Deck 9: Spatial Modeling and Decision Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/11
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Spatial Modeling and Decision Analysis
1
Multi-criteria analysis (MCA) with GIS involves
A) selecting a set of criteria
B) scoring alternatives against the criteria and generating criterion score maps
C) standardising the criterion score maps
D) assigning weights to the criteria
E) all the above
A) selecting a set of criteria
B) scoring alternatives against the criteria and generating criterion score maps
C) standardising the criterion score maps
D) assigning weights to the criteria
E) all the above
E
2
In MCA, weights represent
A) value judgements of the relative importance of the criteria
B) value judgements of the relative performance of the alternatives
C) scientific measurements of the relative importance of the criteria
D) scientific measurements of the relative performance of the alternatives
A) value judgements of the relative importance of the criteria
B) value judgements of the relative performance of the alternatives
C) scientific measurements of the relative importance of the criteria
D) scientific measurements of the relative performance of the alternatives
A
3
In MCA, scores (or ratings) represent
A) social preferences of alternatives
B) social preferences of criteria
C) performance of alternatives in relation to criteria
D) performance of criteria determined based on facts and scientific evidence
A) social preferences of alternatives
B) social preferences of criteria
C) performance of alternatives in relation to criteria
D) performance of criteria determined based on facts and scientific evidence
C
4
Standardisation in MCA is necessary because
A) MCA integrates different views for multiple stakeholders
B) different criteria may have different importance
C) different criteria may use different measurement scales or units
D) different alternatives are at different locations, which may have different environmental conditions
A) MCA integrates different views for multiple stakeholders
B) different criteria may have different importance
C) different criteria may use different measurement scales or units
D) different alternatives are at different locations, which may have different environmental conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For selection of a site for nuclear waste disposal using MCA, we use the proximity to highly populated areas as one of the criteria. The proximity is measured in terms of distance. Suppose xmin is the shortest distance from the proposed disposal sites to the highly populated areas in the study area, xmax is the longest distance from the proposed disposal sites to the highly populated areas, and xi is the shortest distance from the proposed disposal site i to the highly populated areas. Using the score range procedure, which of the following equations should you use to standardise the criterion scores?
A)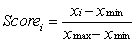
B)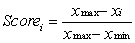
C)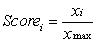
D)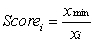
A)
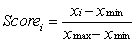
B)
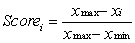
C)
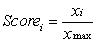
D)
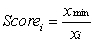

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
One of the roles of GIS in MCA is to
A) assign weights
B) select criteria
C) select alternatives
D) combine criterion maps
A) assign weights
B) select criteria
C) select alternatives
D) combine criterion maps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What are the core functions of GIS for implementing cellular automata (CA)?
A) local functions and conditional operators in map algebra
B) focal functions and conditional operators in map algebra
C) zonal functions and conditional operators in map algebra
D) global functions and conditional operators in map algebra
A) local functions and conditional operators in map algebra
B) focal functions and conditional operators in map algebra
C) zonal functions and conditional operators in map algebra
D) global functions and conditional operators in map algebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A CA is defined in terms of
A) an n-dimensional grid of cells and states of each cell
B) neighbourhood
C) transition rules
D) all of the above
A) an n-dimensional grid of cells and states of each cell
B) neighbourhood
C) transition rules
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In agent-based modelling, agents typically perform actions simultaneously at constant time steps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Weights-of-evidence is based on
A) statistical weights of evidence
B) analyst-assigned weights of evidence
C) persuasiveness of evidence
D) believability of evidence
A) statistical weights of evidence
B) analyst-assigned weights of evidence
C) persuasiveness of evidence
D) believability of evidence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An artificial neural network (ANN) is
A) a linear model that is fit to data
B) a nonlinear model that is fit to data
C) a linear model that learns to perform a function from data
D) a nonlinear model that learns to perform a function from data
A) a linear model that is fit to data
B) a nonlinear model that is fit to data
C) a linear model that learns to perform a function from data
D) a nonlinear model that learns to perform a function from data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



