Deck 9: Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/155
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Monopoly
1
Which of the following best describes the role of the Canadian government in the monopoly market?
A) It encourages the permanent monopolization of all markets in which the monopolist has technical superiority over potential competitors.
B) It forbids the creation of legal impediments to entry into any market.
C) It intervenes to prevent the monopolization of any market.
D) It intervenes to prevent the monopolization of some markets and actively encourages the monopolization of others.
A) It encourages the permanent monopolization of all markets in which the monopolist has technical superiority over potential competitors.
B) It forbids the creation of legal impediments to entry into any market.
C) It intervenes to prevent the monopolization of any market.
D) It intervenes to prevent the monopolization of some markets and actively encourages the monopolization of others.
It intervenes to prevent the monopolization of some markets and actively encourages the monopolization of others.
2
Which of the following is NOT a source of monopoly?
A) patents given by the government to firms to encourage inventive activity
B) technologies that allow each of many small firms to produce at the same per-unit costs as one large firm
C) control of crucial inputs in the production of a good
D) government licensing requirements
A) patents given by the government to firms to encourage inventive activity
B) technologies that allow each of many small firms to produce at the same per-unit costs as one large firm
C) control of crucial inputs in the production of a good
D) government licensing requirements
technologies that allow each of many small firms to produce at the same per-unit costs as one large firm
3
What type of market structure exists when a single firm can produce output over the relevant range of demand more efficiently than two or more firms can because of the existence of economies of scale?
A) diseconomies of scale
B) monopolistic competition
C) a natural monopoly
D) perfect competition
A) diseconomies of scale
B) monopolistic competition
C) a natural monopoly
D) perfect competition
a natural monopoly
4
What is the definition of a natural monopoly?
A) an industry in which one firm is very large relative to other firms that could enter the industry
B) an industry in which a single firm controls crucial inputs to the production process
C) an industry in which a single seller exists as a result of patent protection
D) an industry in which one firm can produce the entire industry output at a lower average cost than can a larger number of firms
A) an industry in which one firm is very large relative to other firms that could enter the industry
B) an industry in which a single firm controls crucial inputs to the production process
C) an industry in which a single seller exists as a result of patent protection
D) an industry in which one firm can produce the entire industry output at a lower average cost than can a larger number of firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following can serve as a barrier to entry?
A) legal restrictions
B) specialization and division of labour
C) shortage of resources
D) the law of supply
A) legal restrictions
B) specialization and division of labour
C) shortage of resources
D) the law of supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is a pure monopoly?
A) It is an industry in which there are many rival firms competing for sales.
B) It is a market structure in which there is a single buyer.
C) It is a market structure in which there are many substitute products.
D) It is an industry in which there is a single seller.
A) It is an industry in which there are many rival firms competing for sales.
B) It is a market structure in which there is a single buyer.
C) It is a market structure in which there are many substitute products.
D) It is an industry in which there is a single seller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is a natural monopoly characterized by?
A) economies of scale over the relevant range of demand
B) economic losses at all output levels in an industry with production by a single seller
C) crucial patents being held by a single firm in an industry
D) diseconomies of scale over the relevant range of demand
A) economies of scale over the relevant range of demand
B) economic losses at all output levels in an industry with production by a single seller
C) crucial patents being held by a single firm in an industry
D) diseconomies of scale over the relevant range of demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Why does a monopoly arise?
A) because of diseconomies of scale
B) because entry to an industry is blocked
C) because of elastic demand
D) because firms are greedy
A) because of diseconomies of scale
B) because entry to an industry is blocked
C) because of elastic demand
D) because firms are greedy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The DeBeers Diamond Company, which owns most of the South African diamond production, has market power over the diamond trade. How was this market power obtained?
A) through control of a scarce resource
B) through illegal means
C) through government licensing
D) through patent protection
A) through control of a scarce resource
B) through illegal means
C) through government licensing
D) through patent protection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a Canadian monopoly?
A) Air Canada
B) Canada Post
C) The Hudson's Bay Company
D) Bell Canada
A) Air Canada
B) Canada Post
C) The Hudson's Bay Company
D) Bell Canada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a key element to preserving a monopoly?
A) keeping potential rivals out of the market
B) increased advertising expenditures
C) guaranteeing the availability of substitute products
D) government subsidization of critical enterprises
A) keeping potential rivals out of the market
B) increased advertising expenditures
C) guaranteeing the availability of substitute products
D) government subsidization of critical enterprises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is a pure monopoly?
A) It is an industry that is characterized by a few suppliers.
B) It is an industry that has no barriers to entry.
C) It is a market structure in which differentiated products are available.
D) It is a market structure that exists when the entry and survival of potential competitors is extremely unlikely.
A) It is an industry that is characterized by a few suppliers.
B) It is an industry that has no barriers to entry.
C) It is a market structure in which differentiated products are available.
D) It is a market structure that exists when the entry and survival of potential competitors is extremely unlikely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is NOT potentially a barrier to entry into a product market?
A) patent protection on the design of the product
B) the absence of economies of scale in the product market
C) the control of a crucial input necessary to produce the product
D) government licensing of the product's producers
A) patent protection on the design of the product
B) the absence of economies of scale in the product market
C) the control of a crucial input necessary to produce the product
D) government licensing of the product's producers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Many communities have granted monopoly rights to cable companies. How have these monopolies been created?
A) through government licensing
B) through smart business practices by entrepreneurs
C) through patent protection
D) through ownership of the cable resources
A) through government licensing
B) through smart business practices by entrepreneurs
C) through patent protection
D) through ownership of the cable resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is NOT consistent with a monopoly?
A) free entry and exit
B) economies of scale
C) a single seller
D) marginal revenue is less than the price
A) free entry and exit
B) economies of scale
C) a single seller
D) marginal revenue is less than the price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why does the government allow some markets to be monopolized by granting patents?
A) to promote a more equal distribution of income
B) to correct for negative externalities
C) to ensure lower prices for consumers in the short run
D) to promote technological progress
A) to promote a more equal distribution of income
B) to correct for negative externalities
C) to ensure lower prices for consumers in the short run
D) to promote technological progress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why might barriers that prevent the entry of new firms arise?
A) There are freely available production inputs.
B) The government protects some firms from competition.
C) Price exceeds marginal cost.
D) Economies of scale never exist over a substantial range of industry demand.
A) There are freely available production inputs.
B) The government protects some firms from competition.
C) Price exceeds marginal cost.
D) Economies of scale never exist over a substantial range of industry demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following best describes Canadian public utilities?
A) They are often perfect competitors.
B) They are often employee-owned public enterprises.
C) They are often created through patent protection.
D) They are often regulated natural monopolies.
A) They are often perfect competitors.
B) They are often employee-owned public enterprises.
C) They are often created through patent protection.
D) They are often regulated natural monopolies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following contributes to the existence of monopoly power?
A) patents
B) constant returns to scale
C) the shortage of critical resources
D) the law of diminishing returns
A) patents
B) constant returns to scale
C) the shortage of critical resources
D) the law of diminishing returns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is NOT a cause of monopoly?
A) economies of scale
B) a copyright
C) freely available critical inputs to production
D) a patent
A) economies of scale
B) a copyright
C) freely available critical inputs to production
D) a patent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a profit-maximizing monopolist is currently charging a price on the inelastic portion of its demand curve, what action should it take to maximize profits?
A) It should reduce both output and price.
B) It should raise the price and decrease output.
C) It should raise the price and hold output constant.
D) It should lower the price and increase output.
A) It should reduce both output and price.
B) It should raise the price and decrease output.
C) It should raise the price and hold output constant.
D) It should lower the price and increase output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the shape of the demand curve of a monopolist?
A) downward sloping and below the marginal revenue curve
B) identical to the marginal cost curve
C) kinked because of recognized interdependence with other firms
D) downward sloping and above the marginal revenue curve
A) downward sloping and below the marginal revenue curve
B) identical to the marginal cost curve
C) kinked because of recognized interdependence with other firms
D) downward sloping and above the marginal revenue curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A natural gas monopoly currently sells 100 gigajoules of natural gas at $11.00 per gigajoule. To sell one more gigajoule, the natural gas company must lower the price of natural gas to $10.90. Which of the following best describes the marginal revenue of the 101st gigajoule of natural gas?
A) The marginal revenue equals the change in price, or $ 0.10.
B) The marginal revenue equals the price, or $10.90.
C) The marginal revenue is greater than $10.90.
D) The marginal revenue is less than $10.90.
A) The marginal revenue equals the change in price, or $ 0.10.
B) The marginal revenue equals the price, or $10.90.
C) The marginal revenue is greater than $10.90.
D) The marginal revenue is less than $10.90.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the term for a market structure in which only one firm survives because of economies of scale?
A) a structural monopoly
B) a government monopoly
C) a patented monopoly
D) a natural monopoly
A) a structural monopoly
B) a government monopoly
C) a patented monopoly
D) a natural monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following describes perfect competition, but does NOT describe a monopoly?
A) Marginal revenue is equal to price.
B) Profits may exist in the short run.
C) The firm's average total cost curve is U-shaped.
D) A profit-maximizing firm chooses output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A) Marginal revenue is equal to price.
B) Profits may exist in the short run.
C) The firm's average total cost curve is U-shaped.
D) A profit-maximizing firm chooses output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The following represents a portion of the demand schedule faced by a monopoly firm.
TABLE 9-1
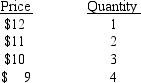
Refer to Table 9-1. What is the marginal revenue of the third unit of output?
A) $1
B) $8
C) $10
D) $12
TABLE 9-1
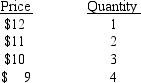
Refer to Table 9-1. What is the marginal revenue of the third unit of output?
A) $1
B) $8
C) $10
D) $12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a monopolist's marginal revenue is less than zero over a range of output, then what must price elasticity of demand be?
A) equal to one
B) equal to zero
C) less than one but greater than zero
D) greater than one
A) equal to one
B) equal to zero
C) less than one but greater than zero
D) greater than one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following output levels will a profit-maximizing monopolist NOT produce at?
A) where marginal cost is less than average total cost
B) where it suffers economic losses in the short run
C) where demand is inelastic
D) where demand is elastic
A) where marginal cost is less than average total cost
B) where it suffers economic losses in the short run
C) where demand is inelastic
D) where demand is elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a firm seeks to maximize total revenue, at what quantity should it produce?
A) where elasticity of demand is greater than 1
B) where marginal revenue is maximized
C) where marginal revenue equals 0
D) where elasticity of demand equals 0
A) where elasticity of demand is greater than 1
B) where marginal revenue is maximized
C) where marginal revenue equals 0
D) where elasticity of demand equals 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is NOT consistent with a monopoly?
A) a downward-sloping demand curve
B) a U-shaped average total cost curve
C) a single seller
D) marginal revenue exceeds price
A) a downward-sloping demand curve
B) a U-shaped average total cost curve
C) a single seller
D) marginal revenue exceeds price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following does NOT describe a profit-maximizing monopolist?
A) The monopolist chooses output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B) The monopolist charges a price that exceeds marginal cost.
C) The monopolist faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
D) The monopolist can potentially continue to earn economic profits in the long run.
A) The monopolist chooses output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B) The monopolist charges a price that exceeds marginal cost.
C) The monopolist faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
D) The monopolist can potentially continue to earn economic profits in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the profit maximizing condition for monopolies?
A) P = ATC
B) P = MR
C) MR = 0
D) MR = MC
A) P = ATC
B) P = MR
C) MR = 0
D) MR = MC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When is a natural monopoly likely to arise?
A) when a firm controls a crucial input to production
B) when economies of scale exist over the relevant range of demand
C) when the government restricts entry through licensing
D) when patents provide protection of intellectual property
A) when a firm controls a crucial input to production
B) when economies of scale exist over the relevant range of demand
C) when the government restricts entry through licensing
D) when patents provide protection of intellectual property

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If marginal revenue on the tenth unit of output equals $4 for a non-discriminating, profit-maximizing monopolist, then what is the price?
A) price is less than $4
B) price must be equal to average total cost
C) price is greater than $4
D) price equals $4
A) price is less than $4
B) price must be equal to average total cost
C) price is greater than $4
D) price equals $4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following best describes the marginal revenue curve of a monopolist graphically?
A) It lies above the demand curve of a monopolist.
B) It lies below the demand curve of a monopolist.
C) It is the same as the marginal cost curve of a monopolist.
D) It is the same as the demand curve of a monopolist.
A) It lies above the demand curve of a monopolist.
B) It lies below the demand curve of a monopolist.
C) It is the same as the marginal cost curve of a monopolist.
D) It is the same as the demand curve of a monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements regarding price best describes a profit-maximizing monopolist?
A) Price is always equal to marginal revenue.
B) Price is always equal to the average total cost of production.
C) Price is always less than marginal revenue.
D) Price is always greater than marginal revenue.
A) Price is always equal to marginal revenue.
B) Price is always equal to the average total cost of production.
C) Price is always less than marginal revenue.
D) Price is always greater than marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following best explains why a monopolist's marginal revenue is less than the sale price?
A) To sell more units, a monopolist must increase the price on all units sold.
B) To sell more units, a monopolist must lower the price of some units that could otherwise have been sold at a higher price.
C) When a firm has a monopoly, consumers have no choice other than to pay the price set by the monopolist.
D) As a monopolist expands output, its average total cost declines.
A) To sell more units, a monopolist must increase the price on all units sold.
B) To sell more units, a monopolist must lower the price of some units that could otherwise have been sold at a higher price.
C) When a firm has a monopoly, consumers have no choice other than to pay the price set by the monopolist.
D) As a monopolist expands output, its average total cost declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Where does a profit-maximizing monopolist operate?
A) where demand is elastic
B) where demand is infinitely elastic
C) where demand is inelastic
D) where demand is unit elastic
A) where demand is elastic
B) where demand is infinitely elastic
C) where demand is inelastic
D) where demand is unit elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Why is marginal revenue for a monopolist less than the sales price?
A) As the monopolist expands output, the average total cost of production declines.
B) To sell more units, the monopolist must reduce price on all units sold.
C) When a firm has a monopoly, consumers have no choice other than to pay the price set by the monopolist.
D) The monopolist charges each consumer the highest possible price.
A) As the monopolist expands output, the average total cost of production declines.
B) To sell more units, the monopolist must reduce price on all units sold.
C) When a firm has a monopoly, consumers have no choice other than to pay the price set by the monopolist.
D) The monopolist charges each consumer the highest possible price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following does a profit-maximizing monopolist set?
A) the product price where marginal revenue is greater than the price
B) the output where marginal cost equals average revenue
C) the output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue
D) the product price where marginal cost equals marginal revenue
A) the product price where marginal revenue is greater than the price
B) the output where marginal cost equals average revenue
C) the output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue
D) the product price where marginal cost equals marginal revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 9-2
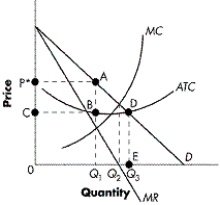
Refer to Figure 9-2. What does the region bounded by CBAP* represent?
A) total profits
B) total losses
C) total costs
D) total consumer surplus

Refer to Figure 9-2. What does the region bounded by CBAP* represent?
A) total profits
B) total losses
C) total costs
D) total consumer surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 9-1
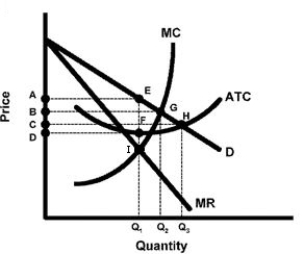
Refer to Figure 9-1. What area indicates the profit-maximizing firm's total revenue?
A) 0BGQ2
B) 0AEQ1
C) DAEF
D) 0DFQ1

Refer to Figure 9-1. What area indicates the profit-maximizing firm's total revenue?
A) 0BGQ2
B) 0AEQ1
C) DAEF
D) 0DFQ1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a profit-maximizing monopolist finds that marginal cost is increasing and exceeds marginal revenue, what action should it take?
A) Increase price and decrease output.
B) Increase both price and output.
C) Increase output and decrease price.
D) Decrease both price and output.
A) Increase price and decrease output.
B) Increase both price and output.
C) Increase output and decrease price.
D) Decrease both price and output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How do profit-maximizing monopolists choose a level of output?
A) such that marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price exceeds average variable cost
B) such that price equals marginal cost but exceeds average variable cost
C) such that price equals marginal revenue but exceeds average variable cost
D) such that average total cost is minimized
A) such that marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price exceeds average variable cost
B) such that price equals marginal cost but exceeds average variable cost
C) such that price equals marginal revenue but exceeds average variable cost
D) such that average total cost is minimized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 9-1

Refer to Figure 9-1. What level of output will the profit-maximizing firm produce at?
A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) zero (shutdown)

Refer to Figure 9-1. What level of output will the profit-maximizing firm produce at?
A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) zero (shutdown)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The following diagram contains information on cost and revenue curves facing a regulated monopoly.
FIGURE 9-3
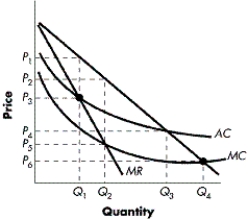
Refer to Figure 9-3. Which of the following price and output combinations would the monopoly prefer?
A) P2 and Q2
B) P3 and Q1
C) P1 and Q1
D) P4 and Q3
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. Which of the following price and output combinations would the monopoly prefer?
A) P2 and Q2
B) P3 and Q1
C) P1 and Q1
D) P4 and Q3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
TABLE 9-2
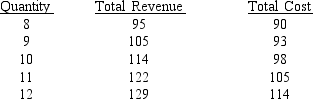
Refer to Table 9-2. What is the marginal cost of the last unit produced at the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) $5
B) $7
C) $8
D) $10

Refer to Table 9-2. What is the marginal cost of the last unit produced at the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) $5
B) $7
C) $8
D) $10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
TABLE 9-2

Refer to Table 9-2. What is the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) 9 units
B) 10 units
C) 11 units
D) 12 units

Refer to Table 9-2. What is the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) 9 units
B) 10 units
C) 11 units
D) 12 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
TABLE 9-2

Refer to Table 9-2. What is average total cost at the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) $9.55
B) $9.80
C) $10.33
D) $11.25

Refer to Table 9-2. What is average total cost at the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) $9.55
B) $9.80
C) $10.33
D) $11.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 9-1

Refer to Figure 9-1. What area indicates the welfare loss due to monopoly?
A) EHF
B) EGQ2Q1
C) FHQ3Q1
D) EGI

Refer to Figure 9-1. What area indicates the welfare loss due to monopoly?
A) EHF
B) EGQ2Q1
C) FHQ3Q1
D) EGI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
At what level of output would a profit-maximizing monopolist choose to produce at?
A) where total cost is minimized
B) where total revenue is maximized
C) where marginal revenue equals marginal cost
D) where average total cost is minimized
A) where total cost is minimized
B) where total revenue is maximized
C) where marginal revenue equals marginal cost
D) where average total cost is minimized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Figure 9-1

Refer to Figure 9-1. What is the socially efficient level of output?
A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) zero (shutdown)

Refer to Figure 9-1. What is the socially efficient level of output?
A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) zero (shutdown)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 9-1

Refer to Figure 9-1. What area indicates total cost when the monopolist is maximizing profits?
A) 0BGQ2
B) 0AEQ1
C) DAEF
D) 0DFQ1

Refer to Figure 9-1. What area indicates total cost when the monopolist is maximizing profits?
A) 0BGQ2
B) 0AEQ1
C) DAEF
D) 0DFQ1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
TABLE 9-2

Refer to Table 9-2. What is marginal revenue at the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) $5
B) $7
C) $8
D) $9

Refer to Table 9-2. What is marginal revenue at the profit-maximizing level of output?
A) $5
B) $7
C) $8
D) $9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
At his current level of output, a monopolist has an MR of $10, an MC of $6, and an economic profit of zero. If the market demand curve is downward sloping and his marginal cost curve is upward sloping, what can we conclude about the monopolist?
A) It could increase profit by increasing his price.
B) It is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output.
C) It should exit the market if significant fixed costs have been incurred.
D) It could increase profit by increasing output.
A) It could increase profit by increasing his price.
B) It is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output.
C) It should exit the market if significant fixed costs have been incurred.
D) It could increase profit by increasing output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements best describes a monopoly?
A) Price exceeds marginal cost.
B) Average revenue equals marginal revenue.
C) Output is greater than the socially efficient level.
D) Average revenue is equal to average cost.
A) Price exceeds marginal cost.
B) Average revenue equals marginal revenue.
C) Output is greater than the socially efficient level.
D) Average revenue is equal to average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 9-1

Refer to Figure 9-1. If the firm is profit maximizing, what does the region bounded by DAEF represent?
A) total consumer surplus
B) total costs
C) total losses
D) total profits

Refer to Figure 9-1. If the firm is profit maximizing, what does the region bounded by DAEF represent?
A) total consumer surplus
B) total costs
C) total losses
D) total profits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
TABLE 9-2

Refer to Table 9-2. If the firm is currently producing 12 units of output, what should the firm do to maximize profits?
A) Reduce output to 11 units.
B) Increase output beyond 12 units.
C) Maintain the current output level.
D) Reduce output to 10 units.

Refer to Table 9-2. If the firm is currently producing 12 units of output, what should the firm do to maximize profits?
A) Reduce output to 11 units.
B) Increase output beyond 12 units.
C) Maintain the current output level.
D) Reduce output to 10 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Figure 9-2

Refer to Figure 9-2. What level of output will the profit-maximizing firm produce at?
A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) 0 units

Refer to Figure 9-2. What level of output will the profit-maximizing firm produce at?
A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) 0 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What quantity will a monopolist operate at?
A) where MR = MC, charging a price equal to average variable cost
B) where MR = MC, charging a price equal to marginal revenue
C) where MR = MC, charging price corresponding to average total cost at that level
D) where MR = MC, charging a price corresponding to demand at that level
A) where MR = MC, charging a price equal to average variable cost
B) where MR = MC, charging a price equal to marginal revenue
C) where MR = MC, charging price corresponding to average total cost at that level
D) where MR = MC, charging a price corresponding to demand at that level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
FIGURE 9-4
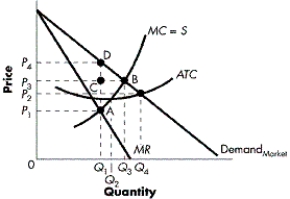
Refer to Figure 9-4. What area indicates the welfare loss due to monopoly pricing and output practices?
A) DCB
B) DAP1P4
C) ACB
D) ADB

Refer to Figure 9-4. What area indicates the welfare loss due to monopoly pricing and output practices?
A) DCB
B) DAP1P4
C) ACB
D) ADB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
FIGURE 9-4

Refer to Figure 9-4. What price would a monopolist charge when maximizing profits?
A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) P4

Refer to Figure 9-4. What price would a monopolist charge when maximizing profits?
A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) P4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
FIGURE 9-5
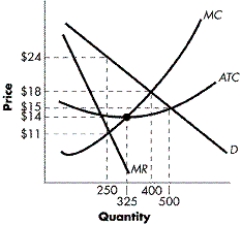
Refer to Figure 9-5. Assuming the firm maximizes profits, how many units of output will it produce each period?
A) 250
B) 325
C) 400
D) 500

Refer to Figure 9-5. Assuming the firm maximizes profits, how many units of output will it produce each period?
A) 250
B) 325
C) 400
D) 500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
FIGURE 9-4

Refer to Figure 9-4. What quantity of output would a profit-maximizing monopolist produce?
A) 0
B) Q1
C) Q2
D) Q3

Refer to Figure 9-4. What quantity of output would a profit-maximizing monopolist produce?
A) 0
B) Q1
C) Q2
D) Q3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
FIGURE 9-5

Refer to Figure 9-5. If the firm sets a price to maximize profits, will it earn a profit or suffer a loss?
A) an economic profit of $3250
B) an economic profit of $2500
C) an economic profit of $1500
D) an economic loss of $1500

Refer to Figure 9-5. If the firm sets a price to maximize profits, will it earn a profit or suffer a loss?
A) an economic profit of $3250
B) an economic profit of $2500
C) an economic profit of $1500
D) an economic loss of $1500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following best describes a monopolist in the long run?
A) It may make an economic loss, an economic profit, or zero economic profits.
B) It always earns an economic profit.
C) It always earns a normal rate of return.
D) It always suffers an economic loss.
A) It may make an economic loss, an economic profit, or zero economic profits.
B) It always earns an economic profit.
C) It always earns a normal rate of return.
D) It always suffers an economic loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
FIGURE 9-5

Refer to Figure 9-5. If the firm sets a price to maximize profits, how much will it charge for its product?
A) $14
B) $15
C) $18
D) $24

Refer to Figure 9-5. If the firm sets a price to maximize profits, how much will it charge for its product?
A) $14
B) $15
C) $18
D) $24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following does NOT describe a profit-maximizing monopolist?
A) The price of output exceeds marginal revenue.
B) The monopolist chooses output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) The monopolist always earns an economic profit.
D) The monopolist faces the downward-sloping market demand curve.
A) The price of output exceeds marginal revenue.
B) The monopolist chooses output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) The monopolist always earns an economic profit.
D) The monopolist faces the downward-sloping market demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following best describes a monopolist in the short run?
A) It always suffers an economic loss.
B) It always earns an economic profit.
C) It always earns a normal rate of return.
D) It may make an economic loss, an economic profit, or zero economic profits.
A) It always suffers an economic loss.
B) It always earns an economic profit.
C) It always earns a normal rate of return.
D) It may make an economic loss, an economic profit, or zero economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The following diagram contains information on cost and revenue curves facing a regulated monopoly.
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. If the government is able to regulate the monopolist using average-cost pricing, what price and output combinations are expected to result?
A) P5 and Q2
B) P4 and Q3
C) P3 and Q1
D) P2 and Q2
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. If the government is able to regulate the monopolist using average-cost pricing, what price and output combinations are expected to result?
A) P5 and Q2
B) P4 and Q3
C) P3 and Q1
D) P2 and Q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
At a given output level, when can a monopolist earn a profit?
A) only if the height of the marginal revenue curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the marginal cost curve at that output
B) only if the height of the demand curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the marginal revenue curve at that output
C) only if the height of the demand curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the average total cost curve at that output
D) only if the slope of the total revenue curve exceeds the slope of the total cost curve
A) only if the height of the marginal revenue curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the marginal cost curve at that output
B) only if the height of the demand curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the marginal revenue curve at that output
C) only if the height of the demand curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the average total cost curve at that output
D) only if the slope of the total revenue curve exceeds the slope of the total cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The following diagram contains information on cost and revenue curves facing a regulated monopoly.
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. If regulators set a price according to average-cost pricing, what can we conclude about the firm?
A) It will make zero economic profits.
B) It will suffer an economic loss.
C) It will earn the same level of profits as it would absent regulation.
D) It will earn positive economic profits.
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. If regulators set a price according to average-cost pricing, what can we conclude about the firm?
A) It will make zero economic profits.
B) It will suffer an economic loss.
C) It will earn the same level of profits as it would absent regulation.
D) It will earn positive economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The following diagram contains information on cost and revenue curves facing a regulated monopoly.
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. Where would the socially efficient level of output occur?
A) where price equals average total cost at Q3
B) where marginal revenue equals marginal cost at Q2
C) where price equals marginal cost at Q4
D) where price equals marginal revenue at Q1
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. Where would the socially efficient level of output occur?
A) where price equals average total cost at Q3
B) where marginal revenue equals marginal cost at Q2
C) where price equals marginal cost at Q4
D) where price equals marginal revenue at Q1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The following diagram contains information on cost and revenue curves facing a regulated monopoly.
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. If regulators set a price according to marginal-cost pricing, what can we conclude about the firm?
A) It will suffer an economic loss.
B) It will earn positive economic profits.
C) It will make zero economic profits.
D) It will earn the same level of profits as it would absent regulation.
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. If regulators set a price according to marginal-cost pricing, what can we conclude about the firm?
A) It will suffer an economic loss.
B) It will earn positive economic profits.
C) It will make zero economic profits.
D) It will earn the same level of profits as it would absent regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is a major difference between a monopolist and firms in perfectly competitive markets?
A) The monopolist may earn short-run profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets cannot.
B) The monopolist maximizes profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets maximize sales.
C) The monopolist is a price taker; firms in other markets are price searchers.
D) The monopolist may earn long-run economic profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets cannot.
A) The monopolist may earn short-run profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets cannot.
B) The monopolist maximizes profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets maximize sales.
C) The monopolist is a price taker; firms in other markets are price searchers.
D) The monopolist may earn long-run economic profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets cannot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What will the use of average-cost pricing for a natural monopoly result in?
A) the socially efficient level of output
B) the firm suffering economic losses
C) a greater than socially efficient level of output
D) a less than socially efficient level of output
A) the socially efficient level of output
B) the firm suffering economic losses
C) a greater than socially efficient level of output
D) a less than socially efficient level of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the average total cost curve is always above the demand curve of a monopolist, what can we conclude?
A) The monopolist will earn an economic profit.
B) Entry will occur, forcing the monopolist to reduce price and expand output.
C) The monopolist will suffer economic losses.
D) The monopolist must be producing inefficiently.
A) The monopolist will earn an economic profit.
B) Entry will occur, forcing the monopolist to reduce price and expand output.
C) The monopolist will suffer economic losses.
D) The monopolist must be producing inefficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Do monopolists need to worry about producing efficiently and reducing costs?
A) Yes, because they are motivated by social considerations rather than profit.
B) Yes, since cost increases will decrease a monopolist's profits.
C) No, because the monopolist is a price taker.
D) No, since they can just pass along any increase in costs to their consumers.
A) Yes, because they are motivated by social considerations rather than profit.
B) Yes, since cost increases will decrease a monopolist's profits.
C) No, because the monopolist is a price taker.
D) No, since they can just pass along any increase in costs to their consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The following diagram contains information on cost and revenue curves facing a regulated monopoly.
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. If the government is able to regulate the monopolist using marginal-cost pricing, what price and output combinations are expected to result?
A) P6 and Q4
B) P5 and Q2
C) P3 and Q1
D) P2 and Q2
FIGURE 9-3

Refer to Figure 9-3. If the government is able to regulate the monopolist using marginal-cost pricing, what price and output combinations are expected to result?
A) P6 and Q4
B) P5 and Q2
C) P3 and Q1
D) P2 and Q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
FIGURE 9-5

Refer to Figure 9-5. Assuming the firm maximizes profits, what will the marginal cost of the last unit produced be?
A) $11
B) $14
C) $15
D) $18

Refer to Figure 9-5. Assuming the firm maximizes profits, what will the marginal cost of the last unit produced be?
A) $11
B) $14
C) $15
D) $18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



