Deck 6: Remote Sensing Data Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Remote Sensing Data Analysis
1
In remote sensing, electromagnetic waves are characterised by
A) their intensity
B) their wave frequency
C) their wavelength location within the electromagnetic spectrum
D) their reflectance
A) their intensity
B) their wave frequency
C) their wavelength location within the electromagnetic spectrum
D) their reflectance
C
2
Microwaves are the longest wavelengths used for remote sensing
True
3
The particle theory of EMR suggests that
A) the remote sensors operating at shorter wavelengths must look at the parcel of ground longer in order to obtain a detectable energy signal
B) microwaves have higher energy contents than near infrared (IR) radiation
C) it is easier to detect visible wavelength energy than those of microwaves
D) thermal IR has higher energy content than reflected IR
A) the remote sensors operating at shorter wavelengths must look at the parcel of ground longer in order to obtain a detectable energy signal
B) microwaves have higher energy contents than near infrared (IR) radiation
C) it is easier to detect visible wavelength energy than those of microwaves
D) thermal IR has higher energy content than reflected IR
C
4
Atmospheric windows are
A) those areas of the spectrum that are not severely influenced by atmospheric absorption
B) those areas of the spectrum that are blocked by atmospheric absorption
C) those areas of the spectrum in which little atmospheric scattering occurs
D) those areas of the spectrum that are not useful for remote sensing
A) those areas of the spectrum that are not severely influenced by atmospheric absorption
B) those areas of the spectrum that are blocked by atmospheric absorption
C) those areas of the spectrum in which little atmospheric scattering occurs
D) those areas of the spectrum that are not useful for remote sensing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Remote sensing is only interested in measuring the radiation
A) absorbed by targets
B) transmitted through targets
C) reflected from targets
A) absorbed by targets
B) transmitted through targets
C) reflected from targets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The spectral reflectance of a particular object varies with wavelength

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In a near IR image, forest appears
A) darker than water body
B) brighter than water body
C) as bright as water body
A) darker than water body
B) brighter than water body
C) as bright as water body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which band of the spectrum is the best for separating water and land?
A) red
B) blue
C) green
D) near IR
A) red
B) blue
C) green
D) near IR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Aerial photography is better than satellite remote sensing because
A) aerial photography allows repetitive imaging of the Earth's surface on a continuing basis
B) aerial photography has a revisit period of several days
C) aerial photography can produce digital images
D) aerial photography has higher spectral resolutions
E) aerial photography provides the highest spatial resolution
A) aerial photography allows repetitive imaging of the Earth's surface on a continuing basis
B) aerial photography has a revisit period of several days
C) aerial photography can produce digital images
D) aerial photography has higher spectral resolutions
E) aerial photography provides the highest spatial resolution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
On a colour infrared image (or photo),
A) targets with high near-infrared reflectance appear red
B) targets with high red reflectance appear red
C) targets with high green reflectance appear red
D) targets with high blue reflectance appear red
A) targets with high near-infrared reflectance appear red
B) targets with high red reflectance appear red
C) targets with high green reflectance appear red
D) targets with high blue reflectance appear red

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The brightness value of a pixel in a digital image is recorded as
A) the absolute average amount of the solar radiance reflected from the pixel
B) a scaled digital number according to the radiometric resolution
C) a digital number ranging from 0 to 8
D) a digital number ranging from 0 to 12
A) the absolute average amount of the solar radiance reflected from the pixel
B) a scaled digital number according to the radiometric resolution
C) a digital number ranging from 0 to 8
D) a digital number ranging from 0 to 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Landsat MSS sensor has a spatial resolution of 80m. It means
A) each pixel covers an area of 6400 m2
B) each pixel covers an area of 80 m2
C) it has a higher spatial resolution than Landsat TM sensor whose spatial resolution is 30m
D) the image of a target it captured is sharper than that captured by Landsat TM sensor
A) each pixel covers an area of 6400 m2
B) each pixel covers an area of 80 m2
C) it has a higher spatial resolution than Landsat TM sensor whose spatial resolution is 30m
D) the image of a target it captured is sharper than that captured by Landsat TM sensor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Georeferencing an image to geographical coordinates (latitude and longitude) is an operation of
A) filtering
B) linear stretching
C) radiometric correction
D) geometric correction
A) filtering
B) linear stretching
C) radiometric correction
D) geometric correction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If an image's orientation does not align with the north-south direction, which type of image procession should be used?
A) filtering
B) linear stretching
C) radiometric correction
D) geometric correction
A) filtering
B) linear stretching
C) radiometric correction
D) geometric correction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In order to monitor the growth of cotton in an area (in the northern hemisphere), we acquired QuickBird images taken every month from June to October. The images have been georeferenced and geometrically corrected. If the images have good contrasts and contain no noises, which type of image processing is still needed for the comparison between these images?
A) histogram equalisation
B) spatial filtering
C) bilinear interpolation
D) sun elevation correction
A) histogram equalisation
B) spatial filtering
C) bilinear interpolation
D) sun elevation correction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Cubic convolution is a geometric correction method, which calculates the DN value of a rectified pixel
A) as the value of its nearest pixel in the input image
B) as the average value of the four nearest pixels in the input image
C) as the average value of the sixteen nearest pixels in the input image
D) using a cubic polynomial function
A) as the value of its nearest pixel in the input image
B) as the average value of the four nearest pixels in the input image
C) as the average value of the sixteen nearest pixels in the input image
D) using a cubic polynomial function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Geometric correction with the nearest neighbour method
A) preserves original DN values
B) calculates the DN value of a rectified pixel as the average value of the pixels within its neighbourhood
C) calculates the DN value of a rectified pixel as the distance-weighted average value of the pixels within its neighbourhood
D) calculates the DN value of a rectified pixel using a moving window
A) preserves original DN values
B) calculates the DN value of a rectified pixel as the average value of the pixels within its neighbourhood
C) calculates the DN value of a rectified pixel as the distance-weighted average value of the pixels within its neighbourhood
D) calculates the DN value of a rectified pixel using a moving window

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Converting DN values to radiance values is an operation of
A) filtering
B) linear stretching
C) radiometric correction
D) geometric correction
A) filtering
B) linear stretching
C) radiometric correction
D) geometric correction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Solar elevation angles at a particular location on the surface of the earth
A) remain the same throughout the year
B) are smaller in winter than in summer
C) are larger in winter than in summer
D) are larger in winter than in autumn
E) are larger in winter than in spring
A) remain the same throughout the year
B) are smaller in winter than in summer
C) are larger in winter than in summer
D) are larger in winter than in autumn
E) are larger in winter than in spring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
With linear stretching,
A) the image would appear darker
B) the image would appear lighter
C) light tonal areas would appear darker and dark areas would appear lighter
D) light tonal areas would appear lighter and dark areas would appear darker
A) the image would appear darker
B) the image would appear lighter
C) light tonal areas would appear darker and dark areas would appear lighter
D) light tonal areas would appear lighter and dark areas would appear darker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
With histogram equalisation, DN values are assigned
A) as their frequencies of occurrence
B) based on their frequencies of occurrence
C) as their original DN values divided by their frequencies of occurrence
D) as their original DN values multiplied by their frequencies of occurrence
A) as their frequencies of occurrence
B) based on their frequencies of occurrence
C) as their original DN values divided by their frequencies of occurrence
D) as their original DN values multiplied by their frequencies of occurrence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
On a ratio image produced by Landsat TM Band 4 (NIR) / Landsat TM Band 3 (Red), if a pixel has a value much larger than 1.0, it is
A) vegetation
B) soil
C) water
D) none of the above
A) vegetation
B) soil
C) water
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A high-pass filter can be used to
A) smooth the appearance of an image
B) sharpen the appearance of an image
C) enhance linear features
D) reduce smaller detail in an image
A) smooth the appearance of an image
B) sharpen the appearance of an image
C) enhance linear features
D) reduce smaller detail in an image

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Image classification is a process of
A) categorising images in terms of their spectral bands
B) categorising images in terms of their resolutions
C) categorising images in terms of sensor types
D) categorising all pixels in an image into thematic classes
A) categorising images in terms of their spectral bands
B) categorising images in terms of their resolutions
C) categorising images in terms of sensor types
D) categorising all pixels in an image into thematic classes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Image classification is based on
A) tone or colour
B) digital numbers
C) site or association
D) shape and texture
A) tone or colour
B) digital numbers
C) site or association
D) shape and texture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Supervised classification requires the selection of training areas, while unsupervised classification does not
B) Supervised classification requires accuracy assessment, while unsupervised classification does not
C) Supervised classification requires the image analyst to have knowledge about the thematic classes present in the image, while unsupervised classification does not
D) Supervised classification does not involve the determination of spectral classes in the image, while unsupervised classification does
A) Supervised classification requires the selection of training areas, while unsupervised classification does not
B) Supervised classification requires accuracy assessment, while unsupervised classification does not
C) Supervised classification requires the image analyst to have knowledge about the thematic classes present in the image, while unsupervised classification does not
D) Supervised classification does not involve the determination of spectral classes in the image, while unsupervised classification does

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In supervised classification, training areas are
A) representative samples of different thematic classes selected by the image analyst
B) representative samples of different thematic classes selected by the computer
C) spectral clusters identified by the image analyst
D) spectral clusters identified by the computer
A) representative samples of different thematic classes selected by the image analyst
B) representative samples of different thematic classes selected by the computer
C) spectral clusters identified by the image analyst
D) spectral clusters identified by the computer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Training areas must
A) be drawn from a single area
B) capture the spectral variability of a class
C) capture the spectral boundary between classes
D) be evenly distributed in the image
A) be drawn from a single area
B) capture the spectral variability of a class
C) capture the spectral boundary between classes
D) be evenly distributed in the image

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The number of pixels used in training does not affect the quality of image classification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The parallelepiped classifier defines the class boundaries in terms of
A) distance to the mean centre of a class
B) probability of being a member of a class
C) the DN ranges for each class
D) the DN standard deviations for each class
A) distance to the mean centre of a class
B) probability of being a member of a class
C) the DN ranges for each class
D) the DN standard deviations for each class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is not a potential problem with unsupervised classification?
A) some spectral classes may be meaningless
B) a training area may contain a mix of different thematic classes
C) reference data used for assigning classes by the analyst may contain errors
D) a single thematic class may be split among two spectral classes
A) some spectral classes may be meaningless
B) a training area may contain a mix of different thematic classes
C) reference data used for assigning classes by the analyst may contain errors
D) a single thematic class may be split among two spectral classes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
With the classification error matrix below, what is the overall accuracy of the land use classification?
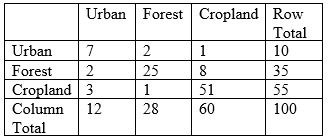
A) 100%
B) 27.7%
C) 29%
D) 83%

A) 100%
B) 27.7%
C) 29%
D) 83%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
According to the classification error matrix below, how many training pixels are omission errors and how many are commission errors with the urban class?
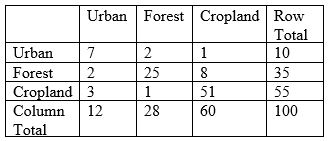
A) 3, 5 (omission, commission)
B) 5, 3
C) 7, 12
D) 7, 10

A) 3, 5 (omission, commission)
B) 5, 3
C) 7, 12
D) 7, 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to the classification error matrix below, what are the producer's accuracy and user's accuracy for the forest class?
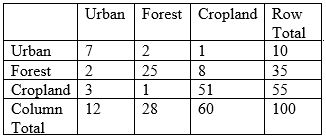
A) 89%, 71% (producer's accuracy, user's accuracy)
B) 71%, 89%
C) 28%, 35%
D) 35%, 28%

A) 89%, 71% (producer's accuracy, user's accuracy)
B) 71%, 89%
C) 28%, 35%
D) 35%, 28%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



