Deck 7: Terrain Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/16
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Terrain Analysis
1
TIN is more efficient than DEM at representing a surface
True
2
If a plateau is eroded by gullies, the remaining plateau would be a flat (planar) area bounded by an irregular, many-sided polygon. In the TIN model
A) it would be represented by the irregular, many-sided polygon
B) it would be represented by a number of triangles, each at a different elevation
C) it would be represented by a number of triangles, each at the same elevation
D) it cannot be represented
A) it would be represented by the irregular, many-sided polygon
B) it would be represented by a number of triangles, each at a different elevation
C) it would be represented by a number of triangles, each at the same elevation
D) it cannot be represented
C
3
Which of the following is not well represented using TIN?
A) glaciated landscapes
B) fluvially eroded landscapes
C) mountainous landscapes
A) glaciated landscapes
B) fluvially eroded landscapes
C) mountainous landscapes
A
4
Below is a DEM. Which landform is at Locations labelled as 1? g 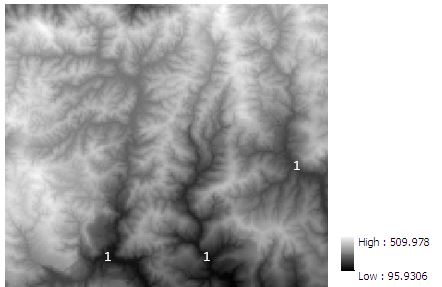
A) hill tops
B) ridges
C) valleys
D) steep slopes

A) hill tops
B) ridges
C) valleys
D) steep slopes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the following flow accumulation map derived from the above DEM, ridge lines can be formed by linking locations with a flow accumulation value of 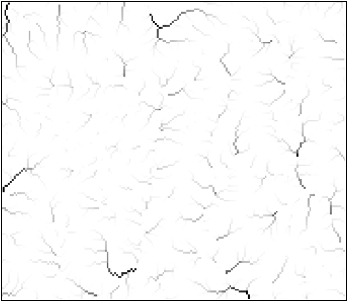

A) 1129
B) 1000
C) 100
D) 0


A) 1129
B) 1000
C) 100
D) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A hydrologically correct DEM is
A) a hydrological model
B) a DEM corrected using a hydrological model
C) a DEM void of depression or sinks
D) a DEM resulted from hydrological analysis
A) a hydrological model
B) a DEM corrected using a hydrological model
C) a DEM void of depression or sinks
D) a DEM resulted from hydrological analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Sinks in a DEM are not caused by
A) sampling effects
B) rounding of elevations to integer numbers
C) spatial variations in the DEM
D) natural depressions on terrain surface
A) sampling effects
B) rounding of elevations to integer numbers
C) spatial variations in the DEM
D) natural depressions on terrain surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
As the spatial resolution of a DEM decreases, the number of sinks
A) increases
B) decreases
C) have no change
A) increases
B) decreases
C) have no change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Slope is measured either in degrees or percentage. 45 degree is equivalent to
A) 1%
B) 45%
C) 100%
D) none of the above
A) 1%
B) 45%
C) 100%
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The flow direction tool in GIS calculates
A) the direction water will flow along a stream channel
B) the direction water will flow into a catchment
C) the direction water will flow out from a catchment
D) the direction water will flow out from each cell
A) the direction water will flow along a stream channel
B) the direction water will flow into a catchment
C) the direction water will flow out from a catchment
D) the direction water will flow out from each cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Flow accumulation is calculated based on
A) amount of rain flowing through each cell
B) amount of water accumulated from upstream areas
C) flow direction
D) flow length
A) amount of rain flowing through each cell
B) amount of water accumulated from upstream areas
C) flow direction
D) flow length

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
On a flow accumulation raster layer, locations having an accumulation value of 0 correspond to
A) stream channels
B) ridge lines
C) pour points
D) none of the above
A) stream channels
B) ridge lines
C) pour points
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The flow length tool in GIS with UPSTREAM option calculates
A) downslope distance along a flow path from each cell to a sink or outlet on the edge of the catchment
B) longest distance along a flow path from each cell to the top of the divide of the catchment
C) length of each stream channel within the catchment
D) shortest distance from the highest point to the outlet of the catchment
A) downslope distance along a flow path from each cell to a sink or outlet on the edge of the catchment
B) longest distance along a flow path from each cell to the top of the divide of the catchment
C) length of each stream channel within the catchment
D) shortest distance from the highest point to the outlet of the catchment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The topographic wetness index is a function of
A) elevation
B) slope
C) aspect
D) catchment size
A) elevation
B) slope
C) aspect
D) catchment size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In order to answer the question 'can a tower in the terrain be seen from a given viewpoint?', which of the following GIS operations is the best?
A) viewshed analysis
B) line-of-sight analysis
C) slope measurement
D) aspect measurement
A) viewshed analysis
B) line-of-sight analysis
C) slope measurement
D) aspect measurement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
To answer the question 'how can an aesthetically unpleasant building be optimally hidden in the terrain in order to preserve the beauty of a landscape?', it is better to use
A) viewshed analysis
B) line-of-sight analysis
C) overlay
D) buffer
A) viewshed analysis
B) line-of-sight analysis
C) overlay
D) buffer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



