the gametophyte produces gametes
B) when the sporophyte produces spores
C) when the egg and sperm fuse to form a zygote
D) when the germinating spore grows to become the gametophyte
A) when the gametophyte produces gametes
B) when the sporophyte produces spores
C) when the egg and sperm fuse to form a zygote
D) when the germinating spore grows to become the gametophyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Apical dominance occurs when auxins produced by
A) lateral buds promote the growth in length of the main stem.
B) the shoot tip inhibits the growth of lateral buds.
C) the shoot tip inhibits the growth of roots.
D) the root tip promotes the growth of the apical meristem.
A) lateral buds promote the growth in length of the main stem.
B) the shoot tip inhibits the growth of lateral buds.
C) the shoot tip inhibits the growth of roots.
D) the root tip promotes the growth of the apical meristem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Flowers, like the ones in the figure below, display spectacular colors, shapes, and odors, in combination with food rewards such as nectar, in order to convince pollinating animals to visit several flowers of the same species to transfer pollen for reproduction. 
How might a flower be specialized to attract hummingbird pollinators (above right) and discourage insect pollinators (above left)?
A) have brightly colored petals
B) open only at night
C) hang downward from the branch tips
D) organize its flowers into a flat landing surface

How might a flower be specialized to attract hummingbird pollinators (above right) and discourage insect pollinators (above left)?
A) have brightly colored petals
B) open only at night
C) hang downward from the branch tips
D) organize its flowers into a flat landing surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Gene-for-gene recognition develops when a plant's resistance gene
A) produces a protein that binds to protein produced by a pathogen.
B) can bind directly to a complementary gene within the pathogen.
C) mutates in such a way as to alter its distinctive chemistry.
D) is activated by the attachment of a pathogen to the plant's cuticle.
A) produces a protein that binds to protein produced by a pathogen.
B) can bind directly to a complementary gene within the pathogen.
C) mutates in such a way as to alter its distinctive chemistry.
D) is activated by the attachment of a pathogen to the plant's cuticle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In what way does endosperm differs from sperm?
A) Endosperm is triploid rather than haploid.
B) Endosperm is the immature sperm prior to its release from the anther.
C) Endosperm develops only in self-pollinating plants.
D) Endosperm is produced by the sporophyte, and sperm by the gametophyte.
A) Endosperm is triploid rather than haploid.
B) Endosperm is the immature sperm prior to its release from the anther.
C) Endosperm develops only in self-pollinating plants.
D) Endosperm is produced by the sporophyte, and sperm by the gametophyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The figure below illustrates the results of a laboratory experiment that simulates potted irises being exposed to differing lengths of darkness. 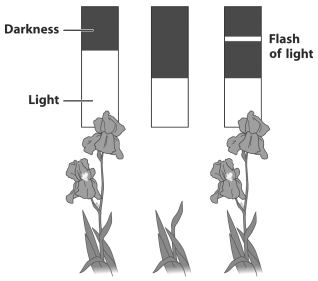
How would flowering in these irises be affected by disrupting the length of their light exposure?
A) It would stimulate flowering.
B) It would suppress flowering.
C) It would stimulate branching and increase total flower production.
D) There would be no effect since irises use the length of darkness to coordinate flowering.

How would flowering in these irises be affected by disrupting the length of their light exposure?
A) It would stimulate flowering.
B) It would suppress flowering.
C) It would stimulate branching and increase total flower production.
D) There would be no effect since irises use the length of darkness to coordinate flowering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Horticulturists often remove the anthers from flowers to
A) promote branching.
B) prevent self-fertilization.
C) increase egg production.
D) attract pollinators.
A) promote branching.
B) prevent self-fertilization.
C) increase egg production.
D) attract pollinators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Anthers are typically attached to filaments and elevated within the flower to
A) improve the transfer of pollen to a pollinator.
B) improve the transfer of pollen to the adjacent stigma.
C) prevent pollen from becoming stuck in the nectar.
D) prevent the pollen from being blown away from the flower.
A) improve the transfer of pollen to a pollinator.
B) improve the transfer of pollen to the adjacent stigma.
C) prevent pollen from becoming stuck in the nectar.
D) prevent the pollen from being blown away from the flower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Some types of the thynnine wasps pollinate the elbow orchid when
A) males carry wingless females to elbow orchid flowers, where the female pollinates the flower.
B) females carry wingless males to elbow orchid flowers, where the males pollinate the flower.
C) elbow orchid flowers imitate the smell of females and trick males into transporting pollen.
D) elbow orchid flowers imitate the smell of males and trick females into transporting pollen.
A) males carry wingless females to elbow orchid flowers, where the female pollinates the flower.
B) females carry wingless males to elbow orchid flowers, where the males pollinate the flower.
C) elbow orchid flowers imitate the smell of females and trick males into transporting pollen.
D) elbow orchid flowers imitate the smell of males and trick females into transporting pollen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following animals would be least likely to disperse seeds?
A) deer
B) mice
C) honeybees
D) humans
A) deer
B) mice
C) honeybees
D) humans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Without a pollen tube,
A) sperm couldn't move from filaments to anthers.
B) the zygote couldn't leave the embryo sac.
C) sperm would be unable to enter the ovule.
D) anthers couldn't produce pollen.
A) sperm couldn't move from filaments to anthers.
B) the zygote couldn't leave the embryo sac.
C) sperm would be unable to enter the ovule.
D) anthers couldn't produce pollen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the purpose for the endosperm found within a seed?
A) Endosperm is the tissue specialized to form roots.
B) It creates a waterproof covering that permits the seed to become dormant.
C) It is a water-storage tissue.
D) It is used as a food source for the developing embryo.
A) Endosperm is the tissue specialized to form roots.
B) It creates a waterproof covering that permits the seed to become dormant.
C) It is a water-storage tissue.
D) It is used as a food source for the developing embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The gene-for-gene recognition immune response involves
A) plant alleles that attack matching alleles in pathogens.
B) crossing-over between plant alleles and pathogen alleles.
C) production of antibodies by plants in response to antigens produced by pathogens.
D) production of proteins by plants that protect against pathogens with a particular genetic makeup.
A) plant alleles that attack matching alleles in pathogens.
B) crossing-over between plant alleles and pathogen alleles.
C) production of antibodies by plants in response to antigens produced by pathogens.
D) production of proteins by plants that protect against pathogens with a particular genetic makeup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The flesh of an apple forms from
A) the stamen.
B) the ovule.
C) the carpel.
D) the ovary.
A) the stamen.
B) the ovule.
C) the carpel.
D) the ovary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The typical conifer growth pattern of narrow tops and broad bases is strongly associated with the action of
A) abscisic acid.
B) gibberrellic acid.
C) auxin.
D) ethylene.
A) abscisic acid.
B) gibberrellic acid.
C) auxin.
D) ethylene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Because its cells are diploid, the ovule is considered to be a part of the
A) gametophyte.
B) carpal.
C) embryo sac.
D) sporophyte.
A) gametophyte.
B) carpal.
C) embryo sac.
D) sporophyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following would be the least likely pollinator?
A) butterfly
B) bat
C) rattlesnake
D) human
A) butterfly
B) bat
C) rattlesnake
D) human

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In flowering plants, sperm is found within the pollen grains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An apical meristem produces lateral roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Meristem cells in plants are similar to ____ cells in vertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Mature pollen grains contain three cells; two sperm cells and a(n) ____ ____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A plant's physiological response to day length is called _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A plant that completes its life cycle in one year is a(n) _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Increases in length due to cell divisions at apical meristems are called _______ growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The protective chemical produced by plants that can be addictive to humans is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Above ground, plants grow by adding new bud-stem- ____ units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Sapwood is xylem that is too clogged to transport water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Seed coats develop from the outer portion of the _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Double fertilization results in the formation of a ______ and __________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The energy used by seedlings before they begin to photosynthesis is stored in the __________ and the _______ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The growth of a plant zygote into an embryo occurs within the ____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Plants that live for three years or more are __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How might the observation that the percentage of plant species with red foliage is greatest among high elevation plants be explained?
A) Atmospheric composition at high elevation reduces the strength of the wavelengths that normally support photosynthesis.
B) High-elevation soils have above-average concentrations of iron, which accumulated to produce iron oxide within the foliage.
C) The red wavelengths exacerbate dehydration at high elevation, so mountain plants reflect it from their surfaces.
D) Red pigments absorb ultraviolet radiation,which is more intense at high elevation.
A) Atmospheric composition at high elevation reduces the strength of the wavelengths that normally support photosynthesis.
B) High-elevation soils have above-average concentrations of iron, which accumulated to produce iron oxide within the foliage.
C) The red wavelengths exacerbate dehydration at high elevation, so mountain plants reflect it from their surfaces.
D) Red pigments absorb ultraviolet radiation,which is more intense at high elevation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In order to fertilize an egg a pollen grain must first arrive at a(n) ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Apical dominance develops when the shoot apex produces ______, a hormone that suppress the outgrowth of lateral buds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A plant that completes its life cycle in two years is a(n) ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The plant body is modular, formed by the repeated addition of the same basic units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Endosperm is the origin of the sperm that fertilize the embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In flowering plants, seeds are haploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Plants that use animals for pollination always provide a reward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Some plants can sense the duration of light or dark during a 24-hour period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A flower consists of four whorls of modified leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Most flowering plants rely on animals rather than wind to transport pollen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In flowering plants, sperm forms the pollen grain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



